BlockChain Demo
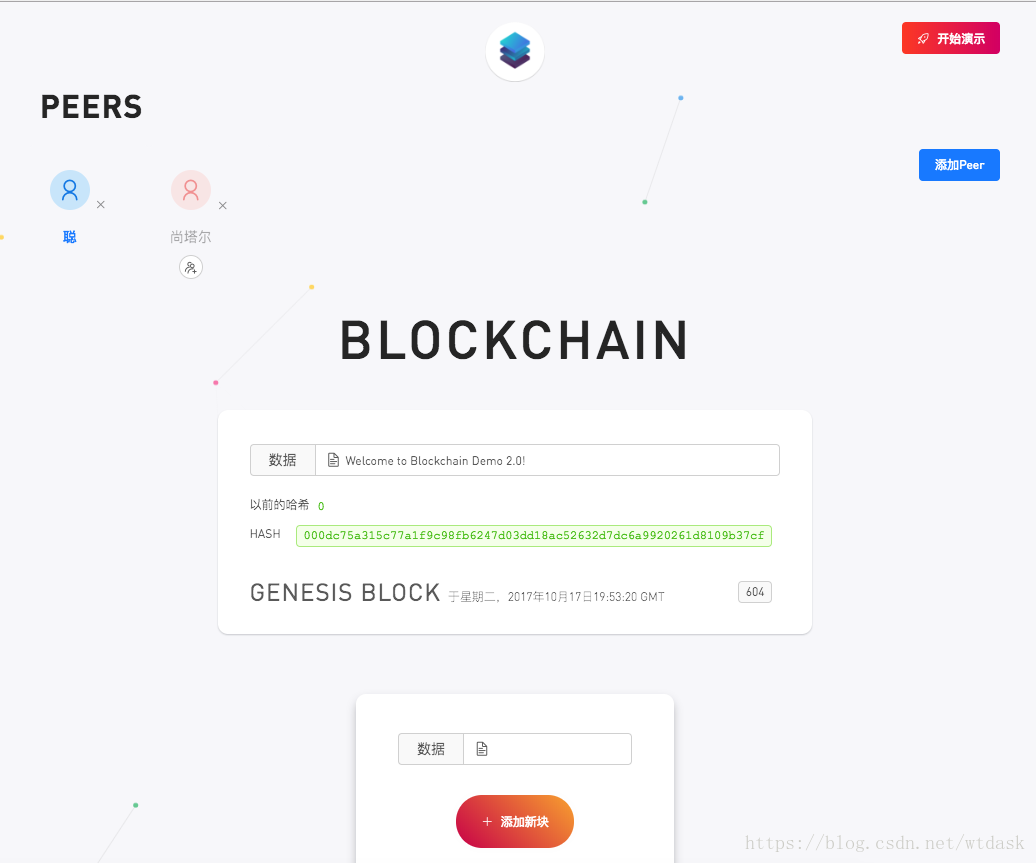
打开比特币Demo演示网页区块链Demo演示地址,我们可以看到如下页面。
点击开始演示
接下来是BlockChain Demo 2.0的新功能介绍
关于Demo功能区的介绍
并附有JavaScript代码和gitHubDemo地址
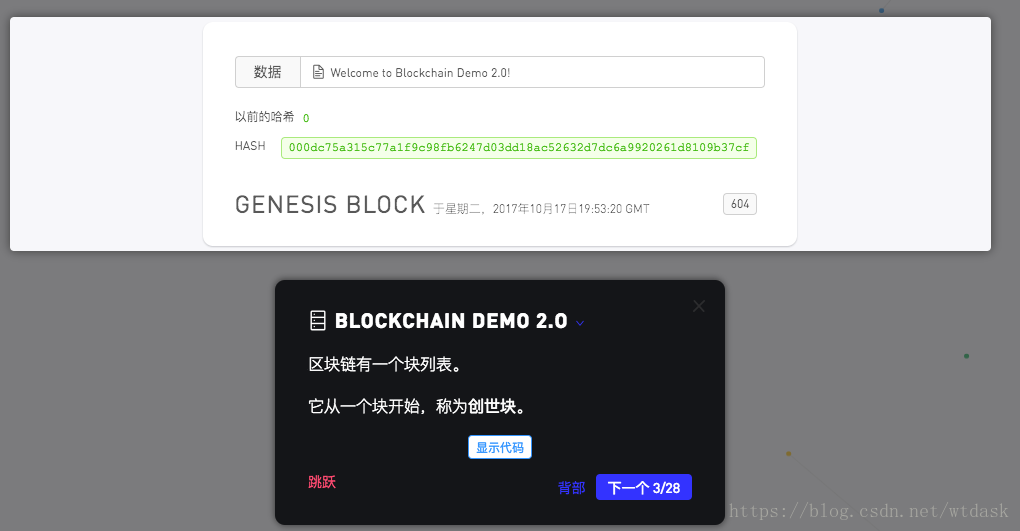
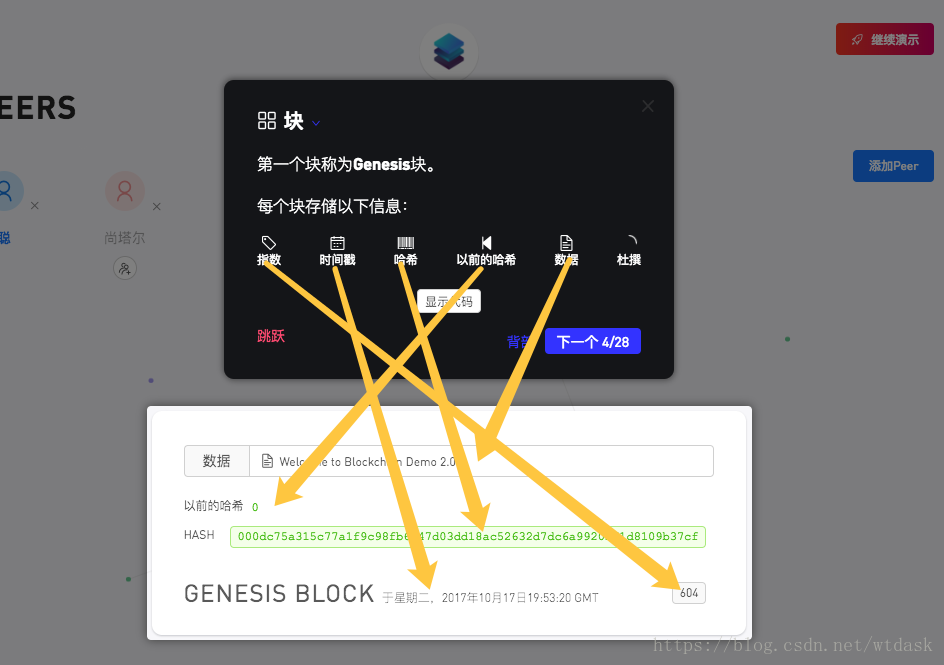
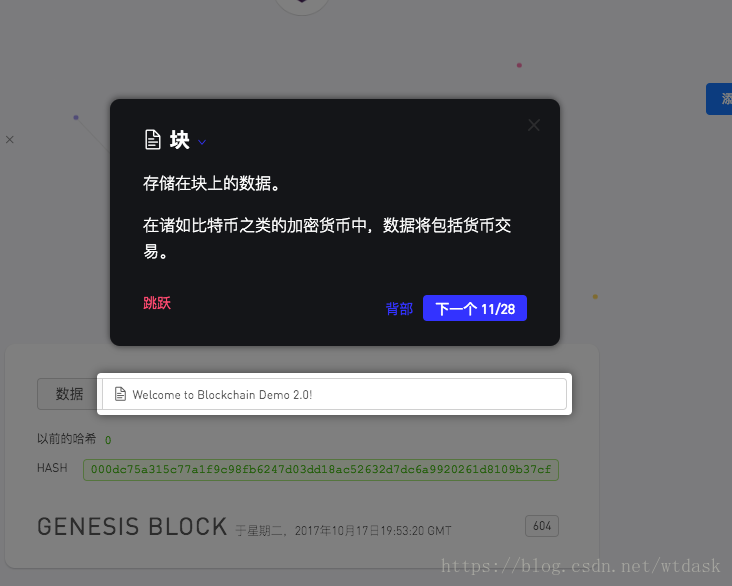
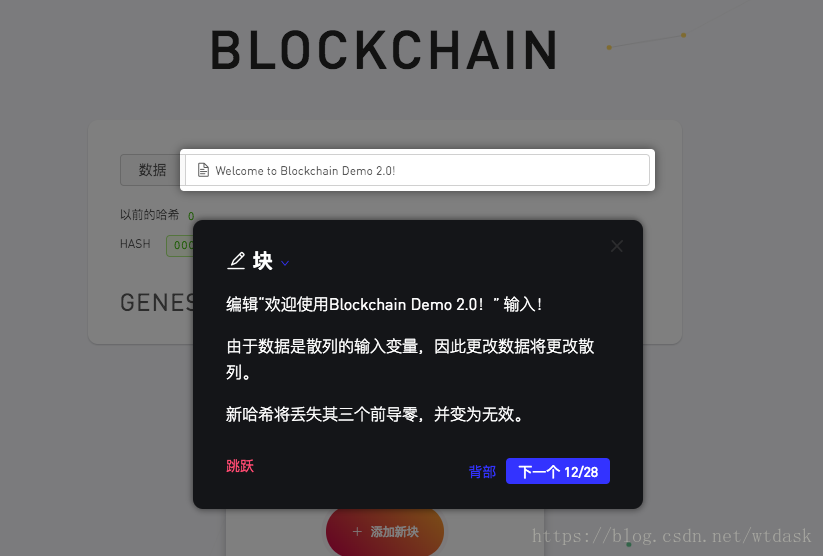
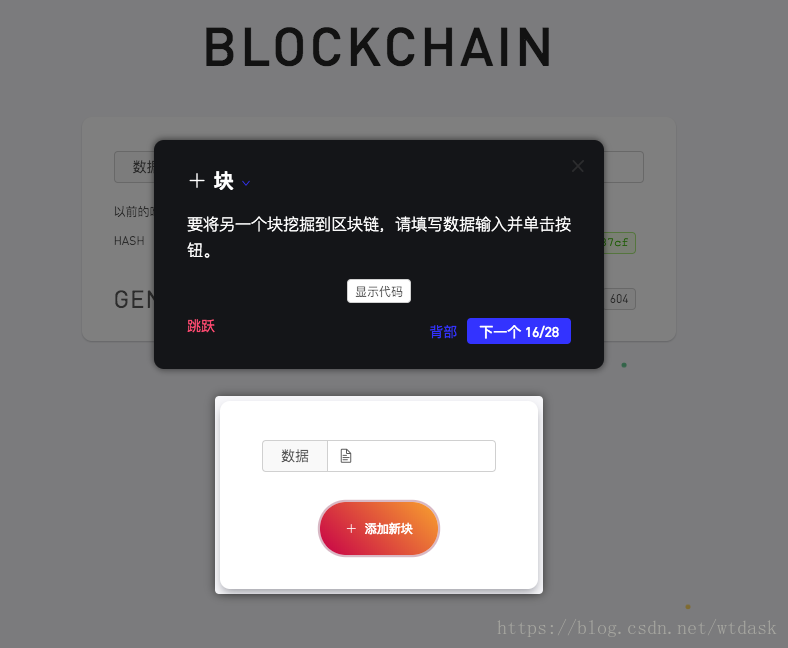
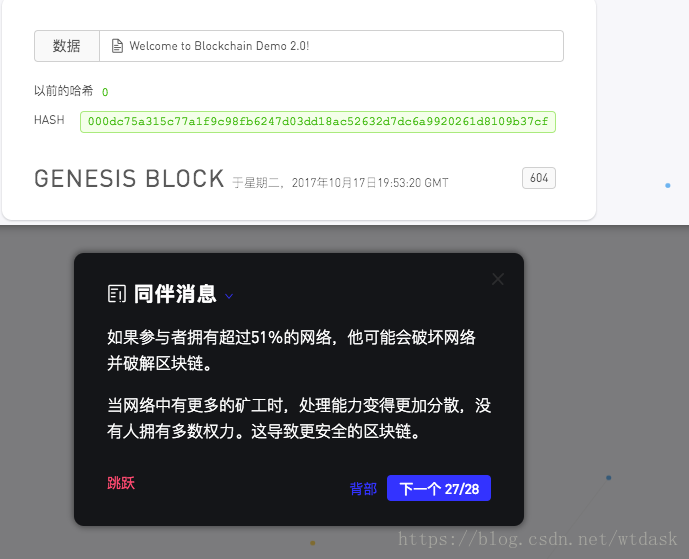
显示每个区块存储的信息
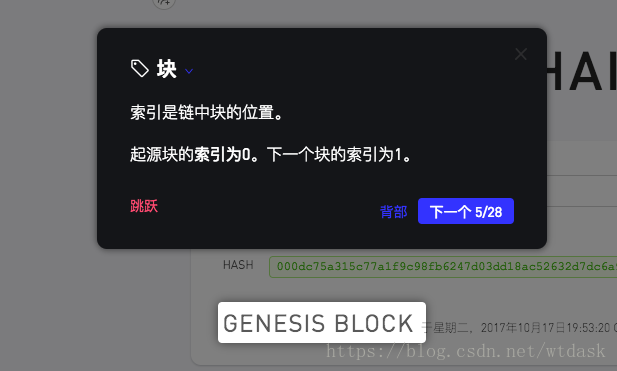
介绍区块链中区块的索引
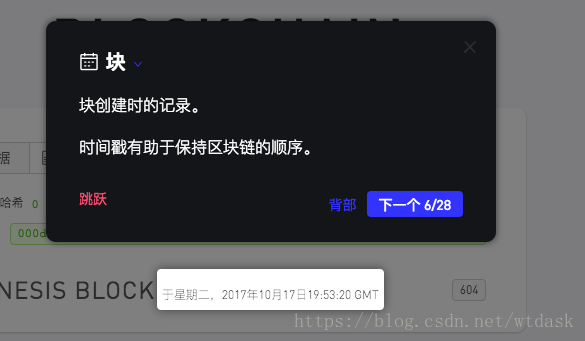
介绍创建区块时候的时间戳
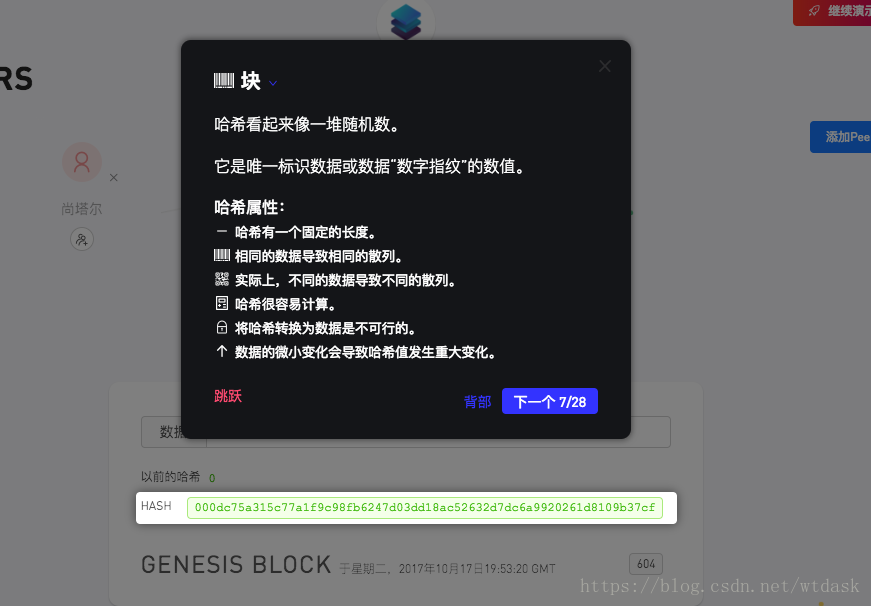
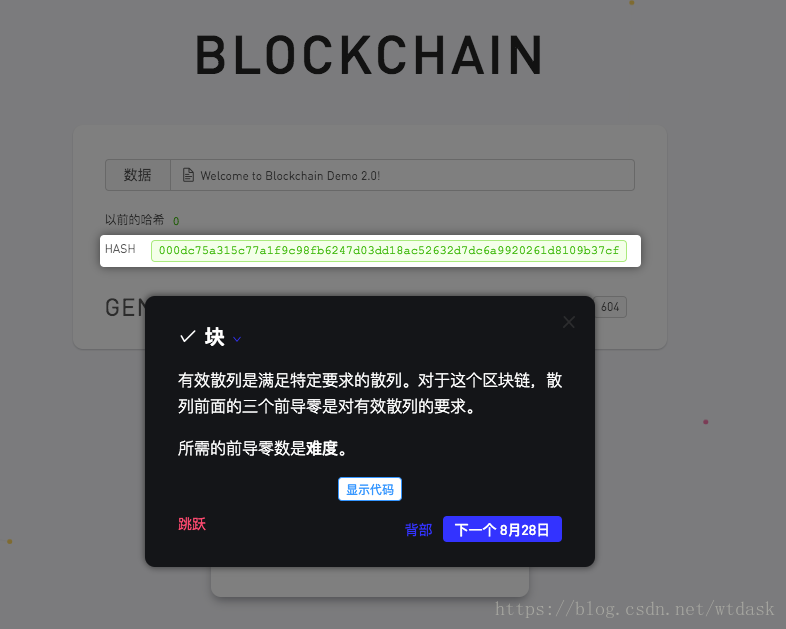
介绍区块中hash散列加密
介绍区块hash散列中前导零也就是难度的介绍
// cosnt Block = reuqire("./Block.js");
// class Blockchain {
// constructor() {
// this.blockchain = [Block.genesis()];
this.difficulty = 3;
// }
// get() { ... }
// get latestBlock() { ... }
isValidHashDifficulty(hash) {
for (var i = 0; i < hash.length; i++) {
if (hash[i] !== "0") {
break;
};
}
return i >= this.difficulty;
}
// };
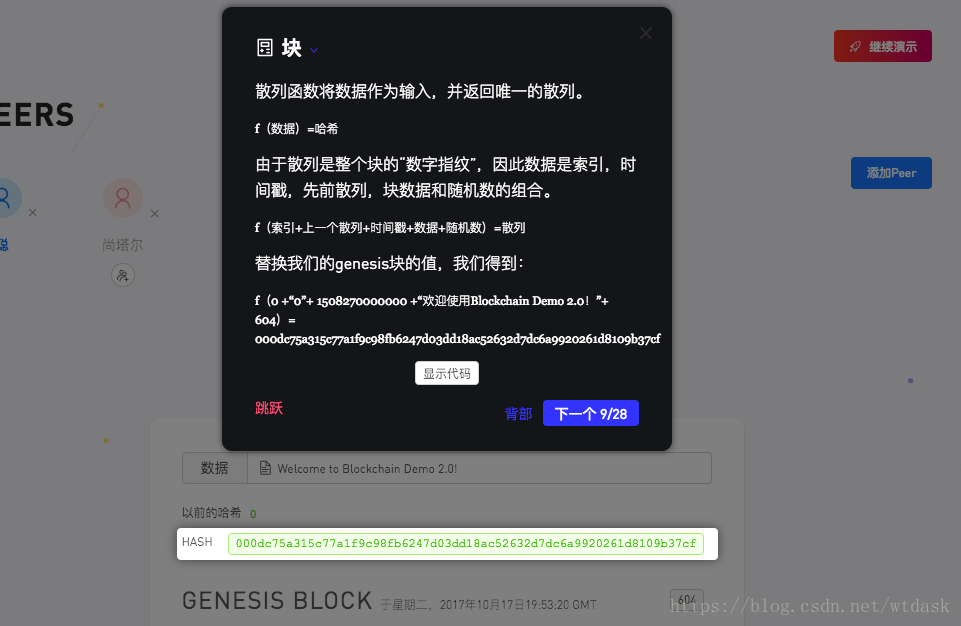
// module.exports = Blockchain;介绍Hash散列的生成规则
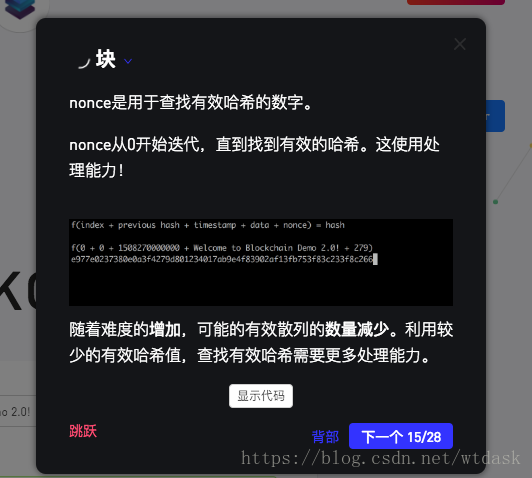
(索引+上一个散列+时间戳+数据+随机数)=散列
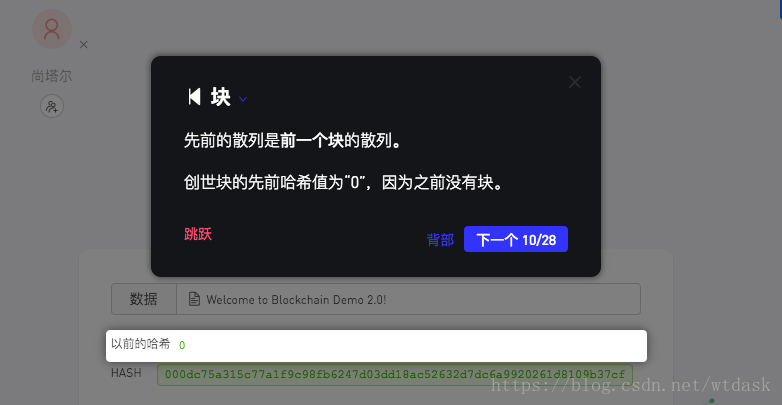
(0 +“0”+ 1508270000000 +“欢迎使用Blockchain Demo 2.0!”+ 604)= 000dc75a315c77a1f9c98fb6247d03dd18ac52632d7dc6a9920261d8109b37cf介绍关于上一个区块中的Hash值
关于区块中的数据,这也是我们关注的
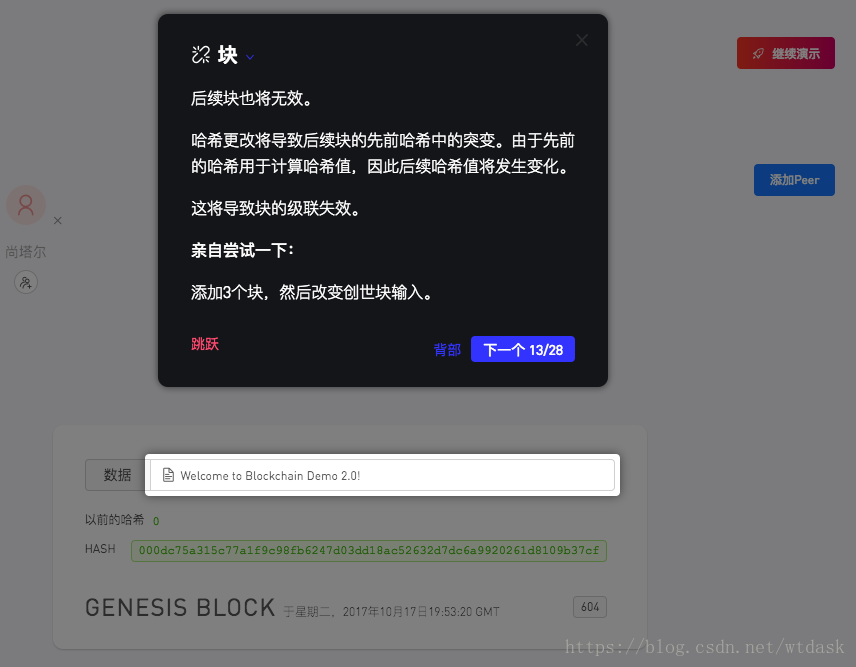
关于数据的变化,数据的微小变化都可以给Hash值带来巨大的变化。Hash值的是否有效,是我们设置的前导零难度决定的,符合前导零难度的规则才算是有效的Hash
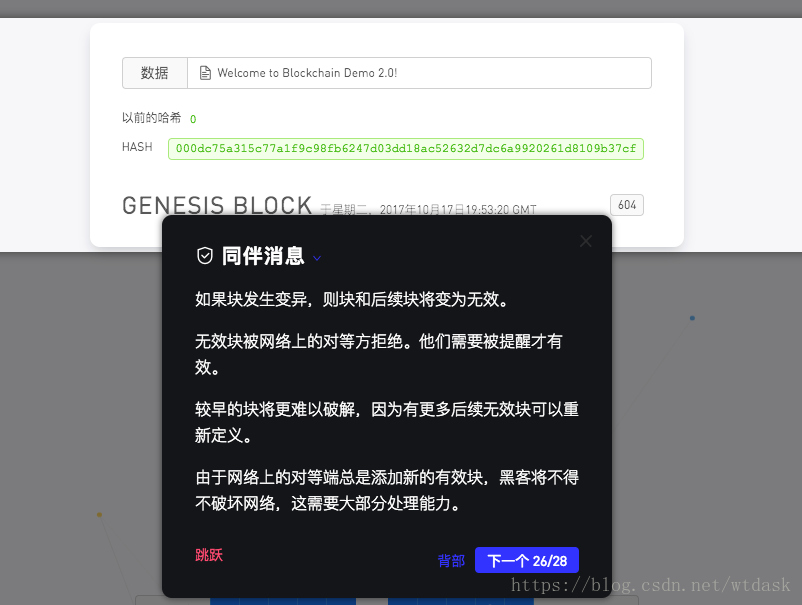
假如一个区块链中的某一个区块中Hash值失效,那么它后面的区块都会失效
生成有效Hash散列的唯二变量就是数据和随机数,当我们需要的数据固定时,只有挖掘匹配的前导零难度的随机数才能寻找到新的区块
// const Block = require("./Block.js");
// const crypto = require("crypto");
// class Blockchain {
// constructor() { ... }
// get() { ... }
// get latestBlock() { ... }
// isValidHashDifficulty(hash) { ... }
// calculateHashForBlock(block) { ... }
// calculateHash(...) { ... }
mine(data) {
const newBlock = this.generateNextBlock(data);
try {
this.addBlock(newBlock);
} catch (err) {
throw err;
};
}
// };
// module.exports = Blockchain;匹配查找有效Hash的数字,从0开始找,直到找到。随着难度的不断增加,有效散列的数量减少,因此匹配的计算力也会逐渐增大。
新增新的区块
// const Block = require("./Block.js");
// const crypto = require("crypto");
// class Blockchain {
// constructor() { ... }
// get() { ... }
// get latestBlock() { ... }
// isValidHashDifficulty(hash) { ... }
// calculateHashForBlock(block) { ... }
// calculateHash(...) { ... }
// mine(data) { ... }
// generateNextBlock(data) { ... }
addBlock(newBlock) {
if (this.isValidNewBlock(newBlock, this.latestBlock)) {
this.blockchain.push(newBlock);
} else {
throw "Error: Invalid block";
}
}
// };
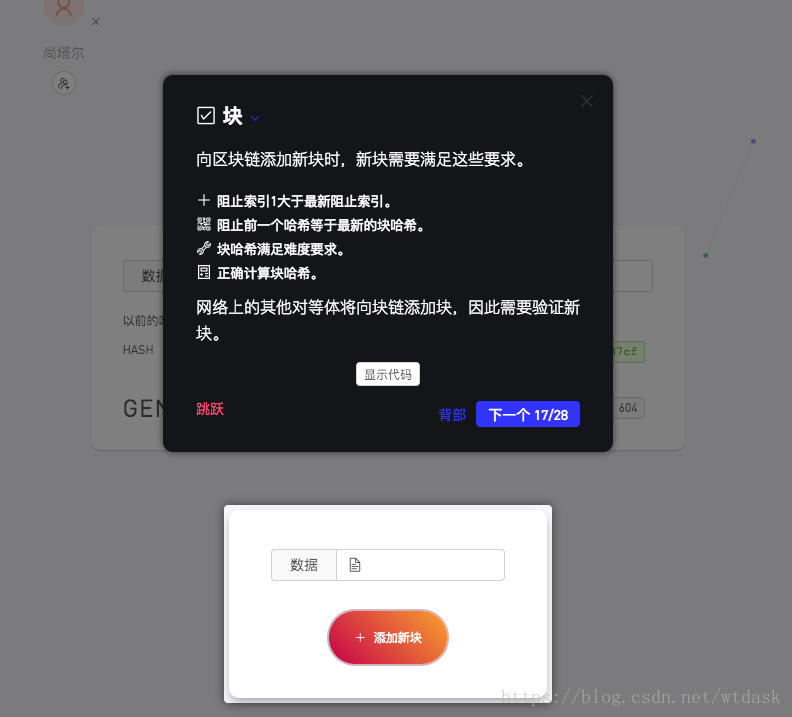
// module.exports = Blockchain;新增区块需要满足的要求
- 上一个区块的索引+1等于新的索引
- 上一个区块的hash要等于下一个区块的前导hash
