一、CGLIB介绍
CGLIB(Code Generation Library)是一个开源项目!是一个强大的,高性能,高质量的Code生成类库,
它可以在运行期扩展Java类与实现Java接口。Hibernate用它来实现PO(Persistent Object 持久化对象)字节码的动态生成。
CGLIB是一个强大的高性能的代码生成包。它广泛的被许多AOP的框架使用,例如Spring AOP为他们提供
方法的interception(拦截)。CGLIB包的底层是通过使用一个小而快的字节码处理框架ASM,来转换字节码并生成新的类。
除了CGLIB包,脚本语言例如Groovy和BeanShell,也是使用ASM来生成java的字节码。当然不鼓励直接使用ASM,
因为它要求你必须对JVM内部结构包括class文件的格式和指令集都很熟悉。
二、CGLIB动态代理实例
实现一个业务类,注意,这个业务类并没有实现任何接口:
package com.lanhuigu.spring.proxy.cglib;
public class HelloService {
public HelloService() {
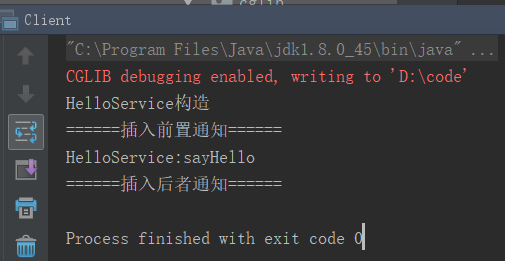
System.out.println("HelloService构造");
}
/**
* 该方法不能被子类覆盖,Cglib是无法代理final修饰的方法的
*/
final public String sayOthers(String name) {
System.out.println("HelloService:sayOthers>>"+name);
return null;
}
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("HelloService:sayHello");
}
}
自定义MethodInterceptor:
package com.lanhuigu.spring.proxy.cglib;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* 自定义MethodInterceptor
*/
public class MyMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor{
/**
* sub:cglib生成的代理对象
* method:被代理对象方法
* objects:方法入参
* methodProxy: 代理方法
*/
@Override
public Object intercept(Object sub, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("======插入前置通知======");
Object object = methodProxy.invokeSuper(sub, objects);
System.out.println("======插入后者通知======");
return object;
}
}生成CGLIB代理对象调用目标方法:
package com.lanhuigu.spring.proxy.cglib;
import net.sf.cglib.core.DebuggingClassWriter;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 代理类class文件存入本地磁盘方便我们反编译查看源码
System.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY, "D:\\code");
// 通过CGLIB动态代理获取代理对象的过程
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
// 设置enhancer对象的父类
enhancer.setSuperclass(HelloService.class);
// 设置enhancer的回调对象
enhancer.setCallback(new MyMethodInterceptor());
// 创建代理对象
HelloService proxy= (HelloService)enhancer.create();
// 通过代理对象调用目标方法
proxy.sayHello();
}
}运行结果:
三 CGLIB动态代理源码分析
实现CGLIB动态代理必须实现MethodInterceptor(方法拦截器)接口,源码如下:
/*
* Copyright 2002,2003 The Apache Software Foundation
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package net.sf.cglib.proxy;
/**
* General-purpose {@link Enhancer} callback which provides for "around advice".
* @author Juozas Baliuka <a href="mailto:[email protected]">[email protected]</a>
* @version $Id: MethodInterceptor.java,v 1.8 2004/06/24 21:15:20 herbyderby Exp $
*/
public interface MethodInterceptor
extends Callback
{
/**
* All generated proxied methods call this method instead of the original method.
* The original method may either be invoked by normal reflection using the Method object,
* or by using the MethodProxy (faster).
* @param obj "this", the enhanced object
* @param method intercepted Method
* @param args argument array; primitive types are wrapped
* @param proxy used to invoke super (non-intercepted method); may be called
* as many times as needed
* @throws Throwable any exception may be thrown; if so, super method will not be invoked
* @return any value compatible with the signature of the proxied method. Method returning void will ignore this value.
* @see MethodProxy
*/
public Object intercept(Object obj, java.lang.reflect.Method method, Object[] args,
MethodProxy proxy) throws Throwable;
}
这个接口只有一个intercept()方法,这个方法有4个参数:
obj表示增强的对象,即实现这个接口类的一个对象;
method表示要被拦截的方法;
args表示要被拦截方法的参数;
proxy表示要触发父类的方法对象;
在上面的Client代码中,通过Enhancer.create()方法创建代理对象,create()方法的源码:
/**
* Generate a new class if necessary and uses the specified
* callbacks (if any) to create a new object instance.
* Uses the no-arg constructor of the superclass.
* @return a new instance
*/
public Object create() {
classOnly = false;
argumentTypes = null;
return createHelper();
}该方法含义就是如果有必要就创建一个新类,并且用指定的回调对象创建一个新的对象实例,
使用的父类的参数的构造方法来实例化父类的部分。核心内容在createHelper()中,源码如下:
private Object createHelper() {
preValidate();
Object key = KEY_FACTORY.newInstance((superclass != null) ? superclass.getName() : null,
ReflectUtils.getNames(interfaces),
filter == ALL_ZERO ? null : new WeakCacheKey<CallbackFilter>(filter),
callbackTypes,
useFactory,
interceptDuringConstruction,
serialVersionUID);
this.currentKey = key;
Object result = super.create(key);
return result;
}preValidate()方法校验callbackTypes、filter是否为空,以及为空时的处理。
通过newInstance()方法创建EnhancerKey对象,作为Enhancer父类AbstractClassGenerator.create()方法
创建代理对象的参数。
protected Object create(Object key) {
try {
ClassLoader loader = getClassLoader();
Map<ClassLoader, ClassLoaderData> cache = CACHE;
ClassLoaderData data = cache.get(loader);
if (data == null) {
synchronized (AbstractClassGenerator.class) {
cache = CACHE;
data = cache.get(loader);
if (data == null) {
Map<ClassLoader, ClassLoaderData> newCache = new WeakHashMap<ClassLoader, ClassLoaderData>(cache);
data = new ClassLoaderData(loader);
newCache.put(loader, data);
CACHE = newCache;
}
}
}
this.key = key;
Object obj = data.get(this, getUseCache());
if (obj instanceof Class) {
return firstInstance((Class) obj);
}
return nextInstance(obj);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Error e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CodeGenerationException(e);
}
}真正创建代理对象方法在nextInstance()方法中,该方法为抽象类AbstractClassGenerator的一个方法,签名如下:
abstract protected Object nextInstance(Object instance) throws Exception;
在子类Enhancer中实现,实现源码如下:
protected Object nextInstance(Object instance) {
EnhancerFactoryData data = (EnhancerFactoryData) instance;
if (classOnly) {
return data.generatedClass;
}
Class[] argumentTypes = this.argumentTypes;
Object[] arguments = this.arguments;
if (argumentTypes == null) {
argumentTypes = Constants.EMPTY_CLASS_ARRAY;
arguments = null;
}
return data.newInstance(argumentTypes, arguments, callbacks);
}看看data.newInstance(argumentTypes, arguments, callbacks)方法,
第一个参数为代理对象的构成器类型,第二个为代理对象构造方法参数,第三个为对应回调对象。
最后根据这些参数,通过反射生成代理对象,源码如下:
/**
* Creates proxy instance for given argument types, and assigns the callbacks.
* Ideally, for each proxy class, just one set of argument types should be used,
* otherwise it would have to spend time on constructor lookup.
* Technically, it is a re-implementation of {@link Enhancer#createUsingReflection(Class)},
* with "cache {@link #setThreadCallbacks} and {@link #primaryConstructor}"
*
* @see #createUsingReflection(Class)
* @param argumentTypes constructor argument types
* @param arguments constructor arguments
* @param callbacks callbacks to set for the new instance
* @return newly created proxy
*/
public Object newInstance(Class[] argumentTypes, Object[] arguments, Callback[] callbacks) {
setThreadCallbacks(callbacks);
try {
// Explicit reference equality is added here just in case Arrays.equals does not have one
if (primaryConstructorArgTypes == argumentTypes ||
Arrays.equals(primaryConstructorArgTypes, argumentTypes)) {
// If we have relevant Constructor instance at hand, just call it
// This skips "get constructors" machinery
return ReflectUtils.newInstance(primaryConstructor, arguments);
}
// Take a slow path if observing unexpected argument types
return ReflectUtils.newInstance(generatedClass, argumentTypes, arguments);
} finally {
// clear thread callbacks to allow them to be gc'd
setThreadCallbacks(null);
}
}最后生成代理对象:
将其反编译后代码如下:
package com.lanhuigu.spring.proxy.cglib;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import net.sf.cglib.core.ReflectUtils;
import net.sf.cglib.core.Signature;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.*;
public class HelloService$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$4da4ebaf extends HelloService
implements Factory
{
private boolean CGLIB$BOUND;
public static Object CGLIB$FACTORY_DATA;
private static final ThreadLocal CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS;
private static final Callback CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS[];
private MethodInterceptor CGLIB$CALLBACK_0; // 拦截器
private static Object CGLIB$CALLBACK_FILTER;
private static final Method CGLIB$sayHello$0$Method; // 被代理方法
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$sayHello$0$Proxy; // 代理方法
private static final Object CGLIB$emptyArgs[];
private static final Method CGLIB$equals$1$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$equals$1$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$toString$2$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$toString$2$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$hashCode$3$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$hashCode$3$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$clone$4$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$clone$4$Proxy;
static void CGLIB$STATICHOOK1()
{
Method amethod[];
Method amethod1[];
CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS = new ThreadLocal();
CGLIB$emptyArgs = new Object[0];
// 代理类
Class class1 = Class.forName("com.lanhuigu.spring.proxy.cglib.HelloService$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$4da4ebaf");
// 被代理类
Class class2;
amethod = ReflectUtils.findMethods(new String[] {
"equals", "(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z", "toString", "()Ljava/lang/String;", "hashCode", "()I", "clone", "()Ljava/lang/Object;"
}, (class2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object")).getDeclaredMethods());
Method[] = amethod;
CGLIB$equals$1$Method = amethod[0];
CGLIB$equals$1$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(class2, class1, "(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z", "equals", "CGLIB$equals$1");
CGLIB$toString$2$Method = amethod[1];
CGLIB$toString$2$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(class2, class1, "()Ljava/lang/String;", "toString", "CGLIB$toString$2");
CGLIB$hashCode$3$Method = amethod[2];
CGLIB$hashCode$3$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(class2, class1, "()I", "hashCode", "CGLIB$hashCode$3");
CGLIB$clone$4$Method = amethod[3];
CGLIB$clone$4$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(class2, class1, "()Ljava/lang/Object;", "clone", "CGLIB$clone$4");
amethod1 = ReflectUtils.findMethods(new String[] {
"sayHello", "()V"
}, (class2 = Class.forName("com.lanhuigu.spring.proxy.cglib.HelloService")).getDeclaredMethods());
Method[] 1 = amethod1;
CGLIB$sayHello$0$Method = amethod1[0];
CGLIB$sayHello$0$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(class2, class1, "()V", "sayHello", "CGLIB$sayHello$0");
}
final void CGLIB$sayHello$0()
{
super.sayHello();
}
public final void sayHello()
{
MethodInterceptor var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if(this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
if(var10000 != null) {
// 调用拦截器
var10000.intercept(this, CGLIB$setPerson$0$Method, CGLIB$emptyArgs, CGLIB$setPerson$0$Proxy);
} else {
super.sayHello();
}
}
......
......
}从代理对象反编译源码可以知道,代理对象继承于HelloService,拦截器调用intercept()方法,
intercept()方法由自定义MyMethodInterceptor实现,所以,最后调用MyMethodInterceptor中
的intercept()方法,从而完成了由代理对象访问到目标对象的动态代理实现。