这一偏主要记录Groovy的数据库操作,然后数据库操作无非就是差删改查。编写代码以前,工作环境是绕不过去的坎。
首先,供上JDBC必须的jar,下载地址:
http://download.csdn.net/download/qq_36006553/9945670
(因为我也需要下载别的资源,所以就收一个积分。万一真的没有积分的加我扣扣709165253,我给你发。但是我的扣扣不是经常在)
然后,把下载好的jar直接复制到Eclipse创建好的项目中,然后选中jar,右键,build Path,add Path。
先供上Java的只有查询操作的源码:
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
/**
* 完成了数据连接的工作
*
* javaee是数据库名字
*
* root是数据库的用户名
*
* 123456是数据库的密码
*
* @author luopan
*
*/
public class Main {
private static String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/javaee";
private static String user = "root";
private static String password = "123456";
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 设置数据库,用户名,密码
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
// 连接数据库
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
// 执行raw的SQL查询语句
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("select * from user");
while (rs.next()) {
// 遍历结果集完成打印
String name = rs.getString(1);
String sex = rs.getString(2);
String birth = rs.getString(3);
String birthAddr = rs.getString(4);
System.out.print("[" + name + " ");
System.out.print(sex + " ");
System.out.print(birth + " ");
System.out.println(birthAddr + "]");
}
conn.close();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
看Groovy的源码,里面有增删改查四个操作:
先定义一个类,Stadium:
//在Groovy中,访问权限全部都是public,不用特意指定
class Stadium {
int id
String name
String city
String state
String team
double latitude
double longitude
String toString(){
"($team,$name,$latitudem,$longitude)"
}
}
主体代码:
import groovy.sql.Sql
//连接数据库
Sql db = Sql.newInstance('jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/javaee',
'root',
'123456',
'com.mysql.jdbc.Driver')
//如果已经存在我们要创建的表,那么久删除它
db.execute "drop table if exists stadium"
//创建我们需要的表
db.execute '''
create table stadium(
id int not null auto_increment,
name varchar(200) not null,
city varchar(200) not null,
state char(2) not null,
team char(2) not null,
latitude double,
longitude double,
primary key(id)
);
'''
//向表中插入数据(增加操作)
db.execute """
insert into stadium(name, city, state, team, latitude, longitude)
values('luopan','wuhan','M','W',30.222,131.88678);
"""
db.execute """
insert into stadium(name, city, state, team, latitude, longitude)
values('qinfei','Taiyuan','W','E',32.222,129.32590);
"""
db.execute """
insert into stadium(name, city, state, team, latitude, longitude)
values('liuzhen','Shenzhen','M','O',29.222,132.56789);
"""
db.execute """
insert into stadium(name, city, state, team, latitude, longitude)
values('xushixing','Shanghai','M','N',30.222,128.123456);
"""
//删除表中的数据(删除数据)
db.execute "delete from stadium where team ='W';"
//执行这句话以后,第一条数据,luopan删除了。
//更新数据(更改数据)
db.execute "update stadium set city ='Wuhan' where city='Taiyuan';"
//执行这句话以后,qinfei那条数据的city的值改为Wuhan了。
//查询数据
db.eachRow('select * from stadium;'){ tp ->
println([
tp.name,
tp.city,
tp.state,
tp.latitude,
tp.longitude
])
}对比一下,Groovy的数据库操作,只需要连接,其他的什么也不用管了,只管自己用即可。
并且,Groovy的数据库操作都是使用的原声的数据库语句,并且最后的分好也是可选的,看下面的语句:
//写法一:最后的双引号之前有一个分号
db.execute "update stadium set city ='Wuhan' where city='Taiyuan';"
//写法二:最后的双引号之前没有分号
db.execute "update stadium set city ='Wuhan' where city='Taiyuan'"这两种写法都可以得到正确的结果。然后在Java中不可以的。自行测试。
Groovy对于SQL的生态很支持。
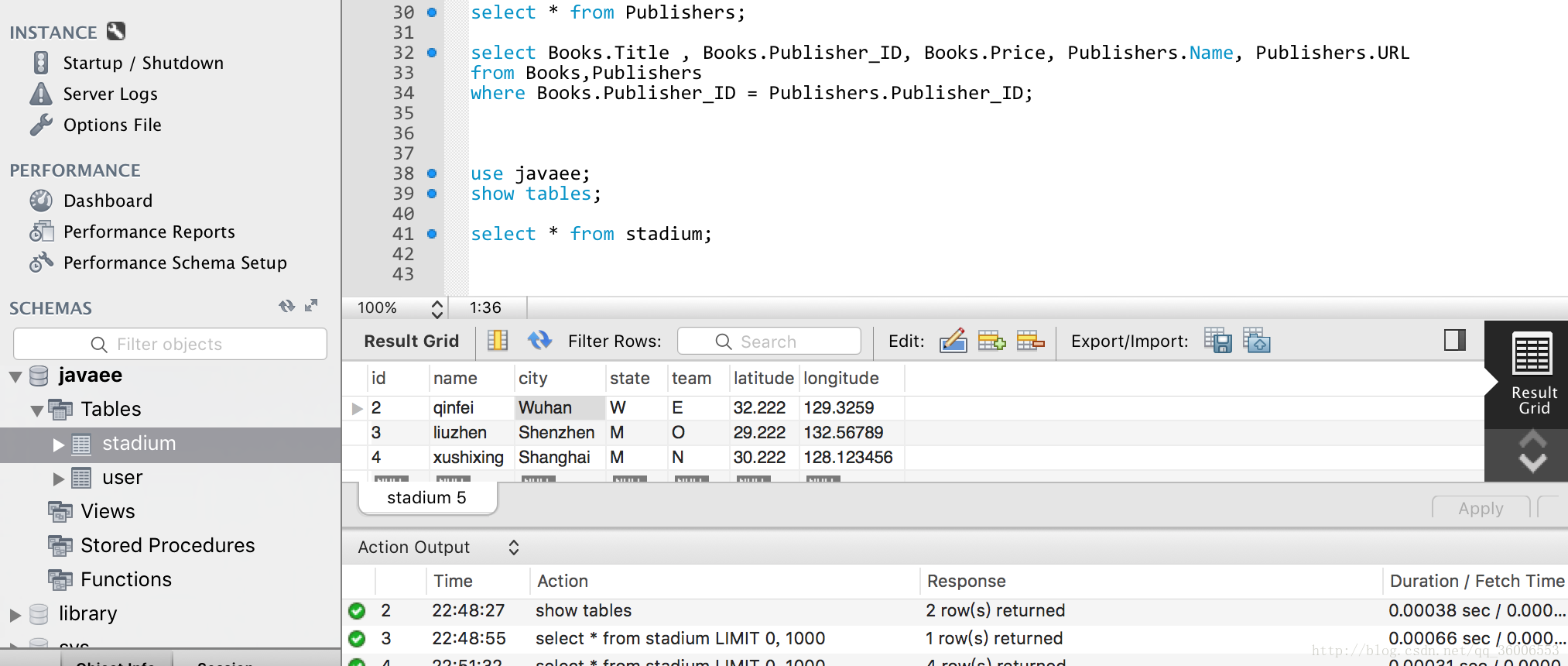
最后贴上我的MySQLWorkBench界面:
可以很明显看到数据库javaee下面有两个表,stadium和user。还有一些数据库的命令行,可以照着尝试一下哟。