第七章目录
- 7.1 Android View动画框架
- 7.1.1 透明度动画
- 7.1.2 旋转动画
- 7.1.3 位移动画
- 7.1.4 缩放动画
- 7.1.5 动画集合
- 7.2 Android属性动画分析
- 7.2.1 ObjectAnimator
- 7.2.2 PropertyValuesHolder
- 7.2.3 ValueAnimator
- 7.2.4 动画事件的监听
- 7.2.5 AnimatorSet
- 7.2.6 在XML中使用属性动画
- 7.2.7 View的animate方法
- 7.3 Android布局动画
- 7.4 Interpolators
- 7.5 自定义动画
- 7.6 Android5.X SVG矢量动画机制
- 7.6.1 <path>标签
- 7.6.2 SVG常用指令
- 7.6.3 SVG编辑器
- 7.6.4 Android中使用SVG
- 7.6.5 SVG动画实例
- 7.7 Android动画特效
- 7.7.1 灵动菜单
- 7.7.2 计时器动画
- 7.7.3 下拉展开动画
第七章读书笔记
动画分为视图动画和属性动画
7.1 Android View动画框架
- View动画定义了透明度、旋转、缩放、位移几种常见的动画
- 实现原理:每次绘制视图时View所在的ViewGroup中的drawChild函数获取该View的Animation的Transformation值,然后调用canvas.concat(transformToApply.getMatrix()),通过矩阵运算完成动画帧
- View动画使用简单,效率高,但是不具备交互性
7.1.1 透明度动画
AlphaAnimation aa = new AlphaAnimation(0,1); aa.setDuration(1000); view.startAnimation(aa);7.1.2 旋转动画
RotateAnimation ra = new RotateAnimation(0,360,100,100); ra.setDuration(1000); view.startAnimation(ra);
- 参数分别为旋转起始角度和中心点的坐标,以自身中心点设置旋转动画:
RotateAnimation ra = new RotateAnimation(0,360, RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,0.5F, RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,0.5F);7.1.3 位移动画
TranslateAnimation ta = new TranslateAnimation(0,200,0,300); ta.setDuration(1000); view.startAnimation(ta);7.1.4 缩放动画
ScaleAnimation sa = new ScaleAnimation(0,2,0,2); sa.setDuration(1000); view.startAnimation(sa);
- 以自身中心点设置缩放动画:
ScaleAnimation sa = new ScaleAnimation(0,1,0,1,RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,0.5F, RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,0.5F); sa.setDuration(1000); view.startAnimation(sa);7.1.5 动画集合
通过AnimationSet,将动画以组合的形式展现出来:
AnimationSet as = new AnimationSet(true); as.setDuration(1000); AlphaAnimation aa = new AlphaAnimation(0,1); aa.setDuration(1000); as.addAnimation(aa); TranslateAnimation ta = new TranslateAnimation(0,200,0,300); ta.setDuration(1000); as.addAnimation(ta); view.startAnimation(as);系统还提供了对应的监听回调,可以得到动画的开始,结束和重复事件:
animation.setAnimationListener(new Animation.AnimationListener() { @Override public void onAnimationStart(Animation animation) { } @Override public void onAnimationEnd(Animation animation) { } @Override public void onAnimationRepeat(Animation animation) { } });
7.2 Android属性动画分析
- Animator框架中使用最多的就是AnimatorSet和ObjectAnimator
- 属性动画通过调用属性的get、set方法来真实地控制了一个View的属性值
7.2.1 ObjectAnimator
- 只需通过静态工厂直接返回一个ObjectAnimator对象
- 参数包括一个对象和对象的属性,这个属性必须有get和set函数
- 调用setInterpolator来设置相应的插值器
- 旧版本的视图动画只是改变了显示,没有改变事件响应的位置
简单的平移动画的实现:
ObjectAnimator animator = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(view,"translationX",300); animator.setDuration(300); animator.start();参数介绍:
- 被操作的View
- 要操作的属性,属性必须有get、set方法,要不无法使用
- 可变数组,传递该属性变化的一个取值过程
一些常用的可以直接使用的属性:
- translationX和translationY:作为一种增量来控制着View对象从它布局容器的左上角坐标偏移的位置
- rotation、rotationX和rotationY:控制View对象围绕支点进行2D和3D旋转
- scaleX和scaleY:控制View对象围绕它的支点进行2D缩放
- pivotX和pivotY:控制View对象的支点位置,围绕这个支点进行旋转和缩放变换处理,默认情况下,该支点的位置就是View对象的中心点
- x和y:它描述了View对象在它的容器中的最终位置,它是最初的左上角坐标和 translationX和 translationY值的累计和
- alpha:它表示View对象的alpha透明度,默认值是1(不透明),0代表完全透明(不可见)
如果某个属性没有get、set方法,两种方案来解决:
- 自定义一个属性或者包装类
- 通过ValueAnimator实现
以自定义一个属性增加get、set方法为例:
private static class WrapperView { private View mTarget; public WrapperView(View target) { mTarget = target; } public int getWidth() { return mTarget.getLayoutParams().width; } public void setWidth(int width) { mTarget.getLayoutParams().width = width; mTarget.requestLayout(); } }通过代码使用:
WrapperView wrapper = new WrapperView(mButton); ObjectAnimator.ofInt(wrapper ,"width",500).setDuration(5000).start();7.2.2 PropertyValuesHolder
