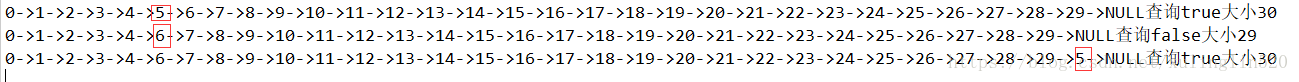创建简单链表类,可以声明为内部类,和外部类。不过一般都是声明的内部类该类用户不需要知道他是什么
Node --> Node --> Node --> Node...
package com.Test;
/**
*
* @author XiaoTian
* @date 2018-08-02
* @param <E>
*/
//E 为泛型
public class NodeList<E> {
//内部类
class Node {
//E 就是所为的value
public E e;
/**
* 这里是关键
* 在原本的类里声明本身就能形成链表结构
*/
public Node next;
//构造器
public Node() {
this(null, null);
}
/**
* 传入参数
* @param e
*/
public Node(E e) {
this(e, null);
}
/**
* 传入参数
* @param e
* @param node
*/
public Node(E e, Node node) {
this.e = e;
this.next = node;
}
// 添加子节点
public void addNode(Node node) {
//判断当前节点是否为空,为空就进行添加
if (this.next == null) {
this.next = node;
} else {
next.addNode(node);
}
}
// 查询某个节点
public boolean searchNode(E e) {
//当前元素是否存在 存在就返回
if (this.e.equals(e)) {
return true;
} else if (this.next != null) {
//不存在就进行本的下一个节点继续查询
return this.next.searchNode(e);
}
return false;
}
// 删除
public void remove(Node node, E e) {
//当前元素是否存在 存在就返回
if (this.e.equals(e)) {
node.next = this.next;
sizo--;
} else {
//不存在就进行本的下一个节点继续删除
this.next.remove(this, e);
}
}
// 打印输出
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
Node cur = this;
while (cur != null) {
s.append(cur.e + "->");
cur = cur.next;
}
s.append("NULL");
return s.toString();
}
}
// 根节点
private Node root;
//大小
private int sizo;
// 添加节点
public void add(E e) {
Node node = new Node(e);
if (this.root == null) {
root = node;
} else {
root.addNode(node);
}
sizo++;
}
// 删除节点
public void remove(E e) {
//判断当前链表是否存在 e
if (search(e)) {
this.root.remove(root, e);
}
}
// 查询节点
public boolean search(E e) {
//递归调用查询
return this.root.searchNode(e);
}
// 大小
public int getSizo() {
return sizo;
}
// 输出
@Override
public String toString() {
return root.toString();
}
}
//测试类
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
NodeList<Integer> nodeList = new NodeList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
nodeList.add(i);
}
System.out.println(nodeList+"查询"+nodeList.search(5)+"大小"+nodeList.getSizo());
nodeList.remove(5);
System.out.println(nodeList+"查询"+nodeList.search(5)+"大小"+nodeList.getSizo());
nodeList.add(5);
System.out.println(nodeList+"查询"+nodeList.search(5)+"大小"+nodeList.getSizo());
}
}
运行的结果
链表结构当你在添加节点的时候是在最后一个节点添加的
结构是这样的
对象里有对象 -->对象 -->对象 --> 这样的规则
你明白了吗。当前这只是一个简单的链表