使用caffe的流程
1. 准备数据(写一个脚本将其转换为LMDB数据库的格式)
2. 定义网络(写一个prototxt)
3. 定义solover(写一个solover prototxt,solver定义了训练用的超参数和要训练的网络)
4. 训练(运行一个脚本,相当于执行shell 命令caffe train --solver=XXX_solver.prototxt)
几个概念
Blob: store data and derivatives
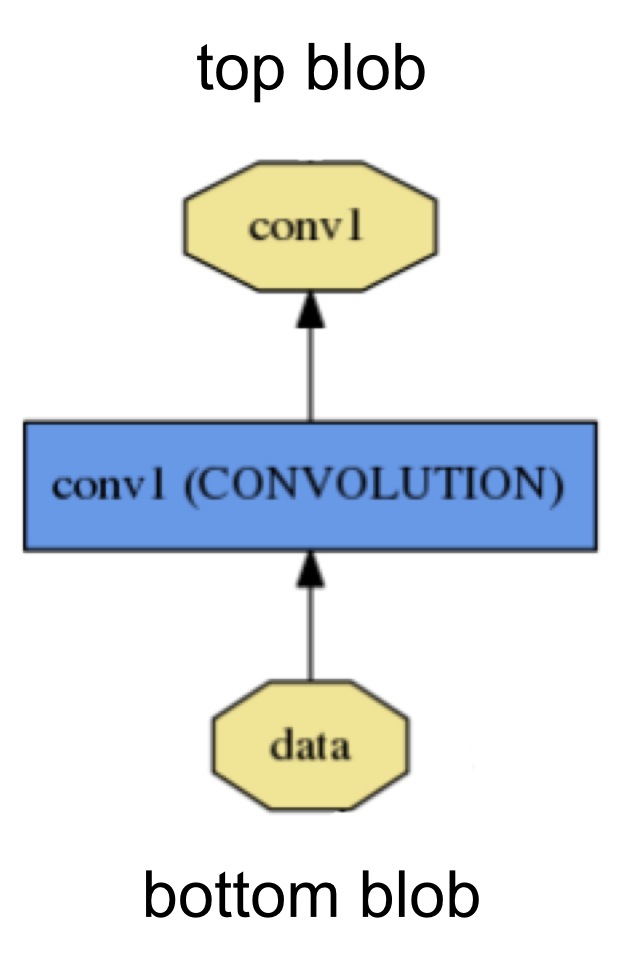
Layer: transforms bottom blob to top blobs
Net: many layers; computes gradients via forward / backward
Solver: uses gradients to update weights. 存放超参数
Blob
blob封装了运行时的数据信息,从数学上来讲,blob是一个连续存储的n维数组。caffe使用blob存储和传输数据。它和layer的关系是,layer的输入是bottom blob,输出是top blob,blob存有数据。
layer
主要有数据层,视觉层,激活层,其他常用层等,各个层有自己的参数需要设置。每个层主要包括设置,forward,backward。可以自定义层(改源码)
Net
Net是由许多layer组成的。是DAG有向无环图。net写在一个prototxt文件里。
一个简单的逻辑回归分类器
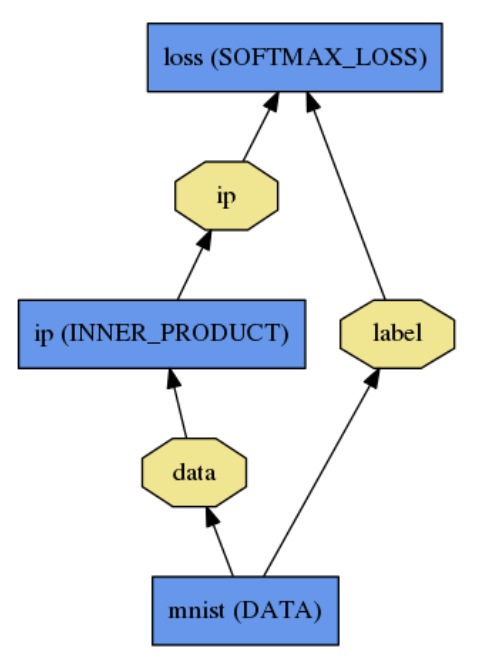
# train_test.prototxt
name: "LogReg"
layer {
name: "mnist"
type: "Data"
top: "data"
top: "label"
data_param {
source: "input_leveldb"
batch_size: 64
}
}
layer {
name: "ip"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "data"
top: "ip"
inner_product_param {
num_output: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "loss"
type: "SoftmaxWithLoss"
bottom: "ip"
bottom: "label"
top: "loss"
}模型初始化由Net::Init()。处理。初始化主要做两件事:通过创建blob和图层来构建整个DAG(对于C ++极客:网络将在其生命周期内保留blob和图层的所有权),并调用图层的SetUp()功能。它还会执行一系列其他簿记操作,例如验证整个网络体系结构的正确性。
solver
solver算是caffe的核心的核心,它协调着整个模型的运作。caffe程序运行必带的一个参数就是solver配置文件。
训练模型命令caffe train --solver=xxx_solver.prototxt
solver的主要作用就是交替调用前向(forward)算法和后向(backward)算法来更新参数,从而最小化loss,实际上就是一种迭代的优化算法。
目前有6中优化算法,实际上对应着tensorflow里的optimizer:
Stochastic Gradient Descent (type: "SGD"),
AdaDelta (type: "AdaDelta"),
Adaptive Gradient (type: "AdaGrad"),
Adam (type: "Adam"),
Nesterov’s Accelerated Gradient (type: "Nesterov") and
RMSprop (type: "RMSProp")具体请看:
例子:
net: "examples/mnist/lenet_train_test.prototxt"
test_iter: 100
test_interval: 500
base_lr: 0.01
momentum: 0.9
type: SGD
weight_decay: 0.0005
lr_policy: "inv"
gamma: 0.0001
power: 0.75
display: 100
max_iter: 20000
snapshot: 5000
snapshot_prefix: "examples/mnist/lenet"
solver_mode: CPUprototxt
prototxt文件是用来存放模型结构的地方,模型的结构主要以layer为单位来构建。
name: "LeNet"
layer {
name: "mnist" #网络层名称
type: "Data" #网络层类型,数据层
top: "data" #这一层的输出,数据
top: "label" #这一层的输出,标签
include { phase: TRAIN } #TRAIN:=用于训练,TEST:=用于测试
transform_param { scale: 0.00390625 } #对数据进行scale
data_param { #数据层配置
source: "examples/mnist/mnist_train_lmdb" #数据存放路径
batch_size: 64 #指定batch大小
backend: LMDB #指定数据库格式,LMDB/LevelDB
}
}
layer {
name: "mnist"
type: "Data"
top: "data"
top: "label"
include { phase: TEST }
transform_param { scale: 0.00390625 }
data_param {
source: "examples/mnist/mnist_test_lmdb"
batch_size: 100
backend: LMDB
}
}
layer{
name:"conv1"
type:"Convolution" #卷积层
bottom:"data" #上一层的输出作为输入
top:"conv1"
param{name:"conv1_w" lr_mult:1 decay_mult:1} #卷积层参数w的名称,学习率和衰减率(相对于base_lr和weight_decay的倍数)
param{name:"conv1_b" lr_mult:2 decay_mult:0} #卷积层参数b的名称,学习率和衰减率
convolution_param{
num_output:20 #卷积层输出的feature map数量
kernel_size:5 #卷积层的大小
pad:0 #卷积层的填充大小
stride:1 #进行卷积的步长
weight_filler{type:"xavier" } #参数w的初始话策略
weight_filler{type:"constant" value:0.1} #参数b的初始化策略
}
}
layer { #BatchNorm层,对feature map进行批规范化处理
name:"bn1"
type:"BatchNorm"
bottom:"conv1"
top:"conv1"
batch_norm_param{ use_global_stats:false} #训练时为false,测试时为true
}
layer { #池化层,即下采样层
name: "pool1"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv1"
top: "pool1"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX #最大值池化,还有AVE均值池化
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "conv2"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "pool1"
top: "conv2"
param { lr_mult: 1 }
param { lr_mult: 2 }
convolution_param {
num_output: 50
kernel_size: 5
stride: 1
weight_filler { type: "xavier" }
bias_filler { type: "constant" }
}
}
layer {
name:"bn2"
type:"BatchNorm"
bottom:"conv2"
top:"conv2"
batch_norm_param{ use_global_stats:false}
}
layer {
name: "pool2"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv2"
top: "pool2"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer { #全连接层
name: "ip1"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "pool2"
top: "ip1"
param { lr_mult: 1 }
param { lr_mult: 2 }
inner_product_param {
num_output: 500
weight_filler { type: "xavier" }
bias_filler { type: "constant" }
}
}
layer { #激活函数层,提供非线性能力
name: "relu1"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "ip1"
top: "ip1"
}
layer {
name: "ip2"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "ip1"
top: "ip2"
param { lr_mult: 1 }
param { lr_mult: 2 }
inner_product_param {
num_output: 10
weight_filler { type: "xavier" }
bias_filler { type: "constant" }
}
}
layer { #损失函数层
name: "prob"
type: "SoftmaxWithLoss"
bottom: "ip2"
bottom: "label"
top: "prob"
}train.sh
TOOLS=/path/to/your/caffe/build/tools
GLOG_logtostderr=0 GLOG_log_dir=log/ \ #该行用于调用glog进行训练日志保存,使用时请把该行注释删除,否则会出错
$TOOLS/caffe train --solver=/path/to/your/solver.prototxt #--snapshot=/path/to/your/snapshot or --weights=/path/to/your/caffemodel ,snapshot和weights两者只是选一,两个参数都可以用来继续训练,区别在于是否保存solver状态数据准备
#!/usr/bin/env sh
# Create the imagenet lmdb inputs
# N.B. set the path to the imagenet train + val data dirs
set -e
EXAMPLE="" #存储路径
DATA="" #数据路径
TOOLS=/path/to/your/caffe/build/tools #caffe所在目录
TRAIN_DATA_ROOT="" #训练数据根目录
VAL_DATA_ROOT="" #测试数据根目录
# RESIZE=true to resize the images to 256x256. Leave as false if images have
# already been resized using another tool.
RESIZE=false #重新调整图片大小
if $RESIZE; then
RESIZE_HEIGHT=256
RESIZE_WIDTH=256
else
RESIZE_HEIGHT=0
RESIZE_WIDTH=0
fi
#检测路径是否存在
if [ ! -d "$TRAIN_DATA_ROOT" ]; then
echo "Error: TRAIN_DATA_ROOT is not a path to a directory: $TRAIN_DATA_ROOT"
echo "Set the TRAIN_DATA_ROOT variable in create_imagenet.sh to the path" \
"where the ImageNet training data is stored."
exit 1
fi
if [ ! -d "$VAL_DATA_ROOT" ]; then
echo "Error: VAL_DATA_ROOT is not a path to a directory: $VAL_DATA_ROOT"
echo "Set the VAL_DATA_ROOT variable in create_imagenet.sh to the path" \
"where the ImageNet validation data is stored."
exit 1
fi
echo "Creating train lmdb..."
GLOG_logtostderr=1 $TOOLS/convert_imageset \
--resize_height=$RESIZE_HEIGHT \
--resize_width=$RESIZE_WIDTH \
--shuffle \
$TRAIN_DATA_ROOT \
$DATA/train.txt \ #训练图片列表,运行时请把该行注释删除,否则会出错
$EXAMPLE/mnist_train_lmdb
echo "Creating val lmdb..."
GLOG_logtostderr=1 $TOOLS/convert_imageset \
--resize_height=$RESIZE_HEIGHT \
--resize_width=$RESIZE_WIDTH \
--shuffle \
$VAL_DATA_ROOT \
$DATA/val.txt \
$EXAMPLE/mnist_test_lmdb
echo "Done."