文件上传是我们项目中经常使用的功能,一般我们的服务器可能都是web服务器,当我们使用非浏览器客户端上传文件时,比如手机(Android)等上传,可能就需要对传输的数据进行规范化的拼接,说白了,就是我们得自己完成浏览器帮我们做的事。
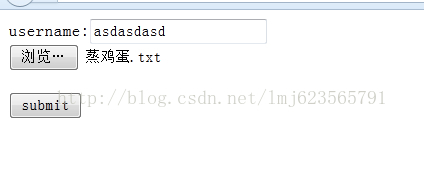
我首先写了服务器端代码,用来接收我们的数据,一会会贴出源码。然后写了个web页面用于上次,便于我们看其中的原理。
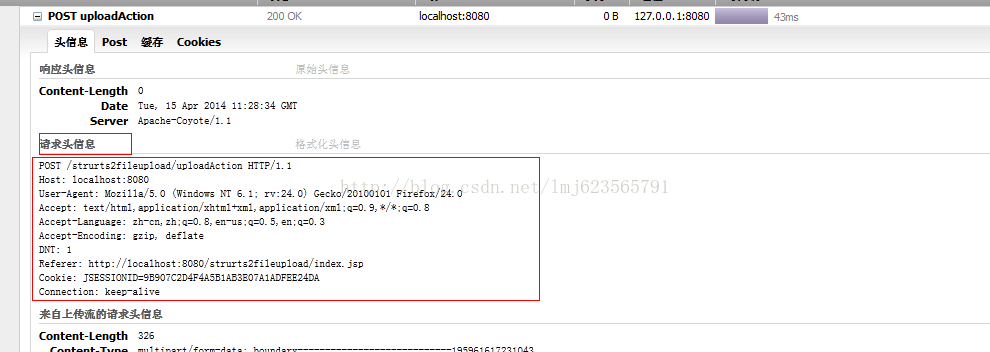
当点击了上传以后,这里我使用了firefox的firebug来观察网络信息,可以看到发出了一个POST请求,下面我框出的是请求头信息。里面包含一些请求的配置数据。
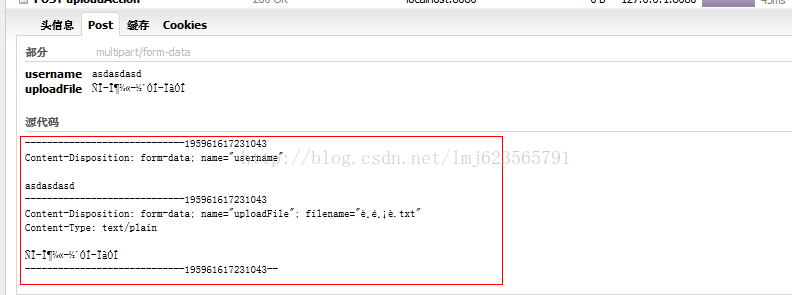
接下来看这张图:
我们可以看到我们发送的数据,一个是name为username的普通表单数据,一个为name为uploadFile的一个文件数据,可以看得出来,浏览器把文件数据转化成了2进制然后按特定的格式发给服务器了。
好了,下面开始实现上传,模拟浏览器的操作。
1、使用HttpUrlConnection
-
private static final String BOUNDARY = "----WebKitFormBoundaryT1HoybnYeFOGFlBR";
-
-
/**
-
*
-
* @param params
-
* 传递的普通参数
-
* @param uploadFile
-
* 需要上传的文件名
-
* @param fileFormName
-
* 需要上传文件表单中的名字
-
* @param newFileName
-
* 上传的文件名称,不填写将为uploadFile的名称
-
* @param urlStr
-
* 上传的服务器的路径
-
* @throws IOException
-
*/
-
public void uploadForm(Map<String, String> params, String fileFormName,
-
File uploadFile, String newFileName, String urlStr)
-
throws IOException {
-
if (newFileName == null || newFileName.trim().equals( "")) {
-
newFileName = uploadFile.getName();
-
}
-
-
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
-
/**
-
* 普通的表单数据
-
*/
-
for (String key : params.keySet()) {
-
sb.append( "--" + BOUNDARY + "\r\n");
-
sb.append( "Content-Disposition: form-data; name=\"" + key + "\""
-
+ "\r\n");
-
sb.append( "\r\n");
-
sb.append(params.get(key) + "\r\n");
-
}
-
/**
-
* 上传文件的头
-
*/
-
sb.append( "--" + BOUNDARY + "\r\n");
-
sb.append( "Content-Disposition: form-data; name=\"" + fileFormName
-
+ "\"; filename=\"" + newFileName + "\"" + "\r\n");
-
sb.append( "Content-Type: image/jpeg" + "\r\n"); // 如果服务器端有文件类型的校验,必须明确指定ContentType
-
sb.append( "\r\n");
-
-
byte[] headerInfo = sb.toString().getBytes( "UTF-8");
-
byte[] endInfo = ( "\r\n--" + BOUNDARY + "--\r\n").getBytes( "UTF-8");
-
System.out.println(sb.toString());
-
URL url = new URL(urlStr);
-
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
-
conn.setRequestMethod( "POST");
-
conn.setRequestProperty( "Content-Type",
-
"multipart/form-data; boundary=" + BOUNDARY);
-
conn.setRequestProperty( "Content-Length", String
-
.valueOf(headerInfo.length + uploadFile.length()
-
+ endInfo.length));
-
conn.setDoOutput( true);
-
-
OutputStream out = conn.getOutputStream();
-
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(uploadFile);
-
out.write(headerInfo);
-
-
byte[] buf = new byte[ 1024];
-
int len;
-
while ((len = in.read(buf)) != - 1)
-
out.write(buf, 0, len);
-
-
out.write(endInfo);
-
in.close();
-
out.close();
-
if (conn.getResponseCode() == 200) {
-
System.out.println( "上传成功");
-
}
-
-
}
于是,我们完成了请求头的设置,以及需要上传数据的拼接,所以我们完成了浏览器的工作,自然就实现文件上传了。
2、使用Socket实现文件上传,参数基本一致,使用HttpUrlConnection上传有一个很致命的问题就是,当上传文件很大时,会发生内存溢出,手机分配给我们app的内存更小,所以就更需要解决这个问题,于是我们可以使用Socket模拟POST进行HTTP文件上传。
-
/**
-
*
-
* @param params
-
* 传递的普通参数
-
* @param uploadFile
-
* 需要上传的文件名
-
* @param fileFormName
-
* 需要上传文件表单中的名字
-
* @param newFileName
-
* 上传的文件名称,不填写将为uploadFile的名称
-
* @param urlStr
-
* 上传的服务器的路径
-
* @throws IOException
-
*/
-
public void uploadFromBySocket(Map<String, String> params,
-
String fileFormName, File uploadFile, String newFileName,
-
String urlStr) throws IOException {
-
if (newFileName == null || newFileName.trim().equals( "")) {
-
newFileName = uploadFile.getName();
-
}
-
-
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
-
/**
-
* 普通的表单数据
-
*/
-
-
if (params != null)
-
for (String key : params.keySet()) {
-
sb.append( "--" + BOUNDARY + "\r\n");
-
sb.append( "Content-Disposition: form-data; name=\"" + key
-
+ "\"" + "\r\n");
-
sb.append( "\r\n");
-
sb.append(params.get(key) + "\r\n");
-
} else{ab.append( "\r\n");}
-
/**
-
* 上传文件的头
-
*/
-
sb.append( "--" + BOUNDARY + "\r\n");
-
sb.append( "Content-Disposition: form-data; name=\"" + fileFormName
-
+ "\"; filename=\"" + newFileName + "\"" + "\r\n");
-
sb.append( "Content-Type: image/jpeg" + "\r\n"); // 如果服务器端有文件类型的校验,必须明确指定ContentType
-
sb.append( "\r\n");
-
-
byte[] headerInfo = sb.toString().getBytes( "UTF-8");
-
byte[] endInfo = ( "\r\n--" + BOUNDARY + "--\r\n").getBytes( "UTF-8");
-
-
System.out.println(sb.toString());
-
-
URL url = new URL(urlStr);
-
Socket socket = new Socket(url.getHost(), url.getPort());
-
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
-
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(os, true, "UTF-8");
-
-
// 写出请求头
-
ps.println( "POST " + urlStr + " HTTP/1.1");
-
ps.println( "Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=" + BOUNDARY);
-
ps.println( "Content-Length: "
-
+ String.valueOf(headerInfo.length + uploadFile.length()
-
+ endInfo.length));
-
ps.println( "Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8");
-
-
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(uploadFile);
-
// 写出数据
-
os.write(headerInfo);
-
-
byte[] buf = new byte[ 1024];
-
int len;
-
while ((len = in.read(buf)) != - 1)
-
os.write(buf, 0, len);
-
-
os.write(endInfo);
-
-
in.close();
-
os.close();
-
}
这里因为我们使用的是Socket,所以自然对于请求头,我们也需要自己拼接了,没有什么属性设置了。参考图二框出的部分,我们使用PrintStream完成了请求头的拼接,接下来就是数据的拼接,这和使用HttpUrlConnection的方式一致。我们也完成了数据的上传。
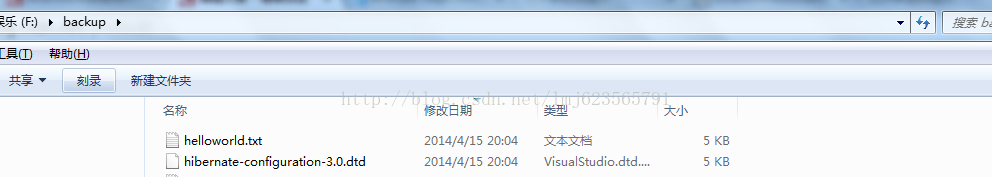
最后测试我们的代码:
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
try {
-
-
File file = new File( "D:/dtd", "dwr30.dtd");
-
-
new Test().uploadForm( null, "uploadFile", file, "helloworld.txt",
-
"http://localhost:8080/strurts2fileupload/uploadAction");
-
-
new Test().uploadFromBySocket( null, "uploadFile", file,
-
"hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd",
-
"http://localhost:8080/strurts2fileupload/uploadAction");
-
-
} catch (Exception e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
}
效果: