2018-07-26 17:38:37
问题描述:

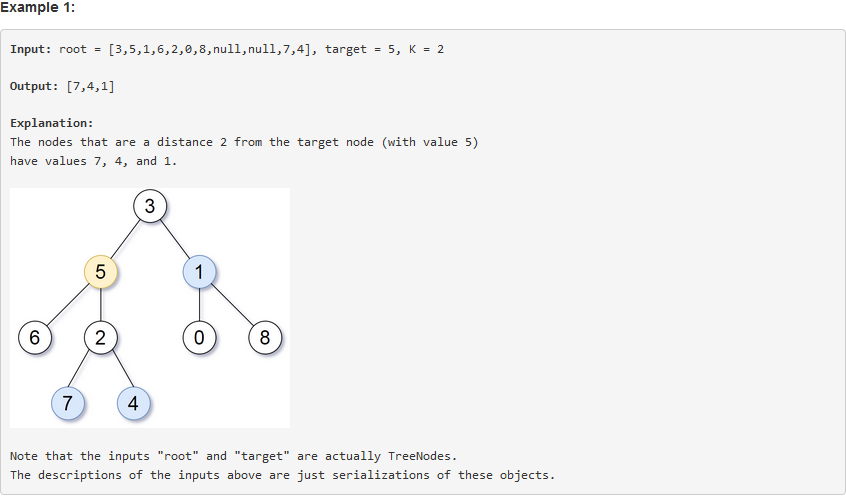

问题求解:
解法一、
第一种解法是使用Graph + BFS。换言之,就是将二叉树转化为无向图,然后在无向图中使用BFS进行层次遍历即可。
这种解法是比较直观的解法,是必须要进行掌握的,时间复杂度为O(n)。
public List<Integer> distanceK(TreeNode root, TreeNode target, int K) {
HashMap<TreeNode, ArrayList<TreeNode>> graph = new HashMap<>();
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
buildGraph(graph, null, root);
Set<TreeNode> visited = new HashSet<>();
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
visited.add(target);
q.add(target);
int k = -1;
while (!q.isEmpty() && k <= K) {
int sz = q.size();
k++;
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
TreeNode cur = q.poll();
if (k == K) res.add(cur.val);
ArrayList<TreeNode> ls = graph.get(cur);
for (TreeNode t : ls) {
if (!visited.contains(t)) {
q.add(t);
visited.add(t);
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
private void buildGraph(HashMap<TreeNode, ArrayList<TreeNode>> graph, TreeNode parent, TreeNode child) {
if (child == null) return;
graph.put(child, new ArrayList<>());
if (parent != null) {
graph.get(parent).add(child);
graph.get(child).add(parent);
}
buildGraph(graph, child, child.left);
buildGraph(graph, child, child.right);
}
解法二、
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
2390636 查看本文章


第二种解法自然就是递归解法了,本题的递归解法还是有点难度的,首先需要计算的是root 到 target的距离,如果距离值正好等于 K,那么就将当前的节点加入res,否则在另一个子树中进行collection。其次如果遍历到target,那么直接对target进行collection。
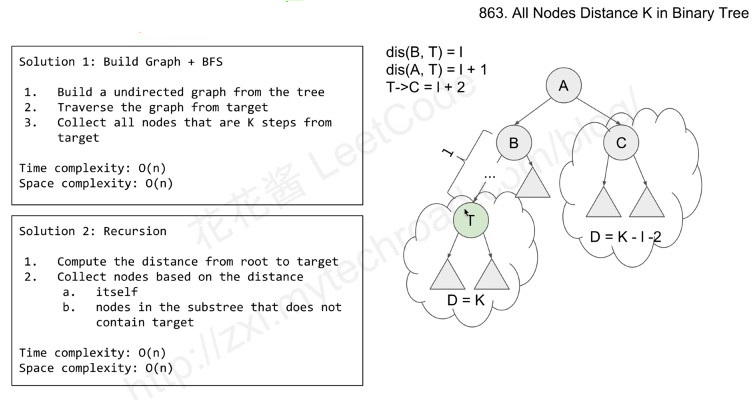
public List<Integer> distanceK(TreeNode root, TreeNode target, int K) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
distance(root, target, K, res);
return res;
}
private int distance(TreeNode root, TreeNode target, int K, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null) return -1;
if (root == target) {
collection(target, K, res);
return 0;
}
int l = distance(root.left, target, K, res);
int r = distance(root.right, target, K, res);
if (l >= 0) {
if (l == K - 1) res.add(root.val);
collection(root.right,K - l - 2, res);
return l + 1;
}
if (r >= 0) {
if (r == K - 1) res.add(root.val);
collection(root.left, K - r - 2, res);
return r + 1;
}
return -1;
}
private void collection(TreeNode root, int K, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null || K < 0) return;
if (K == 0) {
res.add(root.val);
return;
}
collection(root.left, K - 1, res);
collection(root.right, K - 1, res);
}