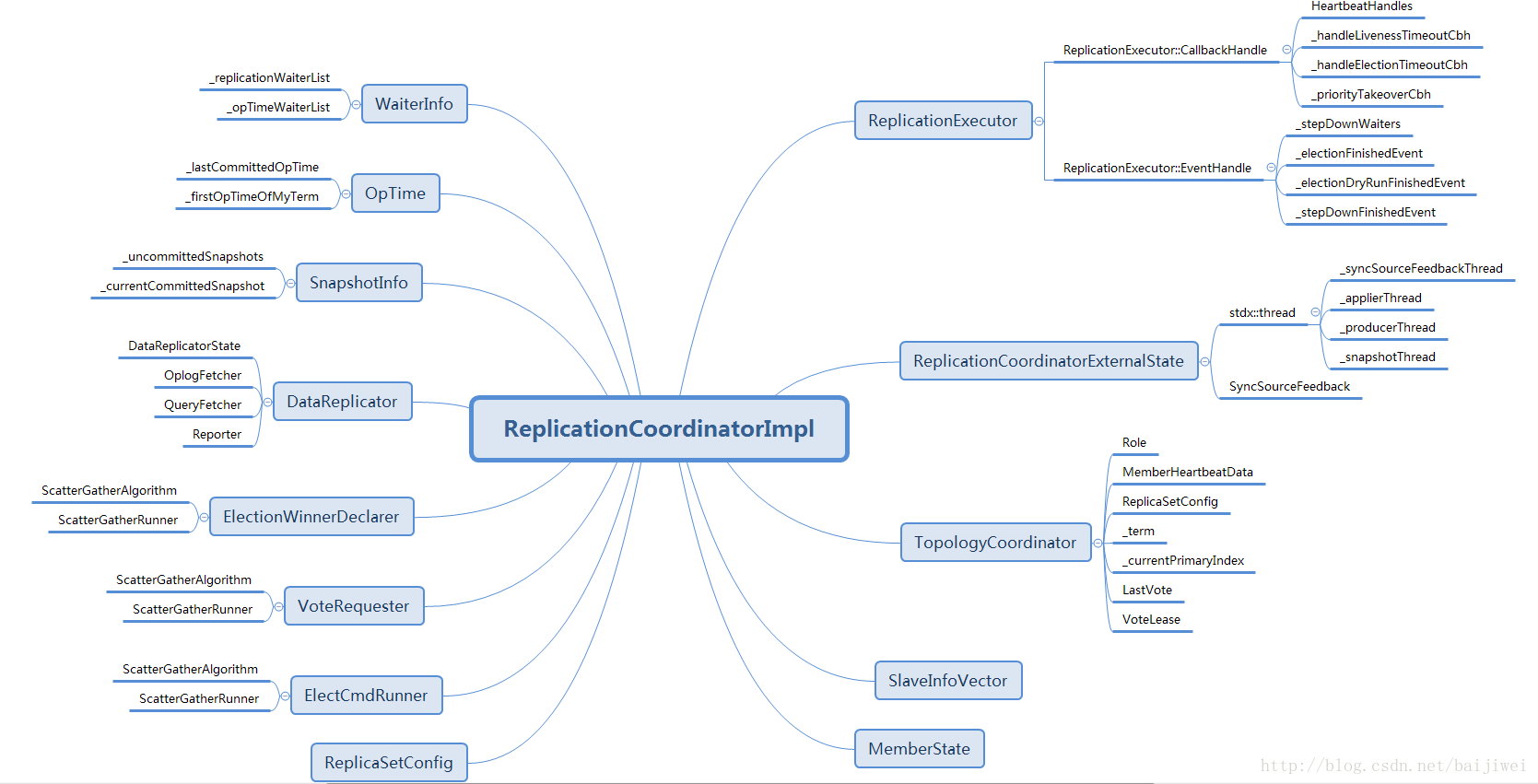
在mongodb的副本集中, 使用了raft协议进行选主、主从切换等来保证副本集的高可用。副本集节点之间通过心跳, 来探测和通知节点的状态, 通过oplog的各个节点的last applied time以及config状态决定采取的处理措施。本文重点介绍一下选主和主从切换这两个方面的实现。
选主
关于选举的代码主要在:src/mongo/db/repl/replication_coordinator_impl_elect_v1.cpp, 我们可以顺着入口函数ReplicationCoordinatorImpl::_startElectSelfV1 来看一下其实现的过程。
在_startElectSelfV1 里面, 它生成了2个event handle:_electionFinishedEvent 和_electionDryRunFinishedEvent, 分别用了记录和通知2个阶段的选举过程, 第一个阶段是dry run, 就是实验性的选举过程, 如果第一个阶段成功了, 才把term数字加1, 进行第二阶段的选举过程。
选举的发送和接受响应, 是通过class VoteRequester 来实现的, 它将replSetRequestVotes命令发送给每一个节点, 并将各个节点的响应在VoteRequester::Algorithm::processResponse里面处理, 计算出赞同的票数, 最终确认是否有超过半数的节点头赞同票。
void ReplicationCoordinatorImpl::_startElectSelfV1() {
auto finishedEvent = _makeEvent();
_electionFinishedEvent = finishedEvent;
auto dryRunFinishedEvent = _makeEvent();
_electionDryRunFinishedEvent = dryRunFinishedEvent;
LoseElectionDryRunGuardV1 lossGuard(this);
long long term = _topCoord->getTerm();
StatusWith<ReplicationExecutor::EventHandle> nextPhaseEvh = _voteRequester->start(
&_replExecutor,
_rsConfig,
_selfIndex,
_topCoord->getTerm(),
true, // dry run
getMyLastDurableOpTime(),
stdx::bind(&ReplicationCoordinatorImpl::_onDryRunComplete, this, term));
}
void ReplicationCoordinatorImpl::_onDryRunComplete(long long originalTerm) {
// 不满足选举条件的, 返回选举失败
// term 更新, 在新的term内开始选举
TopologyCoordinator::UpdateTermResult updateTermResult;
_updateTerm_incallback(originalTerm + 1, &updateTermResult);
invariant(updateTermResult == TopologyCoordinator::UpdateTermResult::kUpdatedTerm);
// Secure our vote for ourself first
_topCoord->voteForMyselfV1();
// Store the vote in persistent storage.
