如果需要保证数据访问的排它性,则需对目标数据加“锁”,使其无法被其它程序修改
一,悲观锁
对数据被外界(包括本系统当前的其它事务和来自外部系统的事务处理)修改持保守态度,通过数据库提供的锁机制实现
最常用的,是对查询进行加锁(LockMode.UPGRADE和LockMode.UPGRADE_NOWAIT):
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = conf.configure().buildSessionFactory();
Session sess = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tran = sess.beginTransaction();
String hql = "from User where id = 1";
Query query = sess.createQuery(hql);
query.setLockOptions(LockOptions.UPGRADE);
List<User> list = query.list();
for(User user : list){
System.out.print(user.getName()+" ");
}
System.out.println();
tran.commit();
sess.close();
}
}Hibernate会在生成的SQL后面加上for update子句:
Hibernate: select user0_.id as id0_, user0_.name as name0_, user0_.age as age0_
from TEST_USER user0_ where user0_.id=1 for update通过for update子句,这条SQL锁定了TEST_USER表中符合检索条件的记录,本次事务提交前,外界无法修改这些记录,事务提交时会释放事务过程中的锁
Hibernate提供了2个锁对象,LockMode和LockOptions:
通过LockOptions的源代码,可以发现LockOptions只是LockMode的简单封装(在LockMode的基础上提供了timeout和scope):
......
/**
* NONE represents LockMode.NONE (timeout + scope do not apply)
*/
public static final LockOptions NONE = new LockOptions(LockMode.NONE);
/**
* READ represents LockMode.READ (timeout + scope do not apply)
*/
public static final LockOptions READ = new LockOptions(LockMode.READ);
/**
* UPGRADE represents LockMode.UPGRADE (will wait forever for lock and
* scope of false meaning only entity is locked)
*/
public static final LockOptions UPGRADE = new LockOptions(LockMode.UPGRADE);
public LockOptions(){}
public LockOptions( LockMode lockMode) {
this.lockMode = lockMode;
}
.....
public static final int NO_WAIT = 0;
/**
* Indicates that there is no timeout for the acquisition.
* @see #getTimeOut
*/
public static final int WAIT_FOREVER = -1;
private int timeout = WAIT_FOREVER;
private boolean scope=false;
......
LockOptions提供的加锁机制要比LockMode少很多,但是LockMode多出的加锁机制一般只是供Hibernate内部实现使用的
保证了操作的独占性,但严重影响数据库性能
二,乐观锁
乐观锁大多基于数据版本记录机制实现,既为数据增加一个版本标识
在数据库中增加version列,用来记录每行数据的版本
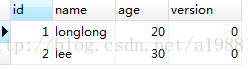
Hibernate配置文件中,version节点需要在id节点之后并紧跟id节点
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd" >
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.po.User"
table="TEST_USER">
<id name="id" column="id" type="java.lang.Integer">
<generator class="assigned"/>
</id>
<version name="version"
column="version"
type="java.lang.Integer"/>
<property name="name"
column="name"
type="java.lang.String"
not-null="true"
unique="true"
length="20"/>
<property name="age"
column="age"
type="java.lang.Integer"
not-null="true"
unique="false"
length="0"/>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>每次更新User对象时时,对应行的version字段都在增加
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = conf.configure().buildSessionFactory();
Session sess1=sessionFactory.openSession();
Session sess2=sessionFactory.openSession();
try{
User user1 = (User)sess1.get(User.class, 1);
User user2 = (User)sess2.get(User.class, 1);
System.out.println("v1="+user1.getVersion()+"--v2="+user2.getVersion());
Transaction tx1 = sess1.beginTransaction();
Transaction tx2 = sess2.beginTransaction();
user1.setName("ll");
tx1.commit();
System.out.println("v1="+user1.getVersion()+"--v2="+user2.getVersion());
user2.setName("LL");
tx2.commit();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
sess1.close();
sess2.close();
}
}
}运行结果如下,可以看到由于tx1提交时,version字段已经被修改,tx2提交时会抛出异常:
Hibernate: select user0_.id as id0_0_, user0_.version as version0_0_, user0_.name as name0_0_, user0_.age as age0_0_
from TEST_USER user0_ where user0_.id=?
Hibernate: select user0_.id as id0_0_, user0_.version as version0_0_, user0_.name as name0_0_, user0_.age as age0_0_
from TEST_USER user0_ where user0_.id=?
v1=0--v2=0
Hibernate: update TEST_USER set version=?, name=?, age=? where id=? and version=?
v1=1--v2=0
Hibernate: update TEST_USER set version=?, name=?, age=? where id=? and version=?
Exception in thread "main" org.hibernate.StaleObjectStateException: Row was updated or deleted by another transaction
(or unsaved-value mapping was incorrect): [com.po.User#1]
at org.hibernate.persister.entity.AbstractEntityPersister.check(AbstractEntityPersister.java:1932)
at org.hibernate.persister.entity.AbstractEntityPersister.update(AbstractEntityPersister.java:2576)
at org.hibernate.persister.entity.AbstractEntityPersister.updateOrInsert(AbstractEntityPersister.java:2476)
at org.hibernate.persister.entity.AbstractEntityPersister.update(AbstractEntityPersister.java:2803)
at org.hibernate.action.EntityUpdateAction.execute(EntityUpdateAction.java:113)
at org.hibernate.engine.ActionQueue.execute(ActionQueue.java:273)
at org.hibernate.engine.ActionQueue.executeActions(ActionQueue.java:265)
at org.hibernate.engine.ActionQueue.executeActions(ActionQueue.java:185)
at org.hibernate.event.def.AbstractFlushingEventListener.performExecutions(AbstractFlushingEventListener.java:321)
at org.hibernate.event.def.DefaultFlushEventListener.onFlush(DefaultFlushEventListener.java:51)
at org.hibernate.impl.SessionImpl.flush(SessionImpl.java:1216)
at org.hibernate.impl.SessionImpl.managedFlush(SessionImpl.java:383)
at org.hibernate.transaction.JDBCTransaction.commit(JDBCTransaction.java:133)
at com.test.Test.main(Test.java:43)除了使用version作为版本标识,还可以使用timestamp作为版本标识
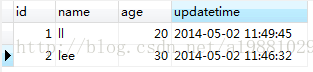
timestamp节点没有type属性:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd" >
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.po.User"
table="TEST_USER">
<id name="id" column="id" type="java.lang.Integer">
<generator class="assigned"/>
</id>
<timestamp name="updatetime"
column="updatetime"/>
<property name="name"
column="name"
type="java.lang.String"
not-null="true"
unique="true"
length="20"/>
<property name="age"
column="age"
type="java.lang.Integer"
not-null="true"
unique="false"
length="0"/>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>在某些情况下,不允许修改数据库的表结构,此时Hibernate也有相应的处理手段:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd" >
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.po.User"
table="TEST_USER"
optimistic-lock="all"
dynamic-update="true"
dynamic-insert="true"
>
<id name="id" column="id" type="java.lang.Integer">
<generator class="assigned"/>
</id>
<property name="name"
column="name"
type="java.lang.String"
not-null="true"
unique="true"
length="20"/>
<property name="age"
column="age"
type="java.lang.Integer"
not-null="true"
unique="false"
length="0"/>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>此时Hibernate将使用User类的所有字段作为版本控制信息
乐观锁相较悲观锁提高了不少性能,但是有一定的局限性,由于是在应用层加锁,如果此时在数据中直接修改数据(或其它应用程序修改数据库中的数据),应用层是无法感知到这种变化的,需要配合其它技术手段一起使用