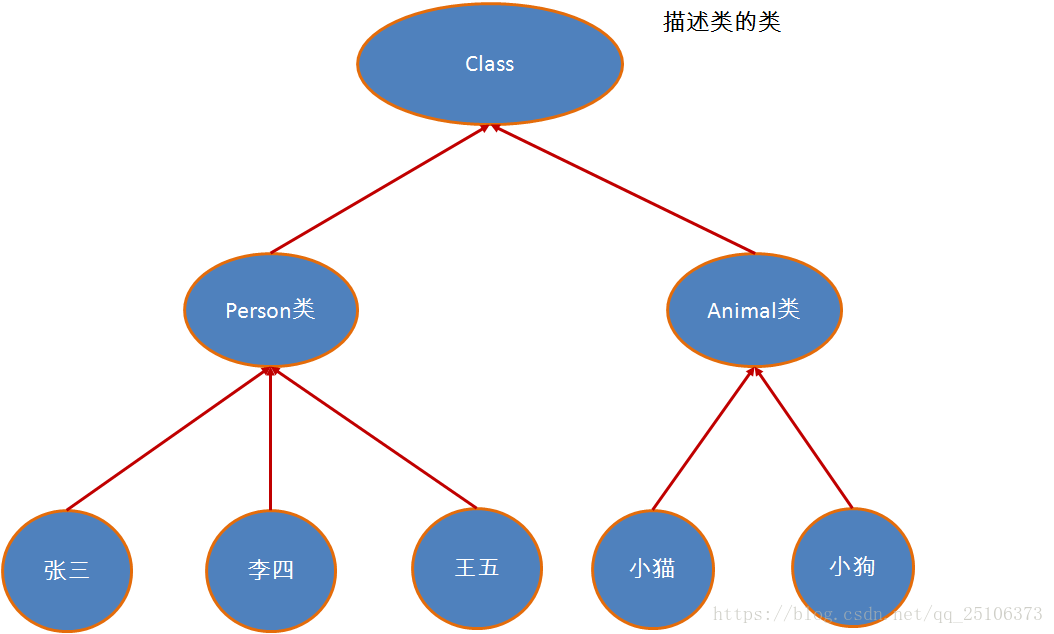
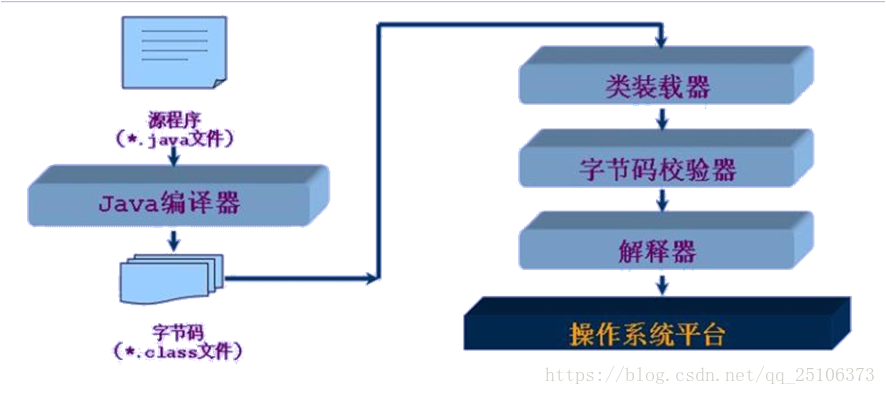
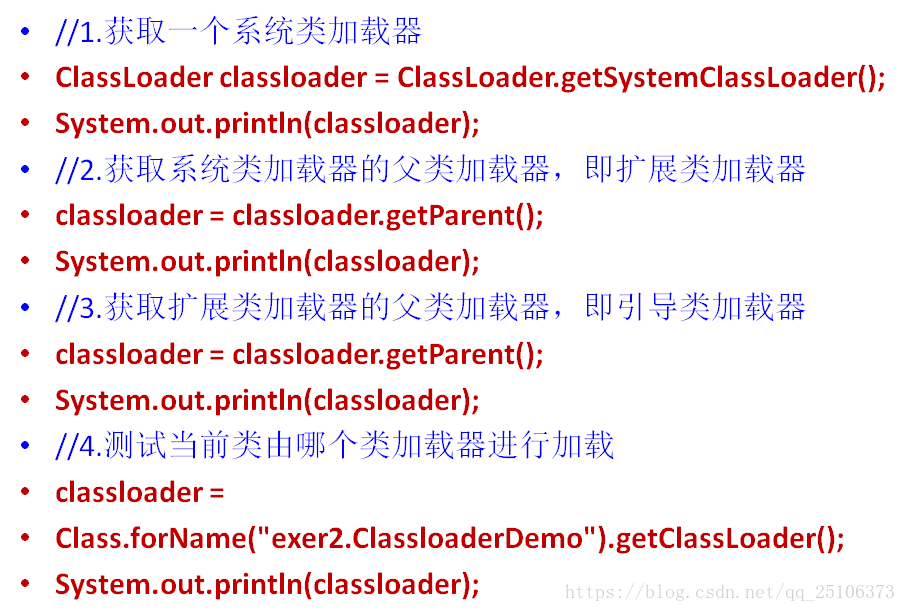
反射研究与应用
使用反射获取类结构
使用反射生成并操作对象
public class TestOther {
//7.在运行时获取运行时类的包
@Test
public void test7(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
Package pk = clazz.getPackage();
System.out.println(pk);
}
//6.在运行时获取运行时类的注解
@Test
public void test6(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
Annotation[] annotations = clazz.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
MyAnnotation ma = (MyAnnotation) annotation;
System.out.println(ma.value());
}
}
//5.在运行时获取运行时类的内部类
@Test
public void test5(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
// Class[] classes = clazz.getClasses();
Class[] declaredClasses = clazz.getDeclaredClasses();
for (Class class1 : declaredClasses) {
System.out.println(class1);
}
}
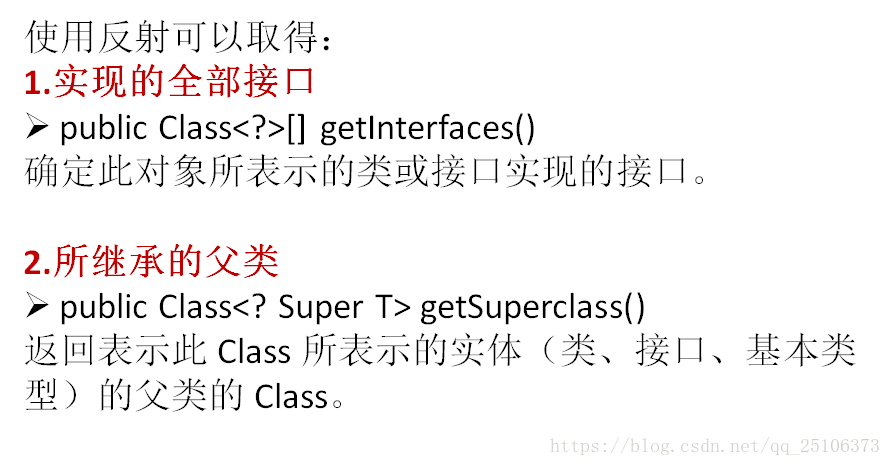
//4.在运行时获取运行时类的接口
@Test
public void test4(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
Class[] interfaces = clazz.getInterfaces();
for (Class c : interfaces) {
System.out.println(c);
}
}
//【重要】3. 在运行时获取运行时类带泛型父类的泛型类型
@Test
public void test3(){//com.atguigu.java.Creature<java.lang.String, java.lang.Integer>
Class clazz = Person.class;
//①获取带泛型父类的父类类型
Type type = clazz.getGenericSuperclass();
//②参数化类型
ParameterizedType pt = (ParameterizedType) type;
//③获取真实参数类型
Type[] types = pt.getActualTypeArguments();
Class clazzType = (Class) types[0];
System.out.println(clazzType.getName());
/*for (Type t : types) {
Class clazzType = (Class) t;
System.out.println(clazzType.getName());
}*/
}
//2. 在运行时获取运行时类带泛型的父类类型 : com.java.Creature<java.lang.String>
@Test
public void test2(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
Type type = clazz.getGenericSuperclass();
System.out.println(type);
}
//1. 在运行时获取运行时类的父类
@Test
public void test1(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
Class superClass = clazz.getSuperclass();
System.out.println(superClass);
