版权声明:转载请注明出处 https://blog.csdn.net/github_37412255/article/details/79981706
- 集合类:满足三个基本性质:确定性、互异性和无序性。实现代码满足了这三个性质,但数学中的集合还包括:元素可以为任何可以描述的类型,即元素的类型不需要相同,但代码实现中很难满足这个性质。
- 代码实现
package org.util.ds;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* 集合类:满足三个基本性质:确定性、互异性和无序性。实现代码满足了这三个性质,但数学中
* 的集合还包括:元素可以为任何可以描述的类型,即元素的类型不需要相同,但代码实现中很难
* 满足这个性质。
* @author Weibing Long
* @since 2018.04.17
* @param <Item>
*/
public class Set<Item> {
private Node root;
private int n;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set = new Set<Integer>();
Random random = new Random();
System.out.println("添加元素");
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
int x = random.nextInt();
set.add(x);
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(set.contains(x));
}
System.out.println(set.contains(12354));
System.out.println(set.contains(9874));
}
public void add(Item item) {
if (item == null)
throw new NullPointerException("元素不能为空!");
if (root == null) {
root = new Node();
root.item = item;
root.next = root;
} else {
long countFind = 0; // 对 root = root.next; 操作进行计数
// 后面这个可以改进,使不需要下面的操作,留给感兴趣的人做。
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (root.next.item.equals(item)) {
if (i > 0) { // 保证root引用指向链表的最后一个元素
for (int j = 0; j < n - countFind; j++) {
root = root.next;
}
}
return;
} else {
root = root.next;
countFind++;
}
}
Node preRootNext = root.next;
root.next = new Node();
root.next.item = item;
root.next.next = preRootNext;
root = root.next;
}
n++;
}
public void remove(Item item) {
if (item == null)
throw new NullPointerException("元素不能为空!");
Node tempRoot = root;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (tempRoot.next.item.equals(item)) {
tempRoot.next = tempRoot.next.next;
n--;
} else {
tempRoot = tempRoot.next;
}
}
}
public long size() {
return n;
}
public boolean contains(Item item) {
if (item == null)
throw new NullPointerException("元素不能为空!");
Node tempRoot = root;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (tempRoot.next.item.equals(item)) {
return true;
} else {
tempRoot = tempRoot.next;
}
}
return false;
}
private class Node {
private Item item;
private Node next;
}
}
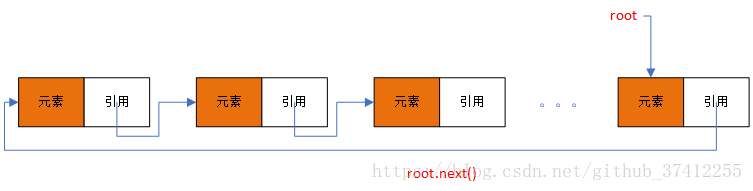
集合实现的底层同样和队列一样(使用循环链表)。
循环链表结构如下: