一、实验目的和要求
了解静态联编和动态联编的概念。掌握动态联编的条件。
二、实验内容
1、分析并调试下列程序。
-
//sy6_1.cpp
-
-
using namespace std;
-
class Base
-
{
-
public:
-
virtual void f(float x){ cout<< "Base::f(float)"<<x<< endl;}
-
void g(float x){ cout<< "Base::g(float)"<<x<< endl;}
-
void h(float x){ cout<< "Base::h(float)"<<x<< endl;}
-
};
-
class Derived: public Base
-
{
-
public:
-
virtual void f(float x){ cout<< "Derived::f(float)"<<x<< endl;}
-
void g(float x){ cout<< "Derived::g(float)"<<x<< endl;}
-
void h(float x){ cout<< "Derived::h(float)"<<x<< endl;}
-
-
};
-
int main()
-
{
-
Derived d;
-
Base * pb=&d;
-
Derived * pd=&d;
-
pb->f( 3.14f);
-
pb->f( 3.14f);
-
pb->g( 3.14f);
-
pb->h( 3.14f);
-
pb->h( 3.14f);
-
return 0;
-
}
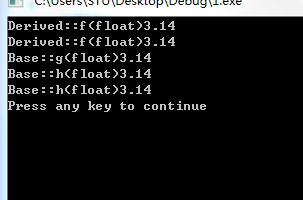
(1)找出以上程序中使用了重载和覆盖的函数。
答:Base类中函数void g(); 和void h();与Derived类中的函数void g(); 和void h();函数名相同,参数类型不同,构成了函数重载。
(2)写出程序的输出结果,并解释输出结果。
2、分析并调试下列程序。
-
//sy6_2.cpp
-
-
using namespace std;
-
class Base
-
{
-
public:
-
void f(int x){ cout<< "Base::f(int)"<<x<< endl;}
-
void f(float x){ cout<< "Base::f(float)"<<x<< endl;}
-
virtual void g(void){ cout<< "Base::g(void)"<< endl;}
-
};
-
class Derived: public Base
-
{
-
public:
-
virtual void g(void){ cout<< "Derived::g(void)"<<x<< endl;}
-
-
};
-
int main()
-
{
-
Derived d;
-
Base * pb=&d;
-
Derived * pd=&d;
-
pb->f( 42);
-
pb->f( 3.14f);
-
pb->g();
-
return 0;
-
}
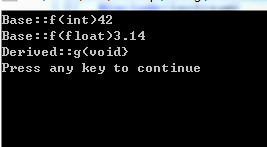
(1)找出以上程序中使用了重载和覆盖的函数。
答:Base类中函数void f(); 在同一作用域中,函数名相同,参数类型不同,构成了函数重载。
(2)写出程序的输出结果,并解释输出结果。
3、分析并调试下列程序
-
//sy6_3.cpp
-
-
using namespace std;
-
class Point
-
{
-
public:
-
Point( double i, double j){x=i;y=j;}
-
double Area(){ return 0.0;}
-
private:
-
double x,y;
-
-
};
-
class Rectangle: public Point
-
{
-
public:
-
Rectangle( double i, double j, double k, double l):Point(i,j){w=k;h=l;}
-
double Area(){ return w*h;}
-
private:
-
double w,h;
-
-
};
-
int main()
-
{
-
Point p(3.5,7);
-
double A=p.Area();
-
cout<< "Area="<<A<< endl;
-
Rectangle r(1.2,3,5,7,8);
-
A=r.Area();
-
cout<< "Area="<<A<< endl;
-
return 0;
-
}
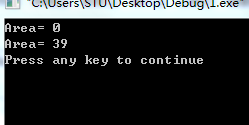
写出程序的输出结果,并解释输出结果。4、分析并调试下列程序。
-
//sy6_4.cpp
-
-
using namespace std;
-
const double PI= 3.1415;
-
class Shap
-
{
-
public:
-
virtual double Area()= 0;
-
-
};
-
class Triangle: public Shap
-
{
-
public:
-
Triangle( double h, double w){H=h;W=w;}
-
double Area(){ return 0.5*H*W;}
-
private:
-
double H,W;
-
-
};
-
class Rectangle: public Shap
-
{
-
public:
-
Rectangle( double h, double w){H=h;W=w;}
-
double Area(){ return 0.5*H*W;}
-
private:
-
double H,W;
-
};
-
class Circle: public Shap
-
{
-
public:
-
Circle( double r){R=r;}
-
double Area(){} return PI*R*R;}
-
private:
-
double R;
-
};
-
class Square: public Shap
-
{
-
public:
-
Square( double s){S=s;}
-
double Area(){} return S*S;}
-
private:
-
double S;
-
};
-
double Total(Shap*s[],int n)
-
{
-
double sum= 0;
-
for( int i= 0;i<n;i++)
-
sum+=s[i]->Area();
-
return sum;
-
}
-
int main()
-
{
-
Shap *s[ 5];
-
s[ 0]= new Square( 8.0);
-
s[ 1]= new Square( 3.0, 8.0);
-
s[ 2]= new Square( 12.0);
-
s[ 3]= new Square( 8.0);
-
s[ 4]= new Square( 5.0, 4.0);
-
double sum=Total(s, 5);
-
cout<< "SUM="<<sum<< endl;
-
return 0;
-
}
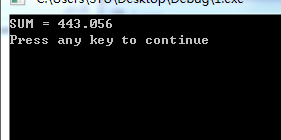
运行结果:
(1)指出抽象类。
(2)指出纯虚函数,并说明它的作用。(3)每个类的作用是什么?整个程序的作用是什么?
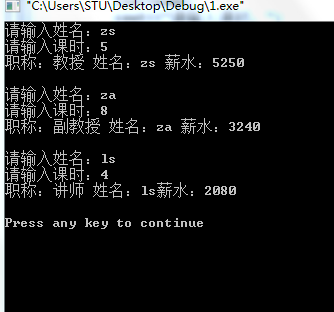
5. 某学校对教师每个月工资的计算规定如下:固定工资+课时补贴;教授的固定工资为5000元,每个课时补贴50;副教授的固定工资为3000,每个课时补贴30元;讲师的固定工资为2000元,每个课时补贴20元。定义教师抽象类,派生不同职称的教师类,编写程序求若干个教师的月工资。(sy6_5.cpp)
-
//sy6_5.cpp
-
-
using namespace std;
-
class Teacher
-
{
-
public:
-
virtual int Salary()= 0;
-
virtual void Print(int)= 0;
-
};
-
-
class Professor: public Teacher
-
{
-
private:
-
char name[ 128];
-
int lessons;
-
public:
-
Professor()
-
{
-
cout<< "请输入姓名:";
-
cin>>name;
-
cout<< "请输入课时:";
-
cin>>lessons;
-
};
-
int Salary()
-
{
-
return ( 5000+lessons* 50);
-
};
-
void Print(int money)
-
{
-
cout<< "职称:教授 姓名:"<<name<< " 薪水:"<<money<< endl<< endl;
-
};
-
};
-
-
class AssociateProfessor: public Teacher
-
{
-
private:
-
char name[ 128];
-
int lessons;
-
public:
-
AssociateProfessor()
-
{
-
cout<< "请输入姓名:";
-
cin>>name;
-
cout<< "请输入课时:";
-
cin>>lessons;
-
};
-
int Salary()
-
{
-
return ( 3000+lessons* 30);
-
};
-
void Print(int money)
-
{
-
cout<< "职称:副教授 姓名:"<<name<< " 薪水:"<<money<< endl<< endl;
-
};
-
};
-
-
class Lecturer: public Teacher
-
{
-
private:
-
char name[ 128];
-
int lessons;
-
public:
-
Lecturer()
-
{
-
cout<< "请输入姓名:";
-
cin>>name;
-
cout<< "请输入课时:";
-
cin>>lessons;
-
};
-
int Salary()
-
{
-
return ( 2000+lessons* 20);
-
};
-
void Print(int money)
-
{
-
cout<< "职称:讲师 姓名:"<<name<< "薪水:"<<money<< endl<< endl;
-
};
-
};
-
-
int main()
-
{
-
Teacher *t = NULL;
-
-
int money= 0;
-
-
t = new Professor();
-
money = t->Salary();
-
t->Print(money);
-
delete t;
-
-
-
t = new AssociateProfessor();
-
money = t->Salary();
-
t->Print(money);
-
delete t;
-
-
-
t = new Lecturer();
-
money = t->Salary();
-
t->Print(money);
-
delete t;
-
t = NULL;
-
return 0;
-
}
运行结果:
6. 把实验5中的第4题的Shape类定义为抽象类,提供共同操作界面的纯虚函数。TwoDimShape类和ThreeDimShape类仍然抽象类,第3层具体类才能提供全部函数的实现。在测试函数中,使用基类指针实现不同派生类对象的操作。
三、分析与讨论
1、结合实验内容中第1题和第2题,说明重载与覆盖的区别。
答:重载与覆盖的区别:1、方法的覆盖是子类和父类之间的关系,是垂直关系;方法的重载是同一个类中方法之间的关系,是水平关系2、覆盖只能由一个方法,或只能由一对方法产生关系;方法的重载是多个方法之间的关系。3、覆盖要求参数列表相同;重载要求参数列表不同。4、覆盖关系中,调用那个方法体,是根据对象的类型(对象对应存储空间类型)来决定;重载关系,是根据调用时的实参表与形参表来选择方法体的。
2、总结静态联编和动态联编的区别和动态联编的条件。
答:静态联编是指联编工作在编译阶段完成的,这种联编过程是在程序运行之前完成的,又称为早期联编。要实现静态联编,在编译阶段就必须确定程序中的操作调用(如函数调用)与执行该操作代码间的关系,确定这种关系称为束定,在编译时的束定称为静态束定。静态联编对函数的选择是基于指向对象的指针或者引用的类型。其优点是效率高,但灵活性差。
动态联编是指联编在程序运行时动态地进行,根据当时的情况来确定调用哪个同名函数,实际上是在运行时虚函数的实现。这种联编又称为晚期联编,或动态束定。动态联编对成员函数的选择是基于对象的类型,针对不同的对象类型将做出不同的编译结果。C++中一般情况下的联编是静态联编,但是当涉及到多态性和虚函数时应该使用动态联编。动态联编的优点是灵活性强,但效率低。
动态联编的条件:必须把动态联编的行为定义为类的虚函数;类之间应满足子类型关系,通常表现为一个类从另一个类公有派生而来;必须先使用基类指针指向子类型的对象,然后直接或者间接使用基类指针调用虚函数。
四、实验小结
通过本次实验我们了解了静态联编和动态联编的概念,学习了动态联编的条件。