friend关键字
c++中有个friend关键字,它能让被修饰的对象冲破本class的封装特性,从而能够访问本class的私有对象。
简单来讲,就是:
-
如果你在A类中,申明了函数func()是你的friend,那么func()就可以使用A类的所有成员变量,无论它在什么地方定义的。
-
如果你在A类中,申明了B类是你的friend,那么B类中的方法就可以访问A类的所有成员变量。
#include<iostream> using namespace std; class A { public: A() { password = 1111; birthday = 808; } ~A() { } friend int func(A a); // 向c++表示,int func(A a)是我的朋友,所以它可以使用我的所有东西。 friend class B; // 向c++表示,class B是我的朋友,所以它可以使用我的所有东西。 private: int password; int birthday; }; int func(A a) { cout << a.password << " and " << a.birthday << endl; //可以访问 a.password = 1; //甚至可以修改 cout << a.password << endl; return 0; } class B { public: B() { } ~B() { } // 因为在A类中已经声明了B类是它的朋友,所以B类中方法就可以访问A类的私有变量了 void show(A a) { cout << "your account is " << a.account << " and with pass: " << a.password << endl; } private: }; int main() { A a; func(a); B b; b.show(a); system("pause"); }
运用friend重载 << 或者 >>操作
利用这一点,我们就可以重载<< 或者 >>操作,
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
A() {
password = 1111;
account = 808;
}
~A() { }
friend ostream& operator << (ostream &os , A a);
private:
int password;
int account;
};
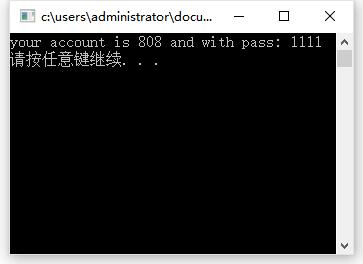
ostream& operator << (ostream &os , A a) {
os << "your account is " << a.account << " and with pass: " << a.password << endl;
return os;
}
int main() {
A a;
cout << a;
system("pause");
} 结果: