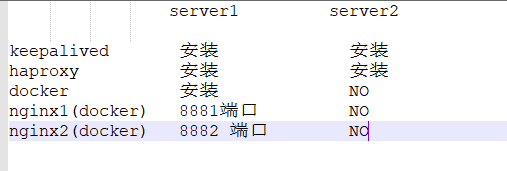
在server1 , server2安装并配置keepalived
[root@docker-server1 ~]# yum install keepalived –y
[root@docker-server1 ~]# cat /etc/keepalived/
主机一的keepalived.conf 的配置文件

1 vrrp_instance MAKE_VIP_INT { 2 state MASTER 3 interface ens32 4 virtual_router_id 1 5 priority 100 6 advert_int 1 7 unicast_src_ip 192.168.153.139 8 unicast_peer { 9 192.168.153.141 10 } 11 12 authentication { 13 auth_type PASS 14 auth_pass 1111 15 } 16 virtual_ipaddress { 17 192.168.153.100/24 dev ens32 label ens32:1 18 } 19 }
[root@docker-server1~]# systemctl restart keepalived && systemctl enable keepalived
[root@docker-server2 ~]# yum install keepalived –y
[root@docker-server2 ~]# cat /etc/keepalived/
主机二的keepalived.conf 的配置文件

1 vrrp_instance MAKE_VIP_INT { 2 state BACKUP 3 interface ens32 4 virtual_router_id 1 5 priority 50 6 advert_int 1 7 unicast_src_ip 192.168.153.141 8 unicast_peer { 9 192.168.153.139 10 } 11 12 authentication { 13 auth_type PASS 14 auth_pass 1111 15 } 16 virtual_ipaddress { 17 192.168.153.100/24 dev ens32 label ens32:1 18 } 19 } 20
[root@docker-server2~]# systemctl restart keepalived && systemctl enable keepalived


在server1,server2 两台主机上安装haproxy,并让keepalived的vip地址 作为前段地址,托管两台 nginx的web服务
通过访问keepalived 的vip的 高可用 访问后面的haproxy 托管的nginx服务,nginx服务托管后端的tomcate 服务
在server1和server2 上安装haproxy
[root@docker-server1 ~]# yum install haproxy –y
[root@docker-server1 ~]# cat /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
[root@docker-server2 ~]# yum install haproxy –y
[root@docker-server2 ~]# cat /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
server1 和server2的haproxy的配置文件相同

1 global 2 maxconn 100000 3 uid 99 4 gid 99 5 daemon 6 nbproc 1 7 log 127.0.0.1 local0 info 8 9 defaults 10 option http-keep-alive 11 #option forwardfor 12 maxconn 100000 13 mode tcp 14 timeout connect 500000ms 15 timeout client 500000ms 16 timeout server 500000ms 17 18 listen stats 19 mode http 20 bind 0.0.0.0:9999 21 stats enable 22 log global 23 stats uri /haproxy-status 24 stats auth haadmin:q1w2e3r4ys 25 26 #================================================================ 27 frontend docker_nginx_web 28 bind 192.168.153.100:80 29 mode http 30 default_backend docker_nginx_hosts 31 32 backend docker_nginx_hosts 33 mode http 34 #balance source 35 balance roundrobin 36 server web1 192.168.153.139:8881 check inter 2000 fall 3 rise 5 37 server web2 192.168.153.139:8882 check inter 2000 fall 3 rise 5
在docker宿主机上即server1上启动两个nginx容器,分别映射 8881 和8882 两个端口
docker run -d -p 8881:80 niginx-web1:v2
docker run -d -p 8882:80 niginx-web2:v2
如haproxy.cfg中所看到的:

需要更改配置文件 让 haproxy 能够使用keepalived的 vip,并对vip生效。
[root@docker1 haproxy]# cat /etc/sysctl.conf

1 # sysctl settings are defined through files in 2 # /usr/lib/sysctl.d/, /run/sysctl.d/, and /etc/sysctl.d/. 3 # 4 # Vendors settings live in /usr/lib/sysctl.d/. 5 # To override a whole file, create a new file with the same in 6 # /etc/sysctl.d/ and put new settings there. To override 7 # only specific settings, add a file with a lexically later 8 # name in /etc/sysctl.d/ and put new settings there. 9 # 10 # For more information, see sysctl.conf(5) and sysctl.d(5). 11 net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1 12 net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1 13 net.ipv4.ip_nonlocal_bind=1
[root@docker1 haproxy]# sysctl -p
nginx代理 tomcat的服务
生成nginx的docker镜像的配置文件

1 user nginx nginx; 2 worker_processes auto; 3 4 #error_log logs/error.log; 5 #error_log logs/error.log notice; 6 #error_log logs/error.log info; 7 8 #pid logs/nginx.pid; 9 daemon off; 10 11 events { 12 worker_connections 1024; 13 } 14 15 16 http { 17 include mime.types; 18 default_type application/octet-stream; 19 20 #log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' 21 # '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' 22 # '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; 23 24 #access_log logs/access.log main; 25 26 sendfile on; 27 #tcp_nopush on; 28 29 #keepalive_timeout 0; 30 keepalive_timeout 65; 31 32 #gzip on; 33 upstream tomcat_webserver { 34 server web1:8080; 35 server web2:8080; 36 } 37 server { 38 listen 80; 39 server_name localhost; 40 41 #charset koi8-r; 42 43 #access_log logs/host.access.log main; 44 45 location / { 46 root html; 47 index index.html index.htm; 48 } 49 location /web { 50 root html; 51 index index.html index.htm; 52 } 53 location /myapp { 54 proxy_pass http://tomcat_webserver; 55 proxy_set_header Host $host; 56 proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; 57 proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; 58 } 59 #error_page 404 /404.html; 60 61 # redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html 62 # 63 error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; 64 location = /50x.html { 65 root html; 66 } 67 68 # proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80 69 # 70 #location ~ \.php$ { 71 # proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1; 72 #} 73 74 # pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000 75 # 76 #location ~ \.php$ { 77 # root html; 78 # fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; 79 # fastcgi_index index.php; 80 # fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name; 81 # include fastcgi_params; 82 #} 83 84 # deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root 85 # concurs with nginx's one 86 # 87 #location ~ /\.ht { 88 # deny all; 89 #} 90 } 91 92 93 # another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration 94 # 95 #server { 96 # listen 8000; 97 # listen somename:8080; 98 # server_name somename alias another.alias; 99 100 # location / { 101 # root html; 102 # index index.html index.htm; 103 # } 104 #} 105 106 107 # HTTPS server 108 # 109 #server { 110 # listen 443 ssl; 111 # server_name localhost; 112 113 # ssl_certificate cert.pem; 114 # ssl_certificate_key cert.key; 115 116 # ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m; 117 # ssl_session_timeout 5m; 118 119 # ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5; 120 # ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; 121 122 # location / { 123 # root html; 124 # index index.html index.htm; 125 # } 126 #} 127 128 }
容器间的关联
docker run -d -p 8081:8080 --name tt1 tomcat-app1:v1
docker run -d -p 8881:80 --link tt1:web1 --link tt2:web2 niginx-web1:v2
启动第二个容器时,通过--link 参数 把第一个容器的 --name 参数后起的名字给加上 ,还可以通过 " : " 后面跟上第一个容器的别名,把第一个容器和第二个容器给关联起来。
