Problem Description
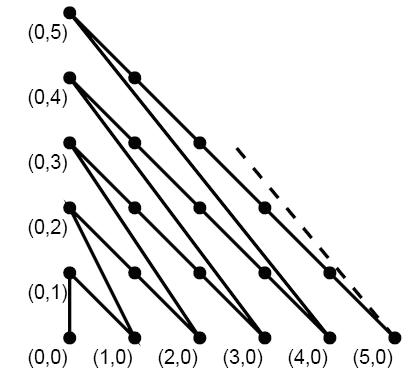
甜甜从小就喜欢画图画,最近他买了一支智能画笔,由于刚刚接触,所以甜甜只会用它来画直线,于是他就在平面直角坐标系中画出如下的图形:
甜甜的好朋友蜜蜜发现上面的图还是有点规则的,于是他问甜甜:在你画的图中,我给你两个点,请你算一算连接两点的折线长度(即沿折线走的路线长度)吧。
Input
第一个数是正整数N(≤100)。代表数据的组数。
每组数据由四个非负整数组成x1,y1,x2,y2;所有的数都不会大于100。
Output
对于每组数据,输出两点(x1,y1),(x2,y2)之间的折线距离。注意输出结果精确到小数点后3位。
Sample Input
5
0 0 0 1
0 0 1 0
2 3 3 1
99 99 9 9
5 5 5 5
Sample Output
1.000
2.414
10.646
54985.047
0.000
思路:
1.
找一下规律,以(2,1)点为例:
先算出(0,0)点的距离到(0,x1+y1)-【方框点】的距离,再算出(0,x1+y1)-【方框点】点到(x1,y1)点的距离
之后(x2,y2)到(x1,y1)点的距离就是他们到原点的距离,减一下就行
2.
(0,x1+y1)-【方框点】的距离
通过找规律就行
double[] nums = new double[201];
nums[0] = 0;
nums[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < nums.length; i++) {
nums[i] = nums[i-1]+(i-1)*(sqrt2)+Math.sqrt(Math.pow(i, 2)+Math.pow(i-1, 2));
}下面是AcCode:
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
private static final double sqrt2 = Math.sqrt(2);
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
double[] nums = new double[201];
nums[0] = 0;
nums[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < nums.length; i++) {
nums[i] = nums[i-1]+(i-1)*(sqrt2)+Math.sqrt(Math.pow(i, 2)+Math.pow(i-1, 2));
}
DecimalFormat format = new DecimalFormat("0.000");
int n = in.nextInt();
while(n!=0) {
double x1 = in.nextDouble();
double y1 = in.nextDouble();
double x2 = in.nextDouble();
double y2 = in.nextDouble();
double sum1 = nums[(int) (x1+y1)]+Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x1, 2)+Math.pow(x1, 2));
double sum2 = nums[(int) (x2+y2)]+Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x2, 2)+Math.pow(x2, 2));
System.out.println(format.format(Math.abs(sum2-sum1)));
n--;
}
}
}