- 类似视图动画的AnimationSet,可以实现多个属性动画的组合
- 在平移的过程中,同时改变X、Y轴的缩放,可以这样实现:
PropertyValuesHolder pvh1 = PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat("translationX",300f); PropertyValuesHolder pvh2 = PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat("scaleX",1f,0,1f); PropertyValuesHolder pvh3 = PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat("scaleY",1f,0,1f); ObjectAnimator.ofPropertyValuesHolder(view,pvh1,pvh2,pvh3).setDuration(1000).start();7.2.3 ValueAnimator
- ObjectAnimator继承自ValueAnimator
- ValueAnimator本身不提供任何动画效果,它更像一个数值发生器,用来产生具有一定规律的数字,从而让调用者来控制动画的实现过程,通过AnimatorUpdateListener监听数值的变换:
ValueAnimator animator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0,100); animator.setTarget(view); animator.setDuration(1000).start(); animator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() { @Override public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) { float value = (float) animation.getAnimatedValue(); //TODO use the value } });7.2.4 动画事件的监听
系统提供了属性动画的监听回调:
ObjectAnimator anim = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(view,"alpha",0.5f); anim.addListener(new Animator.AnimatorListener() { @Override public void onAnimationStart(Animator animation) { } @Override public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) { } @Override public void onAnimationCancel(Animator animation) { } @Override public void onAnimationRepeat(Animator animation) { } });大部分我们只关心End事件,所以Android也提供了一个AnimatorListenerAdapter来让我们选择必要的事件监听:
anim.addListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() { @Override public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) { } });7.2.5 AnimatorSet
- AnimatorSet可以实现和PropertyValuesHolder一样的效果,不同的是Animator还可以实现更精确的顺序控制:
ObjectAnimator animator1 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(view, "translationX", 300f); ObjectAnimator animator2 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(view, "scaleX", 1f, 0, 1f); ObjectAnimator animator3 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(view, "scaleY", 1f, 0, 1f); AnimatorSet set = new AnimatorSet(); set.setDuration(1000); set.playTogether(animator1,animator2,animator3); set.start();
- AnimatorSet不仅仅通过playTogether(),还有其他方法控制多个效果的协同工作:playSequentially()、animSet.play().with()、before()、after()
7.2.6 在XML中使用属性动画
属性动画和视图动画一样,也可以在xml文件中编写:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <objectAnimator xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:duration="1000" android:propertyName="scaleX" android:valueFrom="1.0" android:valueTo="2.0" android:valueType="floatType"> </objectAnimator>在程序中使用也简单:
private void scaleX(View view){ Animator anim = AnimatorInflater.loadAnimator(this,R.animator.scaleX); anim.setTarget(mMv); anim.start(); }7.2.7 View的animate方法
Google给View增加了animate方法来直接驱动属性动画:
animate.animate().alpha(0).y(300).setDuration(300).withStartAction(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { } }).withEndAction(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { runOnUiThread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { } }); } }).start();
7.3 Android布局动画
- 布局动画的作用是指ViewGroup添加view的时候添加一个动画过滤效果
- 最简单的布局动画就是在ViewGroup的XML中打开一个系统默认的效果:
android:animateLayoutChanges="true"还可以通过LayoutAnimationController实现自定义子view的过渡效果
LayoutAnimationController 第一个参数是需要的动画,第二个参数是每个子View显示的delay时间,若时间不为0,还可以setOrder设置子View的显示顺序:
- LayoutAnimationController.ORDER_NORMAL:顺序
- LayoutAnimationController.ORDER_RANDOM:随机
- LayoutAnimationController.ORDER_REVEESE:反序
LinearLayout ll = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.ll); //设置过渡动画 ScaleAnimation sa = new ScaleAnimation(0, 1, 0, 1); sa.setDuration(2000); //设置布局动画的显示属性 LayoutAnimationController lac = new LayoutAnimationController(sa, 0.5F); lac.setOrder(LayoutAnimationController.ORDER_NORMAL); //为ViewGroup设置布局动画 ll.setLayoutAnimation(lac);
7.4 Interpolators(插值器)
- 插值器是可以控制动画变换速率的一个属性值,是匀速的还是先快后慢还是先慢后快还是反弹等等好多种插值器
- 这里就不介绍了,好多种直接用就好
7.5 自定义动画
- 需要实现它的applyTransformation的逻辑
- 需要覆盖父类的initalize方法实现一些初始化工作
模拟电视关闭效果:
@Override protected void applyTransformation(float interpolatedTime, Transformation t) { final Matrix matrix = t.getMatrix(); // 缩放以及缩放的中心点 matrix.preScale(1, 1 - interpolatedTime, mCenterwidth,mCenterheight); super.applyTransformation(interpolatedTime, t); }android.graphics.Camera中的Camera类,它封装了openGL的3D动画,从而可以风场方便地创建3D动画效果,只要移动Camera就能拍摄到具有立体感的图像:
@Override public void initialize(int width, int height, int parentWidth, int parentHeight) { super.initialize(width, height, parentWidth, parentHeight); //设置默认时长 setDuration(2000); //设置动画结束后保留状态 setFillAfter(true); //设置默认插值器 setInterpolator(new BounceInterpolator()); mCenterWidth = width / 2; mCenterHeight = height / 2; } @Override protected void applyTransformation(float interpolatedTime, Transformation t) { final Matrix matrix = t.getMatrix(); mCamera.save(); //使用Camera设置旋转的角度 mCamera.rotateY(mRotateY * interpolatedTime); //将旋转变换作用到matrix上 mCamera.getMatrix(matrix); mCamera.restore(); //通过pre方法设置矩形作用前的偏移量来改变旋转中心 matrix.preTranslate(mCenterWidth, mCenterHeight); matrix.postTranslate(-mCenterWidth, -mCenterHeight); }
7.6 Android 5.X SVG 矢量动画机制
SVG的定义:
- 可伸缩矢量图形(Scalable Vector Graphics)
- 定义用于网络的基于矢量的图形
- 使用XML格式定义图形
- 图片在放大或改变尺寸的情况下其图形质量不会有所损失
- 万维网联盟的标准
- 与诸多DOM和XSL之类的W3C标准是一个整体
Android5.X之后添加了对SVG的<path>标签的支持,其优点是:
- 放大不会失真
- bitmap需要为不同分辨率设计多套图标,而矢量图则不需要
7.6.1 <path> 标签
使用<path>有以下指令:
- M = moveto(M X,Y):将画笔移动到指定的坐标位置,但未发生绘制
- L = lineto(L X,Y):画直线到指定的坐标位置
- H = horizontal lineto( H X):画水平线到指定的X坐标位置
- V = vertical lineto(V Y ):画垂直线到指定的Y坐标
- C = curveto(C ,X1,Y1,X2,Y2,ENDX,ENDY):三次贝塞尔曲线
- S = smooth curveto(S X2,Y2,ENDX,ENDY):三次贝塞尔曲线
- Q = quadratic Belzier curve(Q X Y,ENDX,ENDY):二次贝塞尔曲线
- T = smooth quadratic Belzier curvrto(T,ENDX,ENDY):映射前面路径的终点
- A = elliptical Are(A RX,RY,XROTATION,FLAG1FLAG2,X,Y):弧线
- Z = closepath():关闭路径
使用上面指令时,需要注意以下几点:
- 坐标轴以(0,0)为中心,X轴水平向右,Y轴水平向下
- 所有指令大小写均可,大写绝对定位,参照全局坐标系,小写相对定位,参照父容器坐标系
- 指令和数据间的空格可以无视
- 同一指令出现多次可以只用一个
7.6.2 SVG常用指令
- L
绘制直线的指令是“L”,代表从当前点绘制直线到给定点,“L”之后的参数是一个点坐标,同时,还可以使用“H”和“V”指令来绘制水平、竖直线,后面的参数是x坐标或y坐标- M
M指令类似Android绘图中的path类moveto方法,即代表画笔移动到某一点,但并不发生绘图动作- A
A指令是用来绘制一条弧线,且允许弧线不闭合,可以把A指令绘制的弧度想象成椭圆的某一段,A指令一下有七个参数
- RX,RY:所在的椭圆的半轴大小
- XROTATION:椭圆的X轴与水平方向顺时针方向的夹角,可以想象成一个水平的椭圆饶中心点顺时针旋转XROTATION 的角度
- FLAG1:只有两个值,1表示大角度弧度,0为小角度弧度
- FLAG2:只有两个值,确定从起点到终点的方向1顺时针,0逆时针
- X,Y轴:终点坐标
7.6.3 SVG编辑器
- 在线可视化SVG编辑器官网:http://editor.method.ac/
- 优秀的离线SVG编辑器:Inkscape
7.6.4 Android 中使用SVG
Android5.X提供了两个API来支持SVG:
- VectorDrawable:在XML中可以创建一个静态的SVG图形
- AnimatedVectorDrawable:给VectorDrawable提供动画效果
7.6.4.1 VectorDrawable
VectorDrawable的使用是通过<vector>标签来声明的:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:width="200dp" android:height="200dp" android:viewportHeight="100dp" android:viewportWidth="100dp"> </vector>如果做过Web的应该对viewport应该很熟悉
- height:表示SVG的高度200dp
- width:表示SVG的宽度200dp
- viewportHeight:表示SVG图形被划分成100份
- viewportWidth:表示SVG图形被划分成100份
- 如果在绘图中使用坐标(50,50),则意味着该坐标为正中间
接下来,给<vector>标签增加显示path:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:width="200dp" android:height="200dp" android:viewportHeight="100dp" android:viewportWidth="100dp"> <group android:name="test" android:rotation="0"> <path android:fillColor="@android:color/holo_blue_light" android:pathData=" M 25 50 a 25,25 0 1,0 50,0" /> </group> </vector>布局文件中这样用:
<ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:src="@drawable/vector" />

7.6.4.2 AnimatedVectorDrawable
- AnimatedVectorDrawable使用:Google工程师将其比喻为一个胶水,通过其连接静态的VectorDrawable和动态的objectAnimator
1、首先在XML文件中通过<animated-vector>标签来声明对AnimatedVectorDrawable的使用:
<animated-vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:drawable="@drawable/vector"> <target android:name="test" android:animation="@anim/anim_earth" /> </animated-vector>特别注意的是:这个target里面的name要和VectorDrawable的name对应,animation要和动画资源文件对应
2、对应的VectorDrawable文件:
<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:width="200dp" android:height="200dp" android:viewportHeight="100" android:viewportWidth="100"> <group android:name="test" android:rotation="0"> <path android:pathData=" M 25 50 a 25,25 0 1,0 50,0" android:strokeColor="@android:color/holo_blue_light" android:strokeWidth="2" /> </group> </vector>3、4、对应的animation文件:
<objectAnimator xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:duration="4000" android:propertyName="rotation" android:valueFrom="0" android:valueTo="360" />特别注意的是:在<group>标签和<path>标签中添加了rotate、fillColor、pathData等属性,那么可以通过objectAnimator指定android:propertyName=”XXXX”属性来控制哪一种属性,如果指定属性为pathData,那么需要添加一个属性——android:valueType=”pathType”来告诉系统进行pathData的变换
4、在布局文件中使用:
<ImageView android:id="@+id/image" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:src="@drawable/anim_vector" />5、在Activity中开启动画:
ImageView image = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image); ((Animatable)image.getDrawable()).start();7.6.5 SVG动画实例
7.6.5.1 线图动画
1、定义我们的VectorDrawable
<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:width="200dp" android:height="200dp" android:viewportHeight="100" android:viewportWidth="100"> <group> <path android:name="path1" android:pathData=" M 20,80 L 50,80 80,80" android:strokeColor="@android:color/holo_green_dark" android:strokeLineCap="round" android:strokeWidth="5" /> <path android:name="path2" android:pathData=" M 20,20 L 50,20 80,20" android:strokeColor="@android:color/holo_green_dark" android:strokeLineCap="round" android:strokeWidth="5" /> </group> </vector>2、定义两个Path的objectAnimator,从path1到path2
<objectAnimator xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:duration="5000" android:interpolator="@android:anim/bounce_interpolator" android:propertyName="pathData" android:valueFrom=" M 20,80 L 50,80 80,80" android:valueTo=" M 20,80 L 50,50 80,80" android:valueType="pathType" /><objectAnimator xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:duration="5000" android:interpolator="@android:anim/bounce_interpolator" android:propertyName="pathData" android:valueFrom=" M 20,20 L 50,20 80,20" android:valueTo=" M 20,20 L 50,50 80,20" android:valueType="pathType" />3、定义AnimatedVectorDrawable连接VectorDrawable和objectAnimator
<animated-vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:drawable="@drawable/trick"> <target android:name="path1" android:animation="@anim/anim_path1" /> <target android:name="path2" android:animation="@anim/anim_path2" /> </animated-vector>4、布局文件中使用这个AnimatedVectorDrawable
<ImageView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:src="@drawable/trick_anim" android:id="@+id/image"/>5、代码中启动动画,可以在点击事件中写这些
ImageView image = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image); Drawable drawable = image.getDrawable(); if (drawable instanceof Animatable) { ((Animatable) drawable).start(); }
7.6.5.2 模拟三球仪
1、定义我们的VectorDrawable
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:width="200dp" android:height="200dp" android:viewportHeight="100" android:viewportWidth="100"> <group android:name="sun" android:pivotX="60" android:pivotY="50" android:rotation="0"> <path android:name="path_sun" android:fillColor="@android:color/holo_blue_light" android:pathData=" M 50,50 a 10,10 0 1,0 20,0 a 10,10 0 1,0 -20,0" /> <group android:name="earth" android:pivotX="75" android:pivotY="50" android:rotation="0"> <path android:name="path_earth" android:fillColor="@android:color/holo_orange_dark" android:pathData=" M 70,50 a 5,5 0 1,0 10,0 a 5,5 0 1,0 -10,0" /> <group> <path android:fillColor="@android:color/holo_green_dark" android:pathData=" M 90,50 m -5 0 a 4,4 0 1,0 8 0 a 4,4 0 1,0 -8,0" /> </group> </group> </group> </vector>2、定义两个objectAnimator,代码都是一样的
<objectAnimator xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:duration="4000" android:propertyName="rotation" android:valueFrom="0" android:valueTo="360" /><objectAnimator xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:duration="4000" android:propertyName="rotation" android:valueFrom="0" android:valueTo="360" />3、定义AnimatedVectorDrawable连接VectorDrawable和objectAnimator
<animated-vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:drawable="@drawable/earth_moon_system"> <target android:name="sun" android:animation="@anim/anim_sun" /> <target android:name="earth" android:animation="@anim/anim_earth" /> </animated-vector>4、布局文件中使用这个AnimatedVectorDrawable
<ImageView android:id="@+id/image" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:src="@drawable/sun_system" />5、代码中启动动画
ImageView image = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image); Drawable drawable = image.getDrawable(); if (drawable instanceof Animatable) { ((Animatable) drawable).start(); }
7.6.5.3 轨迹动画
1、定义我们的VectorDrawable
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:width="160dp" android:height="30dp" android:viewportHeight="30" android:viewportWidth="160"> <path android:name="search" android:pathData="M141 , 17 A9 ,9 0 1 , 1 ,142 , 16 L149 ,23" android:strokeAlpha="0.8" android:strokeColor="#ff3570be" android:strokeLineCap="square" android:strokeWidth="2" /> <path android:name="bar" android:pathData="M0,23 L149 ,23" android:strokeAlpha="0.8" android:strokeColor="#ff3570be" android:strokeLineCap="square" android:strokeWidth="2" /> </vector>2、定义两个objectAnimator,代码都是一样的
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <objectAnimator xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:duration="1000" android:interpolator="@android:interpolator/accelerate_decelerate" android:propertyName="trimPathStart" android:valueFrom="0" android:valueTo="1" android:valueType="floatType" />3、定义AnimatedVectorDrawable连接VectorDrawable和objectAnimator
<animated-vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:drawable="@drawable/searchbar"> <target android:name="search" android:animation="@anim/anim_searchbar" /> </animated-vector>4、布局文件中使用这个AnimatedVectorDrawable
<ImageView android:id="@+id/image" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:src="@drawable/search_anim" />5、代码中启动动画
ImageView image = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image); Drawable drawable = image.getDrawable(); if (drawable instanceof Animatable) { ((Animatable) drawable).start(); }
SVG动画的几个基本步骤都是一样的:
1、定义VectorDrawable,相当于整一个静态的图片
2、定义ObjectAnimator,相当于创建一个动画
3、定义AnimatedVectorDrawable去连接以上两个玩意儿
4、在布局文件中使用这个AnimatedVectorDrawable,ImageView的src中使用就行
