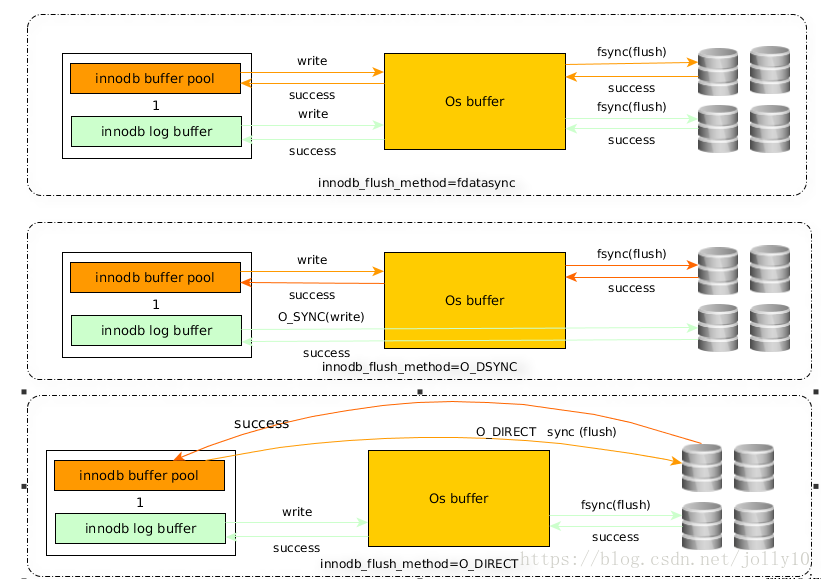
有三个值:fdatasync(默认),O_DSYNC,O_DIRECT(mysql5.7其它几个值
littlesync
,nosync,O_DIRECT_NO_FSYNC官方不建议使用)
默认是fdatasync,调用fsync()去刷数据文件与redo log的buffer
为O_DSYNC时,innodb会使用O_SYNC方式打开和刷写redo log,使用fsync()刷写数据文件
为O_DIRECT时,innodb使用O_DIRECT打开数据文件,使用fsync()刷写数据文件跟redo log
首先文件的写操作包括三步:open,write,flush
上面最常提到的fsync(int fd)函数,该函数作用是flush时将与fd文件描述符所指文件有关的buffer刷写到磁盘,并且flush完元数据信息(比如修改日期、创建日期等)才算flush成功。
使用O_SYNC方式打开redo文件表示当write日志时,数据都write到磁盘,并且元数据也需要更新,才返回成功
O_DIRECT则表示我们的write操作是从mysql innodb buffer里直接向磁盘上写
至此我再总结一下三者写数据方式:
fdatasync模式:写数据时,write这一步并不需要真正写到磁盘才算完成(可能写入到操作系统buffer中就会返回完成),真正完成是flush操作,buffer交给操作系统去flush,并且文件的元数据信息也都需要更新到磁盘。
O_DSYNC模式:写日志操作是在write这步完成,而数据文件的写入是在flush这步通过fsync完成
O_DIRECT模式:数据文件的写入操作是直接从mysql innodb buffer到磁盘的,并不用通过操作系统的缓冲,而真正的完成也是在flush这步,日志还是要经过OS缓冲
官方的建议是这样:
How each setting affects performance depends on hardware configuration and workload. Benchmark your particular configuration to decide which setting to use, or whether to keep the default setting. Examine theInnodb_data_fsyncs status variable to see the overall number of fsync() calls for each setting. The mix of read and write operations in your workload can affect how a setting performs. For example, on a system with a hardware RAID controller and battery-backed write cache, O_DIRECT can help to avoid double buffering between the InnoDBbuffer pool and the operating system file system cache. On some systems where InnoDB data and log files are located on a SAN, the default value or O_DSYNC might be faster for a read-heavy workload with mostly SELECTstatements. Always test this parameter with hardware and workload that reflect your production environment.
也就是说,具体的取值跟硬件配置和工作负载相关,最好做一次压测来决定。不过通常来说,linux环境下具有raid控制器和write-back写策略,o_direct是比较好的选择;如果存储介质是SAN,那么使用默认fsync或者osync或许更好一些。