数据结构与算法-栈与队列
栈
基本概念
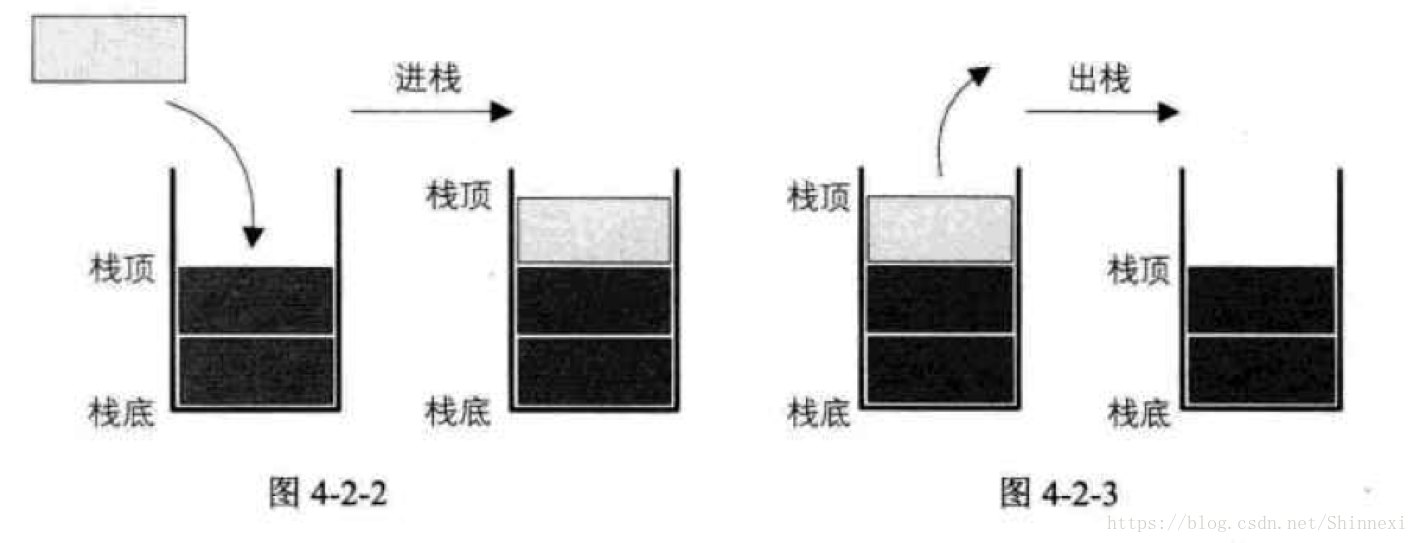
简单表述就是仅在表尾进行插入和删除操作的线性表。
常见操作
入栈和出栈, 均在线性表的尾部进行。
基本原则就是, 先入后出。
队列
基本概念
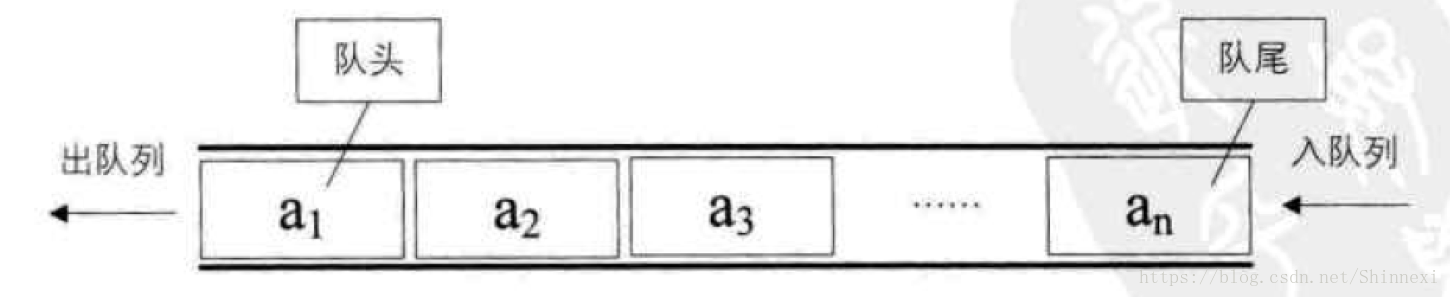
和栈不同的是,队列只允许在一端进行插入操作、而在另一端进行删除操作的线性表。
常见操作
入队列和出队列。
基本原则就是,先入先出。
Java中常见数据结构类分析
Stack & Vector
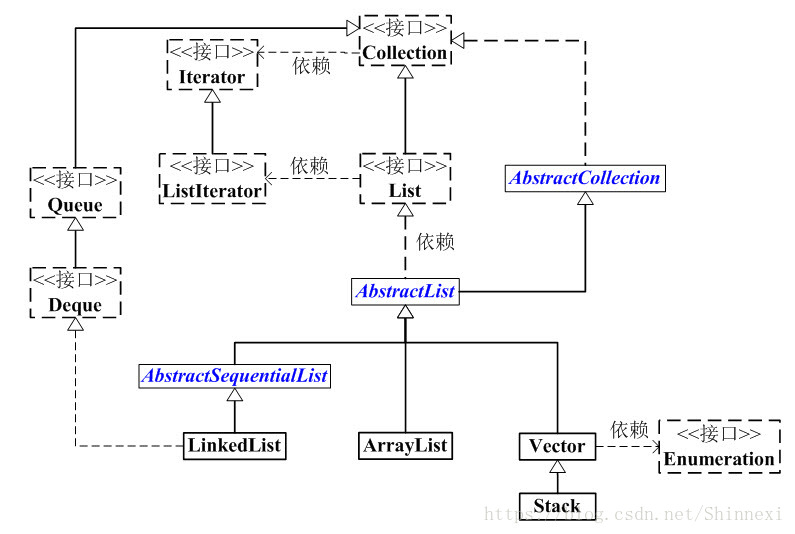
看一下Stack类的继承结构
/**
* {@code Stack} is a Last-In/First-Out(LIFO) data structure which represents a
* stack of objects. It enables users to pop to and push from the stack,
* including null objects. There is no limit to the size of the stack.
*/
public class Stack<E> extends Vector<E> {
可以看到Stack继承自Vector , Vector又继承自AbstractList 实现了List接口
简单看一下Vector类, Vector类在继承结构上和ArrayList和LinkedList是一个级别的。
这个类和ArrayList区别就是Vector用于线程同步容器。
其大部分方法都被synchronized所修饰,所以Vector是线程安全的。
看一下Stack 简单的几个方法
peek , pop , push
入栈
/**
* Pushes the specified object onto the top of the stack.
*
* @param object
* The object to be added on top of the stack.
* @return the object argument.
* @see #peek
* @see #pop
*/
public E push(E object) {
addElement(object);
return object;
}
再看一下Vector的 addElement(object) 方法
/**
* Adds the specified object at the end of this vector.
*
* @param object
* the object to add to the vector.
*/
public synchronized void addElement(E object) {
//当容量不足是进行扩容
if (elementCount == elementData.length) {
growByOne();
}
/// 按照索引将元素添加到线性表尾部,也就是Stack的顶部。
elementData[elementCount++] = object;
modCount++;
}
/**
* 该方法是通过运行时优化的。
* 这里的growByOne 不是指添加一个元素, 而是添加一倍。 默认情况下
*/
private void growByOne() {
/// 要进行扩容的大小
int adding = 0;
if (capacityIncrement <= 0) {
/// 如果列表为空 则添加1
if ((adding = elementData.length) == 0) {
adding = 1;
}
} else {
adding = capacityIncrement;
}
/// 创建新的元素数组 ,使用System.arraycopy
E[] newData = newElementArray(elementData.length + adding);
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, newData, 0, elementCount);
elementData = newData;
}
/**
* How many elements should be added to the vector when it is detected that
* it needs to grow to accommodate extra entries. If this value is zero or
* negative the size will be doubled if an increase is needed.
当容量不足时需要进行扩容的大小, 可以通过构造函数进行设定。默认情况下会进行
*/
protected int capacityIncrement;
// 默认10个
private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 10;再看一下扩容方法
/**
* Ensures that this vector can hold the specified number of elements
* without growing.
*
* @param minimumCapacity
* the minimum number of elements that this vector will hold
* before growing.
* @see #capacity
*/
public synchronized void ensureCapacity(int minimumCapacity) {
// 当元素个数小于需求的大小时
if (elementData.length < minimumCapacity) {
/// 扩容后的大小 = 如果是默认的增长系数则使用原表的大小*2
如果是用户设定过的大小,则使用原大小+增长系数。
int next = (capacityIncrement <= 0 ? elementData.length
: capacityIncrement)
+ elementData.length;
//// 最后去用户需求的和扩容后的大小中大的。
grow(minimumCapacity > next ? minimumCapacity : next);
}
}
出栈
/**
* 只返回顶部元素,不删除
* Returns the element at the top of the stack without removing it.
*
* @return the element at the top of the stack.
* @throws EmptyStackException
* if the stack is empty.
* @see #pop
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public synchronized E peek() {
try {
/// 简单的数组读取,不再赘述。
return (E) elementData[elementCount - 1];
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
throw new EmptyStackException();
}
}
/**
* 返回顶部元素,并且从顶部移除。 这才是stack的正统出栈方法。
* Returns the element at the top of the stack and removes it.
*
* @return the element at the top of the stack.
* @throws EmptyStackException
* if the stack is empty.
* @see #peek
* @see #push
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public synchronized E pop() {
if (elementCount == 0) {
throw new EmptyStackException();
}
final int index = --elementCount;
final E obj = (E) elementData[index];
/// 最简单的置空操作,留着坑下次继续使用。
elementData[index] = null;
modCount++;
return obj;
}
栈的应用实例
- 中缀表达式
- 后缀表达式
Queue
先看接口,这个类太短就直接全部粘了。
public interface Queue<E> extends Collection<E> {
/**
增加一个元索 如果队列已满,则抛出一个IIIegaISlabEepeplian异常
* Inserts the specified element into this queue if it is possible to do so
* immediately without violating capacity restrictions, returning
* <tt>true</tt> upon success and throwing an <tt>IllegalStateException</tt>
* if no space is currently available.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
* @throws IllegalStateException if the element cannot be added at this
* time due to capacity restrictions
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified element
* prevents it from being added to this queue
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and
* this queue does not permit null elements
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of this element
* prevents it from being added to this queue
*/
boolean add(E e);
/**
添加一个元素
* Inserts the specified element into this queue if it is possible to do
* so immediately without violating capacity restrictions.
* When using a capacity-restricted queue, this method is generally
* preferable to {@link #add}, which can fail to insert an element only
* by throwing an exception.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @return 并返回true 如果队列已满,则返回false
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified element
* prevents it from being added to this queue
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and
* this queue does not permit null elements
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of this element
* prevents it from being added to this queue
*/
boolean offer(E e);
/**
移除并返回队列头部的元素 如果队列为空,则抛出一个NoSuchElementException异常
* Retrieves and removes the head of this queue. This method differs
* from {@link #poll poll} only in that it throws an exception if this
* queue is empty.
*
* @return the head of this queue
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty
*/
E remove();
/**
移除并返问队列头部的元素 如果队列为空,则返回null
* Retrieves and removes the head of this queue,
* or returns <tt>null</tt> if this queue is empty.
*
* @return the head of this queue, or <tt>null</tt> if this queue is empty
*/
E poll();
/**
返回队列头部的元素如果队列为空,则抛出一个NoSuchElementException异常
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue. This method
* differs from {@link #peek peek} only in that it throws an exception
* if this queue is empty.
*
* @return the head of this queue
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty
*/
E element();
/**
返回队列头部的元素 不移除 如果队列为空,则返回null
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue,
* or returns <tt>null</tt> if this queue is empty.
*
* @return the head of this queue, or <tt>null</tt> if this queue is empty
*/
E peek();
}
看一下LinkedList这个最常见,也实现了Queue的类
// LinkedList 同时实现了List, Queue, Deque
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements
List<E>, Deque<E>, Queue<E>, Cloneable, Serializable {
下边我们看一下LinkedList中与Queue相关的方法。我们查看的源码是Android-23的 ,可能与jre 中的不一样,但是基本原理是一样的。
还是先说一下LinkedList基本节点结构
/// 头结点,也就是空表时的第一个元素。
transient Link<E> voidLink;
private static final class Link<ET> {
// 节点的数据部分
ET data;
/// 节点中指向前一个元素与后一个元素
Link<ET> previous, next;
/// 构造函数
Link(ET o, Link<ET> p, Link<ET> n) {
data = o;
previous = p;
next = n;
}
}
/**
* Constructs a new empty instance of {@code LinkedList}.
*/
public LinkedList() {
voidLink = new Link<E>(null, null, null);
/// 前一个节点和后一个节点都指向自身。
voidLink.previous = voidLink;
voidLink.next = voidLink;
}
入队列
//入队
public boolean offer(E o) {
return addLastImpl(o);
}
// 添加一个元素到最后
private boolean addLastImpl(E object) {
///队列的头结点的前一个节点设置为oldlast
Link<E> oldLast = voidLink.previous;
/// 新节点的前一个元素是头结点的前一个元素, 后一个元素是头结点
Link<E> newLink = new Link<E>(object, oldLast, voidLink);
/// 头结点的前一个元素是新节点
voidLink.previous = newLink;
/// 原来头结点的前一个节点的后一个节点是新节点
oldLast.next = newLink;
size++;
modCount++;
return true;
}
/// 这样就完成了把一个新元素添加到双向回环链表中的过程。
// 再看一下addFirstImpl方法
// 将一个元素插入到头结点和头结点后边的一个位置。
private boolean addFirstImpl(E object) {
/// 头节点的下一个节点是oldnode
Link<E> oldFirst = voidLink.next;
/// 初始化一个新节点,该节点的前一个节点是头结点,后一个是头结点的下一个节点
Link<E> newLink = new Link<E>(object, voidLink, oldFirst);
/// 把头结点的下一个节点指向新节点
voidLink.next = newLink;
/// 旧节点的前一个节点指向新节点
oldFirst.previous = newLink;
size++;
modCount++;
return true;
}
出队列
public E poll() {
return size == 0 ? null : removeFirst();
}
/**
* Removes the first object from this {@code LinkedList}.
*
* @return the removed object.
* @throws NoSuchElementException
* if this {@code LinkedList} is empty.
*/
public E removeFirst() {
return removeFirstImpl();
}
/// 移除第一个节点
private E removeFirstImpl() {
/// 先记录头结点的下一个节点是要移除的节点
Link<E> first = voidLink.next;
// 如果链表不为空
if (first != voidLink) {
Link<E> next = first.next;
voidLink.next = next;
next.previous = voidLink;
size--;
modCount++;
/// 移除头结点后边的链接,并将头节点的下下个节点指向头结点
/// 返回数据
return first.data;
}
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
看到这里就明白了,LinkedList是个双向回环链表。 既然是回环肯定是一个圈。 也就是VoidLink 是分界点,之前是队尾,之后是队首,从以上的Add方法也可以基本判断出。
LinkedList 实现了Queue也同时实现了Deque , Deque是双向队列。 基本原理都一样, 这里边的方法就不一一赘述了。
总结
理解和学习数据结构的过程很枯燥。 直到我们开始使用的时候,慢慢的明白如何使用,慢慢的理解其中的原理。 慢慢地体会大神们编写这些结构的时候的良苦用心。同时能够更好的应用到实际开发,写出更高质量的代码。