5、在代码中启动动画
7.7 动画特效
7.7.1 灵动菜单
因为具有交互性,必须使用属性动画,设置相应的插值器就可以实现了
布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/imageView_b" android:src="@drawable/b" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" /> <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/imageView_c" android:src="@drawable/c" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" /> <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/imageView_d" android:src="@drawable/d" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" /> <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/imageView_e" android:src="@drawable/e" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" /> <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/imageView_a" android:src="@drawable/a" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" /> </RelativeLayout>Activity文件:
public class PropertyTest extends Activity implements View.OnClickListener { private int[] mRes = {R.id.imageView_a, R.id.imageView_b, R.id.imageView_c, R.id.imageView_d, R.id.imageView_e}; private List<ImageView> mImageViews = new ArrayList<ImageView>(); private boolean mFlag = true; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.property); for (int i = 0; i < mRes.length; i++) { ImageView imageView = (ImageView) findViewById(mRes[i]); imageView.setOnClickListener(this); mImageViews.add(imageView); } } @Override public void onClick(View v) { switch (v.getId()) { case R.id.imageView_a: if (mFlag) { startAnim(); } else { closeAnim(); } break; default: Toast.makeText(PropertyTest.this, "" + v.getId(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); break; } } private void closeAnim() { ObjectAnimator animator0 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mImageViews.get(0), "alpha", 0.5F, 1F); ObjectAnimator animator1 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mImageViews.get(1), "translationY", 200F, 0); ObjectAnimator animator2 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mImageViews.get(2), "translationX", 200F, 0); ObjectAnimator animator3 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mImageViews.get(3), "translationY", -200F, 0); ObjectAnimator animator4 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mImageViews.get(4), "translationX", -200F, 0); AnimatorSet set = new AnimatorSet(); set.setDuration(500); set.setInterpolator(new BounceInterpolator()); set.playTogether(animator0, animator1, animator2, animator3, animator4); set.start(); mFlag = true; } private void startAnim() { ObjectAnimator animator0 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat( mImageViews.get(0), "alpha", 1F, 0.5F); ObjectAnimator animator1 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat( mImageViews.get(1), "translationY", 200F); ObjectAnimator animator2 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat( mImageViews.get(2), "translationX", 200F); ObjectAnimator animator3 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat( mImageViews.get(3), "translationY", -200F); ObjectAnimator animator4 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat( mImageViews.get(4), "translationX", -200F); AnimatorSet set = new AnimatorSet(); set.setDuration(500); set.setInterpolator(new BounceInterpolator()); set.playTogether( animator0, animator1, animator2, animator3, animator4); set.start(); mFlag = false; } }
7.7.2 计时器动画
在这里使用了ValueAnimator,来回顾一下
public class TimerTest extends Activity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.timer); } public void tvTimer(final View view) { ValueAnimator valueAnimator = ValueAnimator.ofInt(0, 100); valueAnimator.addUpdateListener( new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() { @Override public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) { ((TextView) view).setText("$ " + (Integer) animation.getAnimatedValue()); } }); valueAnimator.setDuration(3000); valueAnimator.start(); } }
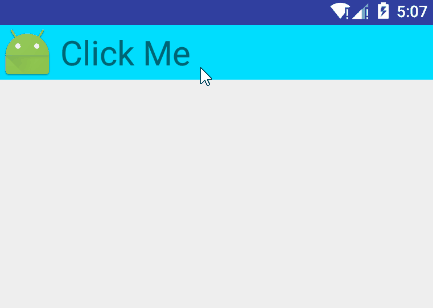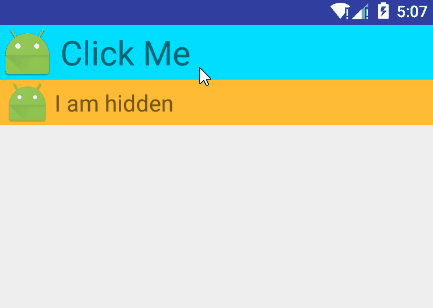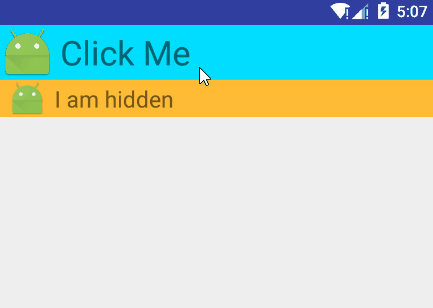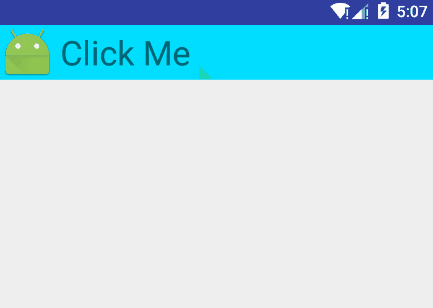
7.7.3 下拉展开动画
还是使用ValueAnimator来实现
布局文件,两个不同的LinearLayout来显示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="vertical"> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:gravity="center_vertical" android:onClick="llClick" android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_bright" android:orientation="horizontal"> <ImageView android:id="@+id/app_icon" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center" android:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher" /> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginLeft="5dp" android:gravity="left" android:text="Click Me" android:textSize="30sp" /> </LinearLayout> <LinearLayout android:id="@+id/hidden_view" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="40dp" android:background="@android:color/holo_orange_light" android:gravity="center_vertical" android:orientation="horizontal" android:visibility="gone"> <ImageView android:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_hidden" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:gravity="center" android:textSize="20sp" android:text="I am hidden" /> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>Activity文件:
public class DropTest extends Activity { private LinearLayout mHiddenView; private float mDensity; private int mHiddenViewMeasuredHeight; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.drop); mHiddenView = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.hidden_view); // 获取像素密度 mDensity = getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density; // 获取布局的高度 mHiddenViewMeasuredHeight = (int) (mDensity * 40 + 0.5); } public void llClick(View view) { if (mHiddenView.getVisibility() == View.GONE) { // 打开动画 animateOpen(mHiddenView); } else { // 关闭动画 animateClose(mHiddenView); } } private void animateOpen(final View view) { view.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); ValueAnimator animator = createDropAnimator( view, 0, mHiddenViewMeasuredHeight); animator.start(); } private void animateClose(final View view) { int origHeight = view.getHeight(); ValueAnimator animator = createDropAnimator(view, origHeight, 0); animator.addListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() { public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) { view.setVisibility(View.GONE); } }); animator.start(); } private ValueAnimator createDropAnimator( final View view, int start, int end) { ValueAnimator animator = ValueAnimator.ofInt(start, end); animator.addUpdateListener( new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() { @Override public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator valueAnimator) { int value = (Integer) valueAnimator.getAnimatedValue(); ViewGroup.LayoutParams layoutParams = view.getLayoutParams(); layoutParams.height = value; view.setLayoutParams(layoutParams); } }); return animator; } }
总结
这一章的动画总体来说还是比较简单,就是几个Android动画框架的使用
- 视图动画Animation,无法交互
- 属性动画Animator,可以实现交互,Google更加提倡,可以实现更加丰富的动画效果
- 布局动画,ViewGroup中添加子View是的一个过渡动画效果
- Android 5.X SVG矢量动画机制,比如一些点击事件的动画效果可以用矢量动画来实现