本文转载自:https://www.jianshu.com/p/616924cd07e6
Java注解Annotation用起来很方便,也越来越流行,由于其简单、简练且易于使用等特点,很多开发工具都提供了注解功能,不好的地方就是代码入侵比较严重,所以使用的时候要有一定的选择性。
这篇文章将利用注解,来做一个Bean的数据校验。
下载
http://pan.baidu.com/s/1mgn2AHa
**项目结构 **
定义注解
该注解可以验证成员属性是否为空,长度,提供了几种常见的正则匹配,也可以使用自定义的正则去判断属性是否合法,同时可以为该成员提供描述信息。
定义注解
该注解可以验证成员属性是否为空,长度,提供了几种常见的正则匹配,也可以使用自定义的正则去判断属性是否合法,同时可以为该成员提供描述信息。
package org.xdemo.validation.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target; import org.xdemo.validation.RegexType; /** * 数据验证 * @author Goofy */ @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.FIELD,ElementType.PARAMETER}) public @interface DV { //是否可以为空 boolean nullable() default false; //最大长度 int maxLength() default 0; //最小长度 int minLength() default 0; //提供几种常用的正则验证 RegexType regexType() default RegexType.NONE; //自定义正则验证 String regexExpression() default ""; //参数或者字段描述,这样能够显示友好的异常信息 String description() default ""; } 注解的解析
package org.xdemo.validation.annotation.support;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import org.xdemo.validation.RegexType;
import org.xdemo.validation.annotation.DV;
import org.xdemo.validation.utils.RegexUtils; import org.xdemo.validation.utils.StringUtils; /** * 注解解析 * @author Goofy */ public class ValidateService { private static DV dv; public ValidateService() { super(); } //解析的入口 public static void valid(Object object) throws Exception{ //获取object的类型 Class<? extends Object> clazz=object.getClass(); //获取该类型声明的成员 Field[] fields=clazz.getDeclaredFields(); //遍历属性 for(Field field:fields){ //对于private私有化的成员变量,通过setAccessible来修改器访问权限 field.setAccessible(true); validate(field,object); //重新设置会私有权限 field.setAccessible(false); } } public static void validate(Field field,Object object) throws Exception{ String description; Object value; //获取对象的成员的注解信息 dv=field.getAnnotation(DV.class); value=field.get(object); if(dv==null)return; description=dv.description().equals("")?field.getName():dv.description(); /*************注解解析工作开始******************/ if(!dv.nullable()){ if(value==null||StringUtils.isBlank(value.toString())){ throw new Exception(description+"不能为空"); } } if(value.toString().length()>dv.maxLength()&&dv.maxLength()!=0){ throw new Exception(description+"长度不能超过"+dv.maxLength()); } if(value.toString().length()<dv.minLength()&&dv.minLength()!=0){ throw new Exception(description+"长度不能小于"+dv.minLength()); } if(dv.regexType()!=RegexType.NONE){ switch (dv.regexType()) { case NONE: break; case SPECIALCHAR: if(RegexUtils.hasSpecialChar(value.toString())){ throw new Exception(description+"不能含有特殊字符"); } break; case CHINESE: if(RegexUtils.isChinese2(value.toString())){ throw new Exception(description+"不能含有中文字符"); } break; case EMAIL: if(!RegexUtils.isEmail(value.toString())){ throw new Exception(description+"地址格式不正确"); } break; case IP: if(!RegexUtils.isIp(value.toString())){ throw new Exception(description+"地址格式不正确"); } break; case NUMBER: if(!RegexUtils.isNumber(value.toString())){ throw new Exception(description+"不是数字"); } break; case PHONENUMBER: if(!RegexUtils.isPhoneNumber(value.toString())){ throw new Exception(description+"不是数字"); } break; default: break; } } if(!dv.regexExpression().equals("")){ if(value.toString().matches(dv.regexExpression())){ throw new Exception(description+"格式不正确"); } } /*************注解解析工作结束******************/ } } 用到的几个类
package org.xdemo.validation;
/**
* 常用的数据类型枚举
* @author Goofy
*
*/
public enum RegexType { NONE, SPECIALCHAR, CHINESE, EMAIL, IP, NUMBER, PHONENUMBER; } 其中正则验证类和字符串工具类请参考以下链接:
使用方法
package org.xdemo.validation.test;
import org.xdemo.validation.RegexType;
import org.xdemo.validation.annotation.DV;
public class User { @DV(description="用户名",minLength=6,maxLength=32,nullable=false) private String userName; private String password; @DV(description="邮件地址",nullable=false,regexType=RegexType.EMAIL) private String email; public User(){} public User(String userName, String password, String email) { super(); this.userName = userName; this.password = password; this.email = email; } public String getUserName() { return userName; } public void setUserName(String userName) { this.userName = userName; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public String getEmail() { return email; } public void setEmail(String email) { this.email = email; } } 测试代码
import org.xdemo.validation.annotation.support.ValidateService;
/**
* @author Goofy
*/
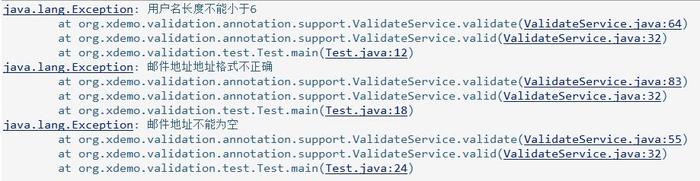
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args){ User user=new User("张三", "xdemo.org", "[email protected]"); try { ValidateService.valid(user); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } user=new User("zhangsan","xdemo.org","xxx@"); try { ValidateService.valid(user); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } user=new User("zhangsan","xdemo.org",""); try { ValidateService.valid(user); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } 运行效果
作者:会编程的小蚂蚁
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/616924cd07e6
來源:简书
简书著作权归作者所有,任何形式的转载都请联系作者获得授权并注明出处。