版权声明:转载请注明出处 https://blog.csdn.net/github_37412255/article/details/79973146
基于单链表的队列实现
package org.util.ds;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* 队列
* @author Weibing Long
* @since 2018.04.16
* @param <Item> 泛型
*/
public class Queue<Item> {
private Node root;
private int n;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new Queue<Integer>();
Random random = new Random();
System.out.println("进队列");
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
int x = random.nextInt();
queue.enqueue(x);
System.out.println(x);
}
System.out.println("出队列");
while (queue.size() > 0)
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
}
private class Node {
private Item item;
private Node next;
}
public void enqueue(Item item) {
if (item == null)
throw new NullPointerException("元素不能为空!");
if (root == null) {
root = new Node();
root.item = item;
root.next = root;
} else {
Node temp = root.next;
root.next = new Node();
root.next.item = item;
root = root.next;
root.next = temp;
}
n++;
}
public Item dequeue() {
if (n == 0)
throw new NullPointerException("队列中元素为空!");
Item item = root.next.item;
root = root.next;
n--;
return item;
}
public int size() {
return n;
}
}基于数组的实现
上面代码是基于循环链表实现的,下面代码基于数组实现
package org.util.ds;
/**
* 队列,基于动态数组
* @author 龙卫兵
*/
public class Queue<Item> {
private Object[] myArray;
private int capacity; // 容量
private int n; // 元素个数
public Queue() {
capacity = 2;
myArray = new Object[capacity];
}
public Queue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
myArray = new Object[capacity];
}
public void push(Item item) {
if (n > capacity/2) {
capacity *= 2;
Object[] temp = new Object[capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < capacity/2; i++)
temp[i] = myArray[i];
myArray = temp;
}
myArray[n++] = item;
}
public void pop() {
if (isEmpty())
throw new NullPointerException("数组为空");
else {
for (int i = 0; i < n-1; i++) {
myArray[i] = myArray[i + 1];
}
myArray[--n] = null;
}
}
public int size() {
return n;
}
public int getCapacity() {
return capacity;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return n == 0;
}
public void printContent() {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.println(myArray[i]);
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Item[] content() {
String itemName = myArray[0].getClass().getSimpleName();
if (itemName.equals("Integer")) {
Integer[] temp = new Integer[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
temp[i] = new Integer(myArray[i].toString());
// System.out.println(temp[i]);
}
return (Item[])temp;
} else if (itemName.equals("String")) {
String[] temp = new String[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
temp[i] = myArray[i].toString();
// System.out.println(temp[i]);
}
return (Item[])temp;
} else if (itemName.equals("Double")) {
Double[] temp = new Double[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
temp[i] = Double.valueOf(myArray[i].toString());
// System.out.println(temp[i]);
}
return (Item[])temp;
}
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("**********************元素为int********************************");
Queue<Integer> queue1 = new Queue<Integer>();
System.out.println("The first capacity of queue1 is " + queue1.getCapacity());
queue1.push(1);
queue1.push(2);
queue1.push(3);
System.out.println("The second capacity of queue1 is " + queue1.getCapacity());
System.out.println("The size of queue1 is " + queue1.size());
queue1.printContent();
System.out.println("**********************删除一个元素后********************************");
queue1.pop();
queue1.printContent();
System.out.println("**********************删除一个元素后********************************");
queue1.pop();
queue1.printContent();
System.out.println("**********************添加一个元素后********************************");
queue1.push(16);
queue1.printContent();
//Integer[] in = (Integer[])queue1.content();
Integer[] m = queue1.content();
for (int i = 0; i < queue1.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(m[i]);
}
System.out.println("**********************************************************");
Queue<Integer> queue2 = new Queue<Integer>(5);
System.out.println("The first capacity of queue2 is " + queue2.getCapacity());
queue2.push(4);
queue2.push(5);
queue2.push(6);
System.out.println("The second capacity of queue2 is " + queue2.getCapacity());
System.out.println("The size of queue2 is " + queue2.size());
queue2.printContent();
System.out.println("********************元素为字符串******************************");
Queue<String> queue3 = new Queue<String>();
queue3.push("nihao");
queue3.push("haha");
queue3.push("zdjd");
String[] mm = queue3.content();
for (int i = 0; i < queue3.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(mm[i]);
}
System.out.println("********************元素为double******************************");
Queue<Double> queue4 = new Queue<Double>();
Double x1 = new Double("5.666");
queue4.push(x1);
Double x2 = new Double("-5.666");
queue4.push(x2);
Double[] mmm = queue4.content();
for (int i = 0; i < queue4.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(mmm[i]);
}
}
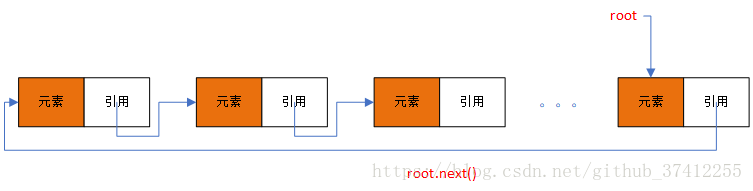
}循环链表的结构如下: