Surround the Trees |
| Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) |
| Total Submission(s): 183 Accepted Submission(s): 93 |
|
|
|
Problem Description
There are a lot of trees in an area. A peasant wants to buy a rope to surround all these trees. So at first he must know the minimal required length of the rope. However, he does not know how to calculate it. Can you help him?
The diameter and length of the trees are omitted, which means a tree can be seen as a point. The thickness of the rope is also omitted which means a rope can be seen as a line. 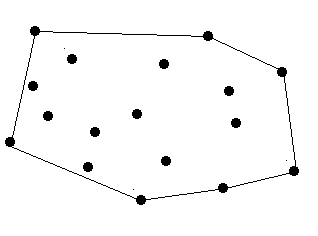
There are no more than 100 trees. |
|
Input
The input contains one or more data sets. At first line of each input data set is number of trees in this data set, it is followed by series of coordinates of the trees. Each coordinate is a positive integer pair, and each integer is less than 32767. Each pair is separated by blank.
Zero at line for number of trees terminates the input for your program. |
|
Output
The minimal length of the rope. The precision should be 10^-2. |
|
Sample Input
9 12 7 24 9 30 5 41 9 80 7 50 87 22 9 45 1 50 7 0 |
|
Sample Output
243.06 凸包 |
Surround the Trees 7.1.4
猜你喜欢
转载自blog.csdn.net/bruce_teng2011/article/details/38645209
今日推荐
周排行