Python常用模块的使用技巧
----Python格式规范
(1)文档说明
在pyCharm中File->Setting->Editor->File and Code Templates->Python Script:
# -*-coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@Project: ${PROJECT_NAME}
@File : ${NAME}.py
@Author : panjq
@E-mail : [email protected]
@Date : ${YEAR}-${MONTH}-${DAY} ${HOUR}:${MINUTE}:${SECOND}
"""(2)函数说明
def my_fun(para1,para2):
'''
函数功能实现简介
:param para1: 输入参数说明,类型
:param para2: 输入参数说明,类型
:return: 返回内容,类型
'''(3)ipynb文件转.py文件
jupyter nbconvert --to script demo.ipynb ----os模块
import os
os.getcwd()#获得当前工作目录
os.path.abspath('.')#获得当前工作目录
os.path.abspath('..')#获得当前工作目录的父目录
os.path.abspath(os.curdir)#获得当前工作目录
os.path.join(os.getcwd(),'filename')#获取当前目录,并组合成新目录
os.path.exists(path)#判断文件是否存在
os.path.isfile(path)#如果path是一个存在的文件,返回True。否则返回False。
os.path.basename('path/to/test.jpg')#获得路径下的文件名:test.jpg
path=os.path.dirname('path/to/test.jpg')#获得路径:path/to
----保存多维array数组的方法
由于np.savetxt()不能直接保存三维以上的数组,因此需要转为向量的形式来保存
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.zeros((3,4,5), dtype='int16') # 创建3*4*5全0三维数组
print("维度:",np.shape(arr1))
arr1[0,:,:]=0
arr1[1,:,:]=1
arr1[2,:,:]=2
print("arr1=",arr1)
# 由于savetxt不能保存三维以上的数组,因此需要转为向量来保存
vector=arr1.reshape((-1,1))
np.savetxt("data.txt", vector)
data= np.loadtxt("data.txt")
print("data=",data)
arr2=data.reshape(arr1.shape)
print("arr2=",arr2)----glob模块
glob模块是最简单的模块之一,内容非常少。用它可以查找符合特定规则的文件路径名。跟使用windows下的文件搜索差不多。查找文件只用到三个匹配符:"*", "?", "[]"。"*"匹配0个或多个字符;"?"匹配单个字符;"[]"匹配指定范围内的字符,如:[0-9]匹配数字。
import glob
#获取指定目录下的所有图片
print glob.glob(r"E:\Picture\*\*.jpg")
#获取上级目录的所有.py文件
print glob.glob(r'../*.py') #相对路径 对于遍历指定目录的jpg图片,可以这样:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import glob
#遍历指定目录下的jpg图片
image_path="/home/ubuntu/TFProject/view-finding-network/test_images/*.jpg"
for per_path in glob.glob(image_path):
print(per_path)若想遍历多个格式的文件,可以这样:
# 遍历'jpg','png','jpeg'的图片
image_format=['jpg','png','jpeg']#图片格式
image_dir='./test_image' #图片目录
image_list=[]
for format in image_format:
path=image_dir+'/*.'+format
image_list.extend(glob.glob(path))
print(image_list)----读取txt
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
def text_save(content,filename,mode='a'):
# Try to save a list variable in txt file.
file = open(filename,mode)
for i in range(len(content)):
file.write(str(content[i])+' ')
file.close()
def text_read(filename):
# Try to read a txt file and return a list.Return [] if there was a mistake.
try:
file = open(filename,'r')
except IOError:
error = []
return error
content = file.readlines()
file.close()
return content
test_text = ['1.jpg','dog',200,300]
text_save(test_text,'test.txt',mode='w')
test_content = text_read('test.txt')
str_list=test_content[0].split()
print(str_list)这是封装好的txt读写模块,这里输入和输出的数据都是list列表:
# -*-coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@Project: TxtStorage
@File : TxtStorage.py
@Author : panjq
@E-mail : [email protected]
@Date : 2018-07-12 17:32:47
"""
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from numpy import *
class TxtStorage:
# def __init__(self):
# 保存txt数据
def save_txt(self, content, filename, mode='a'):
"""保存txt数据
:param content:需要保存的数据
:param filename:文件名
:param mode:读写模式
:return: void
"""
file = open(filename, mode)
for row in range(len(content)):
row_data=content[row]
for col in range(len(row_data)):
data=row_data[col]
if not col==len(row_data)-1:
file.write(str(data) + ' ')
else:
file.write(str(data))
file.write('\n')
file.close()
# 读取txt数据函数
def read_txt(self, fileName):
"""读取txt数据函数
:param filename:文件名
:return: txt的数据列表
:rtype: list
"""
try:
file = open(fileName, 'r')
except IOError:
print('read txt file data failed....')
# error = []
return None
Data = []
with file as txtData:
lines = txtData.readlines()
for line in lines:
lineData = line.strip() # 去除空白和逗号“,”
Data.append(lineData)
return Data
# 按空格分割字符串,并以列表的形式返回
def splitData(self, dataSet):
"""分割字符串
:param dataSet:文件名
:return: 按空格分割字符串,并以列表的形式返回
:rtype: list
"""
re = []
for str in dataSet:
str_list = str.split()
int_list = []
for i in str_list:
if i.isdigit():
int_list.append(int(i))
else:
int_list.append(i)
re.append(int_list)
return re
if __name__ == '__main__':
txt_filename = 'test.txt'
txt_data = [['1.jpg', 'dog', 200, 300], ['2.jpg', 'dog', 20, 30]]
txt_str = TxtStorage()
txt_str.save_txt(txt_data, txt_filename, mode='w')
data = txt_str.read_txt(txt_filename)
print(data)
data = txt_str.splitData(data)
for image_name,label,img_row,img_col in data:
print(image_name,label,img_row,img_col)
----pandas模块
(1)文件数据拼接
假设有'data1.txt', 'data2.txt', 'data3.txt'数据:
#'data1.txt'
1.jpg 11
2.jpg 12
3.jpg 13
#'data2.txt'
1.jpg 110
2.jpg 120
3.jpg 130
#'data3.txt'
1.jpg 1100
2.jpg 1200
3.jpg 1300需要拼接成:
1.jpg 11 110 1100
2.jpg 12 120 1200
3.jpg 13 130 1300
实现代码:
# coding: utf-8
import pandas as pd
def concat_data(page,save_path):
pd_data=[]
for i in range(len(page)):
content=pd.read_csv(page[i], dtype=str, delim_whitespace=True, header=None)
if i==0:
pd_data=pd.concat([content], axis=1)
else:# 每一列数据拼接
pd_data=pd.concat([pd_data,content.iloc[:,1]], axis=1)
pd_data.to_csv(save_path, index=False, sep=' ', header=None)
if __name__=='__main__':
txt_path = ['data1.txt', 'data2.txt', 'data3.txt']
out_path = 'all_data.txt'
concat_data(txt_path,out_path)----csv模块
使用csv模块读取csv文件的数据
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import csv
csv_path='test.csv'
with open(csv_path,'r') as csvfile:
reader = csv.DictReader(csvfile)
for item in reader:#遍历全部元素
print(item)
with open(csv_path, 'r') as csvfile:
reader = csv.DictReader(csvfile)
for item in reader: # 遍历全部元素
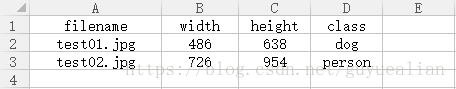
print(item['filename'],item['class'],item.get('height'),item.get('width'))运行结果:
{'filename': 'test01.jpg', 'height': '638', 'class': 'dog', 'width': '486'}
{'filename': 'test02.jpg', 'height': '954', 'class': 'person', 'width': '726'}
test01.jpg dog 638 486
test02.jpg person 954 726读写过程:
import csv
csv_path = 'test.csv'
#写csv
data=["1.jpg",200,300,'dog']
with open(csv_path, 'w+',newline='') as csv_file:
# headers = [k for k in dictionaries[0]]
headers=['filename','width','height', 'class']
print(headers)
writer = csv.DictWriter(csv_file, fieldnames=headers)
writer.writeheader()
dictionary={'filename': data[0],
'width': data[1],
'height': data[2],
'class': data[3],
}
writer.writerow(dictionary)
print(dictionary)
#读csv
with open(csv_path, 'r') as csvfile:
reader = csv.DictReader(csvfile)
for item in reader: # 遍历全部元素
print(item)
with open(csv_path, 'r') as csvfile:
reader = csv.DictReader(csvfile)
for item in reader: # 遍历全部元素
print(item['filename'], item['class'], item.get('height'), item.get('width'))
----读取图片和显示
Python中读取图片和显示图片的方式很多,绝大部分图像处理模块读取图片的通道是RGB格式,只有opencv-python模块读取的图片的BGR格式,如果采用其他模块显示opencv读取的图片,需要转换通道顺序,方法也比较简单,即:
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
temp_img=cv2.imread(image_path) #默认:BGR(不是RGB),uint8,[0,255],ndarry()
cv2.imshow("opencv-python",temp_img5)
cv2.waitKey(0)
# b, g, r = cv2.split(temp_img5)# 将BGR转为RGB格式
# img = cv2.merge([r, g, b])
# 推荐使用cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB->将BGR转为RGB格式
img = cv2.cvtColor(temp_img5, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
plt.imshow(img) # 显示图片
plt.axis('off') # 不显示坐标轴
plt.show()
(1)caffe.io.load_image、matplotlib.image、PIL.Image、cv2模块
# coding: utf-8
'''
在Caffe中,彩色图像的通道要求是BGR格式,输入数据是float32类型,范围[0,255],
对每一层shape=(batch_size, channel_dim, height, width)。
[1]caffe的训练/测试prototxt文件,一般在数据层设置:cale:0.00392156885937,即1/255.0,即将数据归一化到[0,1]
[2]当输入数据为RGB图像,float32,[0,1],则需要转换:
--transformer.set_raw_scale('data',255) # 缩放至0~255
--transformer.set_channel_swap('data',(2,1,0))# 将RGB变换到BGR
[3]当输入数据是RGB图像,int8类型,[0,255],则输入数据之前必须乘以*1.0转换为float32
--transformer.set_raw_scale('data',1.0) # 数据不用缩放了
--transformer.set_channel_swap('data',(2,1,0))#将RGB变换到BGR
--通道:img = img.transpose(2, 0, 1) #通道由[h,w,c]->[c,h,w]
[4]在Python所有读取图片的模块,其图像格式都是shape=[height, width, channels],
比较另类的是,opencv-python读取的图片的BGR(caffe通道要求是BGR格式),而其他模块是RGB格式
'''
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
image_path = 'test_image/C0.jpg'#C0.jpg是高h=400,宽w=200
# 1.caffe
import caffe
img1 = caffe.io.load_image(image_path) # 默认:RGB,float32,[0-1],ndarry,shape=[400,200,3]
# 2.skimage
import skimage.io
img2 = skimage.io.imread(image_path) # 默认:RGB,uint8,[0,255],ndarry,shape=[400,200,3]
# img2=img2/255.0
# 3.matplotlib
import matplotlib.image
img3 = matplotlib.image.imread(image_path) # 默认:RGB,uint8,[0,255],ndarry,shape=[400,200,3]
# 4.PIL
from PIL import Image
temp_img4 = Image.open(image_path) # 默认:RGB,uint8,[0,255],
# temp_img4.show() #会调用系统自定的图片查看器显示图片
img4 = np.array(temp_img4) # 转为ndarry类型,shape=[400,200,3]
# 5.opencv
import cv2
temp_img5 = cv2.imread(image_path) # 默认:BGR(不是RGB),uint8,[0,255],ndarry,shape=[400,200,3]
# cv2.imshow("opencv-python",temp_img5)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# b, g, r = cv2.split(temp_img5)# 将BGR转为RGB格式
# img5 = cv2.merge([r, g, b])
# 推荐使用cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB->将BGR转为RGB格式
img5 = cv2.cvtColor(temp_img5, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img6 = img5.transpose(2, 0, 1) #通道由[h,w,c]->[c,h,w]
# 以上ndarry类型图像数据都可以用下面的方式直接显示
plt.imshow(img5) # 显示图片
plt.axis('off') # 不显示坐标轴
plt.show()
(2)python中PIL.Image和OpenCV图像格式相互转换
PIL.Image转换成OpenCV格式:
import cv2
from PIL import Image
import numpy
image = Image.open("plane.jpg")
image.show()
img = cv2.cvtColor(numpy.asarray(image),cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
cv2.imshow("OpenCV",img)
cv2.waitKey()OpenCV转换成PIL.Image格式:
import cv2
from PIL import Image
import numpy
img = cv2.imread("plane.jpg")
cv2.imshow("OpenCV",img)
image = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
image.show()
cv2.waitKey()判断图像数据是否是OpenCV格式:
isinstance(img, np.ndarray)