}
/*get(Person.class);
get(Customer.class);
get(Order.class);
public <T> T get(Class<T> clazz){
return clazz.newInstance();
}*/
}
public class TestClassLoader {
//重要:利用类加载器操作属性文件
@Test
public void test2() throws IOException{
Properties props = new Properties();
// props.load(new FileInputStream("./jdbc.properties"));
/*ClassLoader cl = this.getClass().getClassLoader();
InputStream in = cl.getResourceAsStream("com/atguigu/java/jdbc.properties");
props.load(in);*/
props.load(this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("com/atguigu/java/jdbc.properties"));
String userName = props.getProperty("userName");
String password = props.getProperty("password");
System.out.println(userName);
System.out.println(password);
}
}
public class TestConstructor {
//1. 在运行时获取运行时类的构造器
@Test
public void test1(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
Constructor[] constructors = clazz.getConstructors();
for (Constructor cons : constructors) {
System.out.println(cons);
}
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------");
Constructor[] declaredConstructors = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor constructor : declaredConstructors) {
System.out.println(constructor);
}
}
//2. 在运行时获取并调用运行时类的构造器
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception{
Class clazz = Person.class;
// Constructor constructor = clazz.getConstructor(String.class, int.class);
Constructor constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, int.class);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
Person p = (Person) constructor.newInstance("张三", 18);
System.out.println(p);
}
}
public class TestMethod {
//1. 在运行时获取运行时类的方法
@Test
public void test1(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
//getMethods() : 获取运行时类 public 修饰的方法,包括父类的
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println(method.getName());
}
System.out.println("-------------------------------------");
//getDeclaredMethods() : 获取运行时类所有声明的方法,包括私有的,不包括父类的