- hash要满足前导零难度要求
- 正确的hash值
// const Block = require("./Block.js");
// const crypto = require("crypto");
// class Blockchain {
// constructor() { ... }
// get() { ... }
// get latestBlock() { ... }
// isValidHashDifficulty(hash) { ... }
// calculateHashForBlock(block) { ... }
// calculateHash(...) { ... }
// mine(data) { ... }
// generateNextBlock(data) { ... }
// addBlock(newBlock) { ... }
isValidNextBlock(nextBlock, previousBlock) {
const nextBlockHash = this.calculateHashForBlock(nextBlock);
if (previousBlock.index + 1 !== nextBlock.index) {
return false;
} else if (previousBlock.hash !== nextBlock.previousHash) {
return false;
} else if (nextBlockHash !== nextBlock.hash) {
return false;
} else if (!this.isValidHashDifficulty(nextBlockHash)) {
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
// };
// module.exports = Blockchain;全球的计算机网络共同维护,因此要确保区块链的安全性,正确性及一致性。
P2p.js
const wrtc = require('wrtc');
const Exchange = require('peer-exchange');
const p2p = new Exchange("Blockchain Demo 2.0", { wrtc: wrtc });
const net = require("net");
class PeerToPeer {
constructor(blockchain) {
this.peers = [];
this.blockchain = blockchain;
}
startServer(port) {
const server = net
.createServer(socket =>
p2p.accept(socket, (err, conn) => {
if (err) {
throw err;
} else {
this.initConnection.call(this, conn);
}
})
)
.listen(port);
}
}
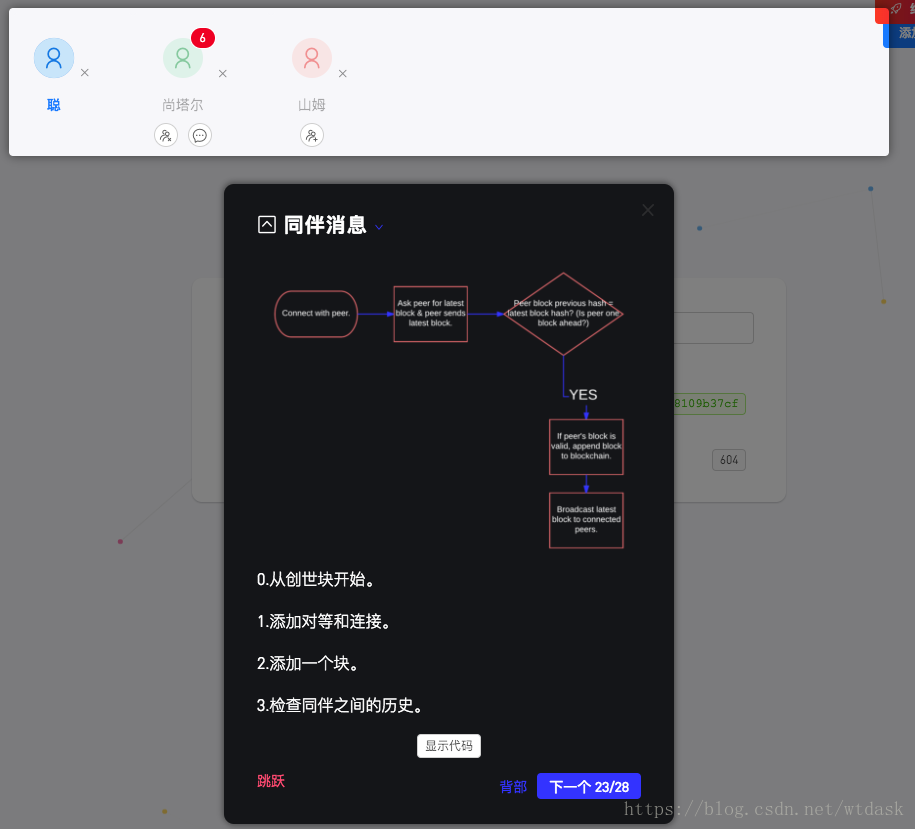
