用python买手机
最近某同学一直碎碎念要买P20,我想说此时买似不太明智,但不知从何说起,恰逢放假,闲来无事,遂用python爬取淘宝、京东手机销售数据做个简单分析,本博客主要实现了以下功能
爬取淘宝上手机的月销售数据并存为excel表格
统计淘宝上不同品牌手机的月销量并以条形图形式展示
使用python代码打开浏览器搜索京东上手机数据并爬取
统计京东上不同手机品牌的评价量并以条形图形式展示
爬取淘宝数据
- URL
电脑浏览器打开淘宝,搜索手机,得到浏览器地址栏链接为https://s.taobao.com/search?ie=utf8&initiative_id=staobaoz_20170905&stats_click=search_radio_all%3A1&js=1&imgfile=&q=%E6%89%8B%E6%9C%BA&suggest=0_1&_input_charset=utf-8&wq=u&suggest_query=u&source=suggest&p4ppushleft=5%2C48&s=48
经过测试,发现q=之后为关键词手机,s=之后为页数乘以48,48为每页显示的商品数量。因此写得URL函数如下:
def key_name( number ):
#获取页面的内容并返回
name = '手机'
URL_1 = "https://s.taobao.com/search?ie=utf8&initiative_id=staobaoz_20170905&stats_click=search_radio_all%3A1&js=1&imgfile=&q="
URL_2 = "&suggest=0_1&_input_charset=utf-8&wq=u&suggest_query=u&source=suggest&p4ppushleft=5%2C48&s="
URL = ( URL_1 + name + URL_2 + str(number))
#print(URL)
res = requests.get( URL )
return res.text- 获取数据块
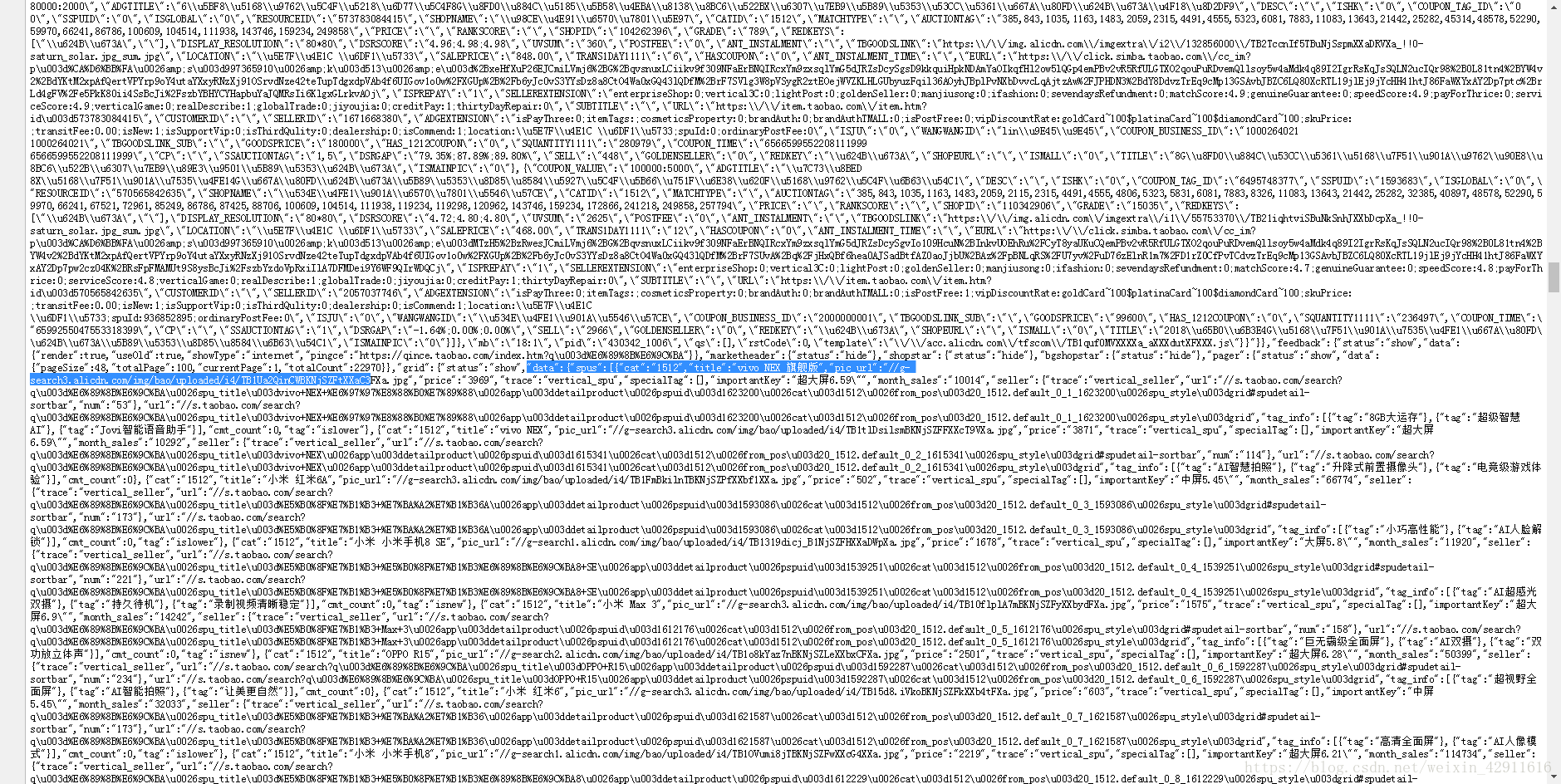
查看淘宝搜索手机后所在页面源代码如图
可以看到,我所需要的手机价格与月销量等数据在data:之后,header之前,因此使用正则表达式来获取数据块,获取数据块代码如下:
def find_date( text):
#根据整个页面的信息,获取商品的数据所在的HTML源码并放回
reg = r',"data":{"spus":\[({.+?)\]}},"header":'
reg = re.compile(reg)
info = re.findall(reg, text)
return info[0]- 解析数据
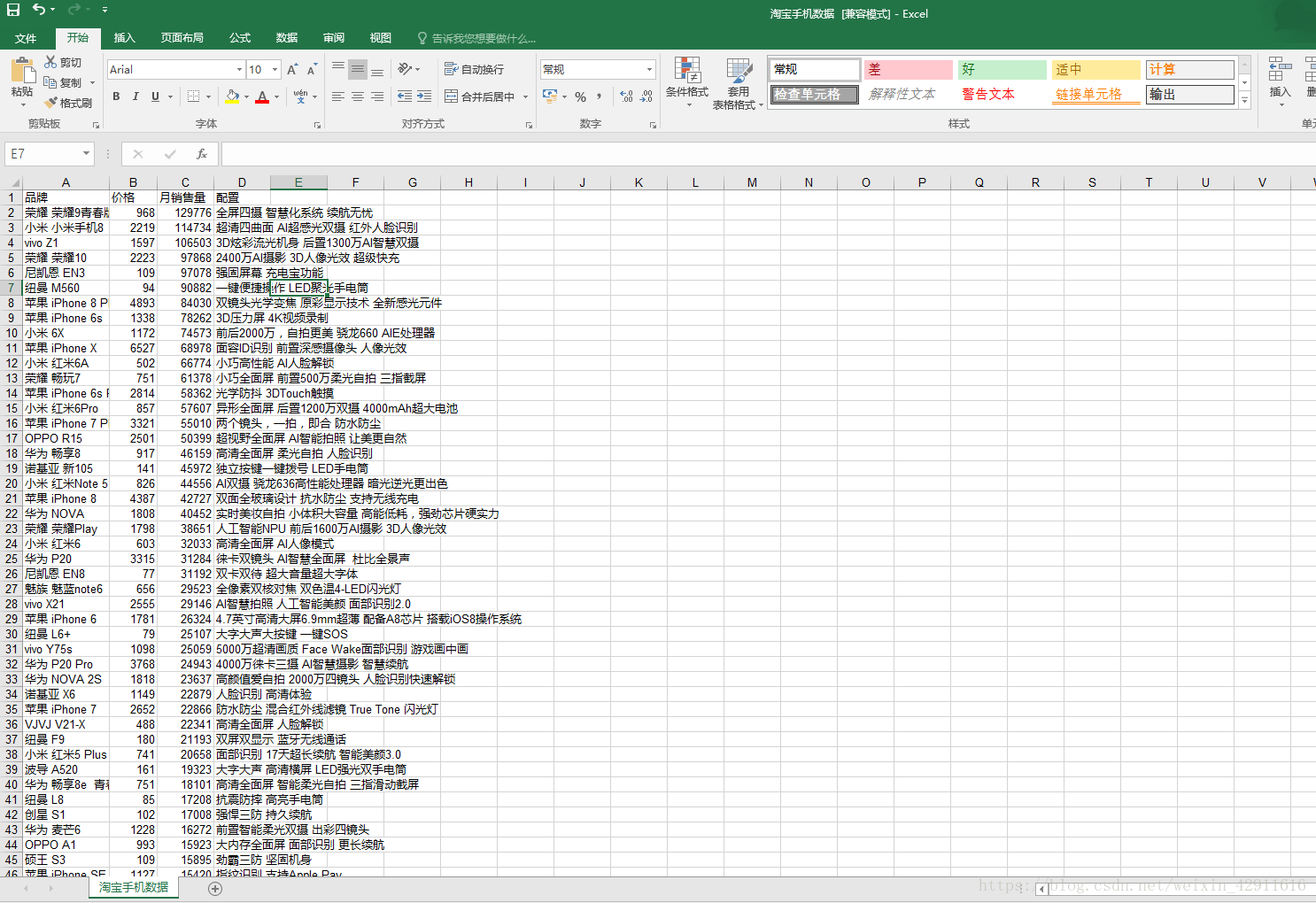
获取到数据块之后,需要从数据块中解析需要的手机品牌、配置、价格、月销量等数据。需要注意的是,代码获取的价格和月销量为字符串形式,需要强制转换为int型再写入excel表格。
对于计算不同品牌手机的月销量问题,采用字符串查找方式,比如华为手机,在手机商品的标题中查找‘华为’、‘荣耀’关键词,如查找到,则该手机则认为是华为手机,月销量加在华为手机上。
代码如下:
def manipulation_data( info, sales_count, sheet ):
#解析获取的HTML源码,获取数据
Date = eval(info)
for d in Date:
T = " ".join([t['tag'] for t in d['tag_info']])
#print(d['title'] + '\t' + d['price'] + '\t' + d['importantKey'][0:len(d['importantKey'])-1] + '\t' + T)
#将数据写入对应的excel表格中
sheet.write(sales_count['line'],0,d['title'])
sheet.write(sales_count['line'],1,int(d['price']))
sheet.write(sales_count['line'],2,int(d['month_sales']))
sheet.write(sales_count['line'],3,T)
#统计不同品牌手机的月销售量
for key in sales_count.keys():
if str(d['title']).find('荣耀')>=0:
sales_count['华为']=sales_count['华为']+(int(d['month_sales']))
elif str(d['title']).find(str(key))>=0:
sales_count[key]=sales_count[key]+(int(d['month_sales']))
sales_count['line']= sales_count['line'] + 1
return sales_count- 绘制条形图
得到不同品牌手机月销量后,需要对其进行按月销量进行排序,使用sorted方法,排序完成后再使用dict方法强制转换为字典形式,我写了两个绘制条形图函数,可根据需要调用,使用包主要是matplotlib和pygal:
def show(sales_count):
#按照手机销售量进行排序并绘图(网页版)
sales_count=dict(sorted(sales_count.items(),key=lambda d:d[1],reverse=True))
print('正在绘制直方图')
picture=pygal.Bar()
picture.title="各大品牌手机月销售量直方图 by社会主义接班人1号"
picture.x_labels=sales_count.keys()
sales_count.keys()
picture.x_title="手机品牌"
picture.y_title="月销售量"
picture.add('淘宝',sales_count.values())
picture.render_to_file('淘宝手机月销售量直方图.svg')
print('绘制完成')
print(sales_count)
def show2(sales_count):
#按照手机销售量进行排序并绘图(图片版)
sales_count=dict(sorted(sales_count.items(),key=lambda d:d[1],reverse=True))
print('正在绘制直方图')
x=[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
picture=plt.bar(x,sales_count.values(),width=0.4,tick_label=list(sales_count.keys()),fc='r')
for rect in picture:
h=rect.get_height()
plt.text(rect.get_x()+rect.get_width()-0.6,1.03*h,'%d'% int(h))
plt.xlabel('手机品牌')
plt.ylabel('月销售量')
plt.title('各大品牌手机月销售量直方图 by社会主义接班人1号')
plt.savefig("淘宝手机月销售量直方图.jpg")
print('绘制完成')
plt.show()
print(sales_count)
- 主函数
主函数如下:
def main():
#初始化建立字典,key为手机品牌,value为月销量
sales_count={'华为':0,'小米':0,'苹果':0,'vivo':0,'OPPO':0,'魅族':0,'纽曼':0,'尼凯恩':0,'诺基亚':0,'三星':0,'联想':0,'line':1}
book = Workbook()
#建立excel表格
sheet = book.add_sheet('淘宝手机数据')
sheet.write(0,0,'品牌')
sheet.write(0,1,'价格')
sheet.write(0,2,'月销售量')
sheet.write(0,3,'配置')
book.save('淘宝手机数据.xls')
#k用于生成链接,每个链接的最后面的数字相差48.
#sales_count['line']用于记录表格的数据行数,便于写入数据
#end为结束页数,可通过end控制获取数据数量
k = 0
end=20
for i in range(end+1):
text = key_name( k + i * 48 )
info = find_date(text)
sales_count= manipulation_data( info ,sales_count, sheet )
book.save('淘宝手机数据.xls')
print('爬取第' + str(i) + '页数据完成,共'+str(end)+'页')
del sales_count['line']
#show(sales_count)
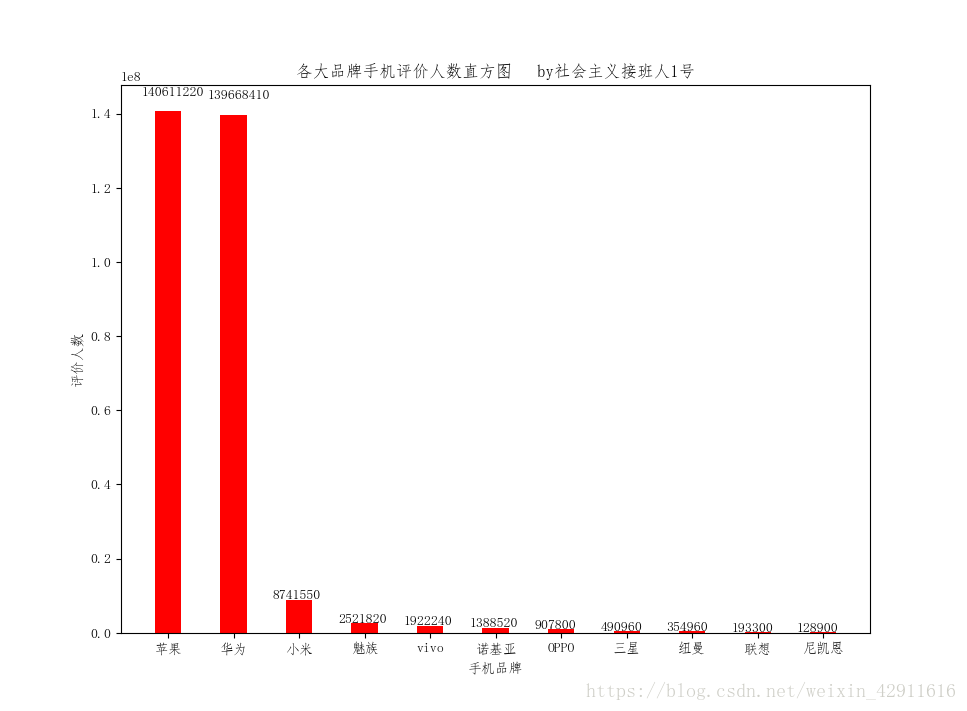
show2(sales_count)- 运行结果
爬取京东数据
京东的情况与淘宝略有不同,京东是搜索一页商品后,鼠标下滑加载下一页,因此需要用到webdriver模拟浏览器打开鼠标下滑操作,并且京东数据块也与淘宝有所不同。并且京东并没有月销量,只有评价人数。不同代码如下:
def key_name( driver,number ):
#获取页面的内容并返回
name = '手机'
URL_1 = "https://search.jd.com/Search?keyword="
URL_2 = "&enc=utf-8&qrst=1&rt=1&stop=1&vt=2&wq="
URL_3="&cid2=653&cid3=655&page="
URL_4 = "&s=1&click=0"
URL = ( URL_1 + name + URL_2 + name + URL_3+ str(number)+URL_4)
#driver = webdriver.Firefox()
#driver.implicitly_wait(3)
driver.get(URL)
# 模拟下滑到底部操作
for i in range(1, 5):
driver.execute_script("window.scrollTo(0, document.body.scrollHeight);")
time.sleep(1)
# 将加载好的页面源码给bs4解析
soup = BeautifulSoup(driver.page_source, "html.parser")
t=0
# 进行信息的抽取(商品名称,价格)
goods_info = soup.select(".gl-item")
#driver.close()
return goods_info
def manipulation_data( goods_info, sales_count, sheet ):
#解析获取的HTML源码,获取数据并对数据进行解析
for info in goods_info:
title = info.select(".p-name.p-name-type-2 a")[0].text.strip()
price_str = info.select(".p-price")[0].text.strip()
count_str = info.select(".p-commit")[0].text.strip()
#print (title)
price_start=price_str.find('¥')+1
price_end=price_str.find('.')
price=int(price_str[price_start:price_end])
#print (price)
if(count_str.find('\n'))>=0:
count_start=count_str.find('\n')+1
else:
count_start=0
if(count_str.find('万+'))>=0:
count=float(count_str[count_start:count_str.find('万')])*10000
elif(count_str.find('+'))>=0:
count=int(count_str[count_start:count_str.find('+')])
#print(count)
sheet.write(sales_count['line'],0,title)
sheet.write(sales_count['line'],1,int(price))
sheet.write(sales_count['line'],2,int(count))
for key in sales_count.keys():
if str(title).find('荣耀')>=0:
sales_count['华为']=sales_count['华为']+(int(count))
elif str(title).find('Apple')>=0:
sales_count['苹果']=sales_count['苹果']+(int(count))
elif str(title).find(str(key))>=0:
sales_count[key]=sales_count[key]+(int(count))
sales_count['line']= sales_count['line'] + 1
return sales_count
def main():
sales_count={'华为':0,'小米':0,'苹果':0,'vivo':0,'OPPO':0,'魅族':0,'纽曼':0,'尼凯恩':0,'诺基亚':0,'三星':0,'联想':0,'line':1}
book = Workbook()
sheet = book.add_sheet('京东手机数据')
sheet.write(0,0,'手机')
sheet.write(0,1,'价格')
sheet.write(0,2,'评价数量')
book.save('京东手机数据.xls')
driver = webdriver.Firefox()
driver.implicitly_wait(3)
end=30
#sales_count['line']用于记录表格的数据行数,便于写入数据
for i in range(end):
goods_info = key_name(driver,i*2)
sales_count= manipulation_data( goods_info ,sales_count, sheet )
book.save('京东手机数据.xls')
print('爬取第' + str(i+1) + '页数据完成,共'+str(end)+'页')
del sales_count['line']
#show(sales_count)
show2(sales_count)- 运行结果
对比淘宝和京东数据发现,淘宝上华为一马当先,京东上几乎是华为、苹果各占半壁江山,都说华为赚钱,这次我信了。
爬取淘宝全部源代码https://download.csdn.net/download/weixin_42911616/10605090
爬取京东全部源代码https://download.csdn.net/download/weixin_42911616/10605100
本文完
1- 部分代码来源网络,如有侵权,请联系 ↩