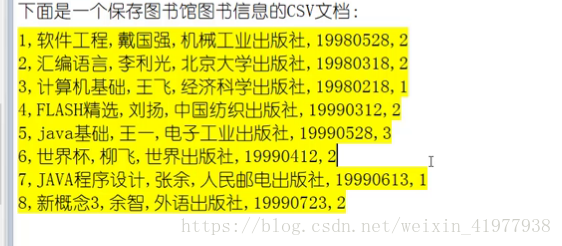
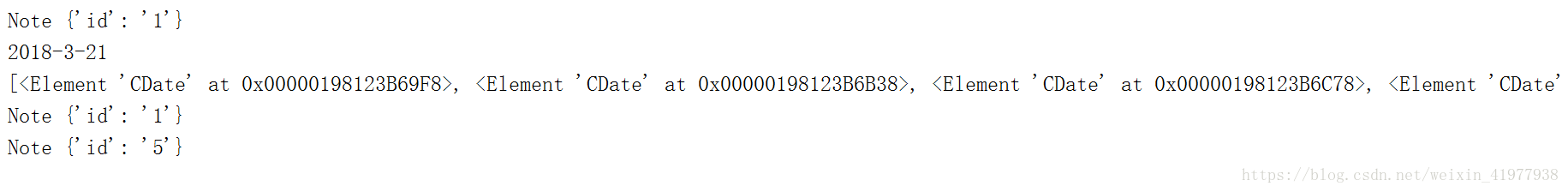1 csv
要用逗号分隔,有局限性 ,应用范围较窄
列:
读写csv文件
csv.reader()
import csv
with open('books.csv','r',encoding='gbk') as csv_open:
read=csv.reader(csv_open,dialect='excel')
#读入了一行行的数据
for i in read:
print(i) #list类型结果:
写入:csv.writer()
import csv
file_name = 'books2.cvs'
with open('books.csv', 'r', encoding='gbk') as csv_open:
read = csv.reader(csv_open, dialect='excel')
with open(file_name, 'w', encoding='gbk') as csv_w:
writer = csv.writer(csv_w, delimiter='\t') # 间隔符 使用 \t 水平制表符
for i in read:
writer.writerow(i) # 写入行
writer.writerow([40, '黑幕', '李仪', '华光出版社', 20000508, 24])
2 .xml 可扩展标记语言,使用标签表示
解析方式:SAX 只能解析 DOM可做修改(占用内存也大大,一次读一棵树),ElementTree 优于DOM
例子:一个xml文档如下
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
tree = ET.parse('Notes.xml')
print(type(tree))
root = tree.getroot() # 根元素
print(type(root))
print(root.tag) # tag标签名
for index, child in enumerate(root):
print(index, child.tag, child.attrib, child.text) # attrib 标签属性
for i, child_c in enumerate(child):
print(' ' + child_c.tag, child_c.text) #子标签 text 文本内容
输出:
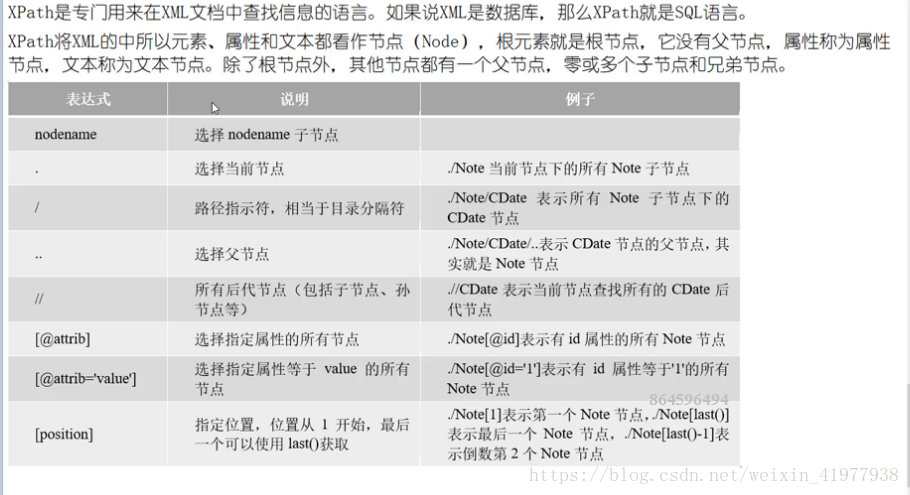
xpath
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
tree = ET.parse('Notes.xml')
root=tree.getroot()
node=root.find('./Note') #找第一个Note子节点
print(node.tag,node.attrib)
node= root.find('./Note/CDate') #子节点的子节点
print(node.text)
node_list=root.findall('.//CDate') #找root下的所有CDate
print(node_list)
node= root.find('./Note[1]') #root下第一个位置的
print(node.tag,node.attrib)
node= root.find('./Note[last()]') #root下第最后位置的
print(node.tag,node.attrib)结果:
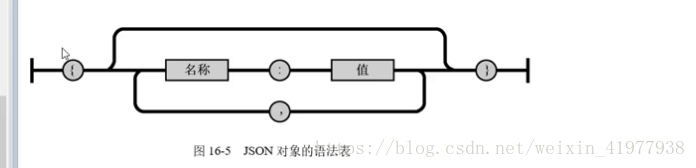
3 .Json
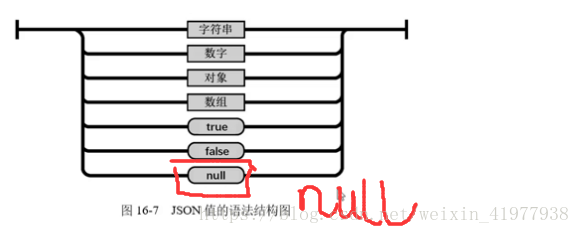
数据类型:字符串要用双引号
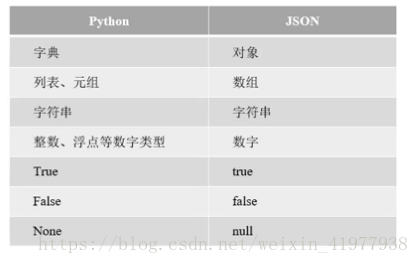
python数据转Json数据:
import json
dic = {'name': 'tom', 'age': 19, 'alive': True, 'a': [1, 3, '233'], 'b': ('1', '22')}
js = json.dumps(dic) # 返回字符串类型
print(type(js))
print(js)
with open('d1.json','w') as J:
json.dump(dic,J) #返回文件结果:
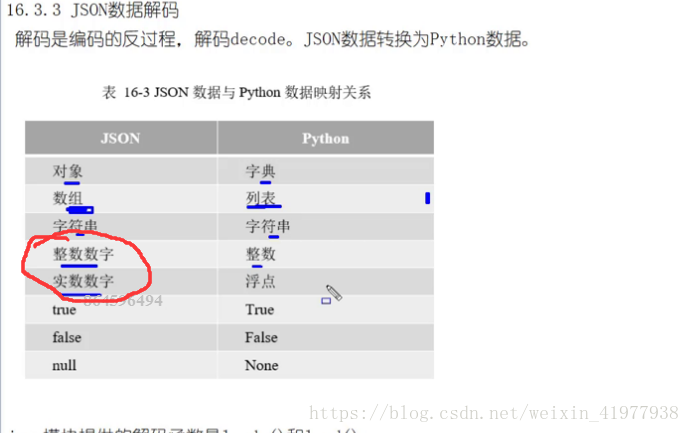
json解码
import json
js=r'{"b": ["1", "22"], "age": 19, "alive": true, "name": "tom", "a": [1, 3, "233"]}' #要带r。。
outpython=json.loads(js) #json字符解析
print(type(outpython))
print(outpython)
with open('d1.json','r') as JtoP:
otpython=json.load(JtoP) #json文件解析
print(otpython)结果:
python配置文件:
一个ini文件如下
读配置文件
import configparser
config = configparser.ConfigParser() # 解释器
config.read('Setup.ini', encoding='utf-8') # 读入内存 注意编码格式
sect = config.sections() # 取所有节
print(sect)
sect_name=config.options('Startup') #返回一个节的 所有项
print(sect_name)
print(config['Startup']['requireos']) #取项里的内容结果:
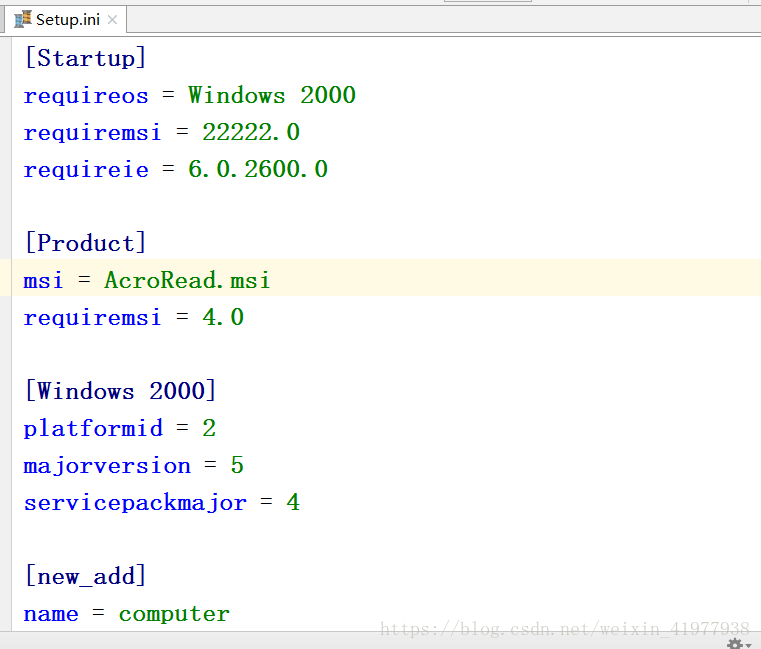
import configparser
config = configparser.ConfigParser() # 解释器
config.read('Setup.ini', encoding='utf-8') # 读入内存 注意编码格式
#修改
config['Startup']['requiremsi']='22222.0' #内容都是字符串类型
# 增加
config.add_section('new_add')
config.set('new_add','name','computer') #set(节,项名,值)
with open('Setup.ini','w') as f:
config.write(f) #写入!!!!!!!!!!!!结果