Method[] methods2 = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : methods2) {
System.out.println(method.getName());
}
}
//2. 在运行时获取运行时类方法的详细信息: 注解 修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数类型1 参数名1, 参数类型2 参数名2 ……) 异常
@Test
public void test2(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
// Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
//注解
Annotation[] annotations = method.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
//①修饰符
String mod = Modifier.toString(method.getModifiers());
System.out.print(mod + "\t");
//②返回值类型
Class returnType = method.getReturnType();
System.out.print(returnType.getName() + "\t");
//③方法名
System.out.print(method.getName() + "(");
//④参数列表
Class[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
for (Class c : paramTypes) {
System.out.print(c.getName() + ",");
}
System.out.print(")");
//⑤异常
Class[] exceptionTypes = method.getExceptionTypes();
for (Class c : exceptionTypes) {
System.out.println(c.getName());
}
System.out.println();
}
}
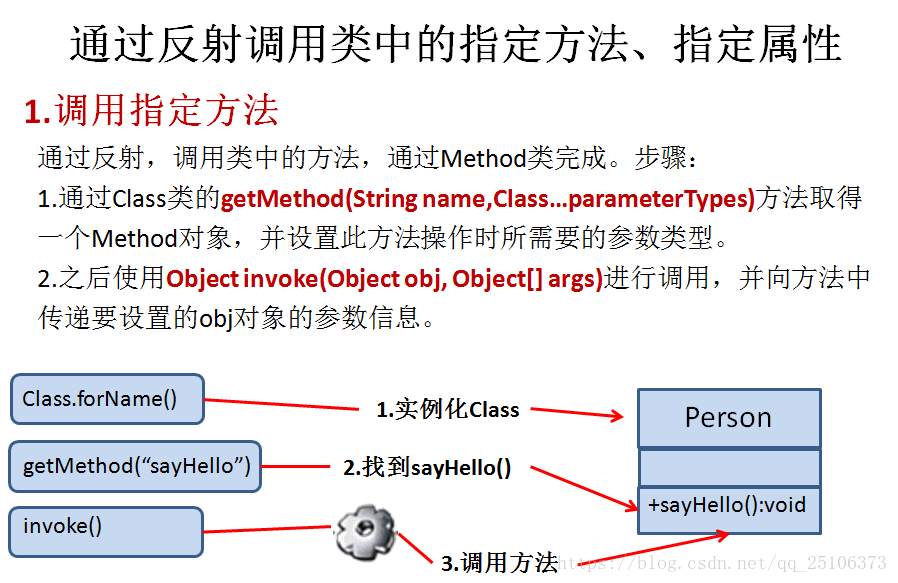
//3. 在运行时获取并调用运行时类对象的方法
@Test
public void test3() throws Exception{
String className = "Person";
Class clazz = Class.forName(className);
Person p = (Person) clazz.newInstance();
Method method = clazz.getMethod("eat");
method.invoke(p);
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
Method method2 = clazz.getMethod("setName", String.class, int.class, double.class);
Object obj = method2.invoke(p, "张三", 18, 99.99);
System.out.println(obj);
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
// Method method3 = clazz.getMethod("sleep");
Method method3 = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("sleep");
method3.setAccessible(true);
Object obj2 = method3.invoke(p);
System.out.println("--" + obj2);
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
Method method4 = clazz.getMethod("get", String.class);
Object obj3 = method4.invoke(p, "abc");
System.out.println(obj3);
}
}
动态代理