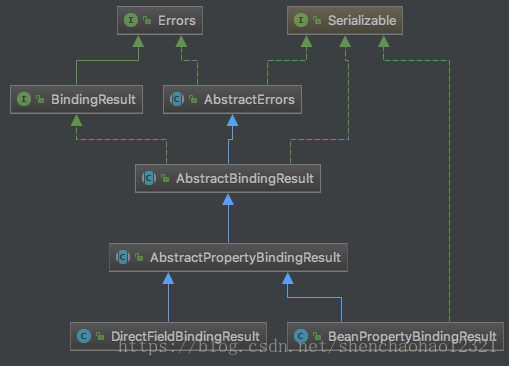
DataBinder实现了TypeConverter和PropertyEditorRegistry接口提供了类型转换功能,并且在设置值的同时做Validation。DataBinder有个重要的成员变量bindingResult是AbstractPropertyBindingResult,我们先分析他的用处。
Errors接口定义了存储与展示关于数据绑定和validation到指定对象的错误信息,AbstractErrors是一个抽象实现。对于错误信息存储的四个方法:
@Override
public void reject(String errorCode) {
reject(errorCode, null, null);
}
@Override
public void reject(String errorCode, String defaultMessage) {
reject(errorCode, null, defaultMessage);
}
@Override
public void rejectValue(@Nullable String field, String errorCode) {
rejectValue(field, errorCode, null, null);
}
@Override
public void rejectValue(@Nullable String field, String errorCode, String defaultMessage) {
rejectValue(field, errorCode, null, defaultMessage);
}reject()和rejectValue()最终的实现方法被定义在了子类AbstractBindingResult,reject()方法用于为指定对象注册一个全局的错误信息,rejectValue()方法用于为一个对象的指定字段注册一个错误消息。
同样获取错误信息的方法也是给出了基本实现,最终的实现还是定义在了子类中。
@Override
@Nullable
public ObjectError getGlobalError() {
List<ObjectError> globalErrors = getGlobalErrors();
return (!globalErrors.isEmpty() ? globalErrors.get(0) : null);
}
@Override
public boolean hasFieldErrors() {
return (getFieldErrorCount() > 0);
}
@Override
public int getFieldErrorCount() {
return getFieldErrors().size();
}
@Override
@Nullable
public FieldError getFieldError() {
List<FieldError> fieldErrors = getFieldErrors();
return (!fieldErrors.isEmpty() ? fieldErrors.get(0) : null);
}
@Override
public boolean hasFieldErrors(String field) {
return (getFieldErrorCount(field) > 0);
}
@Override
public int getFieldErrorCount(String field) {
return getFieldErrors(field).size();
}
@Override
public List<FieldError> getFieldErrors(String field) {
List<FieldError> fieldErrors = getFieldErrors();
List<FieldError> result = new LinkedList<>();
String fixedField = fixedField(field);
for (FieldError error : fieldErrors) {
if (isMatchingFieldError(fixedField, error)) {
result.add(error);
}
}
return Collections.unmodifiableList(result);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public FieldError getFieldError(String field) {
List<FieldError> fieldErrors = getFieldErrors(field);
return (!fieldErrors.isEmpty() ? fieldErrors.get(0) : null);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Class<?> getFieldType(String field) {
Object value = getFieldValue(field);
return (value != null ? value.getClass() : null);
}BindingResult接口扩展了Errors接口,额外定义了一些与数据绑定结果相关的方法,下面就看一看BindingResult与AbstractBindingResult共同的子类AbstractBindingResult。
主要成员变量:
private final String objectName;//为绑定对象起个名字,会作用域错误码和getModel()
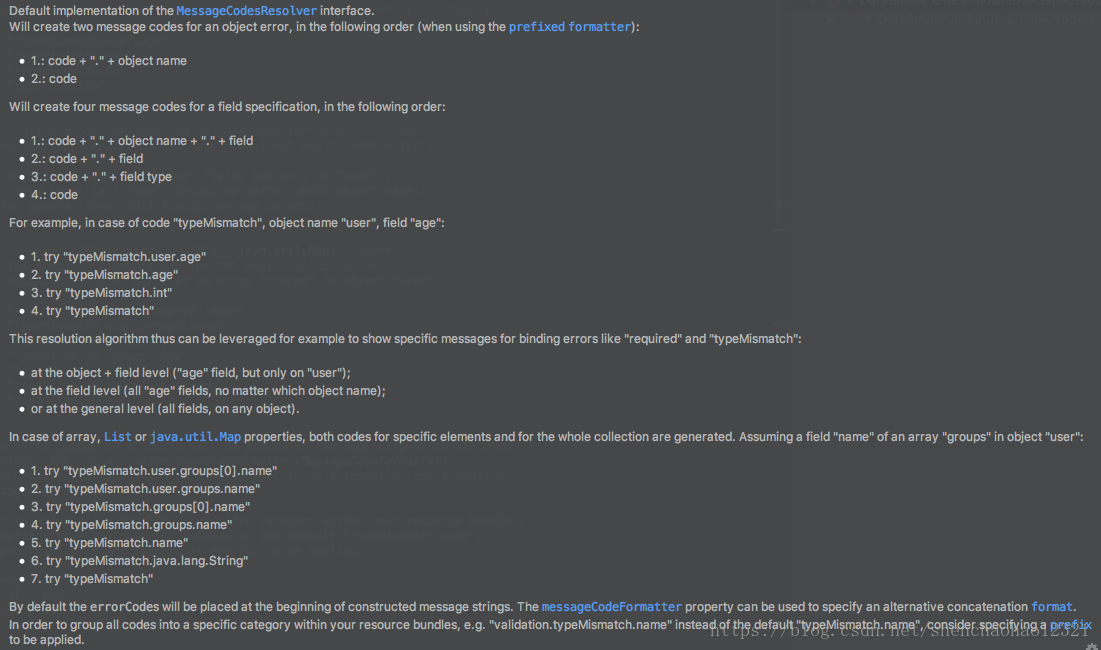
private MessageCodesResolver messageCodesResolver = new DefaultMessageCodesResolver();//用于处理错误码,看下面解释
private final List<ObjectError> errors = new LinkedList<>();//存储数据绑定校验出现的错误
private final Map<String, Class<?>> fieldTypes = new HashMap<>(0);//字段名与字段类型
private final Map<String, Object> fieldValues = new HashMap<>(0);//字段名与字段值
private final Set<String> suppressedFields = new HashSet<>();//存储数据绑定不被允许的字段reject()方法内部会将ObjectError或FieldError对象添加到成员变量errors中,这两个对象需要一个String[] codes,messageCodesResolver就是将reject方法参数errorCode转换为codes的作用。看一下他的文档描述。
下面是注册错误消息的实现:
@Override
public void reject(String errorCode, @Nullable Object[] errorArgs, @Nullable String defaultMessage) {
addError(new ObjectError(getObjectName(), resolveMessageCodes(errorCode), errorArgs, defaultMessage));
}
@Override
public void rejectValue(@Nullable String field, String errorCode, @Nullable Object[] errorArgs,@Nullable String defaultMessage) {
if ("".equals(getNestedPath()) && !StringUtils.hasLength(field)) {
// We're at the top of the nested object hierarchy,
// so the present level is not a field but rather the top object.
// The best we can do is register a global error here...
reject(errorCode, errorArgs, defaultMessage);
return;
}
String fixedField = fixedField(field);
Object newVal = getActualFieldValue(fixedField);
FieldError fe = new FieldError(getObjectName(), fixedField, newVal, false, resolveMessageCodes(errorCode, field), errorArgs, defaultMessage);
addError(fe);
}
@Override
public void addError(ObjectError error) {
this.errors.add(error);
}对于全局错误使用ObjectError,对于字段错误使用FieldError多了字段名字与字段值。

获取错误信息:
@Override
public List<ObjectError> getGlobalErrors() {
List<ObjectError> result = new LinkedList<>();
for (ObjectError objectError : this.errors) {
if (!(objectError instanceof FieldError)) {
result.add(objectError);
}
}
return Collections.unmodifiableList(result);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public ObjectError getGlobalError() {
for (ObjectError objectError : this.errors) {
if (!(objectError instanceof FieldError)) {
return objectError;
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public List<FieldError> getFieldErrors() {
List<FieldError> result = new LinkedList<>();
for (ObjectError objectError : this.errors) {
if (objectError instanceof FieldError) {
result.add((FieldError) objectError);
}
}
return Collections.unmodifiableList(result);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public FieldError getFieldError() {
for (ObjectError objectError : this.errors) {
if (objectError instanceof FieldError) {
return (FieldError) objectError;
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public List<FieldError> getFieldErrors(String field) {
List<FieldError> result = new LinkedList<>();
String fixedField = fixedField(field);
for (ObjectError objectError : this.errors) {
if (objectError instanceof FieldError && isMatchingFieldError(fixedField, (FieldError) objectError)) {
result.add((FieldError) objectError);
}
}
return Collections.unmodifiableList(result);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public FieldError getFieldError(String field) {
String fixedField = fixedField(field);
for (ObjectError objectError : this.errors) {
if (objectError instanceof FieldError) {
FieldError fieldError = (FieldError) objectError;
if (isMatchingFieldError(fixedField, fieldError)) {
return fieldError;
}
}
}
return null;
}
isMatchingFieldError()方法支持*号匹配。
protected boolean isMatchingFieldError(String field, FieldError fieldError) {
if (field.equals(fieldError.getField())) {
return true;
}
// Optimization: use charAt and regionMatches instead of endsWith and startsWith (SPR-11304)
int endIndex = field.length() - 1;
return (endIndex >= 0 && field.charAt(endIndex) == '*' &&
(endIndex == 0 || field.regionMatches(0, fieldError.getField(), 0, endIndex)));
}@Override
@Nullable
public Object getFieldValue(String field) {
FieldError fieldError = getFieldError(field);
// Use rejected value in case of error, current field value otherwise.
if (fieldError != null) {
Object value = fieldError.getRejectedValue();
// Do not apply formatting on binding failures like type mismatches.
return (fieldError.isBindingFailure() ? value : formatFieldValue(field, value));
}
else if (getTarget() != null) {
Object value = getActualFieldValue(fixedField(field));
return formatFieldValue(field, value);
}
else {
return this.fieldValues.get(field);
}
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Class<?> getFieldType(@Nullable String field) {
if (getTarget() != null) {
Object value = getActualFieldValue(fixedField(field));
if (value != null) {
return value.getClass();
}
}
return this.fieldTypes.get(field);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object getRawFieldValue(String field) {
return (getTarget() != null ? getActualFieldValue(fixedField(field)) : null);
}上面方法中会用到子类实现方法getActualFieldValue(),formatFieldValue()。看一下在AbstractPropertyBindingResult中的实现:
@Override
@Nullable
public Class<?> getFieldType(@Nullable String field) {
return (getTarget() != null ? getPropertyAccessor().getPropertyType(fixedField(field)) :
super.getFieldType(field));
}
@Override
@Nullable
protected Object getActualFieldValue(String field) {
return getPropertyAccessor().getPropertyValue(field);
}
@Override
protected Object formatFieldValue(String field, @Nullable Object value) {
String fixedField = fixedField(field);
// Try custom editor...
PropertyEditor customEditor = getCustomEditor(fixedField);
if (customEditor != null) {
customEditor.setValue(value);
String textValue = customEditor.getAsText();
// If the PropertyEditor returned null, there is no appropriate
// text representation for this value: only use it if non-null.
if (textValue != null) {
return textValue;
}
}
if (this.conversionService != null) {
// Try custom converter...
TypeDescriptor fieldDesc = getPropertyAccessor().getPropertyTypeDescriptor(fixedField);
TypeDescriptor strDesc = TypeDescriptor.valueOf(String.class);
if (fieldDesc != null && this.conversionService.canConvert(fieldDesc, strDesc)) {
return this.conversionService.convert(value, fieldDesc, strDesc);
}
}
return value;
}getPropertyAccessor()方法是一个抽象方法,由子类实现,看下在 BeanPropertyBindingResult中的实现:
@Override
public final ConfigurablePropertyAccessor getPropertyAccessor() {
if (this.beanWrapper == null) {
this.beanWrapper = createBeanWrapper();
this.beanWrapper.setExtractOldValueForEditor(true);
this.beanWrapper.setAutoGrowNestedPaths(this.autoGrowNestedPaths);
this.beanWrapper.setAutoGrowCollectionLimit(this.autoGrowCollectionLimit);
}
return this.beanWrapper;
}
protected BeanWrapper createBeanWrapper() {
if (this.target == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot access properties on null bean instance '" + getObjectName() + "'");
}
return PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this.target);
}我们已经知道了BindingResult的体系机构了,下面正式说一下DataBinder了。
@Nullable
private final Object target;//需要数据绑定的对象
private final String objectName;//给对象起得名字默认target
@Nullable
private AbstractPropertyBindingResult bindingResult;//数据绑定后的结果
@Nullable
private SimpleTypeConverter typeConverter;//当target!=null时不会用到
private boolean ignoreUnknownFields = true;//忽略target不存在的属性,作用于PropertyAccessor的setPropertyValues()方法
private boolean ignoreInvalidFields = false;//忽略target不能访问的属性
private boolean autoGrowNestedPaths = true;//当嵌套属性为空时,是否可以实例化该属性
private int autoGrowCollectionLimit = DEFAULT_AUTO_GROW_COLLECTION_LIMIT;//对于集合类型容量的最大值
@Nullable
private String[] allowedFields;//允许数据绑定的资源
@Nullable
private String[] disallowedFields;//不允许的
@Nullable
private String[] requiredFields;//数据绑定必须存在的字段
@Nullable
private ConversionService conversionService;//为getPropertyAccessor().setConversionService(conversionService);
@Nullable
private MessageCodesResolver messageCodesResolver;//同bindingResult的
private BindingErrorProcessor bindingErrorProcessor = new DefaultBindingErrorProcessor();
private final List<Validator> validators = new ArrayList<>();//自定义数据校验器BindingErrorProcessor接口定义了两个方法,用于处理不能存在的属性和将PropertyAccessException转换成一个FieldError。
public class DefaultBindingErrorProcessor implements BindingErrorProcessor {
public static final String MISSING_FIELD_ERROR_CODE = "required";
@Override
public void processMissingFieldError(String missingField, BindingResult bindingResult) {
// Create field error with code "required".
String fixedField = bindingResult.getNestedPath() + missingField;
String[] codes = bindingResult.resolveMessageCodes(MISSING_FIELD_ERROR_CODE, missingField);
Object[] arguments = getArgumentsForBindError(bindingResult.getObjectName(), fixedField);
FieldError error = new FieldError(bindingResult.getObjectName(), fixedField, "", true,
codes, arguments, "Field '" + fixedField + "' is required");
bindingResult.addError(error);
}
@Override
public void processPropertyAccessException(PropertyAccessException ex, BindingResult bindingResult) {
// Create field error with the exceptions's code, e.g. "typeMismatch".
String field = ex.getPropertyName();
Assert.state(field != null, "No field in exception");
String[] codes = bindingResult.resolveMessageCodes(ex.getErrorCode(), field);
Object[] arguments = getArgumentsForBindError(bindingResult.getObjectName(), field);
Object rejectedValue = ex.getValue();
if (ObjectUtils.isArray(rejectedValue)) {
rejectedValue = StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(ObjectUtils.toObjectArray(rejectedValue));
}
FieldError error = new FieldError(bindingResult.getObjectName(), field, rejectedValue, true,
codes, arguments, ex.getLocalizedMessage());
error.wrap(ex);
bindingResult.addError(error);
}
protected Object[] getArgumentsForBindError(String objectName, String field) {
String[] codes = new String[] {objectName + Errors.NESTED_PATH_SEPARATOR + field, field};
return new Object[] {new DefaultMessageSourceResolvable(codes, field)};
}
}DataBinder实现了PropertyEditorRegistry接口需要实现接口的方法,采用了代理的方式,bindingResult是BeanPropertyBindingResult的实例,内部会持有一个BeanWrapperImpl,PropertyEditorRegistry接口的实现都是委托了BeanWrapperImpl。
@Override
public void registerCustomEditor(Class<?> requiredType, PropertyEditor propertyEditor) {
getPropertyEditorRegistry().registerCustomEditor(requiredType, propertyEditor);
}
protected PropertyEditorRegistry getPropertyEditorRegistry() {
if (getTarget() != null) {
return getInternalBindingResult().getPropertyAccessor();
}
else {
return getSimpleTypeConverter();
}
}
protected AbstractPropertyBindingResult getInternalBindingResult() {
if (this.bindingResult == null) {
initBeanPropertyAccess();
}
return this.bindingResult;
}
public void initBeanPropertyAccess() {
Assert.state(this.bindingResult == null,"DataBinder is already initialized - call initBeanPropertyAccess before other configuration methods");
this.bindingResult = createBeanPropertyBindingResult();
}
protected AbstractPropertyBindingResult createBeanPropertyBindingResult() {
BeanPropertyBindingResult result = new BeanPropertyBindingResult(getTarget(),getObjectName(), isAutoGrowNestedPaths(), getAutoGrowCollectionLimit());
if (this.conversionService != null) {
result.initConversion(this.conversionService);
}
if (this.messageCodesResolver != null) {
result.setMessageCodesResolver(this.messageCodesResolver);
}
return result;
}BeanPropertyBindingResult。
public class BeanPropertyBindingResult extends AbstractPropertyBindingResult implements Serializable {
@Nullable
private final Object target;
private final boolean autoGrowNestedPaths;
private final int autoGrowCollectionLimit;
@Nullable
private transient BeanWrapper beanWrapper;
public BeanPropertyBindingResult(@Nullable Object target, String objectName) {
this(target, objectName, true, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
public BeanPropertyBindingResult(@Nullable Object target, String objectName, boolean autoGrowNestedPaths, int autoGrowCollectionLimit) {
super(objectName);
this.target = target;
this.autoGrowNestedPaths = autoGrowNestedPaths;
this.autoGrowCollectionLimit = autoGrowCollectionLimit;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public final Object getTarget() {
return this.target;
}
@Override
public final ConfigurablePropertyAccessor getPropertyAccessor() {
if (this.beanWrapper == null) {
this.beanWrapper = createBeanWrapper();
this.beanWrapper.setExtractOldValueForEditor(true);
this.beanWrapper.setAutoGrowNestedPaths(this.autoGrowNestedPaths);
this.beanWrapper.setAutoGrowCollectionLimit(this.autoGrowCollectionLimit);
}
return this.beanWrapper;
}
protected BeanWrapper createBeanWrapper() {
if (this.target == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot access properties on null bean instance '" + getObjectName() + "'");
}
return PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this.target);
}
}核心方法:
public void bind(PropertyValues pvs) {
MutablePropertyValues mpvs = (pvs instanceof MutablePropertyValues) ?
(MutablePropertyValues) pvs : new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
doBind(mpvs);
}
protected void doBind(MutablePropertyValues mpvs) {
checkAllowedFields(mpvs);
checkRequiredFields(mpvs);
applyPropertyValues(mpvs);
}checkAllowedFields()方法不被允许的字段将移除,加入到bindingResult的suppressedFields中,这样就不会对该字段赋值并且记录下来。
protected void checkAllowedFields(MutablePropertyValues mpvs) {
PropertyValue[] pvs = mpvs.getPropertyValues();
for (PropertyValue pv : pvs) {
String field = PropertyAccessorUtils.canonicalPropertyName(pv.getName());
if (!isAllowed(field)) {
mpvs.removePropertyValue(pv);
getBindingResult().recordSuppressedField(field);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Field [" + field + "] has been removed from PropertyValues " +
"and will not be bound, because it has not been found in the list of allowed fields");
}
}
}
}
protected boolean isAllowed(String field) {
String[] allowed = getAllowedFields();
String[] disallowed = getDisallowedFields();
return ((ObjectUtils.isEmpty(allowed) || PatternMatchUtils.simpleMatch(allowed, field)) &&
(ObjectUtils.isEmpty(disallowed) || !PatternMatchUtils.simpleMatch(disallowed, field)));
}checkRequiredFields()方法检查必须的字段是否存在或者可以访问,不满足则加入resultBinding中一个errorCode为required的FieldError对象。
protected void checkRequiredFields(MutablePropertyValues mpvs) {
String[] requiredFields = getRequiredFields();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(requiredFields)) {
Map<String, PropertyValue> propertyValues = new HashMap<>();
PropertyValue[] pvs = mpvs.getPropertyValues();
for (PropertyValue pv : pvs) {
String canonicalName = PropertyAccessorUtils.canonicalPropertyName(pv.getName());
propertyValues.put(canonicalName, pv);
}
for (String field : requiredFields) {
PropertyValue pv = propertyValues.get(field);
boolean empty = (pv == null || pv.getValue() == null);
if (!empty) {
if (pv.getValue() instanceof String) {
empty = !StringUtils.hasText((String) pv.getValue());
}
else if (pv.getValue() instanceof String[]) {
String[] values = (String[]) pv.getValue();
empty = (values.length == 0 || !StringUtils.hasText(values[0]));
}
}
if (empty) {
// Use bind error processor to create FieldError.
getBindingErrorProcessor().processMissingFieldError(field, getInternalBindingResult());
// Remove property from property values to bind:
// It has already caused a field error with a rejected value.
if (pv != null) {
mpvs.removePropertyValue(pv);
propertyValues.remove(field);
}
}
}
}
}applyPropertyValues()方法使用resultBinding对象内的BeanWraperImpl对象完成属性的赋值操作,这个上篇讲过。需要注意的是,在PropertyAccessor的setPropertyValues()方法实现中AbstractPropertyAccessor给出了一个模板方法的实现:
public void setPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, boolean ignoreUnknown, boolean ignoreInvalid)
throws BeansException {
List<PropertyAccessException> propertyAccessExceptions = null;
List<PropertyValue> propertyValues = (pvs instanceof MutablePropertyValues ?
((MutablePropertyValues) pvs).getPropertyValueList() : Arrays.asList(pvs.getPropertyValues()));
for (PropertyValue pv : propertyValues) {
try {
// This method may throw any BeansException, which won't be caught
// here, if there is a critical failure such as no matching field.
// We can attempt to deal only with less serious exceptions.
setPropertyValue(pv);
}
catch (NotWritablePropertyException ex) {
if (!ignoreUnknown) {
throw ex;
}
// Otherwise, just ignore it and continue...
}
catch (NullValueInNestedPathException ex) {
if (!ignoreInvalid) {
throw ex;
}
// Otherwise, just ignore it and continue...
}
catch (PropertyAccessException ex) {
if (propertyAccessExceptions == null) {
propertyAccessExceptions = new LinkedList<>();
}
propertyAccessExceptions.add(ex);
}
}
// If we encountered individual exceptions, throw the composite exception.
if (propertyAccessExceptions != null) {
PropertyAccessException[] paeArray =
propertyAccessExceptions.toArray(new PropertyAccessException[propertyAccessExceptions.size()]);
throw new PropertyBatchUpdateException(paeArray);
}
}setPropertyValue()方法运行的过程中可能会抛出各种PropertyAccessException,每种具体PropertyAccessException子类都有一个errorCode。抛出的这些异常会集中放入PropertyBatchUpdateException中打包发出。这是DataBinder的applyPropertyValues方法内会捕获这个异常,使用BindingErrorProcessor处理这些异常,转换为FieldError对象存储。
protected void applyPropertyValues(MutablePropertyValues mpvs) {
try {
// Bind request parameters onto target object.
getPropertyAccessor().setPropertyValues(mpvs, isIgnoreUnknownFields(), isIgnoreInvalidFields());
}
catch (PropertyBatchUpdateException ex) {
// Use bind error processor to create FieldErrors.
for (PropertyAccessException pae : ex.getPropertyAccessExceptions()) {
getBindingErrorProcessor().processPropertyAccessException(pae, getInternalBindingResult());
}
}
}对象完成数据绑定后可以调用getBindingResult()方法,查看数据绑定后的各种数据。
WebDataBinder在doBind()方法中加入了两个检查方法用于处理参数带前缀“!”和“_”。
@Override
protected void doBind(MutablePropertyValues mpvs) {
checkFieldDefaults(mpvs);//_
checkFieldMarkers(mpvs);//!
super.doBind(mpvs);
}
protected void checkFieldDefaults(MutablePropertyValues mpvs) {
String fieldDefaultPrefix = getFieldDefaultPrefix();
if (fieldDefaultPrefix != null) {
PropertyValue[] pvArray = mpvs.getPropertyValues();
for (PropertyValue pv : pvArray) {
if (pv.getName().startsWith(fieldDefaultPrefix)) {
String field = pv.getName().substring(fieldDefaultPrefix.length());
if (getPropertyAccessor().isWritableProperty(field) && !mpvs.contains(field)) {
mpvs.add(field, pv.getValue());
}
mpvs.removePropertyValue(pv);
}
}
}
}
protected void checkFieldMarkers(MutablePropertyValues mpvs) {
String fieldMarkerPrefix = getFieldMarkerPrefix();
if (fieldMarkerPrefix != null) {
PropertyValue[] pvArray = mpvs.getPropertyValues();
for (PropertyValue pv : pvArray) {
if (pv.getName().startsWith(fieldMarkerPrefix)) {
String field = pv.getName().substring(fieldMarkerPrefix.length());
if (getPropertyAccessor().isWritableProperty(field) && !mpvs.contains(field)) {
Class<?> fieldType = getPropertyAccessor().getPropertyType(field);
mpvs.add(field, getEmptyValue(field, fieldType));
}
mpvs.removePropertyValue(pv);
}
}
}
}
@Nullable
protected Object getEmptyValue(String field, @Nullable Class<?> fieldType) {
return (fieldType != null ? getEmptyValue(fieldType) : null);
}
@Nullable
public Object getEmptyValue(Class<?> fieldType) {
try {
if (boolean.class == fieldType || Boolean.class == fieldType) {
// Special handling of boolean property.
return Boolean.FALSE;
}
else if (fieldType.isArray()) {
// Special handling of array property.
return Array.newInstance(fieldType.getComponentType(), 0);
}
else if (Collection.class.isAssignableFrom(fieldType)) {
return CollectionFactory.createCollection(fieldType, 0);
}
else if (Map.class.isAssignableFrom(fieldType)) {
return CollectionFactory.createMap(fieldType, 0);
}
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Failed to create default value - falling back to null: " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
// Default value: null.
return null;
}ServletRequestDataBinder将bind()方法的 ServletRequest转换成 MutablePropertyValues再由父类做数据绑定。
具体测试请看org.springframework.web.bind.ServletRequestDataBinderTests
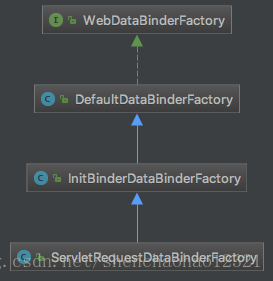
Spring提供了一系列工厂类来创建对应的WebDataBinder对象:
顶级接口定义了创建一个WebDataBinder的方法。
public interface WebDataBinderFactory {
/**
* Create a {@link WebDataBinder} for the given object.
* @param webRequest the current request
* @param target the object to create a data binder for,
* or {@code null} if creating a binder for a simple type
* @param objectName the name of the target object
* @return the created {@link WebDataBinder} instance, never null
* @throws Exception raised if the creation and initialization of the data binder fails
*/
WebDataBinder createBinder(NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable Object target, String objectName) throws Exception;
}关于WebDataBinderFactory的部分我们再介绍到RequestMappingHandlerAdapter的时候再介绍。