module.exports = PeerToPeer;同伴消息:链接对等方添加到网络
// const wrtc = require('wrtc');
// const Exchange = require('peer-exchange');
// const p2p = new Exchange(...);
// const net = require("net");
// class PeerToPeer {
// constructor(blockchain) { ... }
// startServer(port) { ... }
discoverPeers() {
p2p.getNewPeer((err, conn) => {
if (err) {
throw err;
} else {
this.initConnection.call(this, conn);
}
});
}
// }
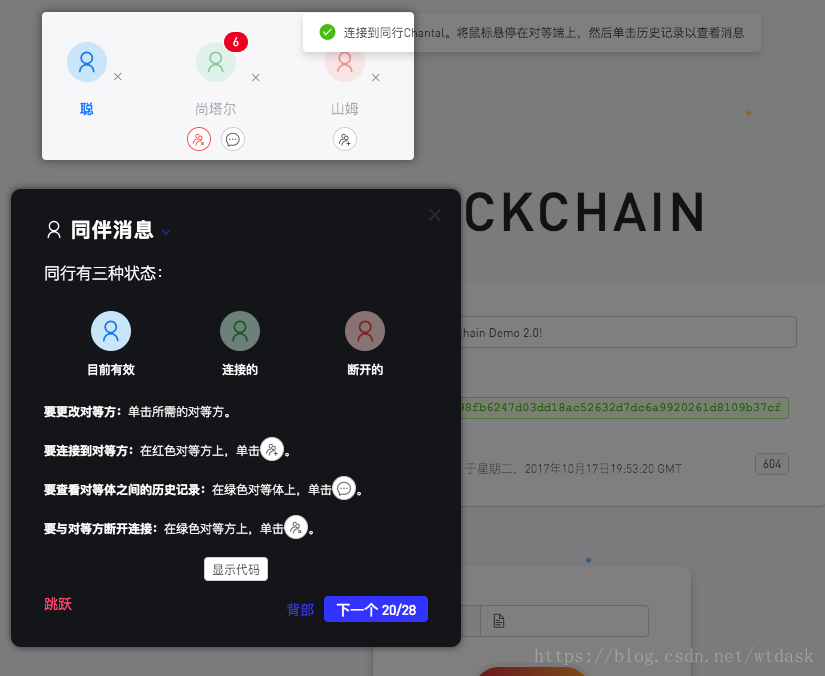
// module.exports = PeerToPeer;同伴消息:Demo的三种同伴消息的状态
- 蓝色:当前有效的
- 绿色:连接的
- 红色:断开连接的
改变:直接点击头像
链接:在红色对等方单击加号的图标
查看:在绿色的对等体单击短信图标
断开:点击绿色对等方上面的加号图标
P2p.js
// const wrtc = require('wrtc');
// const Exchange = require('peer-exchange');
// const p2p = new Exchange(...);
// const net = require("net");
// class PeerToPeer {
// constructor(blockchain) { ... }
// startServer(port) { ... }
// discoverPeers() { ... }
connectToPeer(host, port) {
const socket = net.connect(port, host, () =>
p2p.connect(socket, (err, conn) => {
if (err) {
throw err;
} else {
this.initConnection.call(this, conn);
}
})
);
}
closeConnection() {
p2p.close(err => {
throw err;
})
}
// }
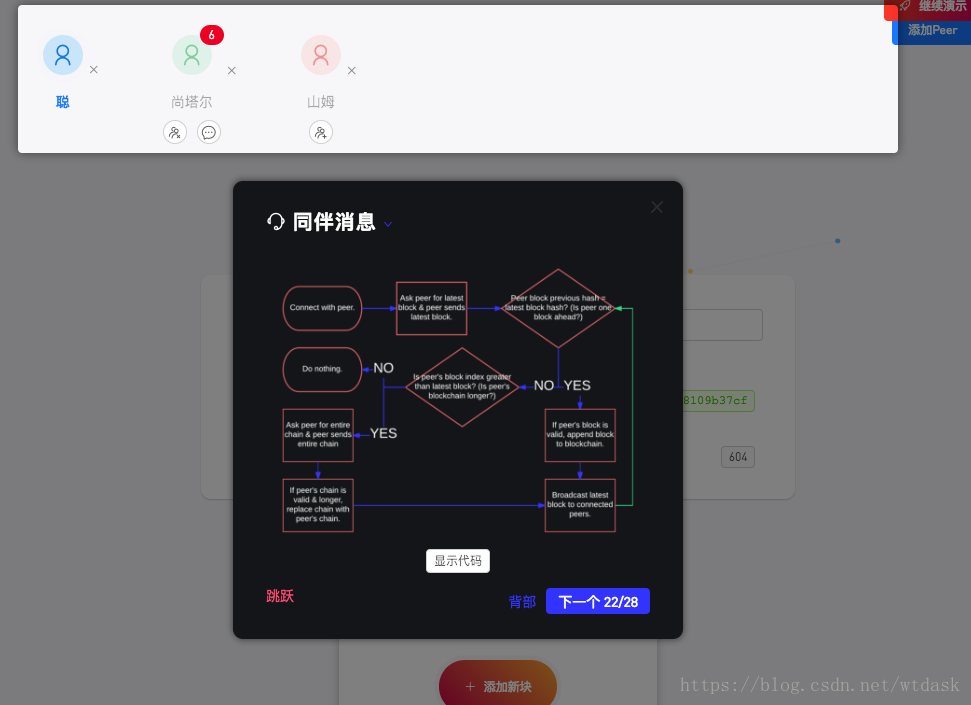
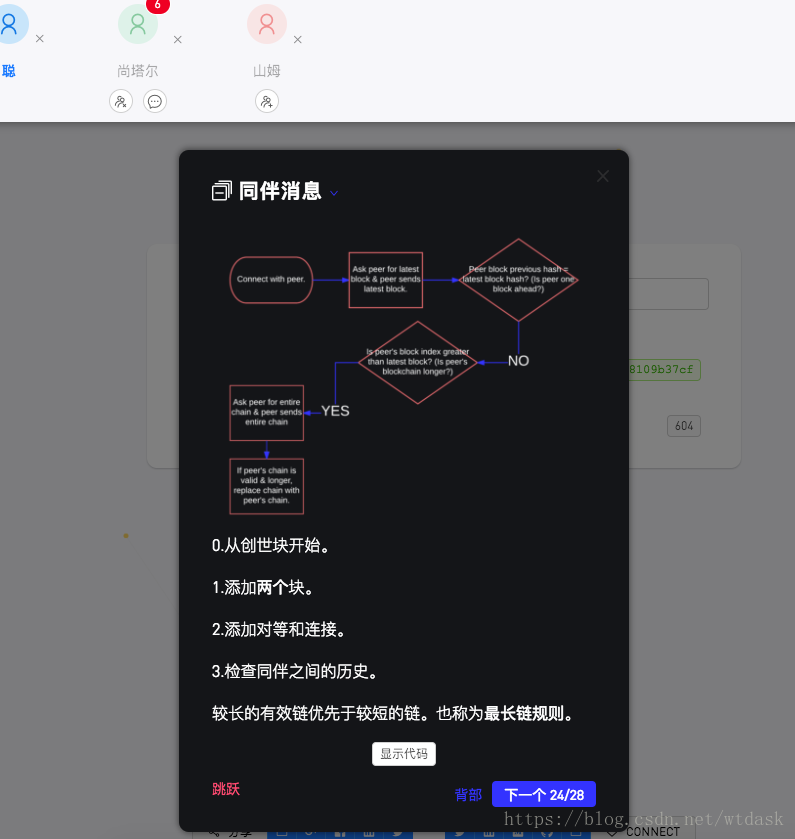
// module.exports = PeerToPeer;同伴消息:确定谁拥有最新的区块链
Blockchain.js
// const wrtc = require('wrtc');
// const Exchange = require('peer-exchange');
// const p2p = new Exchange(...);
// const net = require("net");
const messageType = {
REQUEST_LATEST_BLOCK: 0,
RECEIVE_LATEST_BLOCK: 1,
REQUEST_BLOCKCHAIN: 2,
RECEIVE_BLOCKCHAIN: 3,
};
const {
REQUEST_LATEST_BLOCK,
RECEIVE_LATEST_BLOCK,
REQUEST_BLOCKCHAIN,
RECEIVE_BLOCKCHAIN,
REQUEST_TRANSACTIONS,
RECEIVE_TRANSACTIONS
} = messageType;
// class PeerToPeer { ... }
// module.exports = PeerToPeer;
class Messages {
static getLatestBlock() {
return {
type: REQUEST_LATEST_BLOCK
};
}
static sendLatestBlock(block) {
return {
type: RECEIVE_LATEST_BLOCK,
data: block
};
}
static getBlockchain() {
return {
type: REQUEST_BLOCKCHAIN
};
}
static sendBlockchain(blockchain) {
return {
type: RECEIVE_BLOCKCHAIN,
data: blockchain
};
}
}逻辑图
P2p.js
// const wrtc = require('wrtc');
// const Exchange = require('peer-exchange');
// const p2p = new Exchange(...);
// const net = require("net");
// const messageType = { ... };
// const { ... } = messageType;
// class PeerToPeer {
// constructor(blockchain) { ... }
// startServer(port) { ... }
// discoverPeers() { ... }
// connectToPeer(host, port) { ... }
// closeConnection() { ... }
broadcastLatest() {
this.broadcast(Messages.sendLatestBlock(this.blockchain.latestBlock));
}
broadcast(message) {
this.peers.forEach(peer => this.write(peer, message));
}
write(peer, message) {
peer.write(JSON.stringify(message));
}
initConnection(connection) {
this.peers.push(connection);
