
英文 | https://javascript.plainenglish.io/tiktok-interview-4-front-end-questions-youll-be-interested-to-know-about-0c00d4154786
最近,我的好朋友正在换工作,在网上收到了很多offer。
其中之一就有来自一家名为 TikTok 公司的Offer,你可能非常熟悉该公司,也有可能不是很熟悉它。
朋友在面试的时候,他们让我的朋友当场写代码来实现4个复杂方法的功能。
1. 尝试实现Promise.all API
Promise.all() 方法将可迭代的 Promise 作为输入,并返回单个 Promise,该 Promise 解析为输入 Promise 结果的数组。
当所有输入的 Promise 都已解决,或者输入的可迭代对象不包含 Promise 时,返回的 Promise 将得到解决。
它会在任何输入Promise拒绝或非承诺抛出错误时立即拒绝,并将拒绝第一个拒绝消息/错误。
const promise1 = Promise.resolve(3);
const promise2 = 42;
const promise3 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(resolve, 100, 'foo');
});
Promise.all([promise1, promise2, promise3]).then((values) => {
console.log(values);
});
// expected output: Array [3, 42, "foo"]现在,自己实现了一个
Promise.myAll = (promises) => {
return new Promise((rs, rj) => {
// counter
let count = 0
// Storage results
let result = []
const len = promises.length
if (len === 0) {
return rs([])
}
promises.forEach((p, i) => {
// Some array items may not be Promise and need to be converted manually
Promise.resolve(p).then((res) => {
count += 1
// Collect the return value of each Promise
result[ i ] = res
// Set the value of Promise to result, when all Promises are successful
if (count === len) {
rs(result)
}
// As long as one promise fails, the result is failure
}).catch(rj)
})
})
}进行测试如下:
const p1 = Promise.resolve(1)
const p2 = new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve(2), 1000)
})
const p3 = new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve(3), 3000)
})
const p4 = Promise.reject('err4')
const p5 = Promise.reject('err5')
// 1. All promise succeeded
const p11 = Promise.myAll([ p1, p2, p3 ])
.then(console.log) // [ 1, 2, 3 ]
.catch(console.log)
// 2. One promise failed
const p12 = Promise.myAll([ p1, p2, p4 ])
.then(console.log)
.catch(console.log) // err4
// 3. Two promises failed. The final output is err4. The return value of the first failure
const p13 = Promise.myAll([ p1, p4, p5 ])
.then(console.log)
.catch(console.log) // err42.设计一个可以设置过期日期的localstorage API
localstorage不会像cookie一样自动过期,所以过期时间需要自己维护。
我的思路是:
使用setItem时,保存过期时间。使用getItem时,将时间与当前时间进行比较,如果大于当前时间,则返回该值,否则,需要通过removeItem移除该值,并返回null。
const storage = {
prefix: 'fatFish',
timeSign: '|fatFish|',
setItem (key, value, time) {
// Protect the key from being overwritten
key = `${this.prefix}${key}`
// There is no incoming time, the default expiration time is one month, of course, it can be other times or not set
time = time ? new Date(time).getTime() : Date.now() + 24 * 60 * 60 * 31 * 1000
// Constructs a string of the form 1646094676134|fatFish|"Front-end Fat Fish"
window.localStorage.setItem(key, `${time}${this.timeSign}${JSON.stringify(value)}`)
},
getItem (key) {
key = `${this.prefix}${key}`
let value = window.localStorage.getItem(key)
if (value) {
let index = value.indexOf(this.timeSign)
let time = +value.slice(0, index)
// Determine if time has expired
if (time > Date.now()) {
value = JSON.parse(value.slice(index + this.timeSign.length))
} else {
value = null
window.localStorage.removeItem(key)
}
}
return value
}
}现在,进行测试
storage.setItem('name', 'front-end-fat-head', Date.now() + 100 * 1000) // fatFishname 1646095230191|fatFish|"front-end-fat-head"
storage.getItem('name') // front-end-fat-head
// 100s later
storage.getItem('name') // null
storage.setItem('obj', { name: 'front-end-fat-head', age: 100 }, Date.now() + 100 * 1000) // fatFishobj 1646095311366|fatFish|{"name":"front-end-fat-head","age":100}
storage.getItem('obj') // {name: 'front-end-fat-head', age: 100}基本上符合题主的要求。当然,我们也可以处理异常情况,比如空间已满、设置错误等。
3.找到两个节点最近的公共父节点,包括节点本身
介绍:
oNode1 和 oNode2 位于同一文档中,并且不会是同一节点。
function findCommonParent(oNode1, oNode2) {
// fill here
}相信看到这道题你一定会用递归,但是没有明确的思路。
这个时候不要紧张。从问题中找出更有效的信息,尽量用更多的笔来画(如果是现场面试,记得只带一支铅笔,有时候画多了想法就出来了)。
1.1 两个节点处于同一级别
让我们尝试画出这两个节点之间可能的关系。如下图所示,它们的直接父节点就是答案。

1.2 两个节点互为祖先
oNode1 是目标节点。当然,反过来也是一样的。oNode2 也可以是 oNode1 的祖先。
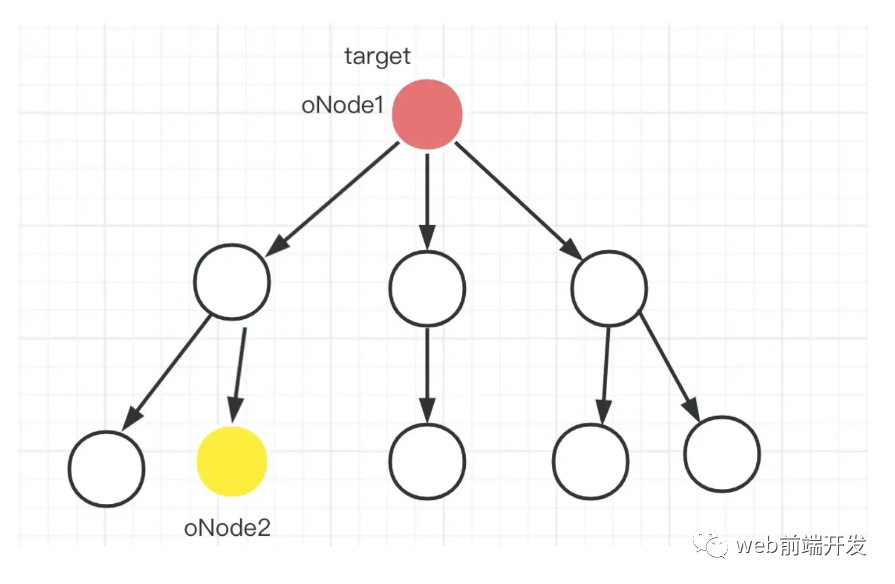
1.3 两个节点之间没有关系
如下图所示,两个节点之间的距离很远,看似没有任何关系,但从其中任意一个向上查找,肯定能找到包含oNode1或oNode2的点。
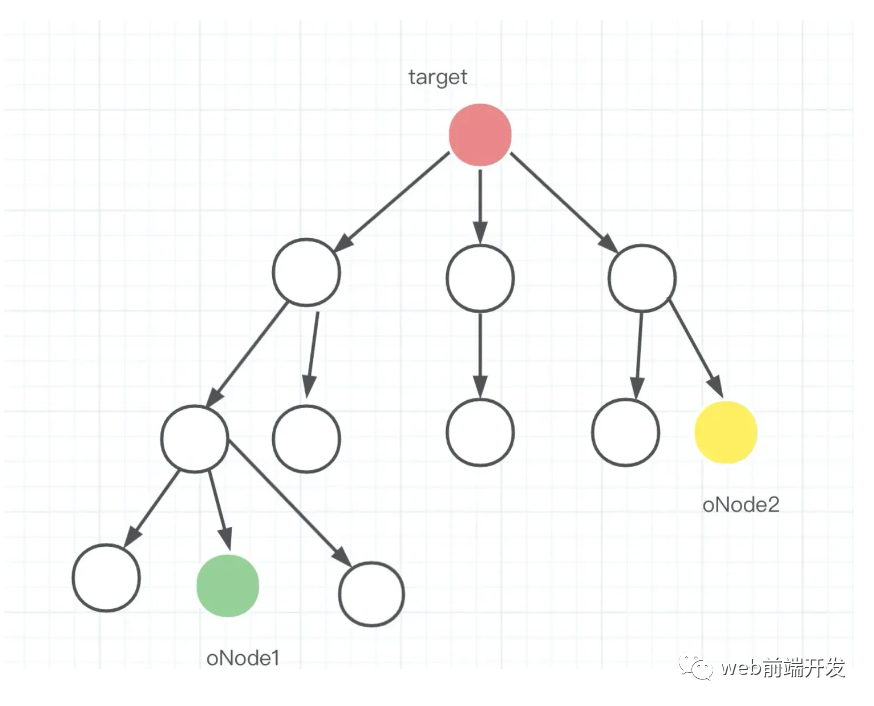
1.4 递归实现版本
根据上面的分析,相信你很快就能写出下面的代码。
function findCommonParent(oNode1, oNode2) {
// Cases 1 and 2
if (oNode1.contains(oNode2)) {
return oNode1
// Cases 1 and 2
} else if (oNode2.contains(oNode1)) {
return oNode2
} else {
// Case 3, if you look up one of the nodes, you will find a common ancestor node
return findCommonParent(oNode1.parentNode, oNode2)
}
}1.5 遍历实现版本
递归很好理解,仅仅通过遍历就可以实现吗?事实上,递归问题往往可以通过遍历来解决。
function findCommonParent (oNode1, oNode2) {
// Using oNode2 here is the same
// If a node contains another node, return directly, otherwise keep looking up
while (!oNode1.contains(oNode2)) {
oNode1 = oNode1.parentNode
}
return oNode1
}4.使用reduce实现map功能
这个问题会比较简单,我们直接写代码吧。
Input: [1, 2, 3]
Output: [2, 4, 6]Array.prototype.map2 = function (callback, ctx = null) {
if (typeof callback !== 'function') {
throw('callback must be a function')
}
return this.reduce((result, cur, index, array) => {
return result.concat(callback.call(ctx, cur, index, array))
}, [])
}
let arr = [ 1, 2 ]
let arr2 = arr.map2(function (it, i, array) {
console.log(it, i, array, this)
return it * 2
}, { name: 'fatfish' })
console.log(arr2)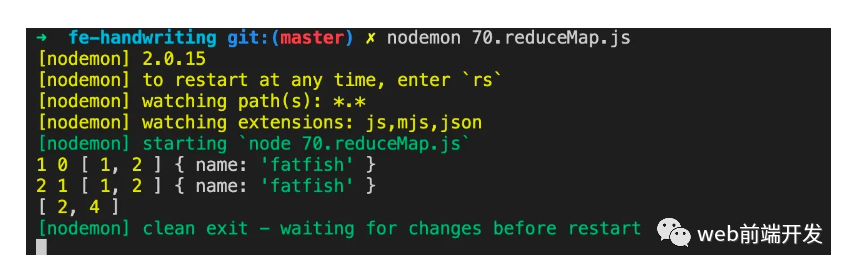
最后
看到这里,我想你已经明白了,如果还不明白的话,那就是我还没有说清楚,下次,我争取说的更加清楚一些。当然,如果你觉得这个内容对你有帮助的话,请记得点赞我,关注我,以便学习能够内容,同时,也不会错过我们的优质内容。
最后,感谢你的阅读,祝编程愉快!