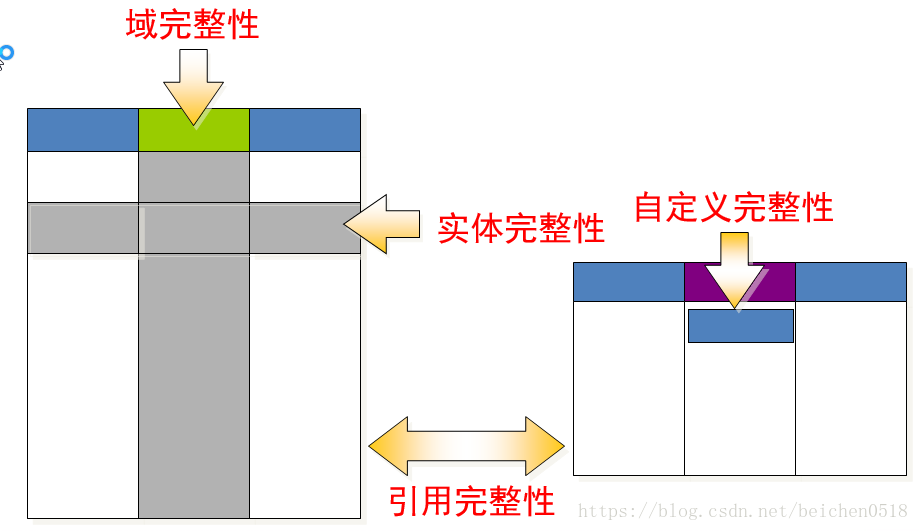
1.数据的完整性
1.实体的完整性:一个实体就是一条记录,如果记录无法区分,称之为失去了数据的完整性.
2.域完整性:如果两个字段无法区分,称之为失去了域的完整性.
3.引用的完整性:两个表的对应记录不完整.(不可避免的)
4.自定义完整性:自己制定的规则在实现后出现了偏差.user
| id | usename | pwd |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | [email protected] | 123456 |
| 3 | [email protected] | 123456 |
userinfo
| uid | name | sex | idcard | age | num |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 王大恒 | 男 | 不祥 | 18 | 1 |
| 19 | 贾乃亮 | 男 | 不详 | 32 | 2 |
select * from user left join userinfo on user.id=userinfo.num;
(1).保证实体的完整性
1.自动增长列(auto_increment)
2.主键的约束(primary key)
3.唯一键(unique)(2).保证域的完整性
1.数据类型的约束
2.默认值约束
3.非空的约束(3)保证引用的完整性
建立外键->只用主表有的,从表一定会有(从表中还不能删除)(4)自定义完整性
1.存储过程(比较像python的自定义函数)
2.触发器2外键(foreign key)
外键:从表的公共字段
外键约束用来保证引用的完整性,主外键的名字可以不一样,但是数据类型必须一样.
特点:
1.主表中不存在的记录,从表中不能插入
2.从表中存在记录,主表中不能先删除
3.必须先删除从表,再删除主表(1)创建外键
--学生表(主表)
create table stuinfo(
id int auto_increment comment'主键',
stu_name varchar(255),
primary key(id)
)engine=innodb;
#添加一条数据
insert into stuinfo set `stu_name`='王大恒';
--成绩表(从表)
create table stumarks(
stuno int comment'主键',
ch float,
math float
#foreign key(stuno) references stuinfo(id)
#foreign key (stuno) references stuinfo(id) on delete set null on update cascade
)engine=innodb;
#修改表的时候添加一个外键
修改 表 成绩表 增加 外键 学号 关联 学生信息表的id字段
alter table stumarks add foreign key (stuno) references stuinfo(id);
#当主表删除 从表设置为空(指的是外键字段)
#on delete set null
#当主表删除 从表中整条数据跟着删除
#on delete set cascade
#当修改主表时 从表的关联字段也跟着修改
#on update cascade
alter table stumarks add foreign key (stuno) references stuinfo(id) on delete set null on update cascade;
#添加一条数据
insert into stumarks values(1,88,99);
mysql> show create table stumarks\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: stumarks
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `stumarks` (
`stuno` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '主键',
`ch` float DEFAULT NULL,
`math` float DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`stuno`),
CONSTRAINT `stumarks_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`stuno`) REFERENCES `stuinfo`(`id`) on delete set null on update cascade ;
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
#CONSTRAINT `stumarks_ibfk_1`:是mysql分配给外键的名字
#指定一个名字给外键(添加一个索引)
alter table stumarks add CONSTRAINT `stuno` foreign key (stuno) references stuinfo(id) on delete cascade on update cascade;
#删除外键
alter table stumarks drop foreign key stumarks_ibfk_1;
#提醒:
如果要在某个字段上添加外键,这个字段必须有索引才可以,如果这个字段没有索引就直接添加外键,那么mysql会自动创建索引.(2)外键的操作
1.严格约束(外键约束),保证引用的完整性
2.置空操作(set null):主表记录删除或者更新,从表的外键字段设置为null
3.联级操作(cascade): 主表的记录删除或者更新,从表外键字段一起发生变化
4.一般都是删除的时候外键字段置空,修改的时候更新关联alter table stumarks add foreign key (stuno) references stuinfo(id) on delete set null on update cascade;
注意:从表的关联(外键)字段一定不能是主键外键在数据量特别小的时候会用上,一般是开发者自己清楚数据库表的设计,你知道那个是主表,那个是从表,然后手动修改,使用'事务',为什么了?
1.mysql表中设置外键会影响效率.
2.一般来说,每个从表都是单独数据,需要用到单独操作.
3.实体之间的关系
什么是实体?
我们所看到的每一条记录就是一个实体.
1.一对一的关系
2.一对多的关系
3.多对一的关系
4.多对多的关系(1)一对一的关系:主键关系
stuinfo
| stuno(学号) | stuname(学生的姓名) |
|---|---|
| 1 | tom |
| 2 | jack |
stumarks
| stuno | score |
|---|---|
| 1 | 180 |
| 2 | 170 |
主键关系一一对应
应用:分表操作
垂直分表
(2)一对多(多对一)的关系
stuinfo
| stuno(学号) | stuname(学生的姓名) |
|---|---|
| 1 | tom |
| 2 | jack |
stumarks
| stuno(他不是主键) | score | create_at |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 180 | 2018-01-14 14:20:00 |
| 1 | 170 | 2018-01-15 15:20:00 |
| 2 | 181 | 2018-01-14 14:20:00 |
| 2 | 171 | 2018-01-15 15:20:00 |
(3)多对多的关系
class
| id | name | stu |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | python | 1,2,3 |
| 2 | java | 1,2,3 |
stu
| stuno | 姓名 | class |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | tom | 1,2 |
| 2 | jack | 2,1 |
| 3 | lily | 1,2 |
4.数据库的设计
公司要做一个项目,首先产品经理会告诉你做个什么类型的项目,然后他会把他设计的需要理解图发给你.
读取需要图,判断需要那些表,那些字段,做那些关联(意淫能力)
你(泛指项目经理)需要根据你的判断,画出E-R图.
把E-R图发给每个开发者,他们看图建数据库和表.(1)标识的实体
博客:
用户注册,用户登陆,用户关注,发帖,回帖,删帖,发帖拿积分,点赞数量,黑贴就封号
用户注册,用户登陆:可以建立一个表
users
uid username password create_at sex(null) email(null) mobile(null) id_card jifen
用户关注:
guanzhu
uid byuid
1 2,3,100,1000,11
2 4,3,1
发帖:
news
id uid content title num status
1 1 不详 不详 1000 1(可见)2(被封了)
回帖:
评论
id pid(父级id,如果为0自己就是一级恢复) uid content news_id评论 详解python是世界上最好的语言 101
| id | pid | uid | content | new_id |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 10 | 狗屁 | 101 |
| 2 | 1 | 1011 | 空怕是SB吧 | 101 |
(2)写出实体的属性
(3)标识实体之间的关系
设计表的人(设计数据库的人自己看图理解)
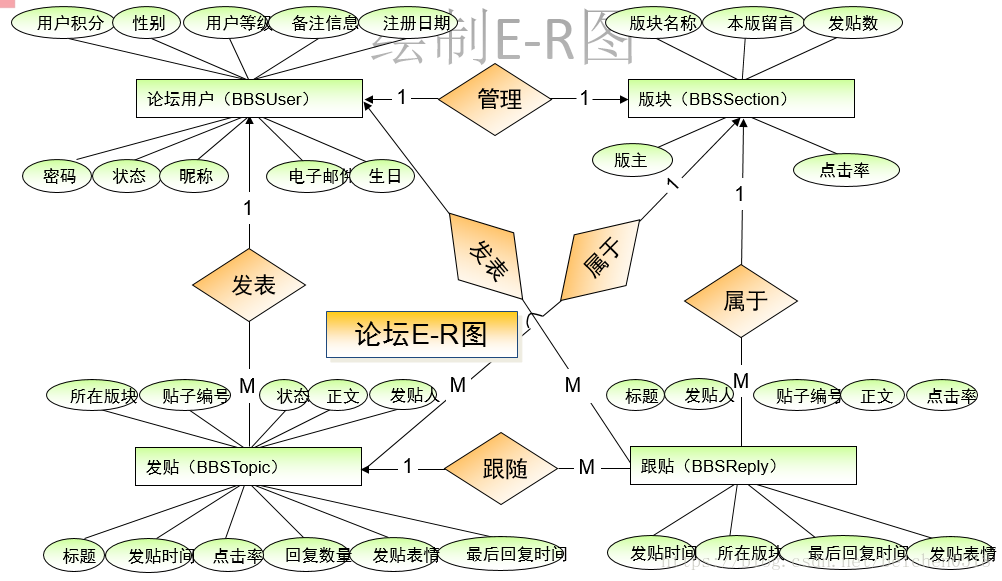
(4)E-R图(语法)
1.矩形代表实体
2.椭圆形代表属性(字段)
3.菱形代表关系create table users(
uid int primary key auto_increment comment'主键',
email char(32) not null,
nickname char(32) not null,
pwd char(32) not null,
status bool comment'1是启用,0是禁用'
);
#注册
insert into users values(null,'123456qq.com','李狗蛋','123456',1); ->1
insert into users values(null,'654321qq.com','张全蛋','123456',1); ->2
create table section(
sid int primary key auto_increment comment'主键',
suid int comment'关联users.uid',
sname char(16) comment'板块名称'
);
insert into section values(null,1,'娱乐头条'); ->1
insert into section values(null,0,'技术大神'); ->2
create table top(
tid int primary key auto_increment comment'帖子编号',
tsid int not null comment'属于那个板块的,关联section.sid',
tuid int not null comment'谁发的贴,关联users.uid',
title char(32) not null,
content varchar(20000) not null,
tstatus tinyint(2) comment'1表示启用,0是禁用,2是优质贴'
);
insert into top values(null,2,2,'三星检测报告','三星垃圾,韩国棒子滚粗!',1); ->1
create table rep(
rid int primary key auto_increment comment'主键',
ruid int not null,
rtid int not null,
rsid int not null,
rcontent varchar(10000)
);
insert into rep values(null,1,1,2,'熬到开');
select * from users left join top on users.uid=top.tuid left join rep on top.tid=rep.rtid where uid=2;将E-R图转成表,自己玩.
如果表中没有适合的字段做主键怎么破?
答:自己加一个就是喽
#用户和板块之间的关系?
1.某个用户是摸个板块的版主
2.普通用在摸个板块中发表帖子或评论(你发表的帖子或评论属于某个板块)
#用户和帖子之间的关系?
1.用户发表的帖子
2.你评论了某个帖子(间接关系)
#用户和评论(回帖)
1.用户发表了评论
2.用户发表的帖子被某某用户给评论
3.用户发表的评论被另一个用户评论了
#帖子和版块之间的关系?
1.用户发表的帖子属于那个大版块
2.用户发表评论,评论的帖子属于某个大板块4.数据的规范化
(1)第一范式
第一范式:确保每一列的数据原子化(不可在分割)地址到底可不可以在分,那么需要看你有没有这个需求(2)第二范式
第二范式:非主键字段必须依赖主键字段(一个表只描述一件事情)第二范式是约束普通字段和主键字段的
(3)第三范式
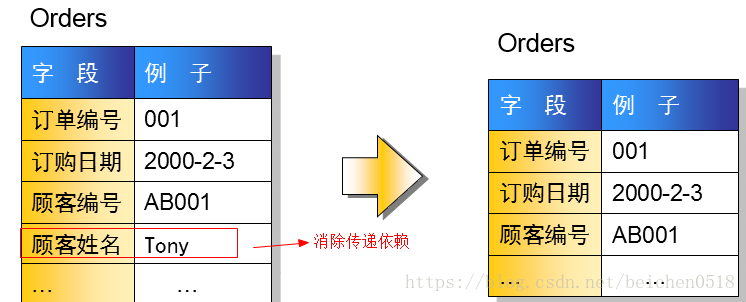
第三范式:在非主键字段中,一个字段确定了,其它字段也确定称为传递依赖第三范式的约束是非主键之间的
5.数据库设计
需求分析:
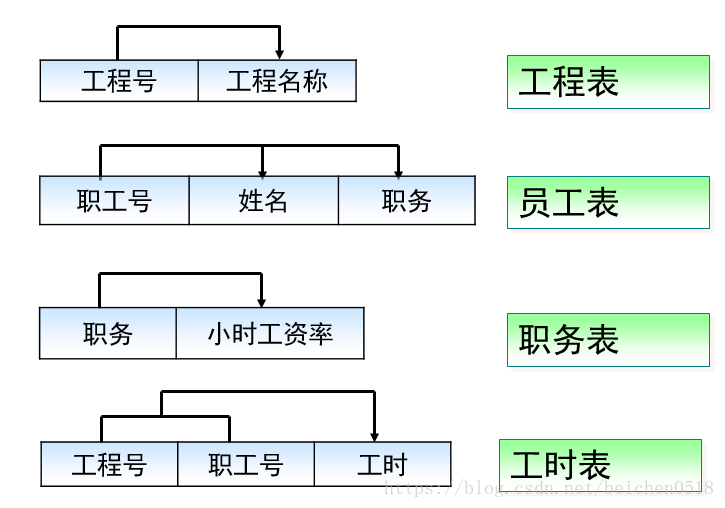
假如某建筑公司要设计一个数据库.公司的业务规则如下:
1.公司承担多个工程项目,每一个项目要有:工程号,工程名称,施工人员.
2.公司有多名职工,每一名职工都有:职工号,姓名,性别,职务等
3.公司按照工时和小时工资率支付工资,小时的工资率由职务决定(例如,技术人员的小时工资率与工程师不同)| 工程号 | 工程名称 |
|---|---|
| 0001 | 一带一路工程 |
| 0002 | 拯救日本沉没 |
| 职工号 | 姓名 | 职务 |
|---|---|---|
| 001 | 张三 | 桥梁工程师 |
| 002 | 李四 | 大陆架测量师 |
| 职务 | 小时工资率 |
|---|---|
| 桥梁工程师 | 100 |
| 大陆架测量师 | 20000 |
| 工程号 | 职工号 | 工时 |
|---|---|---|
| 0001 | 001 | 5 |
| 0002 | 002 | 5 |
6.规范化和性能的关系
| 学号stu | 姓名 | 语文成绩 | 数学成绩 | 总分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 小明 | 100 | 120 | 220 |
语文和数学成绩确定了,总分就确定了,我在把总分作为一个表.
| 学号 | 姓名 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 小明 |
| 学号 | 语文 | 数学 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100 | 120 |
select * from stu where id = 1;
select *,sum(ch+math) from stu left join score on stu.id=score.id where id=1;性能和规范我们优先选择性能.
7.查询语句
select 字段(结果集) from 表名(数据源) [where 条件] [group by 分组][having 条件][order by 排序 asc|desc][limit限制 s,n]create table stuinfo(
sid int auto_increment primary key comment'学号(主键)',
sname varchar(255) comment'学生名字',
sex enum('男','女') comment'性别',
age tinyint comment'年龄',
city varchar(64) comment'地级市'
)engine=innodb;
create table stumarks(
stuno int primary key comment'学号(主键)',
ch tinyint comment'语文成绩',
math tinyint comment'数学成绩'
)engine=innodb;
insert into stuinfo values(null,'大恒',2,18,'宿州'),(null,'小京',1,20,'北京'),(null,'小强',1,22,'北京'),(null,'小力',1,20,'天津'),(null,'小丽',2,21,'重庆'),(null,'小芳',2,20,'天津');
insert into stumarks values(1,88,99),(2,89,100),(3,67,76),(4,50,59),(5,100,99),(6,96,91);(1)字段表达式
select 查询也可以用来做计算
select unix_timestamp(); --显示系统时间戳
select rand();--显示随机数(2)from子句
from后面跟的是什么?是数据源(也就是表)
数据源可以有多张表,返回的是笛卡尔积.(3)dual表
dual表不是一个实实在在存在的表,它是为了保证select语句的完整性的.(4)where子句
where子句在数据源进行筛选;
select * from stuinfo where sex=1;(5)is null|is not null
筛选数据为空或不为空
select * from stumarks where ch is null or math is null;(6)between| not between
筛选指定范围内的数据
select * from stumarks where ch between 75 and 100;
select * from stumarks where ch>=75 and ch<=100;(7)运算符
a.算数运算符
+ - * / % ++ --b.比较运算符
> < >= <= (<> !=)不等于c.逻辑运算符
and 与
or 或
not 非(8)聚合函数
sum() #求和
avg() #求平均值
max() #最大值
min() #最小值
count() #统计 (9)通配符
_ #匹配一个字符
% #匹配所有(10)模糊查询(like)
select * from stuinfo where sname like '_明';
select * from stuinfo where sname like '%佰%';(11)分组查询 group by
将查询的结果分组显示,分组的目的在于方便统计.
select sid,group_concat(sname),sex,age,city from stuinfo group by city;
#每个结果只显示一个
select stuno,ch,math,(ch+math) as score from stumarks group by score;
#group_concat()可以将同一组的字段连接在一起
mysql> select sid,group_concat(sname),sex,age,city from stuinfo group by city;
+-----+---------------------+------+------+------+
| sid | group_concat(sname) | sex | age | city |
+-----+---------------------+------+------+------+
| 1 | 小明 | ? | 18 | 上海 |
| 2 | 小刚,小强 | ? | 20 | 北京 |
| 4 | 尹佰力,小芳 | ? | 20 | 天津 |
| 5 | 小丽 | ? | 21 | 重庆 |
+-----+---------------------+------+------+------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
#安数字分组,会按照升序排列
select * from stuinfo group by age;
#多列分组
select sid,group_concat(sname),sex,age,city from stuinfo group by sex,city;(12)回溯统计
#在统计的基础上在统计一次
#group_concat()
select sid,group_concat(sname),sex,age,city from stuinfo group by sex,city with rollup;(13)having条件
where:设置查询的条件,字段必须是存在的
having: 设置查询的条件,条件字段必须在结果集中;
#having 的查询效率要高于where
select * from stuinfo where age>20; #正确
select * from stuinfo having age>20; #正确
select sname from stuinfo where age>20; #正确
select sname from stuinfo having age>20; #错误,原因age不在结果集中(没有查询age这个字段)
select sname,age from stuinfo having age>20; #正确(14)order by排序[asc|desc]
用书数据排序的
select * from stuinfo order by age asc; #asc 可以不写 ,它是默认值
select * from stuinfo order by age desc;#降序排列(15)limit(限制)
limit 起始位置,显示长度
select * from stuinfo limit 3; #第一个不写默认从1开始
select * from stuinfo limit 2,3;(16)查询语句中的选项
all :和 * 是一个意思,表示查询所有的
distinct: 去除重复的数据
select all from stuinfo;
select distinct city from stuinfo;(17)insert…select…
CREATE TABLE `stuinfoo` (
`sid` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT ,
`sname` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`sex` enum('男','女') DEFAULT NULL ,
`age` tinyint(4) DEFAULT NULL ,
`city` varchar(64) DEFAULT NULL ,
PRIMARY KEY (`sid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=7 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
#选择一个表中的数据插入到另一个表中(两个表结构要一致)
insert into stuinfoo select * from stuinfo;(18)on duplicate key update
作用:在插入数据的时候,如果这个数据已经存在或不满足唯一约束的条件就执行更新;
insert into stuinfo values(2,'小月',2,18,'重庆') on duplicate key update sname='小月',sex=2;