this.initMessageHandler(connection);
this.initErrorHandler(connection);
this.write(connection, Messages.getLatestBlock());
}
initMessageHandler(connection) {
connection.on("data", data => {
const message = JSON.parse(data.toString("utf8"));
this.handleMessage(connection, message);
});
}
initErrorHandler(connection) {
connection.on("error", err => {
throw err;
});
}
handleMessage(peer, message) {
switch (message.type) {
case REQUEST_LATEST_BLOCK:
this.write(peer, Messages.sendLatestBlock(this.blockchain.latestBlock));
break;
case REQUEST_BLOCKCHAIN:
this.write(peer, Messages.sendBlockchain(this.blockchain.get()));
break;
case RECEIVE_LATEST_BLOCK:
this.handleReceivedLatestBlock(message, peer);
break;
case RECEIVE_BLOCKCHAIN:
this.handleReceivedBlockchain(message);
break;
default:
throw "Received invalid message.";
}
}
// }
// module.exports = PeerToPeer;
// class Messages { ... }P2p.js
// const wrtc = require('wrtc');
// const Exchange = require('peer-exchange');
// const p2p = new Exchange(...);
// const net = require("net");
// const messageType = { ... };
// const { ... } = messageType;
// class PeerToPeer {
// constructor(blockchain) { ... }
// startServer(port) { ... }
// discoverPeers() { ... }
// connectToPeer(host, port) { ... }
// closeConnection() { ... }
// broadcastLatest() { ... }
// broadcast(message) { ... }
// write(peer, message) { ... }
// initConnection(connection) { ... }
// initMessageHandler(connection) { ... }
// initErrorHandler(connection) { ... }
// handleMessage(peer, message) { ... }
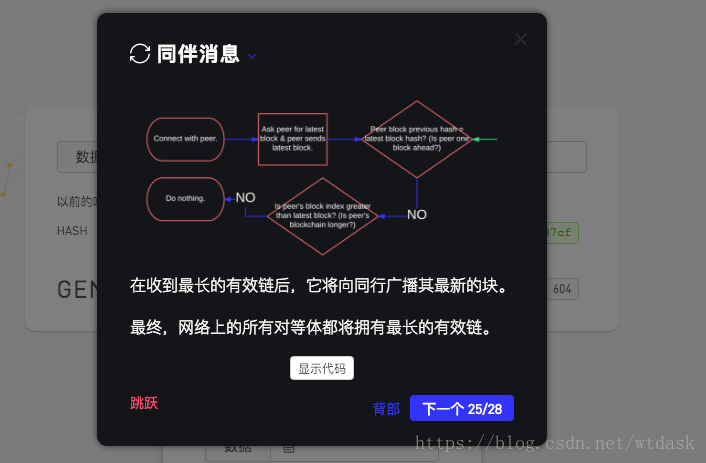
handleReceivedLatestBlock(message, peer) {
const receivedBlock = message.data;
const latestBlock = this.blockchain.latestBlock;
if (latestBlock.hash === receivedBlock.previousHash) {
try {
this.blockchain.addBlock(receivedBlock);
} catch(err) {
throw err;
}
} else if (receivedBlock.index > latestBlock.index) {
this.write(peer, Messages.getBlockchain());
} else {
// Do nothing.
}
}
// }
// module.exports = PeerToPeer;
// class Messages { ... }P2p.js
handleReceivedLatestBlock(message, peer) {
// if (latestBlock.hash === receivedBlock.previousHash) {
// ...
} else if (receivedBlock.index > latestBlock.index) {
this.write(peer, Messages.getBlockchain());
} else {
// Do nothing.
}
}
handleReceivedBlockchain(message) {
const receivedChain = message.data;
try {
this.blockchain.replaceChain(receivedChain);
} catch(err) {
throw err;
}
} isValidChain(chain) {
if (JSON.stringify(chain[0]) !== JSON.stringify(Block.genesis)) {
return false;
}
const tempChain = [chain[0]];
for (let i = 1; i < chain.length; i = i + 1) {
if (this.isValidNextBlock(chain[i], tempChain[i - 1])) {
tempChain.push(chain[i]);
} else {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
