RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ是一个在AMQP基础上完整的,可复用的企业消息系统。他遵循Mozilla Public License开源协议。
MQ全称为Message Queue, 消息队列(MQ)是一种应用程序对应用程序的通信方法。应用程序通过读写出入队列的消息(针对应用程序的数据)来通信,而无需专用连接来链接它们。消 息传递指的是程序之间通过在消息中发送数据进行通信,而不是通过直接调用彼此来通信,直接调用通常是用于诸如远程过程调用的技术。排队指的是应用程序通过 队列来通信。队列的使用除去了接收和发送应用程序同时执行的要求。
RabbitMQ安装
安装配置epel源
$ rpm -ivh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/i386/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
安装erlang
$ yum -y install erlang
安装RabbitMQ
$ yum -y install rabbitmq-server注意:service rabbitmq-server start/stop
安装API
pip install pika
or
easy_install pika
or
源码
https://pypi.python.org/pypi/pika使用API操作RabbitMQ
基于Queue实现生产者消费者模型
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import Queue import threading message = Queue.Queue(10) def producer(i): while True: message.put(i) def consumer(i): while True: msg = message.get() for i in range(12): t = threading.Thread(target=producer, args=(i,)) t.start() for i in range(10): t = threading.Thread(target=consumer, args=(i,)) t.start()
对于RabbitMQ来说,生产和消费不再针对内存里的一个Queue对象,而是某台服务器上的RabbitMQ Server实现的消息队列。
#!/usr/bin/env python
import pika
# ######################### 生产者 #########################
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.queue_declare(queue='hello')
channel.basic_publish(exchange='',
routing_key='hello',
body='Hello World!')
print(" [x] Sent 'Hello World!'")
connection.close()#!/usr/bin/env python
import pika
# ########################## 消费者 ##########################
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.queue_declare(queue='hello')
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] Received %r" % body)
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue='hello',
no_ack=True)
print(' [*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C')
channel.start_consuming()1、acknowledgment 消息不丢失
no-ack = False,如果消费者遇到情况(its channel is closed, connection is closed, or TCP connection is lost)挂掉了,那么,RabbitMQ会重新将该任务添加到队列中。
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='10.211.55.4'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.queue_declare(queue='hello')
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] Received %r" % body)
import time
time.sleep(10)
print 'ok'
ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag = method.delivery_tag)
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue='hello',
no_ack=False)
print(' [*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C')
channel.start_consuming()#!/usr/bin/env python
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='10.211.55.4'))
channel = connection.channel()
# make message persistent
channel.queue_declare(queue='hello', durable=True)
channel.basic_publish(exchange='',
routing_key='hello',
body='Hello World!',
properties=pika.BasicProperties(
delivery_mode=2, # make message persistent
))
print(" [x] Sent 'Hello World!'")
connection.close()#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='10.211.55.4'))
channel = connection.channel()
# make message persistent
channel.queue_declare(queue='hello', durable=True)
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] Received %r" % body)
import time
time.sleep(10)
print 'ok'
ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag = method.delivery_tag)
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue='hello',
no_ack=False)
print(' [*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C')
channel.start_consuming()3、消息获取顺序
默认消息队列里的数据是按照顺序被消费者拿走,例如:消费者1 去队列中获取 奇数 序列的任务,消费者1去队列中获取 偶数 序列的任务。
channel.basic_qos(prefetch_count=1) 表示谁来谁取,不再按照奇偶数排列
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='10.211.55.4'))
channel = connection.channel()
# make message persistent
channel.queue_declare(queue='hello')
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] Received %r" % body)
import time
time.sleep(10)
print 'ok'
ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag = method.delivery_tag)
channel.basic_qos(prefetch_count=1)
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue='hello',
no_ack=False)
print(' [*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C')
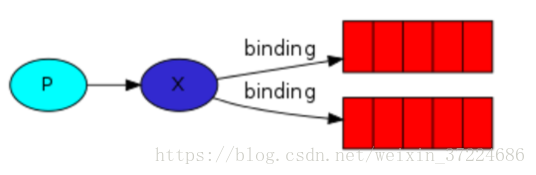
channel.start_consuming()发布订阅和简单的消息队列区别在于,发布订阅会将消息发送给所有的订阅者,而消息队列中的数据被消费一次便消失。所以,RabbitMQ实现发布和订阅时,会为每一个订阅者创建一个队列,而发布者发布消息时,会将消息放置在所有相关队列中。
#!/usr/bin/env python
import pika
import sys
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='logs',
type='fanout')
message = ' '.join(sys.argv[1:]) or "info: Hello World!"
channel.basic_publish(exchange='logs',
routing_key='',
body=message)
print(" [x] Sent %r" % message)
connection.close()#!/usr/bin/env python
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='logs',
type='fanout')
result = channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True)
queue_name = result.method.queue
channel.queue_bind(exchange='logs',
queue=queue_name)
print(' [*] Waiting for logs. To exit press CTRL+C')
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] %r" % body)
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue=queue_name,
no_ack=True)
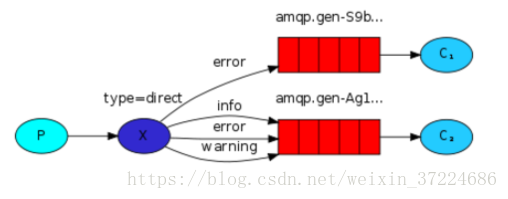
channel.start_consuming()exchange type = direct
之前事例,发送消息时明确指定某个队列并向其中发送消息,RabbitMQ还支持根据关键字发送,即:队列绑定关键字,发送者将数据根据关键字发送到消息exchange,exchange根据 关键字 判定应该将数据发送至指定队列。
#!/usr/bin/env python
import pika
import sys
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='direct_logs',
type='direct')
result = channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True)
queue_name = result.method.queue
severities = sys.argv[1:]
if not severities:
sys.stderr.write("Usage: %s [info] [warning] [error]\n" % sys.argv[0])
sys.exit(1)
for severity in severities:
channel.queue_bind(exchange='direct_logs',
queue=queue_name,
routing_key=severity)
print(' [*] Waiting for logs. To exit press CTRL+C')
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] %r:%r" % (method.routing_key, body))
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue=queue_name,
no_ack=True)
channel.start_consuming()#!/usr/bin/env python
import pika
import sys
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='direct_logs',
type='direct')
severity = sys.argv[1] if len(sys.argv) > 1 else 'info'
message = ' '.join(sys.argv[2:]) or 'Hello World!'
channel.basic_publish(exchange='direct_logs',
routing_key=severity,
body=message)
print(" [x] Sent %r:%r" % (severity, message))
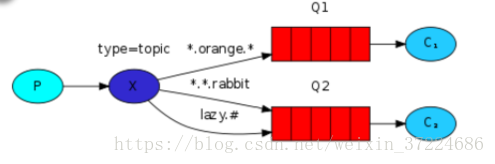
connection.close()exchange type = topic
在topic类型下,可以让队列绑定几个模糊的关键字,之后发送者将数据发送到exchange,exchange将传入”路由值“和 ”关键字“进行匹配,匹配成功,则将数据发送到指定队列。
- # 表示可以匹配 0 个 或 多个 单词
- * 表示只能匹配 一个 单词
发送者路由值 队列中
old.boy.python old.* -- 不匹配
old.boy.python old.# -- 匹配#!/usr/bin/env python
import pika
import sys
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='topic_logs',
type='topic')
result = channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True)
queue_name = result.method.queue
binding_keys = sys.argv[1:]
if not binding_keys:
sys.stderr.write("Usage: %s [binding_key]...\n" % sys.argv[0])
sys.exit(1)
for binding_key in binding_keys:
channel.queue_bind(exchange='topic_logs',
queue=queue_name,
routing_key=binding_key)
print(' [*] Waiting for logs. To exit press CTRL+C')
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] %r:%r" % (method.routing_key, body))
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue=queue_name,
no_ack=True)
channel.start_consuming()#!/usr/bin/env python
import pika
import sys
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='topic_logs',
type='topic')
routing_key = sys.argv[1] if len(sys.argv) > 1 else 'anonymous.info'
message = ' '.join(sys.argv[2:]) or 'Hello World!'
channel.basic_publish(exchange='topic_logs',
routing_key=routing_key,
body=message)
print(" [x] Sent %r:%r" % (routing_key, message))
connection.close()注意:
sudo rabbitmqctl add_user alex 123
# 设置用户为administrator角色
sudo rabbitmqctl set_user_tags alex administrator
# 设置权限
sudo rabbitmqctl set_permissions -p "/" alex '.''.''.'
# 然后重启rabbiMQ服务
sudo /etc/init.d/rabbitmq-server restart
# 然后可以使用刚才的用户远程连接rabbitmq server了。
------------------------------
credentials = pika.PlainCredentials("alex","123")
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters('192.168.14.47',credentials=credentials))7.Remote procedure call (RPC)
RPC server
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
__author__ = 'Alex Li'
import pika
import time
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.queue_declare(queue='rpc_queue')
def fib(n):
if n == 0:
return 0
elif n == 1:
return 1
else:
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2)
def on_request(ch, method, props, body):
n = int(body)
print(" [.] fib(%s)" % n)
response = fib(n)
ch.basic_publish(exchange='',
routing_key=props.reply_to,
properties=pika.BasicProperties(correlation_id = \
props.correlation_id),
body=str(response))
ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag = method.delivery_tag)
channel.basic_qos(prefetch_count=1)
channel.basic_consume(on_request, queue='rpc_queue')
print(" [x] Awaiting RPC requests")
channel.start_consuming()
|
RPC client
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
import pika
import uuid
class FibonacciRpcClient(object):
def __init__(self):
self.connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
self.channel = self.connection.channel()
result = self.channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True)
self.callback_queue = result.method.queue
self.channel.basic_consume(self.on_response, no_ack=True,
queue=self.callback_queue)
def on_response(self, ch, method, props, body):
if self.corr_id == props.correlation_id:
self.response = body
def call(self, n):
self.response = None
self.corr_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
self.channel.basic_publish(exchange='',
routing_key='rpc_queue',
properties=pika.BasicProperties(
reply_to = self.callback_queue,
correlation_id = self.corr_id,
),
body=str(n))
while self.response is None:
self.connection.process_data_events()
return int(self.response)
fibonacci_rpc = FibonacciRpcClient()
print(" [x] Requesting fib(30)")
response = fibonacci_rpc.call(30)
print(" [.] Got %r" % response)
|
注:转载自cnblogs/wupeiqi