上一节实现了线性表顺序结构的实现,这节来实现链式结构的线性表。还是利用C++语言来实现。
linklineartable.h
#pragma once
typedef int TypeName;
struct Node
{
TypeName data;
Node * next;
}Snode;
typedef struct Node* Pnode;
void initTable(Pnode *node);
bool isEmpty(Pnode *node);
bool findItem(Pnode *node,int position, TypeName *item);
bool insertItem(Pnode *node,const TypeName &item, int position);
bool deleteItem(Pnode *node,int postion, TypeName *item);
void clearList(Pnode *node);
int getLength(Pnode *node);
void display(Pnode *node);linklineartable.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
/*
初始化链式线性表
带表头链式线性表
@param node 头指针 指向表头
*/
void initTable(Pnode *node) {
//初始化一个头节点
*node = (Pnode)malloc(sizeof(Node));
(*node)->next = nullptr;
}
/*
判断链表是否为空表
@return true为空 否则false
*/
bool isEmpty(Pnode *node) {
return (*node)->next == nullptr;
}
/*
查找某个位置的数据
@param node 头指针
@param postion 位置 从1开始
@param item 返回的数据
@return 返回是否成功
*/
bool findItem(Pnode *node,int position, TypeName *item) {
Node *p = (*node)->next;//让p指向第一个元素
int j = 1;
//让p循环直到p指针指到要查找的元素那个节点
while(p&&j < position) {
p = p->next;
j++;
}
if (p == nullptr) {
return false;
}
*item = p->data;
return true;
}
/*
在某个位置插入数据
@param node 头指针
@param item 要插入的数据
@param position 要插入的位置 从1开始
@return 返回是否成功
*/
bool insertItem(Pnode *node, const TypeName &item, int position) {
Node *p = (*node);//让p指向头节点
int j = 1;
while(p&&j < position) {
p = p->next;
j++;
}
if (p == nullptr||j>position) return false;
Node *q = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));//生成新的结点
q->data = item;
//下面两句实现新节点插入
q->next = p->next;
p->next = q;
return true;
}
/*
在某个位置删除数据
@param node 头指针
@param position 要删除的位置 从1开始
@param item 删除节点中的数据
@return 返回是否成功
*/
bool deleteItem(Pnode *node, int position, TypeName *item) {
Node *p = (*node);//让p指向头节点
int j = 1;
while(p&&j < position) {
p = p->next;
j++;
}
if (p == nullptr||p->next==nullptr||j>position) return false;
Node *q = p->next;
p->next = q->next;
*item = q->data;
free(q); //释放要删除节点的空间
return true;
}
/*
清空表
@param node 头指针
*/
void clearList(Pnode *node) {
Node *p = (*node)->next;//让p指向第一个元素
Node *q = nullptr;
//循环释放节点
while (p) {
q = p->next;
free(p);
p = q;
}
(*node)->next = nullptr;
}
/*
获取链式线性表的长度
*/
int getLength(Pnode *node) {
Node *p =(*node)->next;//让p指向第一个元素
int j = 0;
while (p) {
j++;
p = p->next;
}
return j;
}
void display(Pnode *node) {
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
Node *p = (*node)->next;//让p指向第一个元素
while(p)
{
cout << p->data << "\t";
p= p->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
main.cpp
测试测试
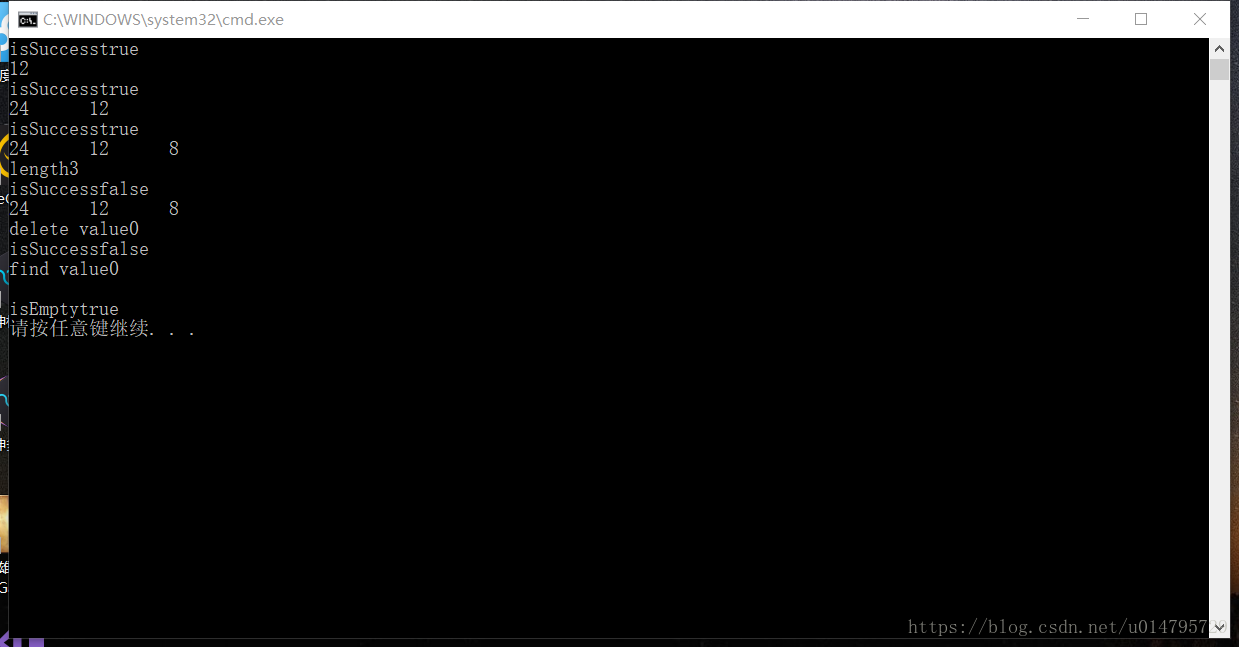
void LinkLinearTableTest() {
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::boolalpha;
Node *node = nullptr;
initTable(&node);
bool isSuccess=insertItem(&node, 12, 1);
cout << "isSuccess" <<boolalpha<< isSuccess << endl;
display(&node);
isSuccess = insertItem(&node,24, 1);
cout << "isSuccess" << boolalpha << isSuccess << endl;
display(&node);
isSuccess = insertItem(&node,8, 3);
cout << "isSuccess" << boolalpha << isSuccess << endl;
display(&node);
int length = getLength(&node);
cout << "length" << length << endl;
TypeName value = 0;
isSuccess = deleteItem(&node, 4, &value);
cout << "isSuccess" << isSuccess << endl;
display(&node);
cout << "delete value" << value << endl;
isSuccess=findItem(&node, 4, &value);
cout << "isSuccess" << isSuccess << endl;
cout << "find value" << value << endl;
clearList(&node);
display(&node);
isSuccess=isEmpty(&node);
cout << "isEmpty" << boolalpha << isSuccess << endl;
}执行情况
总结
链式结构适合插入和删除操作很频繁的情况,可以动态的增加元素个数,不会造成空间的浪费,在插入和删除操作中,需先查找要插入和删除的位置,所用时间复杂度为O(n),之后插入和删除元素的时间复杂度都为O(1)。