2018-7-30 17:31:41
学了几天的数据库,今天开始进入了python操作数据库啦.
数据库最重要的就是前几天的SQL语句 还有查数据的
整理一下笔记 有点懒,直接手动摘抄啦!
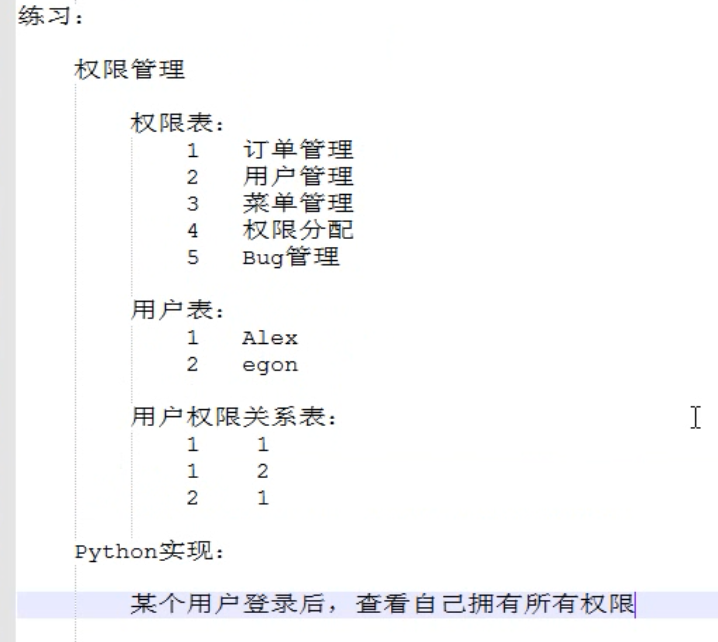
s4day60 上节回顾: 1. MySQL:文件管理的软件 2. 三部分: - 服务端 - SQL语句 - 客户端 3. 客户端: - mysql - navicat 4. 授权操作 - 用户操作 - 授权操作 5. SQL语句 - 数据库操作 - create database xx default charset utf8; - drop database xx; - 数据表 - 列 - 数字 整数 小数 - 字符串 - 时间 - 二进制 - 其他:引擎,字符编码,起始值 - 主键索引 - 唯一索引 - 外键 - 一对多 - 一对一 - 多对多 - 数据行 - 增 - 删 - 改 - 查 - in not in - between and - limit - group by having - order by - like "%a" - left join xx on 关系 - 临时表 select * from (select * from tb where id< 10) as B; - select id, name, 1, (select count(1) from tb) from tb2 SELECT student_id, (select num from score as s2 where s2.student_id=s1.student_id and course_id = 1) as 语文, (select num from score as s2 where s2.student_id=s1.student_id and course_id = 2) as 数学, (select num from score as s2 where s2.student_id=s1.student_id and course_id = 3) as 英语 from score as s1; - 条件 select course_id, max(num), min(num), min(num)+1, case when min(num) <10 THEN 0 ELSE min(num) END as c from score GROUP BY course_id select course_id,avg(num),sum(case when num <60 THEN 0 ELSE 1 END),sum(1),sum(case when num <60 THEN 0 ELSE 1 END)/sum(1) as jgl from score GROUP BY course_id order by AVG(num) asc,jgl desc; PS: 数据放在硬盘上 思想: - 操作 - 设计 今日内容: 1. 练习题 7、查询学过“001”并且也学过编号“002”课程的同学的学号、姓名; -- select score.student_id,student.sname from score -- -- left join student on score.student_id=student.sid -- -- where course_id =1 or course_id =2 GROUP BY student_id HAVING count(course_id) > 1 8、查询学过“叶平”老师所教的所有课的同学的学号、姓名; -- select student_id from score where course_id in ( -- select cid from course left JOIN teacher on course.teacher_id = teacher.tid where teacher.tname = "李平老师" -- ) GROUP BY student_id having count(course_id) = (select count(cid) from course left JOIN teacher on course.teacher_id = teacher.tid where teacher.tname = "李平老师") -- -- 10、查询有课程成绩小于60分的同学的学号、姓名; -- select student_id from score where num < 60 GROUP BY student_id -- select DISTINCT student_id from score where num < 60 -- 查询没有学全所有课的同学的学号、姓名; 11、查询没有学全所有课的同学的学号、姓名; -- select student_id,count(1) from score GROUP BY student_id HAVING count(1) < (select count(cid) from course); -- -- 12、查询至少有一门课与学号为“001”的同学所学相同的同学的学号和姓名; -- select course_id from score where student_id = 1; -- select student_id from score where student_id != 1 and course_id in (select course_id from score where student_id = 1) GROUP BY student_id -- 13、查询至少学过学号为“001”同学所有课的其他同学学号和姓名; -- select course_id from score where student_id = 1; -- select student_id,count(1) from score where student_id != 1 and course_id in (select course_id from score where student_id = 1) GROUP BY student_id HAVING count(1) = (select count(course_id) from score where student_id = 1) -- 14、查询和“002”号的同学学习的课程完全相同的其他同学学号和姓名; -- 获取和方少伟选课个数相同的通许 -- select count(1) from score where student_id = 1; -- -- select student_id from score where student_id in ( -- select student_id from score where student_id !=1 GROUP BY student_id HAVING count(1) = (select count(1) from score where student_id = 1) -- ) and course_id in (select course_id from score where student_id = 1) GROUP BY student_id HAVING count(1) = (select count(1) from score where student_id = 1) -- -- -- insert into tb(student_id,course_id,num) -- -- select student_id,2,(SELECT AVG(num) from score where course_id = 2) from score where course_id != 2 -- 17、按平均成绩从低到高 显示所有学生的“语文”、“数学”、“英语”三门的课程成绩,按如下形式显示: 学生ID,语文,数学,英语,有效课程数,有效平均分; -- 1 90 80 99 -- 2 90 80 99 -- SELECT -- student_id, -- (select num from score as s2 where s2.student_id=s1.student_id and course_id = 1) as 语文, -- (select num from score as s2 where s2.student_id=s1.student_id and course_id = 2) as 数学, -- (select num from score as s2 where s2.student_id=s1.student_id and course_id = 3) as 英语 -- from score as s1; -- -- 18、查询各科成绩最高和最低的分:以如下形式显示:课程ID,最高分,最低分; -- select course_id,max(num),min(num),min(num)+1,case when min(num) <10 THEN 0 ELSE min(num) END as c from score GROUP BY course_id -- 19、按各科平均成绩从低到高和及格率的百分数从高到低顺序; select course_id,avg(num),sum(case when num <60 THEN 0 ELSE 1 END),sum(1),sum(case when num <60 THEN 0 ELSE 1 END)/sum(1) as jgl from score GROUP BY course_id order by AVG(num) asc,jgl desc; pymysql模块: pip3 install pymysql -i https://pypi.douban.com/simple Python模块:对数据库进行操作(SQL语句) 1. Python实现用户登录 2. MySQL保存数据 - 连接、关闭(游标) - execute() -- SQL注入 - 增删改: conn.commit() - fetchone fetchall - 获取插入数据自增ID 练习: 权限管理 权限表: 1 订单管理 2 用户管理 3 菜单管理 4 权限分配 5 Bug管理 用户表: 1 Alex 2 egon 用户权限关系表: 1 1 1 2 2 1 Python实现: 某个用户登录后,查看自己拥有所有权限
已经实现了,就是有点繁琐,应该还有更好地方法
# !/usr/bin/env python # !--*--coding:utf-8 --*-- # !@Time :2018/7/30 16:26 # !@Author TrueNewBee import pymysql # 思路 # 1.创建好了表 # 2.先登入成功,显示个人职位 # 3.关于SQL语句书写思路 # 1.首先先把user_work这个表和users这个表链表 left join on # 2 通过输入的用户名,在连过的表A中查找work_id AS A # 3.得到work_id后表A与works表连接,然后通过work_id找到所对应的权限 # select work_name from B left join A on A.work_id = B.id # 意识就是我的思路 user = input('请输入账户') pwd = input('请输入密码') conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='123', database='db1') cursor = conn.cursor() sql = "select * from user where username='%s' and password='%s' " cursor.execute(sql, [user, pwd]) result = cursor.fetchone() if result: print('登入成功,你的权限如下:') w_sql = "select works.workname from (select work_id from user_work left join users on users.id=user_work.use_id WHERE users.`user`='%s') as A LEFT JOIN works on A.work_id=works.id " % user cursor.execute(w_sql) result = cursor.fetchone() print(result) else: print('登入失败') cursor.close() conn.close()
先把其他的代码粘贴过来
1 # !/usr/bin/env python 2 # !--*--coding:utf-8 --*-- 3 # !@Time :2018/7/30 11:58 4 # !@Author TrueNewBee 5 # 练习使用pyMySQL 6 # 对数据库的交互 7 import pymysql 8 9 10 user = input('请输入账号:') 11 pwd = input('请输入密码:') 12 13 # 创建与数据库的连接 14 conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='123', database='db666') 15 cursor = conn.cursor() 16 # 通过sql语句查询数据 这种是错误的,容易被SQL注入 asdasdas' or 1=1 -- 17 sql = "select * from userinfo where username='%s' and password='%s' " % (user, pwd) 18 cursor.execute(sql) 19 # 获取数据 20 result = cursor.fetchone() 21 # 关闭 22 cursor.close() 23 conn.close() 24 25 if result: 26 print('登入成功') 27 else: 28 print('登入失败')

1 # !/usr/bin/env python 2 # !--*--coding:utf-8 --*-- 3 # !@Time :2018/7/30 12:40 4 # !@Author TrueNewBee 5 import pymysql 6 7 8 # 增加 删 9 # conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='123', database='db666') 10 # cursor = conn.cursor() 11 # sql = "insert into userinfo(username,password)values('root','123')" 12 # 守影响的行数 13 # r = cursor.execute(sql) 14 # cursor.execute(sql) 15 # # 选择增加的时候要 提交数据 16 # conn.commit() 17 # result = cursor.fetchone() 18 # cursor.close() 19 # conn.close() 20 21 # 2018-7-30 15:38:06 22 23 # 批量增加 24 # conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='123', database='db666') 25 # cursor = conn.cursor() 26 # sql = "insert into userinfo(username,password)values(%s, %s)" 27 # # 守影响的行数 28 # r = cursor.execute(sql) 29 # cursor.executemany(sql, [('egon', 'sb'), ('laoyao', 'BS')]) 30 # conn.commit() 31 # result = cursor.fetchone() 32 # cursor.close() 33 # conn.close() 34 35 36 # # 查 37 # conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='123', database='db666') 38 # cursor = conn.cursor() 39 # sql = "select * from userinfo" 40 # cursor.execute(sql) 41 # # cursor.scroll(1,mode='relative') # 相对当前位置移动 42 # # cursor.scroll(2,mode='absolute') # 相对绝对位置移动 43 # result = cursor.fetchone() 44 # print(result) 45 # cursor.close() 46 # conn.close() 47 48 49 # 新插入数据的自增ID 50 51 conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='123', database='db666') 52 cursor = conn.cursor() 53 sql = "insert into userinfo(username,password) values ('asdfasdf', '123')" 54 cursor.execute(sql) 55 conn.commit() 56 print(cursor.lastrowid) # 显示新插入数据的自增ID 57 cursor.close() 58 conn.close()

1 # !/usr/bin/env python 2 # !--*--coding:utf-8 --*-- 3 # !@Time :2018/7/30 12:29 4 # !@Author TrueNewBee 5 import pymysql 6 7 8 user = input('请输入账号:') 9 pwd = input('请输入密码:') 10 11 # 创建与数据库的连接 12 conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='123', database='db666') 13 cursor = conn.cursor() 14 # 通过sql语句查询数据 这种是错误的,容易被SQL注入 asdasdas' or 1=1 -- 15 # sql = "select * from userinfo where username='%s' and password='%s' " 16 sql = "select * from userinfo where username='%(u)' and password='%(p)' " 17 # 通过内部的传参拼接 18 # cursor.execute(sql,user, pwd) 19 # cursor.execute(sql, [user, pwd]) 20 cursor.execute(sql, {'u': user, 'p': pwd}) # 占位符也支持字典 21 # 获取数据 22 result = cursor.fetchone() 23 cursor.close() 24 conn.close()
