SensorManager 基于Android 5.1源码分析:2016-04-23
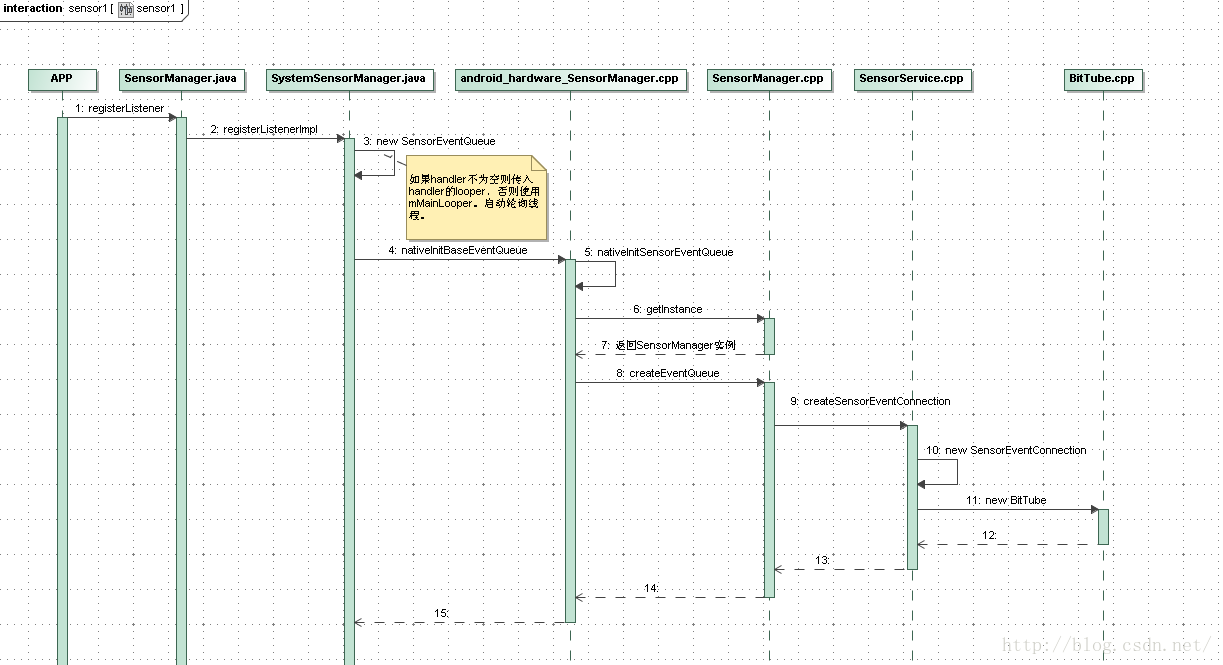
1、Java层启动轮询线程的流程
SensorManager.java
这里有4个供上层APP使用的注册接口。
public boolean registerListener(SensorListener listener, int sensors)
public boolean registerListener(SensorListener listener, int sensors,int rate)//以上两个方法在5.1版本上已被废弃
public boolean registerListener(SensorEventListener listener, Sensor sensor,int samplingPeriodUs)
public boolean registerListener(SensorEventListener listener, Sensor sensor, int samplingPeriodUs,int maxReportLatencyUs){
int delay =getDelay(samplingPeriodUs);
return registerListenerImpl(listener, sensor, delay,null, maxReportLatencyUs, 0);//SensorManager类的registerListenerImpl方法是抽象法,真正的实现在其子类SystemSensorManager.java中。
}
SystemSensorManager.java
public class SystemSensorManagerextends SensorManager {//SystemSensorManager是SensorManager的子类。
@Override
protected boolean registerListenerImpl(SensorEventListener listener, Sensor sensor,
int delayUs, Handler handler,int maxBatchReportLatencyUs,int reservedFlags) {
......
synchronized (mSensorListeners) {
SensorEventQueue queue = mSensorListeners.get(listener);
if (queue ==null) {
Looper looper = (handler !=null) ? handler.getLooper() : mMainLooper;
queue = new SensorEventQueue(listener, looper,this);//将looper传入启动轮询线程。
......
mSensorListeners.put(listener, queue);
return true;
} else {
return queue.addSensor(sensor, delayUs, maxBatchReportLatencyUs, reservedFlags);
}
}
}
}
//SensorEventQueue构造方法中调用父类构造方法。
static final class SensorEventQueue extends BaseEventQueue {
private final SensorEventListener mListener;
private final SparseArray<SensorEvent> mSensorsEvents = new SparseArray<SensorEvent>();
public SensorEventQueue(SensorEventListener listener, Looper looper,
SystemSensorManager manager) {
super(looper, manager);
mListener = listener;
}
}
//SensorEventQueue和TriggerEventQueue是BaseEventQueue的两个子类。在BaseEventQueue类中声明了以下几个native方法
private static abstract class BaseEventQueue {
private native long nativeInitBaseEventQueue(BaseEventQueue eventQ, MessageQueue msgQ,
float[] scratch);
private static native int nativeEnableSensor(long eventQ,int handle,int rateUs,
int maxBatchReportLatencyUs,int reservedFlags);
private static native int nativeDisableSensor(long eventQ,int handle);
private static native void nativeDestroySensorEventQueue(long eventQ);
private static native int nativeFlushSensor(long eventQ);
BaseEventQueue(Looper looper, SystemSensorManager manager) {
nSensorEventQueue = nativeInitBaseEventQueue(this, looper.getQueue(), mScratch);//调用JNI native中的消息队列初始化
mCloseGuard.open("dispose");
mManager = manager;
}
}
2、native中的消息队列初始化流程
android_hardware_SensorManager.cpp
static JNINativeMethod gBaseEventQueueMethods[] = {
{"nativeInitBaseEventQueue",
"(Landroid/hardware/SystemSensorManager$BaseEventQueue;Landroid/os/MessageQueue;[F)J",
(void*)nativeInitSensorEventQueue},//对应的native函数nativeInitSensorEventQueue指针
{"nativeEnableSensor",
"(JIIII)I",
(void*)nativeEnableSensor },
{"nativeDisableSensor",
"(JI)I",
(void*)nativeDisableSensor },
{"nativeDestroySensorEventQueue",
"(J)V",
(void*)nativeDestroySensorEventQueue },
{"nativeFlushSensor",
"(J)I",
(void*)nativeFlushSensor },
};
static jlongnativeInitSensorEventQueue(JNIEnv *env, jclass clazz, jobject eventQ, jobject msgQ, jfloatArray scratch) {
SensorManager& mgr(SensorManager::getInstance());//单例模式(通过继承Singleton实现),所调用的构造函数在SensorManager.cpp中
sp<SensorEventQueue> queue(mgr.createEventQueue());//创建消息队列
......
sp<Receiver> receiver = new Receiver(queue, messageQueue, eventQ, scratch);
receiver->incStrong((void*)nativeInitSensorEventQueue);
return jlong(receiver.get());
}
SensorManager.h
class SensorManager :
public AsensorManager,//ASensorManager是NDK的接口,应该是个结构体,c++是可以继承结构体的
public Singleton<SensorManager>//Singleton是一个单例泛型类(详见附1节),提供了getInstance与hasInstance两个方法
{
……
mutable sp<ISensorServer> mSensorServer;//注意,sp是强引用,要关注onFirstRef回调,这个变量的初始化是在SensorManager::assertStateLocked()中
……
}
SensorManager.cpp
SensorManager::SensorManager()
: mSensorList(0)
{
// okay we're not locked here, but it's not needed during construction
assertStateLocked();
}
status_t SensorManager::assertStateLocked()const {
if (mSensorServer == NULL) {
// try for one second
const String16 name("sensorservice");
for (int i=0 ; i<4 ; i++) {
status_t err = getService(name, &mSensorServer);
//得到服务SensorService,注意mSensorServer是强引用类型,要关注onFirstRef回调
//另外getService定义在IServiceManager.h中,是一个全局函数,不属于任何类,但会通过另一个全局函数defaultServiceManager()调用到IServiceManager.cpp中的BpServiceManager::getService
//而服务也是通过defaultServiceManager()调用IServiceManager.cpp中的BpServiceManager::addService注册的(详见第4节开头)
if (err == NAME_NOT_FOUND) {
usleep(250000);
continue;
}
if (err != NO_ERROR) {
return err;
}
break;
}
class DeathObserver :public IBinder::DeathRecipient {//服务SensorService的死亡监听
SensorManager& mSensorManger;
virtual void binderDied(const wp<IBinder>& who) {
ALOGW("sensorservice died [%p]", who.unsafe_get());
mSensorManger.sensorManagerDied();//若服务SensorService死亡,则同时结束SensorManager
}
public:
DeathObserver(SensorManager& mgr) : mSensorManger(mgr) { }
};
//注册服务SensorService的死亡监听
mDeathObserver = new DeathObserver(*const_cast<SensorManager *>(this));
mSensorServer->asBinder()->linkToDeath(mDeathObserver);
//从服务SensorService获取sensor列表,并保存在SensorManager中
mSensors = mSensorServer->getSensorList();
size_t count = mSensors.size();
mSensorList = (Sensor const**)malloc(count *sizeof(Sensor*));
for (size_t i=0 ; i<count ; i++) {
mSensorList[i] = mSensors.array() + i;
}
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
SensorManager.cpp
sp<SensorEventQueue> SensorManager::createEventQueue()
{
sp<SensorEventQueue> queue;
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
while (assertStateLocked() == NO_ERROR) {
sp<ISensorEventConnection> connection =
mSensorServer->createSensorEventConnection();//创建连接接口(详见第2.1节),需要注意:这是客户端在调用服务端的接口
if (connection == NULL) {
// SensorService just died.
ALOGE("createEventQueue: connection is NULL. SensorService died.");
usleep(100000);
continue;
}
queue = new SensorEventQueue(connection);//创建消息队列(详见第2.2节)
break;
}
return queue;
}
2.1、创建连接接口的过程
SensorService.cpp
sp<ISensorEventConnection> SensorService::createSensorEventConnection()
{
uid_t uid = IPCThreadState::self()->getCallingUid();
sp<SensorEventConnection> result(new SensorEventConnection(this, uid));
return result;
}
SensorService::SensorEventConnection::SensorEventConnection(
const sp<SensorService>& service, uid_t uid)
: mService(service), mUid(uid), mWakeLockRefCount(0), mHasLooperCallbacks(false),
mDead(false), mEventCache(NULL), mCacheSize(0), mMaxCacheSize(0) {
mChannel = new BitTube(mService->mSocketBufferSize);
//BitTube的作用是创建一对管道(详见附2节)
//sp<BitTube> const mChannel;保存的管道会在SensorService::SensorEventConnection::sendEvents中用到,而sendEvents在native服务线程中用到(详见4.2节)
2.2、创建消息队列的过程
SensorEventQueue.h
class SensorEventQueue : public ASensorEventQueue, public RefBase
SensorEventQueue.cpp
SensorEventQueue::SensorEventQueue(const sp<ISensorEventConnection>& connection)
: mSensorEventConnection(connection), mRecBuffer(NULL), mAvailable(0), mConsumed(0),
mNumAcksToSend(0) {
mRecBuffer = new ASensorEvent[MAX_RECEIVE_BUFFER_EVENT_COUNT];//赋值
}
3、SystemSensorManager的初始化流程
3.1、从开机到实例化SystemSensorManager
SystemServer.java
public final class SystemServer {
......
/**
* Called to initialize native system services.
*/
private static native void nativeInit();
/**
* The main entry point from zygote.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SystemServer().run();
}
private void run() {
......
// Initialize native services.
System.loadLibrary("android_servers");
nativeInit();//第1步,JNI到com_android_server_SystemServer.cpp中去
......
// Create the system service manager.
mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager(mSystemContext);
LocalServices.addService(SystemServiceManager.class, mSystemServiceManager);
// Start services.
try {
startBootstrapServices();
startCoreServices();
startOtherServices();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Slog.e("System", "******************************************");
Slog.e("System", "************ Failure starting system services", ex);
/// M: RecoveryManagerService @{
if (mRecoveryManagerService !=null && exinstanceof RuntimeException) {
mRecoveryManagerService.handleException((RuntimeException)ex,true);
}
/// @}
}
private void startBootstrapServices() {
......
mPowerManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(PowerManagerService.class);//第4步
......
}
}
private void startOtherServices() {
......
mPowerManagerService.systemReady(mActivityManagerService.getAppOpsService());//第5步
......
}
}
PowerManagerService.cpp
public final class PowerManagerServiceextends SystemServiceimplements Watchdog.Monitor {
......
public void systemReady(IAppOpsService appOps) {
synchronized (mLock) {
......
SensorManager sensorManager =new SystemSensorManager(mContext, mHandler.getLooper()); //第6步,实例化SystemSensorManager
......
}
......
}
com_android_server_SystemServer.cpp
static void android_server_SystemServer_nativeInit(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz) {//第2步
char propBuf[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
property_get("system_init.startsensorservice", propBuf, "1");
if (strcmp(propBuf, "1") == 0) {
// Start the sensor service
SensorService::instantiate(); //第3步SensorService实例化启动
}
static JNINativeMethod gMethods[] = { //函数签名信息
/* name, signature, funcPtr */
{ "nativeInit", "()V", (void*)android_server_SystemServer_nativeInit },
};
int register_android_server_SystemServer(JNIEnv* env)//动态注册JNI函数
{
return jniRegisterNativeMethods(env, "com/android/server/SystemServer",
gMethods, NELEM(gMethods));
}
3.2、实例化SystemSensorManager
SystemSensorManager.java
public class SystemSensorManager extends SensorManager {
......
public SystemSensorManager(Context context, Looper mainLooper) {
mMainLooper = mainLooper;
mTargetSdkLevel = context.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion;
synchronized(sSensorModuleLock) {
if (!sSensorModuleInitialized) {
sSensorModuleInitialized = true;
nativeClassInit();//编号3.2.1 JNI调用android_hardware_SensorManager.cpp中的方法
// initialize the sensor list
final ArrayList<Sensor> fullList = sFullSensorsList;
int i = 0;
do {
Sensor sensor = new Sensor();
i = nativeGetNextSensor(sensor, i);//编号3.2.2 JNI调用android_hardware_SensorManager.cpp中的方法;并最终将sensor列表保存在sHandleToSensor变量中
if (i>=0) {
//Log.d(TAG, "found sensor: " + sensor.getName() +
// ", handle=" + sensor.getHandle());
fullList.add(sensor);
sHandleToSensor.append(sensor.getHandle(), sensor);
}
} while (i>0);
}
}
}
}
android_hardware_SensorManager.cpp
static JNINativeMethod gSystemSensorManagerMethods[] = {
{"nativeClassInit",
"()V",
(void*)nativeClassInit },
{"nativeGetNextSensor",
"(Landroid/hardware/Sensor;I)I",
(void*)nativeGetNextSensor },
};
3.2.1
android_hardware_SensorManager.cpp
struct SensorOffsets
{
jfieldID name;
jfieldID vendor;
jfieldID version;
jfieldID handle;
jfieldID type;
jfieldID range;
jfieldID resolution;
jfieldID power;
jfieldID minDelay;
jfieldID fifoReservedEventCount;
jfieldID fifoMaxEventCount;
jfieldID stringType;
jfieldID requiredPermission;
jfieldID maxDelay;
jfieldID flags;
} gSensorOffsets;//用于保存java类中数据域的FieldID,而非具体java对象的ID
static void
nativeClassInit (JNIEnv *_env, jclass _this)
{
jclass sensorClass = _env->FindClass("android/hardware/Sensor");//Sensor.java
SensorOffsets& sensorOffsets = gSensorOffsets;//这里使用的是C++的引用,即下面是对gSensorOffsets的赋值
sensorOffsets.name = _env->GetFieldID(sensorClass, "mName", "Ljava/lang/String;");
sensorOffsets.vendor = _env->GetFieldID(sensorClass, "mVendor", "Ljava/lang/String;");
sensorOffsets.version = _env->GetFieldID(sensorClass, "mVersion", "I");
sensorOffsets.handle = _env->GetFieldID(sensorClass, "mHandle", "I");
sensorOffsets.type = _env->GetFieldID(sensorClass, "mType", "I");
sensorOffsets.range = _env->GetFieldID(sensorClass, "mMaxRange", "F");
sensorOffsets.resolution = _env->GetFieldID(sensorClass, "mResolution","F");
sensorOffsets.power = _env->GetFieldID(sensorClass, "mPower", "F");
sensorOffsets.minDelay = _env->GetFieldID(sensorClass, "mMinDelay", "I");
sensorOffsets.fifoReservedEventCount =
_env->GetFieldID(sensorClass, "mFifoReservedEventCount", "I");
sensorOffsets.fifoMaxEventCount = _env->GetFieldID(sensorClass, "mFifoMaxEventCount", "I");
sensorOffsets.stringType = _env->GetFieldID(sensorClass, "mStringType", "Ljava/lang/String;");
sensorOffsets.requiredPermission = _env->GetFieldID(sensorClass, "mRequiredPermission",
"Ljava/lang/String;");
sensorOffsets.maxDelay = _env->GetFieldID(sensorClass, "mMaxDelay", "I");
sensorOffsets.flags = _env->GetFieldID(sensorClass, "mFlags", "I");
}
Sensor.java
public final class Sensor {
......
/* Some of these fields are set only by the native bindings in
* SensorManager.
*/
private String mName;
private String mVendor;
private int mVersion;
private int mHandle;
private int mType;
private float mMaxRange;
private float mResolution;
private float mPower;
private int mMinDelay;
private int mFifoReservedEventCount;
private int mFifoMaxEventCount;
private String mStringType;
private String mRequiredPermission;
private int mMaxDelay;
private int mFlags;
......
}
3.2.2
android_hardware_SensorManager.cpp
static jint
nativeGetNextSensor(JNIEnv *env, jclass clazz, jobject sensor, jint next)
{
SensorManager& mgr(SensorManager::getInstance());
Sensor const*const* sensorList;
size_t count = mgr.getSensorList(&sensorList);//通过SensorManager获取sensor列表,SensorManager的列表是在SensorManager初始化时从SensorService获得到的
if (size_t(next) >= count)
return -1;
Sensor const*const list = sensorList[next];
const SensorOffsets& sensorOffsets(gSensorOffsets);
jstring name = env->NewStringUTF(list->getName().string());
jstring vendor = env->NewStringUTF(list->getVendor().string());
jstring stringType = env->NewStringUTF(list->getStringType().string());
jstring requiredPermission = env->NewStringUTF(list->getRequiredPermission().string());
env->SetObjectField(sensor, sensorOffsets.name, name);
env->SetObjectField(sensor, sensorOffsets.vendor, vendor);
env->SetIntField(sensor, sensorOffsets.version, list->getVersion());
env->SetIntField(sensor, sensorOffsets.handle, list->getHandle());
env->SetIntField(sensor, sensorOffsets.type, list->getType());
env->SetFloatField(sensor, sensorOffsets.range, list->getMaxValue());
env->SetFloatField(sensor, sensorOffsets.resolution, list->getResolution());
env->SetFloatField(sensor, sensorOffsets.power, list->getPowerUsage());
env->SetIntField(sensor, sensorOffsets.minDelay, list->getMinDelay());
env->SetIntField(sensor, sensorOffsets.fifoReservedEventCount,
list->getFifoReservedEventCount());
env->SetIntField(sensor, sensorOffsets.fifoMaxEventCount,
list->getFifoMaxEventCount());
env->SetObjectField(sensor, sensorOffsets.stringType, stringType);
env->SetObjectField(sensor, sensorOffsets.requiredPermission,
requiredPermission);
env->SetIntField(sensor, sensorOffsets.maxDelay, list->getMaxDelay());
env->SetIntField(sensor, sensorOffsets.flags, list->getFlags());
next++;
return size_t(next) < count ? next : 0;
}
4、服务端的初始化流程
//启动过程类似于,可参考3.1节中前3步的流程
com_android_server_SystemServer.cpp
static void android_server_SystemServer_nativeInit(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz) {
char propBuf[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
property_get("system_init.startsensorservice", propBuf, "1");//property_get()是c/c++的接口,对应的java接口是SystemProperties_get*(),读取build.prop中的值
if (strcmp(propBuf, "1") == 0) {//判断是否要启动服务,默认是启动
// Start the sensor service
SensorService::instantiate(); //SensorService继承了模板类BinderService<SensorService>,instantiate就是模板类的方法
}
BinderService.h
template<typename SERVICE>
class BinderService
{
public:
static status_t publish(bool allowIsolated = false) {
sp<IServiceManager> sm(defaultServiceManager());//defaultServiceManager()定义在IServiceManager.cpp中
return sm->addService(String16(SERVICE::getServiceName()), new SERVICE(), allowIsolated);
//new了一个SensorService的实例,并将其添加到系统服务管理器中
//这样就可以用defaultServiceManager:getService()获取到Sensor服务的实例
}
……
static void instantiate() { publish(); }
……
};
IServiceManager.h
sp<IServiceManager> defaultServiceManager();//这是原型定义,实体在IServiceManager.cpp中
template<typename INTERFACE>
status_t getService(const String16& name, sp<INTERFACE>* outService)
{
const sp<IServiceManager> sm = defaultServiceManager();
if (sm != NULL) {
*outService = interface_cast<INTERFACE>(sm->getService(name));//getService与addService都是接口IServiceManager中定义的方法
if ((*outService) != NULL) return NO_ERROR;
}
return NAME_NOT_FOUND;
}
SensorService.h
class SensorService :
public BinderService<SensorService>,
public BnSensorServer,
protected Thread//线程类,在SensorService::onFirstRef()中由run方法启动
{
……
// ISensorServer interface
virtual Vector<Sensor> getSensorList();//sensor列表,在SensorService::getSensorList()中获取,在SensorService::onFirstRef()中赋值
virtual sp<ISensorEventConnection> createSensorEventConnection();
……
}
SensorService.cpp
Vector<Sensor> SensorService::getSensorList()
{
char value[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
property_get("debug.sensors", value, "0");
const Vector<Sensor>& initialSensorList = (atoi(value)) ?//atoi是字符串转整型的意思
mUserSensorListDebug : mUserSensorList;//在SensorService::onFirstRef()中赋值
Vector<Sensor> accessibleSensorList;
for (size_t i = 0; i < initialSensorList.size(); i++) {
Sensor sensor = initialSensorList[i];
if (canAccessSensor(sensor)) {
accessibleSensorList.add(sensor);
} else {
String8 infoMessage;
infoMessage.appendFormat(
"Skipped sensor %s because it requires permission %s",
sensor.getName().string(),
sensor.getRequiredPermission().string());
ALOGI(infoMessage.string());
}
}
return accessibleSensorList;
}
void SensorService::onFirstRef()
{
ALOGD("nuSensorService starting...");
SensorDevice& dev(SensorDevice::getInstance());//编号4.1 单例创建SensorDevice
if (dev.initCheck() == NO_ERROR) {//获得sensor列表
sensor_t const* list;
ssize_t count = dev.getSensorList(&list);
if (count > 0) {
ssize_t orientationIndex = -1;
bool hasGyro = false;//硬件上是否有陀螺仪的标志
uint32_t virtualSensorsNeeds =//是否需要记录某些sensor的标志
(1<<SENSOR_TYPE_GRAVITY) |
(1<<SENSOR_TYPE_LINEAR_ACCELERATION) |
(1<<SENSOR_TYPE_ROTATION_VECTOR);
mLastEventSeen.setCapacity(count);
for (ssize_t i=0 ; i<count ; i++) {//扫描sensor列表
registerSensor( new HardwareSensor(list[i]) );
switch (list[i].type) {
case SENSOR_TYPE_ORIENTATION:
orientationIndex = i;
break;
case SENSOR_TYPE_GYROSCOPE:
case SENSOR_TYPE_GYROSCOPE_UNCALIBRATED:
hasGyro = true;
break;
case SENSOR_TYPE_GRAVITY:
case SENSOR_TYPE_LINEAR_ACCELERATION:
case SENSOR_TYPE_ROTATION_VECTOR:
virtualSensorsNeeds &= ~(1<<list[i].type);
break;
}
}
// it's safe to instantiate the SensorFusion object here
// (it wants to be instantiated after h/w sensors have been
// registered)
const SensorFusion& fusion(SensorFusion::getInstance());//单例创建SensorFusion
// build the sensor list returned to users
mUserSensorList = mSensorList;//Sensor列表赋值
//如果有陀螺仪设备,则先注册和陀螺仪有关的虚拟传感器设备
//旋转,重力,加速器,方向等,这些设备都对应同一个物理硬件――陀螺仪
//这些逻辑上存在,物理上不存在的设备叫虚拟设备
if (hasGyro) {
Sensor aSensor;
// Add Android virtual sensors if they're not already
// available in the HAL
aSensor = registerVirtualSensor( new RotationVectorSensor() );//虚拟旋转传感器
if (virtualSensorsNeeds & (1<<SENSOR_TYPE_ROTATION_VECTOR)) {
mUserSensorList.add(aSensor);
}
aSensor = registerVirtualSensor( new GravitySensor(list, count) );//虚拟重力传感器
if (virtualSensorsNeeds & (1<<SENSOR_TYPE_GRAVITY)) {
mUserSensorList.add(aSensor);
}
aSensor = registerVirtualSensor( new LinearAccelerationSensor(list, count) );//虚拟线性加速度传感器器
if (virtualSensorsNeeds & (1<<SENSOR_TYPE_LINEAR_ACCELERATION)) {
mUserSensorList.add(aSensor);
}
aSensor = registerVirtualSensor( new OrientationSensor() );//虚拟方向传感器
if (virtualSensorsNeeds & (1<<SENSOR_TYPE_ROTATION_VECTOR)) {
// if we are doing our own rotation-vector, also add
// the orientation sensor and remove the HAL provided one.
mUserSensorList.replaceAt(aSensor, orientationIndex);
}
// virtual debugging sensors are not added to mUserSensorList//虚拟调试传感器不被添加到mUserSensorList中
registerVirtualSensor( new CorrectedGyroSensor(list, count) );//修正陀螺传感器
registerVirtualSensor( new GyroDriftSensor() );//虚拟陀螺测漂传感器
}
// debugging sensor list
mUserSensorListDebug = mSensorList;
......
mWakeLockAcquired = false;
mLooper = new Looper(false);
const size_t minBufferSize = SensorEventQueue::MAX_RECEIVE_BUFFER_EVENT_COUNT;
mSensorEventBuffer = new sensors_event_t[minBufferSize];
mSensorEventScratch = new sensors_event_t[minBufferSize];
mMapFlushEventsToConnections = new SensorEventConnection const * [minBufferSize];
mAckReceiver = new SensorEventAckReceiver(this);
mAckReceiver->run("SensorEventAckReceiver", PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY);
mInitCheck = NO_ERROR;
run("SensorService", PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY);//编号4.2开始运行SensorService线程,即启动SensorService::threadLoop()方法
}
}
}
Sensor SensorService::registerVirtualSensor(SensorInterface* s)
{
Sensor sensor = registerSensor(s);
mVirtualSensorList.add( s );//记录虚拟sensor
return sensor;
}
Sensor SensorService::registerSensor(SensorInterface* s)
{
sensors_event_t event;
memset(&event, 0, sizeof(event));
const Sensor sensor(s->getSensor());
//添加到Sensor列表,给客户端使用
// add to the sensor list (returned to clients)
mSensorList.add(sensor);
// add to our handle->SensorInterface mapping
mSensorMap.add(sensor.getHandle(), s);
// create an entry in the mLastEventSeen array
mLastEventSeen.add(sensor.getHandle(), event);
return sensor;
}
4.1
SensorDevice.cpp
SensorDevice::SensorDevice()
: mSensorDevice(0),
mSensorModule(0)
{
status_t err = hw_get_module(SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
(hw_module_t const**)&mSensorModule);//调用HAL层的hw_get_modele()方法,加载Sensor模块so文件
ALOGE_IF(err, "couldn't load %s module (%s)",
SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, strerror(-err));
if (mSensorModule) {
err = sensors_open_1(&mSensorModule->common, &mSensorDevice);//调用sensor.h的sensors_open方法打开设备
ALOGE_IF(err, "couldn't open device for module %s (%s)",
SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, strerror(-err));
if (mSensorDevice) {
if (mSensorDevice->common.version == SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_1 ||
mSensorDevice->common.version == SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_2) {
ALOGE(">>>> WARNING <<< Upgrade sensor HAL to version 1_3");
}
sensor_t const* list;
ssize_t count = mSensorModule->get_sensors_list(mSensorModule, &list);
mActivationCount.setCapacity(count);
Info model;
for (size_t i=0 ; i<size_t(count) ; i++) {
mActivationCount.add(list[i].handle, model);
mSensorDevice->activate(
reinterpret_cast<struct sensors_poll_device_t *>(mSensorDevice),//调用sensors_poll_device_t->activate()对Sensor模块使能
list[i].handle, 0);
}
}
}
}
4.2
SensorService.cpp
bool SensorService::threadLoop()
{
ALOGD("nuSensorService thread starting...");
const size_t minBufferSize = SensorEventQueue::MAX_RECEIVE_BUFFER_EVENT_COUNT;
const size_t numEventMax = minBufferSize / (1 + mVirtualSensorList.size());
SensorDevice& device(SensorDevice::getInstance());
const size_t vcount = mVirtualSensorList.size();
const int halVersion = device.getHalDeviceVersion();
do {
ssize_t count = device.poll(mSensorEventBuffer, numEventMax);//轮询
if (count < 0) {
ALOGE("sensor poll failed (%s)", strerror(-count));
break;
}
// Reset sensors_event_t.flags to zero for all events in the buffer.
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
mSensorEventBuffer[i].flags = 0;
}
SortedVector< sp<SensorEventConnection> > activeConnections;
populateActiveConnections(&activeConnections);
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
bool bufferHasWakeUpEvent = false;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if (isWakeUpSensorEvent(mSensorEventBuffer[i])) {
bufferHasWakeUpEvent = true;
break;
}
}
if (bufferHasWakeUpEvent && !mWakeLockAcquired) {
setWakeLockAcquiredLocked(true);
}
recordLastValueLocked(mSensorEventBuffer, count);
// handle virtual sensors
//从底层读上来的应该都是物理存在的sensor的信息,但上层使用的sensor有一部分是虚拟的(陀螺仪派生的),所以需要先处理一下
if (count && vcount) {
sensors_event_t const * const event = mSensorEventBuffer;
const size_t activeVirtualSensorCount = mActiveVirtualSensors.size();
if (activeVirtualSensorCount) {
size_t k = 0;
SensorFusion& fusion(SensorFusion::getInstance());
if (fusion.isEnabled()) {
for (size_t i=0 ; i<size_t(count) ; i++) {
fusion.process(event[i]);
}
}
for (size_t i=0 ; i<size_t(count) && k<minBufferSize ; i++) {
for (size_t j=0 ; j<activeVirtualSensorCount ; j++) {
if (count + k >= minBufferSize) {
ALOGE("buffer too small to hold all events: "
"count=%zd, k=%zu, size=%zu",
count, k, minBufferSize);
break;
}
sensors_event_t out;
SensorInterface* si = mActiveVirtualSensors.valueAt(j);
if (si->process(&out, event[i])) {
mSensorEventBuffer[count + k] = out;
k++;
}
}
}
if (k) {
// record the last synthesized values
recordLastValueLocked(&mSensorEventBuffer[count], k);
count += k;
// sort the buffer by time-stamps
sortEventBuffer(mSensorEventBuffer, count);
}
}
}
// handle backward compatibility for RotationVector sensor
if (halVersion < SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_0) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if (mSensorEventBuffer[i].type == SENSOR_TYPE_ROTATION_VECTOR) {
// All the 4 components of the quaternion should be available
// No heading accuracy. Set it to -1
mSensorEventBuffer[i].data[4] = -1;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
mMapFlushEventsToConnections[i] = NULL;
if (mSensorEventBuffer[i].type == SENSOR_TYPE_META_DATA) {
const int sensor_handle = mSensorEventBuffer[i].meta_data.sensor;
SensorRecord* rec = mActiveSensors.valueFor(sensor_handle);
if (rec != NULL) {
mMapFlushEventsToConnections[i] = rec->getFirstPendingFlushConnection();
rec->removeFirstPendingFlushConnection();
}
}
}
bool needsWakeLock = false;
size_t numConnections = activeConnections.size();
for (size_t i=0 ; i < numConnections; ++i) {
if (activeConnections[i] != 0) {
activeConnections[i]->sendEvents(mSensorEventBuffer, count, mSensorEventScratch,
mMapFlushEventsToConnections);//将数据写到管道中
needsWakeLock |= activeConnections[i]->needsWakeLock();
// If the connection has one-shot sensors, it may be cleaned up after first trigger.
// Early check for one-shot sensors.
if (activeConnections[i]->hasOneShotSensors()) {
cleanupAutoDisabledSensorLocked(activeConnections[i], mSensorEventBuffer,
count);
}
}
}
if (mWakeLockAcquired && !needsWakeLock) {
setWakeLockAcquiredLocked(false);
}
} while (!Thread::exitPending());
ALOGW("Exiting SensorService::threadLoop => aborting...");
abort();
return false;
}
4、消息传递
总结一下:
1、APP用registerListener注册回调
2、java层的客户端在SystemSensorManager.java
中的SystemSensorManager::SensorThreadRunnable::run()中
轮询服务端
3、服务端在
SensorService.cpp
中的bool SensorService::threadLoop()中
轮询HAL
4、服务端向客户端写数据是通过管道进行的,且使用的结构体如下
./hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/sensors.h
typedef struct sensors_event_t {
/* must be sizeof(struct sensors_event_t) */
int32_t version;
/* sensor identifier */
int32_t sensor;
/* sensor type */
int32_t type;
/* reserved */
int32_t reserved0;
/* time is in nanosecond */
int64_t timestamp;
union {
union {
float data[16];
/* acceleration values are in meter per second per second (m/s^2) */
sensors_vec_t acceleration;
/* magnetic vector values are in micro-Tesla (uT) */
sensors_vec_t magnetic;
/* orientation values are in degrees */
sensors_vec_t orientation;
/* gyroscope values are in rad/s */
sensors_vec_t gyro;
/* temperature is in degrees centigrade (Celsius) */
float temperature;
/* distance in centimeters */
float distance;
/* light in SI lux units */
float light;
/* pressure in hectopascal (hPa) */
float pressure;
/* relative humidity in percent */
float relative_humidity;
/* uncalibrated gyroscope values are in rad/s */
uncalibrated_event_t uncalibrated_gyro;
/* uncalibrated magnetometer values are in micro-Teslas */
uncalibrated_event_t uncalibrated_magnetic;
/* heart rate data containing value in bpm and status */
heart_rate_event_t heart_rate;
/* this is a special event. see SENSOR_TYPE_META_DATA above.
* sensors_meta_data_event_t events are all reported with a type of
* SENSOR_TYPE_META_DATA. The handle is ignored and must be zero.
*/
meta_data_event_t meta_data;
};
union {
uint64_t data[8];
/* step-counter */
uint64_t step_counter;
} u64;
};
/* Reserved flags for internal use. Set to zero. */
uint32_t flags;
uint32_t reserved1[3];
} sensors_event_t;
5、客户端从服务端读数据(通过android_hardware_SensorManager.cpp中的JNI接口sensors_data_poll)使用的结构体如下,可以看出和服务端使用的结构体基本一致,差异在联合体部分,且差异不会影响到联合体的大小
frameworks/native/include/android/sensor.h
/* NOTE: Must match hardware/sensors.h */
typedef struct ASensorEvent {
int32_t version; /* sizeof(struct ASensorEvent) */
int32_t sensor;
int32_t type;
int32_t reserved0;
int64_t timestamp;
union {
union {
float data[16];
ASensorVector vector;
ASensorVector acceleration;
ASensorVector magnetic;
float temperature;
float distance;
float light;
float pressure;
float relative_humidity;
AUncalibratedEvent uncalibrated_gyro;
AUncalibratedEvent uncalibrated_magnetic;
AMetaDataEvent meta_data;
AHeartRateEvent heart_rate;
};
union {
uint64_t data[8];
uint64_t step_counter;
} u64;
};
uint32_t flags;
int32_t reserved1[3];
} ASensorEvent;