LastVote lastVote;
lastVote.setTerm(originalTerm + 1);
lastVote.setCandidateIndex(_selfIndex);
// 在callback里面把新的last vote的term 和candidateIndex写入文档
auto cbStatus = _replExecutor.scheduleDBWork(
[this, lastVote](const ReplicationExecutor::CallbackArgs& cbData) {
_writeLastVoteForMyElection(lastVote, cbData);
});
}
void ReplicationCoordinatorImpl::_writeLastVoteForMyElection(
LastVote lastVote, const ReplicationExecutor::CallbackArgs& cbData) {
Status status = _externalState->storeLocalLastVoteDocument(cbData.txn, lastVote);
auto cbStatus = _replExecutor.scheduleWork(
[this, lastVote](const ReplicationExecutor::CallbackArgs& cbData) {
// 发出event, dry run阶段结束 _replExecutor.signalEvent(_electionDryRunFinishedEvent);
// 开始新的一轮选举
_startVoteRequester(lastVote.getTerm());
});
}第二轮的选举就比较简单啦, 从ReplicationCoordinatorImpl::_startVoteRequester开始, 通过VoteRequester开始一个选举任务, 返回一个event handle, 经过callback函数:ReplicationCoordinatorImpl::_onVoteRequestComplete来完成选举成功后的declare win election等操作。
void ReplicationCoordinatorImpl::_startVoteRequester(long long newTerm) {
_voteRequester.reset(new VoteRequester);
StatusWith<ReplicationExecutor::EventHandle> nextPhaseEvh = _voteRequester->start(
&_replExecutor,
_rsConfig,
_selfIndex,
_topCoord->getTerm(),
false, // 不是dry run
getMyLastDurableOpTime(),
stdx::bind(&ReplicationCoordinatorImpl::_onVoteRequestComplete, this, newTerm));
}
void ReplicationCoordinatorImpl::_onVoteRequestComplete(long long originalTerm) {
const VoteRequester::Result endResult = _voteRequester->getResult();
// vote result 不成功的部分,比较简单跳过;
// 所有有响应的节点都是up的
// Prevent last committed optime from updating until we finish draining.
_setFirstOpTimeOfMyTerm(
OpTime(Timestamp(std::numeric_limits<int>::max(), 0), std::numeric_limits<int>::max()));
// 这个节点是赢得了选举, 需要通知其他的节点
_performPostMemberStateUpdateAction(kActionWinElection);
}
void ReplicationCoordinatorImpl::_performPostMemberStateUpdateAction(
case kActionWinElection: {
_topCoord->processWinElection(_electionId, getNextGlobalTimestamp());
_isWaitingForDrainToComplete = true;
_externalState->signalApplierToCancelFetcher();
const PostMemberStateUpdateAction nextAction =
_updateMemberStateFromTopologyCoordinator_inlock();
_performPostMemberStateUpdateAction(nextAction);
// Notify all secondaries of the election win.
_scheduleElectionWinNotification();
break;
}
}最后就是, 通知其他的secondary节点,Secondary收到之后,trigger _electionFinishedEvent函数, 使得secondary停止选举, 并且把自己设定为follower, 并且重新开始节点之间的heartbeat;
主从切换
当某一副本集的primary在指定的时间内无法得到heartbeat响应, 从节点会认为primary挂掉了, 就会开始上面的主的过程。
副本集的command处理
在副本集下, 我们有各种command, 例如,re.reconfig, rs.initate等, 这些命令的处理在: src/mongo/db/repl/replset_commands.cpp, 实现过程比较简单, 我们以Reconfig为例子, 来简单分析一下。
class CmdReplSetReconfig : public ReplSetCommand {
public:
virtual Status checkAuthForCommand(ClientBasic* client,
const std::string& dbname,
const BSONObj& cmdObj) {
ActionSet actions;
actions.addAction(ActionType::replSetConfigure);
if (!AuthorizationSession::get(client)->isAuthorizedForActionsOnResource(
ResourcePattern::forClusterResource(), actions)) {
return Status(ErrorCodes::Unauthorized, "Unauthorized");
}
return Status::OK();
}
CmdReplSetReconfig() : ReplSetCommand("replSetReconfig") {}
virtual bool run(OperationContext* txn,
const string&,
BSONObj& cmdObj,
int,
string& errmsg,
BSONObjBuilder& result) {
// 该命令的权限认证
Status status = getGlobalReplicationCoordinator()->checkReplEnabledForCommand(&result);
if (!status.isOK()) {
return appendCommandStatus(result, status);
}
if (cmdObj["replSetReconfig"].type() != Object) {
errmsg = "no configuration specified";
return false;
}
// 根据参数生成 ReplSetReconfigArgs,传递给 processReplSetReconfig
ReplicationCoordinator::ReplSetReconfigArgs parsedArgs;
parsedArgs.newConfigObj = cmdObj["replSetReconfig"].Obj();
parsedArgs.force = cmdObj.hasField("force") && cmdObj["force"].trueValue();
status =
getGlobalReplicationCoordinator()->processReplSetReconfig(txn, parsedArgs, &result);
ScopedTransaction scopedXact(txn, MODE_X);
Lock::GlobalWrite globalWrite(txn->lockState());
WriteUnitOfWork wuow(txn);
if (status.isOK() && !parsedArgs.force) {
// 将命令写入到oplog内, 并更新相关的项
getGlobalServiceContext()->getOpObserver()->onOpMessage(
txn,
BSON("msg"
<< "Reconfig set"
<< "version" << parsedArgs.newConfigObj["version"]));
}
wuow.commit();
return appendCommandStatus(result, status);
}
} cmdReplSetReconfig;总体来讲, 副本集内部实现是比较复杂的, 我们可以参考如下的知识图谱, 来加深自己的理解: