前言
国内关于build.xml的配置资料太零散了,实在是受不了,故而将自己的笔记整理成博文,方便大家查阅和理解。
build.xml配置参数
构建文件默认叫build.xml,其有很多配置参数。
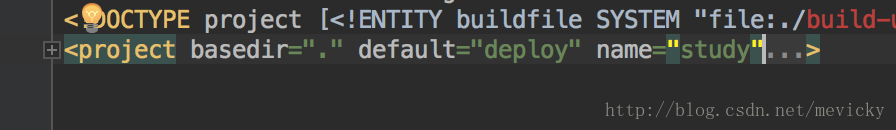
project
每个构建文件都有一个project标签,有以下属性:
- default:表示默认的运行目标,这个属性是必须的。
- basedir:表示项目的基准目录。
- name:表示项目名。
- description:表示项目的描述。
如下:
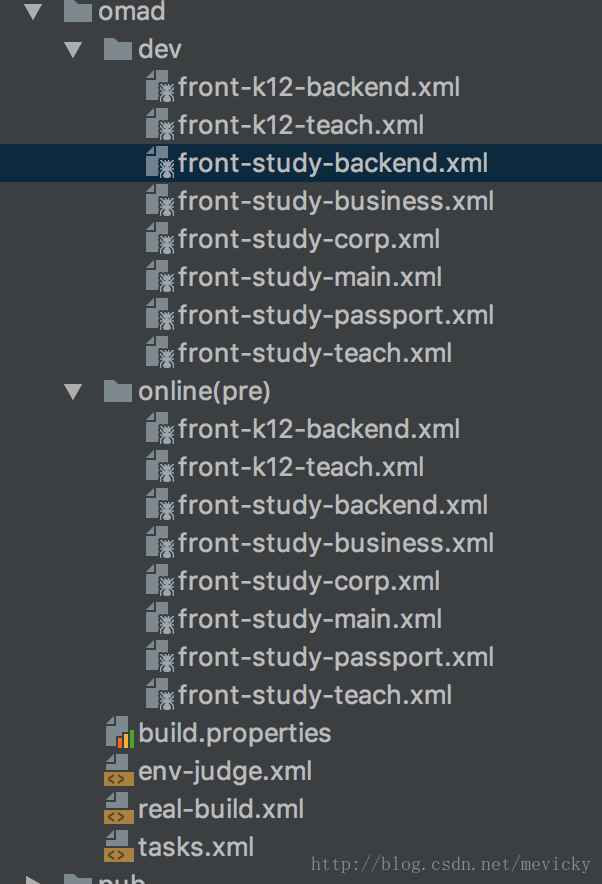
每个项目对应一个构建文件,但是如果项目比较复杂,业务线比较多,则有可能对应很多个构建文件,比如:
这时我们需要注意,每个构建文件都需要以project标签包含起来。
property
类似于常量,可以供给build.xml中的其他标签使用。有两个特点:
- 大小写敏感
- 不可改变,谁先设定,之后的都不能改变。
该标签可以与多个属性配合使用。
- name和value: <property name="module_name" value="admin"/>
后面直接使用即可: <echo message="begin nej-build ${module_name}..."/>
- name和refid: <property name="srcpath" refid="dao.compile.classpath"/>
其中的dao.compile.classpath在别的地方进行了定义。当然,也可以通过直接引用的方式: <property name="baseline.dir" value="${ob_baseline.dir}"/>
- name和location: <property name="srcdir" location="src"/>
将srcdir的值设置为当前文件路径/src。
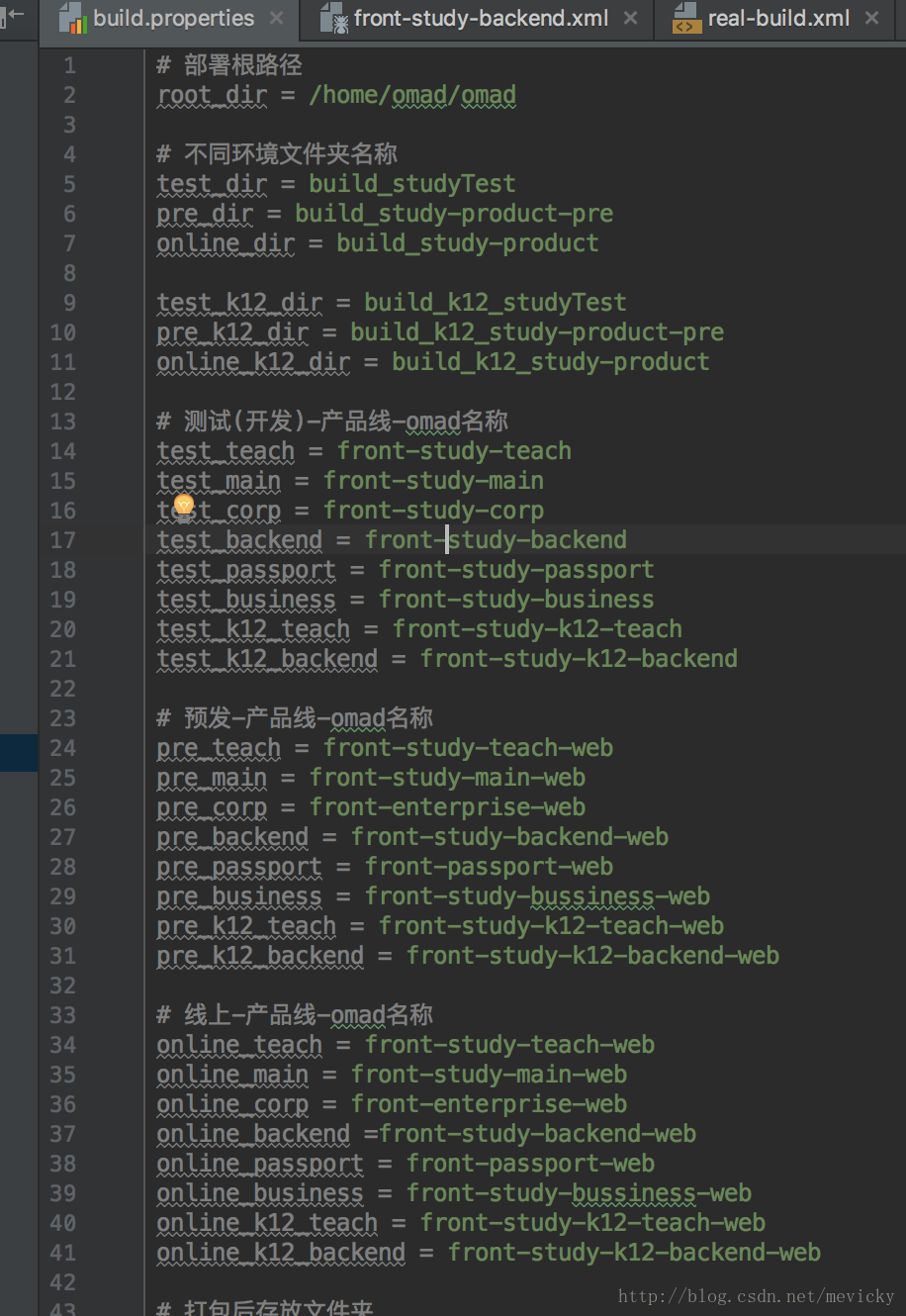
- file: <property file="./omad/build.properties"/>
导入相对文件中的所有变量,这里的build.properties专门用来存放各种变量,示例如下:
- url:
<property url="http://www.mysite.com/bla/props/foo.properties"/>
导入对应文件的属性 - environment:
<property environment="env"/>
设置系统的环境变量前缀为env。比如<property name="tomcat.home" value="${env.CATALINA_HOME}"/>
将系统的tomcat安装目录设置到tomcat.home属性中。
import
引入别的xml文件,提高复用性:
<import file="./env-judge.xml"/>
<import file="./tasks.xml"/>- 1
- 2
甚至可以批量匹配:
<copy todir="${basedir}/src/html/${html.dir}" overwrite="true" includeEmptyDirs="true">
<fileset dir="${basedir}/lib">
<include name="module-*/**" />
</fileset>
</copy>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
target
任务,一个project标签下有一个或多个target标签,代表任务,任务间可以存在依赖关系。有如下属性:
- name:用于标识,这个是必须的
- depends:用来指定所依赖的任务。
<!-- 初始化任务 -->
<target name="init">
<echo message=" init ${init} ..."/>
</target>
<!-- 编译 -->
<target name="compile" depends="init">
<delete dir="${classes.dir}" />
<mkdir dir="${classes.dir}" />
<javac srcdir="${src.dir}" destdir="${classes.dir}">
<classpath refid="master-classpath" />
</javac>
</target> - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- if:当属性设置时才执行该任务。
<target name="sync_module_k12_teach" if="${is_k12_teach}">
<antcall target="sync_module_item">
<param name="html.dir" value="org"/>
</antcall>
</target>
<target name="sync_module_backend" if="${is_backend}">
<antcall target="sync_module_item">
<param name="html.dir" value="admin"/>
</antcall>
</target>
<target name="sync_module_k12_backend" if="${is_k12_backend}">
<antcall target="sync_module_item">
<param name="html.dir" value="admin"/>
</antcall>
</target>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
通过判断变量是否存在,执行不同的任务。
- unless:当属性未设置时才执行。
- description:任务描述。
echo
控制台显示
<echo message="begin clean res/module-xx、component-xx、res-base..."/>- 1
delete
删除文件或文件目录,有如下属性
- file:删除文件
- dir:删除目录
- includeEmptyDirs:值得是否删除空目录,默认是true
- failonerror:报错是否停止,默认是true
- verbose:是否列出删除的文件,默认是false
示例如下:
<!--clean other dir-->
<target name="clean_other_dir">
<echo message="begin clean_other_dir..."/>
<delete dir="${basedir}/${compress.dir}"/>
<delete dir="${basedir}/pub"/>
<echo message="begin clean html module-xx..."/>
<delete includeemptydirs="true">
<fileset dir="${basedir}/src/html" >
<include name="**/module-*/**"/>
</fileset>
</delete>
<echo message="begin clean res/module-xx、component-xx、res-base..."/>
<delete includeemptydirs="true">
<fileset dir="${basedir}/res" >
<include name="module-*/**"/>
<include name="component-*/**"/>
<include name="res-base/**"/>
</fileset>
</delete>
</target>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
mkdir
创建一个目录
<mkdir dir=”${class.root}”/>- 1
copy
拷贝文件或文件目录,属性如下:
- file:表示源文件。
- tofile:表示目标文件。
- todir:表示目标目录。
- overwrite:是否覆盖目标文件,默认为false。
- includeEmptyDirs:是否拷贝空目录,默认为true。
- failonerror:如目标没有发现是否自动停止,默认值true。
- verbose:是否显示详细信息,默认值false。
示例:
<target name="cp">
<copy todir="${compress.dir}" overwrite="true">
<fileset dir="${ob_baseline.dir}">
<include name="pub/" />
<include name="res/" />
<include name="mail_template/" />
</fileset>
</copy>
</target>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
fileset
文件集标签,通常与任务结合来使用,例如上面的copy的demo中,通过将fileset定义的文件路径下的文件,拷贝到todir指定的路径中。
也可以用于批量删除:
<delete includeemptydirs="true">
<fileset dir="${basedir}/src/html" >
<include name="**/module-*/**"/>
</fileset>
</delete>
<echo message="begin clean res/module-xx、component-xx、res-base..."/>
<delete includeemptydirs="true">
<fileset dir="${basedir}/res" >
<include name="module-*/**"/>
<include name="component-*/**"/>
<include name="res-base/**"/>
</fileset>
</delete>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
也就是说,但凡遇到文件集操作,都需要用到fileset标签。
exec
用来执行系统命令,或者指定环境的命令。
比如:
<target name="test">
<exec executable="cmd.exe">
<arg line="/c dir"/>
</exec>
</target>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
打开命名行,并转到c盘执行dir命令。
能够执行系统命令,就相当于可以执行各种环境比如node、gulp、bower等等:
<!--build style-->
<target name="build_style">
<echo message="begin build_style..."/>
<exec dir="." executable="gulp" failonerror="true">
<arg line="scss"/>
</exec>
</target>
<!--bower cache clean if必须是${]才是判断true,false, 否则只要有设定值即可执行-->
<target name="bower_cache_clean" if="${is_bower_cache_clean}">
<echo message="begin bower_cache_clean ..."/>
<exec dir="." executable="bower" failonerror="true">
<arg line="cache clean" />
</exec>
</target>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
antcall
执行某个定义的任务。
<target name="sync_module_teach" if="${is_teach}">
<antcall target="sync_module_item">
<param name="html.dir" value="org"/>
</antcall>
</target>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
执行sync_module_item任务,并设置参数html.dir的值为org。
该任务定义如下:
<target name="sync_module_item">
<echo message="begin sync_module ${html.dir}..."/>
<copy todir="${basedir}/src/html/${html.dir}" overwrite="true" includeEmptyDirs="true">
<fileset dir="${basedir}/lib">
<include name="module-*/**" />
</fileset>
</copy>
</target>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
或者更为简单的表达:
<target name="deploy">
<echo message="begin auto deploy......"/>
<antcall target="clean"/>
<antcall target="bower_install"/>
<antcall target="cnpm_install"/>
<antcall target="sync_module"/>
<antcall target="build_style"/>
<antcall target="nej_build" />
<antcall target="cp"/>
</target>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
parallel
并行执行多个子任务。
<parallel failonany="true">
<antcall target="sync_module_corp"/>
<antcall target="sync_module_main"/>
<antcall target="sync_module_teach"/>
<antcall target="sync_module_backend"/>
<antcall target="sync_module_passport"/>
<antcall target="sync_module_business"/>
<antcall target="sync_module_k12_teach"/>
<antcall target="sync_module_k12_backend"/>
<antcall target="build_style"/>
</parallel>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
通过failonany控制如果一个失败,则不执行。通过并行执行,来提升性能,降低构建花费的时间。
regexp
用于正则的定义的使用,可以与matches结合使用。
比如,定义正则:
<regexp id="regexp_env_test" pattern="^${root_dir}/(${test_dir}|${test_k12_dir})/.+"/>
<regexp id="regexp_env_pre" pattern="^${root_dir}/(${pre_dir}|${pre_k12_dir})/.+"/>- 1
- 2
通过pattern指定正则内容,通过id标识。
在需要匹配的时候,使用之:
<condition property="is_test">
<matches string="${basedir}">
<regexp refid="regexp_env_test"/>
</matches>
</condition>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
condition
用来判断,如果包含的内容符合条件,则将property指定的属性设置为true,否则为false。
比如上面的例子中,就是将basedir变量的值和regexp_env_test对应的正则匹配,如果正确,就将is_test设置为true,然后后面的流程再去判断。
与之配合的标签有很多,下面一一介绍:
- istrue,isfalse:断言
<condition property="is_test_backend">
<and>
<istrue value="${is_test}"/>
<istrue value="${is_backend}"/>
</and>
</condition>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
只有is_test和is_backend变量的值均为true,is_test_backend的值才为true。
- and:逻辑与,需要都满足条件才行,如上例所述。
- not:逻辑非,反过来的结果。
- or,xor:逻辑或和逻辑异或。
- isset:指定属性是否存在:
<condition property="scondition">
<!--如果属性name不存在则返回false-->
<isset property="name"/>
</condition>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- equils:指定属性是否相等:
<condition property="scondition">
<!--如果arg1的值与arg2的值相等返回true,否则为false-->
<equals arg1="${name}" arg2="this is name"/>
</condition>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- filesmatch:指定文件是否相等:
<condition property="scondition">
<!--如果file1所代表的文件与file2所代表的文件相等返回true,否则为false-->
<filesmatch file1="testfile1.txt" file2="testfile2.txt"/>
</condition>