isChainLonger(chain) {
return chain.length > this.blockchain.length;
}
replaceChain(newChain) {
if (this.isValidChain(newChain) && this.isChainLonger(newChain)) {
this.blockchain = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(newChain));
} else {
throw "Error: invalid chain";
}
}终端演示
安装命令行工具
npm install blockchain-cli -g
blockchain
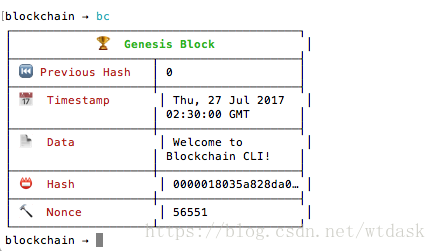
在blockchian ->后面输入blockchain或者bc查看创始区块结构。
创世区块
Index (Block #):第几个区块? (创世区块链的索引为0)Hash:当前区块的hash值Previous Hash:上一个区块的hash值Timestamp:当前区块创建时的时间戳Data:存储在当前区块上的交易信息Nonce:在找到有效区块之前,我们经历的迭代次数
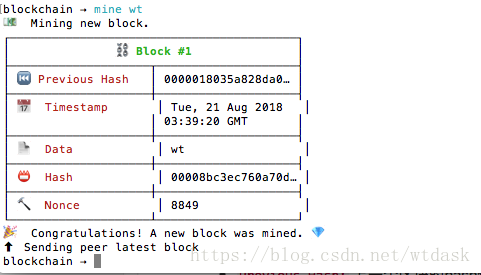
mine data数据
创建好了第一个区块
Hash是怎么计算的?
Hash值是一个十六进制固定长度为64位的唯一的标识。
hash值是由index, previous block hash, timestamp, block data, 和 nonce 作为输入数据计算而得。
CryptoJS.SHA256(index + previousHash + timestamp + data + nonce)四个前导0是有效散列的最低要求。 所需的前导0的数量称为难度。
下面的方法验证hash难度是否有效。
function isValidHashDifficulty(hash, difficulty) {
for (var i = 0, b = hash.length; i < b; i ++) {
if (hash[i] !== '0') {
break;
}
}
return i >= difficulty;
}nonce是一个用来找到满足条件的hash值的数字。
let nonce = 0;
let hash;
let input;
while(!isValidHashDifficulty(hash)) {
nonce = nonce + 1;
input = index + previousHash + timestamp + data + nonce;
hash = CryptoJS.SHA256(input)
}nonce值一直迭代,直到hash值有效为止。在我们案例中一个有效的hash值是最少有4个前导0。找到nonce值以满足合适条件的hash值的过程就叫做挖矿。
随着难度的增加,可能的有效散列数减少。 使用较少可能的有效散列,需要更多的处理能力才能找到有效的散列。