一、Pyecharts简介和安装
1、简介
Echarts 是一个由百度开源的数据可视化,凭借着良好的交互性,精巧的图表设计,得到了众多开发者的认可。而 Python 是一门富有表达力的语言,很适合用于数据处理。当数据分析遇上数据可视化时,pyecharts 诞生了。
-
简洁的 API 设计,使用如丝滑般流畅,支持链式调用
-
囊括了 30+ 种常见图表,应有尽有
-
支持主流 Notebook 环境,Jupyter Notebook 和 JupyterLab
-
可轻松集成至 Flask,Sanic,Django 等主流 Web 框架
-
高度灵活的配置项,可轻松搭配出精美的图表
-
详细的文档和示例,帮助开发者更快的上手项目
-
多达 400+ 地图文件,并且支持原生百度地图,为地理数据可视化提供强有力的支持
pyecharts版本v0.5.x 和 v1 间不兼容,v1 是一个全新的版本,语法也有很大不同。
2、安装
安装 pyecharts
pip install pyecharts -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple --trusted-host pypi.douban.com
import pyecharts
print(pyecharts.__version__) # 查看pyecharts版本
安装相关的地图扩展包
pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple echarts-countries-pypkg # 全球国家地图
pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple echarts-china-provinces-pypkg # 中国省级地图
pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple echarts-china-cities-pypkg # 中国市级地图
pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple echarts-china-counties-pypkg # 中国县区级地图
二、绘制地理图表
1、世界地图—数据可视化
利用 Starbucks.csv 中的数据,首先计算每个国家(Country)对应的门店数量,然后使用世界地图表示星巴克门面店在全球的分布。
import pandas as pd
from pyecharts.charts import Map
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.globals import ThemeType, CurrentConfig
CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/'
# 用pandas读取csv文件里的数据
df = pd.read_csv("Starbucks.csv")['Country']
data = df.value_counts()
datas = [(i, int(j)) for i, j in zip(data.index, data.values)]
# 实例化一个Map对象
map_ = Map(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(theme=ThemeType.PURPLE_PASSION))
# 世界地图
map_.add("门店数量", data_pair=datas, maptype="world")
map_.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False)) # 不显示label
map_.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="星巴克门店数量在全球分布", pos_left='40%', pos_top='10'), # 调整title位置
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(is_show=False),
visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts(max_=13608, min_=1, is_piecewise=True,
pieces=[{
"max": 9, "min": 1, "label": "1-9", "color": "#00FFFF"}, # 分段 添加图例注释和颜色
{
"max": 99, "min": 10, "label": "10-99", "color": "#A52A2A"},
{
"max": 499, "min": 100, "label": "100-499", "color": "#0000FF "},
{
"max": 999, "min": 500, "label": "500-999", "color": "#FF00FF"},
{
"max": 2000, "min": 1000, "label": "1000-2000", "color": "#228B22"},
{
"max": 3000, "min": 2000, "label": "2000-3000", "color": "#FF0000"},
{
"max": 20000, "min": 10000, "label": ">=10000", "color": "#FFD700"}
])
)
# 渲染在网页上 有交互性
map_.render('星巴克门店在全球的分布.html')
运行效果如下:

2、国家地图—数据可视化
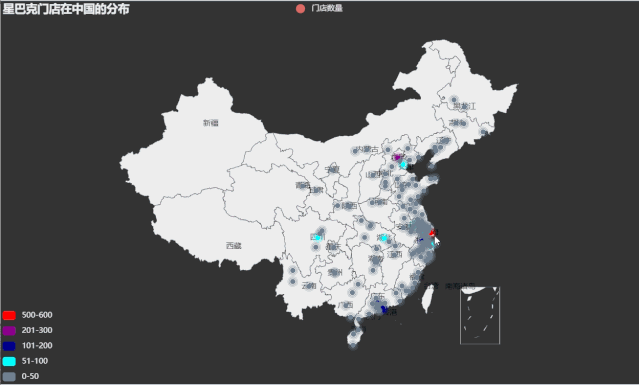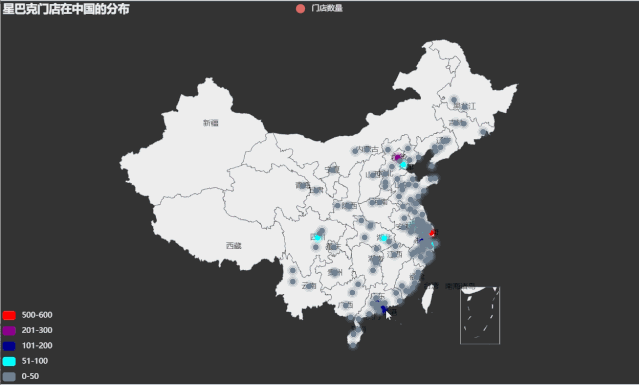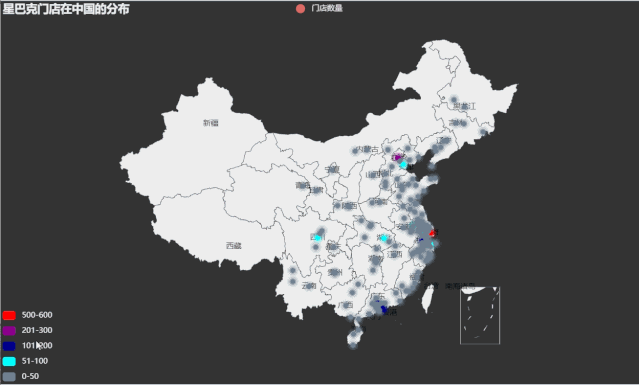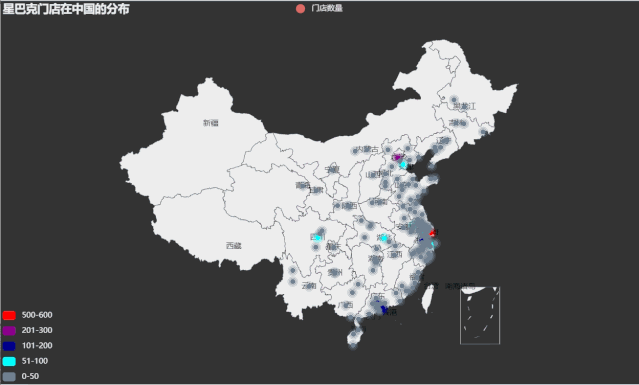
涟漪散点图
利用china.csv 中的数据,首先计算每个城市(City)对应的门店数量,然后使用 pyecharts包内 Geo 模块绘制星巴克门面店在中国分布的涟漪散点地图。
import pandas as pd
from pyecharts.globals import ThemeType, CurrentConfig, GeoType
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Geo
CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/'
# pandas读取csv文件数据
df = pd.read_csv("china.csv")['City']
data = df.value_counts()
datas = [(i, int(j)) for i, j in zip(data.index, data.values)]
print(datas)
geo = Geo(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(width='1000px', height='600px', theme=ThemeType.DARK))
geo.add_schema(maptype='china', label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=True)) # 显示label 省名
geo.add('门店数量', data_pair=datas, type_=GeoType.EFFECT_SCATTER, symbol_size=8)
geo.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False))
geo.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title='星巴克门店在中国的分布'),
visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts(max_=550, is_piecewise=True,
pieces=[{
"max": 50, "min": 0, "label": "0-50", "color": "#708090"}, # 分段 添加图例注释 和颜色
{
"max": 100, "min": 51, "label": "51-100", "color": "#00FFFF"},
{
"max": 200, "min": 101, "label": "101-200", "color": "#00008B"},
{
"max": 300, "min": 201, "label": "201-300", "color": "#8B008B"},
{
"max": 600, "min": 500, "label": "500-600", "color": "#FF0000"},
])
)
geo.render("星巴克门店在中国的分布.html")
运行效果如下:
动态轨迹图
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Geo
from pyecharts.globals import ChartType, SymbolType, CurrentConfig
CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/'
# 链式调用
c = (
Geo()
.add_schema(
maptype="china",
itemstyle_opts=opts.ItemStyleOpts(color="#323c48", border_color="#111"),
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=True)
)
.add(
"",
[("广州", 55), ("北京", 66), ("杭州", 77), ("重庆", 88), ('成都', 100), ('海口', 80)],
type_=ChartType.EFFECT_SCATTER,
color="white",
)
.add(
"",
[("广州", "上海"), ("广州", "北京"), ("广州", "杭州"), ("广州", "重庆"),
('成都', '海口'), ('海口', '北京'), ('海口', '重庆'), ('重庆', '上海')
],
type_=ChartType.LINES,
effect_opts=opts.EffectOpts(
symbol=SymbolType.ARROW, symbol_size=6, color="blue"
),
linestyle_opts=opts.LineStyleOpts(curve=0.2),
)
.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False))
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="动态轨迹图"))
.render("geo_lines_background.html")
)
运行效果如下:

3、省市地图—数据可视化
热力图
代码如下:
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Geo
from pyecharts.faker import Faker
from pyecharts.globals import GeoType, CurrentConfig
CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/'
c = (
Geo()
.add_schema(maptype="广东", label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=True))
.add(
"热力图",
[list(z) for z in zip(Faker.guangdong_city, Faker.values())],
type_=GeoType.HEATMAP,
)
.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=True))
.set_global_opts(
visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts(), title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Geo-广东地图")
)
.render("geo_guangdong.html")
)
运行效果如下:
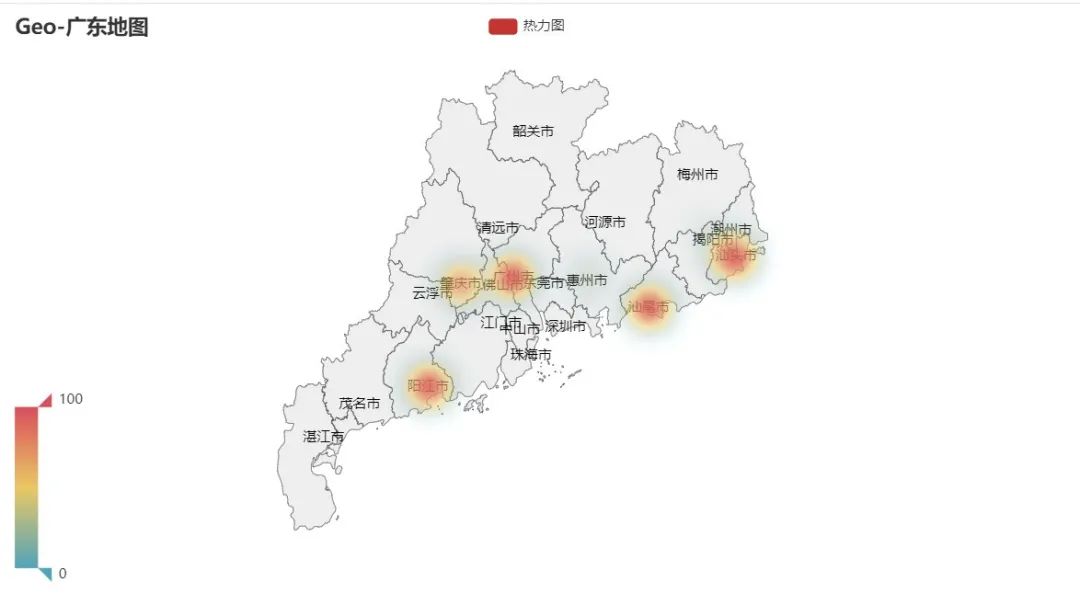
在地图上批量添加地址、经纬度数据,地理数据可视化
代码如下:
import pandas as pd # 导入数据分析模块
from pyecharts.charts import Geo # 导入地理信息处理模块
from pyecharts import options as opts # 配置
from pyecharts.globals import GeoType, CurrentConfig, ThemeType
CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/'
df = pd.read_excel("hotel.xlsx")
# 获取 地点 经纬度信息
geo_sight_coord = {
df.iloc[i]['酒店地址']: [df.iloc[i]['经度'], df.iloc[i]['纬度']] for i in range(len(df))}
data = [(df['酒店地址'][j], f"{int(df['最低价'][j])}元(最低价)") for j in range(len(df))]
# print(data)
# print(geo_sight_coord)
g = Geo(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(theme=ThemeType.PURPLE_PASSION, width="1000px", height="600px"))
g.add_schema(maptype="北京")
for k, v in list(geo_sight_coord.items()):
# 添加地址、经纬度数据
g.add_coordinate(k, v[0], v[1])
# 涟漪散点图
g.add("", data_pair=data, type_=GeoType.EFFECT_SCATTER, symbol_size=6)
g.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False))
g.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="北京-酒店地址分布"))
g.render("酒店地址分布.html")
运行效果如下:

三、柱形图
代码如下:
from pyecharts.charts import Bar
from pyecharts.faker import Faker
from pyecharts.globals import ThemeType, CurrentConfig
from pyecharts import options as opts
CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/'
# 链式调用
c = (
Bar(
init_opts=opts.InitOpts( # 初始配置项
theme=ThemeType.MACARONS,
animation_opts=opts.AnimationOpts(
animation_delay=1000, animation_easing="cubicOut" # 初始动画延迟和缓动效果
))
)
.add_xaxis(xaxis_data=Faker.choose()) # x轴
.add_yaxis(series_name="商家A", yaxis_data=Faker.values()) # y轴
.add_yaxis(series_name="商家B", yaxis_data=Faker.values()) # y轴
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title='标题', subtitle='副标题', # 标题配置和调整位置
title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(
font_family='SimHei', font_size=25, font_weight='bold', color='red',
), pos_left="90%", pos_top="10",
),
xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(name='x轴名称', axislabel_opts=opts.LabelOpts(rotate=45)), # 设置x名称和Label rotate解决标签名字过长使用
yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(name='y轴名称'),
)
.render("bar_001.html")
)
运行效果如下:
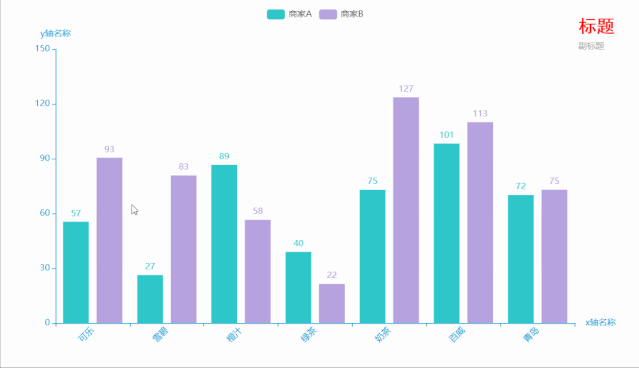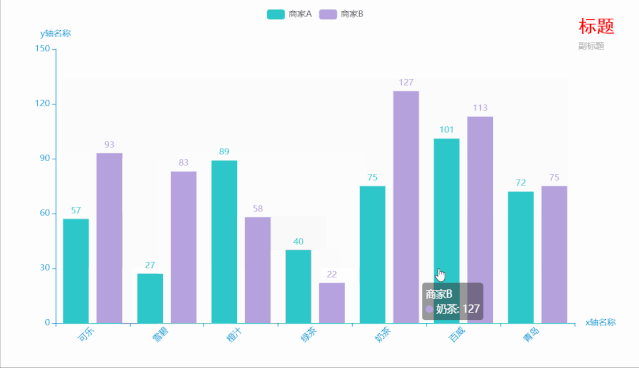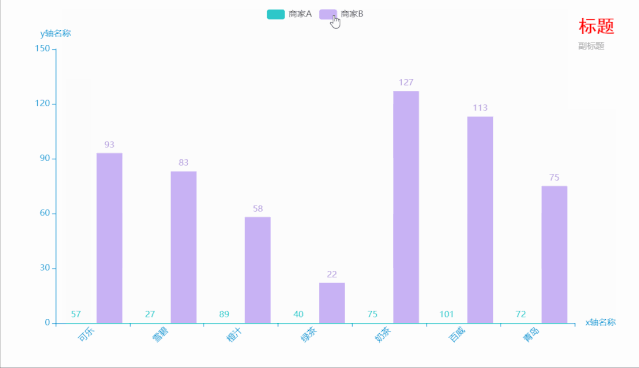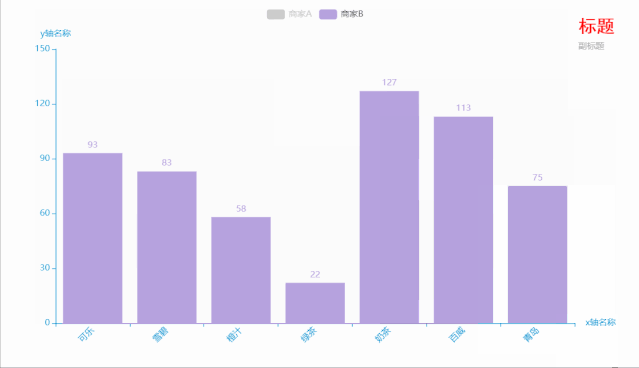
代码如下:
import pandas as pd
import collections
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Bar
from pyecharts.globals import ThemeType, CurrentConfig
import random
CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/'
df = pd.read_excel("hotel.xlsx")
area = list(df['酒店地址'])
area_list = []
for i in area:
_index = i.find("区")
# 字符串切片得到行政区名
i = i[:_index + 1]
area_list.append(i)
area_count = collections.Counter(area_list)
area_dic = dict(area_count)
# 两个列表对应 行政区 对应的酒店数量
area = [x for x in list(area_dic.keys())][0:10]
nums = [y for y in list(area_dic.values())][:10]
# 定制风格
bar = Bar(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(theme=ThemeType.MACARONS))
colors = ['red', '#0000CD', '#000000', '#008000', '#FF1493', '#FFD700', '#FF4500', '#00FA9A', '#191970', '#9932CC']
random.shuffle(colors)
# 配置y轴数据 Baritem
y = []
for i in range(10):
y.append(
opts.BarItem(
value=nums[i],
itemstyle_opts=opts.ItemStyleOpts(color=colors[i]) # 设置每根柱子的颜色
)
)
bar.add_xaxis(xaxis_data=area)
bar.add_yaxis("酒店数量", yaxis_data=y)
bar.set_global_opts(xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(
name='行政区',
axislabel_opts=opts.LabelOpts(rotate=45)
),
yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(
name='酒店数量', min_=0, max_=330, # y轴刻度的最小值 最大值
),
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(
title="行政区-酒店数量",
title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(
font_family="KaiTi", font_size=25, color="black"
)
))
# 标记最大值 最小值 平均值 标记平均线
bar.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False),
markpoint_opts=opts.MarkPointOpts(
data=[
opts.MarkPointItem(type_="max", name="最大值"),
opts.MarkPointItem(type_="min", name="最小值"),
opts.MarkPointItem(type_="average", name="平均值")]),
markline_opts=opts.MarkLineOpts(
data=[
opts.MarkLineItem(type_="average", name="平均值")]))
bar.render("行政区酒店数量最多的Top10.html")
运行效果如下:
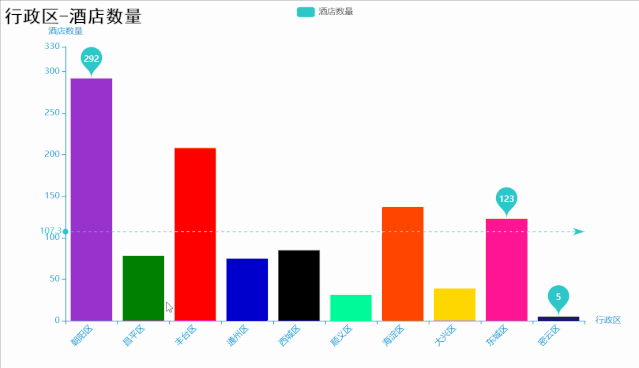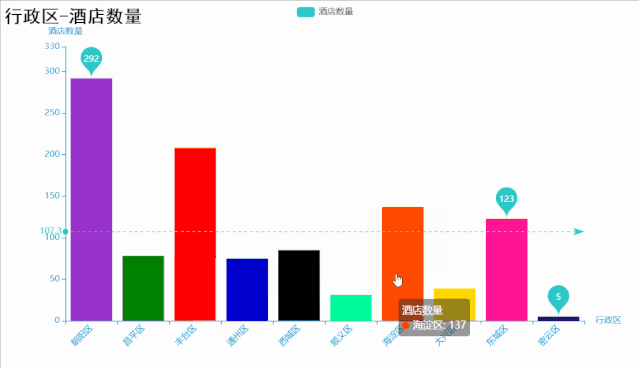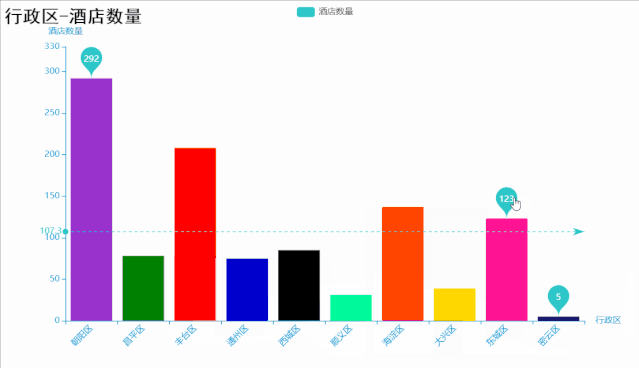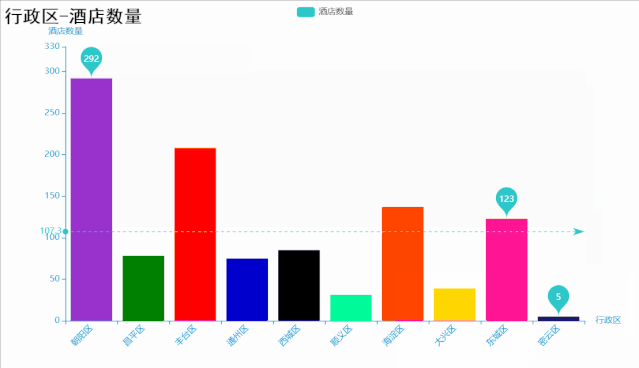
代码如下:
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Bar
from pyecharts.faker import Faker
from pyecharts.globals import ThemeType, CurrentConfig
CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/'
c = (
Bar(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(theme=ThemeType.DARK))
.add_xaxis(xaxis_data=Faker.days_attrs)
.add_yaxis("商家A", yaxis_data=Faker.days_values)
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Bar-DataZoom(slider+inside)"),
datazoom_opts=[opts.DataZoomOpts(), opts.DataZoomOpts(type_="inside")],
)
.render("bar_datazoom_both.html")
)
运行效果如下:

四、饼图
代码如下:
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Pie
from pyecharts.faker import Faker
from pyecharts.globals import CurrentConfig
CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/'
c = (
Pie()
.add(
"",
[list(z) for z in zip(Faker.choose(), Faker.values())],
# 饼图的中心(圆心)坐标,数组的第一项是横坐标,第二项是纵坐标
# 默认设置成百分比,设置成百分比时第一项是相对于容器宽度,第二项是相对于容器高度
center=["35%", "50%"],
)
.set_colors(["blue", "green", "yellow", "red", "pink", "orange", "purple"]) # 设置颜色
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Pie-设置颜色-调整图例位置"),
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(type_="scroll", pos_left="70%", orient="vertical"), # 调整图例位置
)
.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(formatter="{b}: {c}"))
.render("pie_set_color.html")
)
运行效果如下:
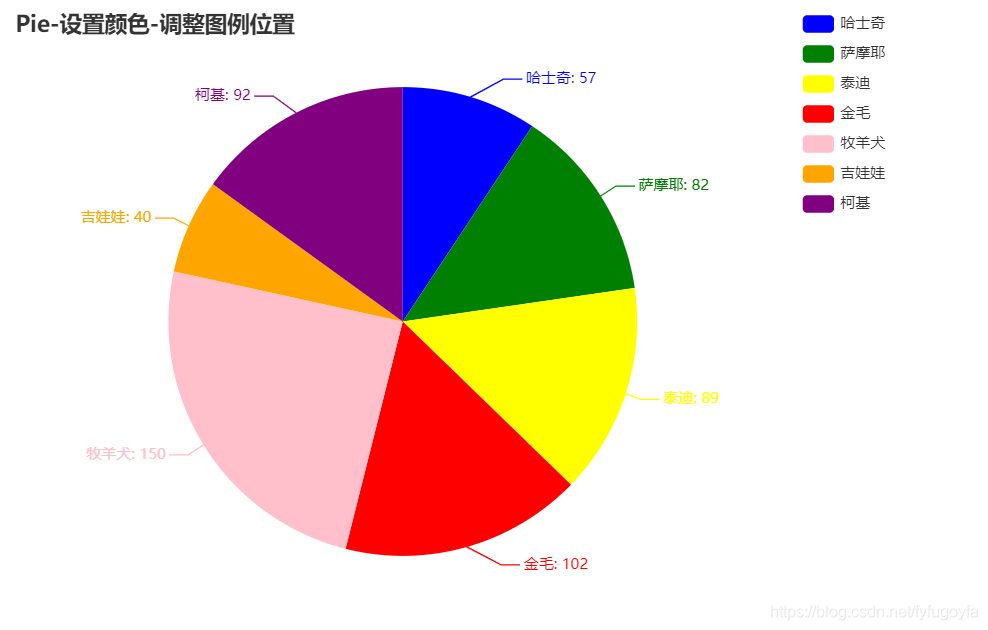
代码如下:
import pyecharts.options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Pie
from pyecharts.globals import CurrentConfig
CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/'
x_data = ["深度学习", "数据分析", "Web开发", "爬虫", "图像处理"]
y_data = [688, 888, 560, 388, 480]
data_pair = [list(z) for z in zip(x_data, y_data)]
data_pair.sort(key=lambda x: x[1])
c = (
# 宽 高 背景颜色
Pie(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(width="1200px", height="800px", bg_color="#2c343c"))
.add(
series_name="学习方向", # 系列名称
data_pair=data_pair, # 系列数据项,格式为 [(key1, value1), (key2, value2)]
rosetype="radius", # radius:扇区圆心角展现数据的百分比,半径展现数据的大小
radius="55%", # 饼图的半径
center=["50%", "50%"], # 饼图的中心(圆心)坐标,数组的第一项是横坐标,第二项是纵坐标
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False, position="center"), # 标签配置项
)
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(
title="Customized Pie",
pos_left="center",
pos_top="20",
title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color="#fff"),
),
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(is_show=False),
)
.set_series_opts(
tooltip_opts=opts.TooltipOpts(
trigger="item", formatter="{a} <br/>{b}: {c} ({d}%)" # 'item': 数据项图形触发,主要在散点图,饼图等无类目轴的图表中使用
),
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(color="rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.3)"),
)
.render("customized_pie.html")
)
运行效果如下:
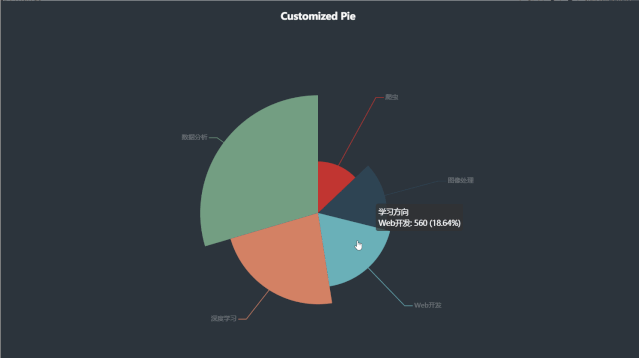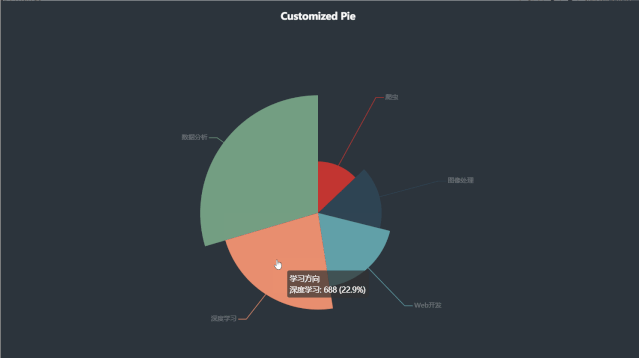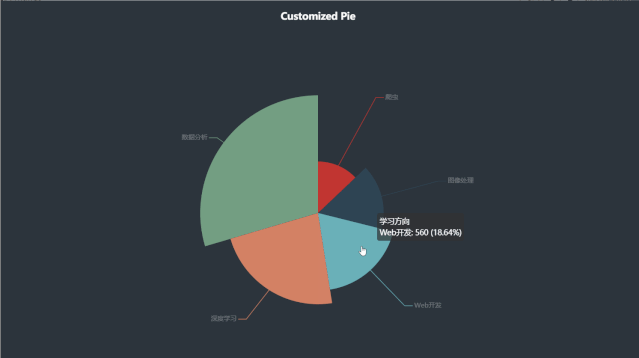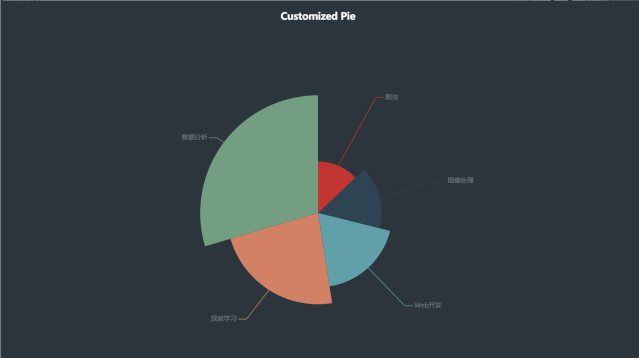
五、环图
代码如下:
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Pie
from pyecharts.faker import Faker
from pyecharts.globals import CurrentConfig
CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/'
c = (
Pie()
.add(
"",
[list(z) for z in zip(Faker.choose(), Faker.values())],
# 饼图的半径,数组的第一项是内半径,第二项是外半径
# 默认设置成百分比,相对于容器高宽中较小的一项的一半
radius=["40%", "60%"],
)
.set_colors(["blue", "green", " #800000", "red", "#000000", "orange", "purple"])
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Pie-Radius"),
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(orient="vertical", pos_top="15%", pos_left="2%"),
)
.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(formatter="{b}: {c}"))
.render("pie_radius.html")
)
运行效果如下:

代码如下:
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Pie
from pyecharts.faker import Faker
from pyecharts.globals import CurrentConfig
CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/'
c = (
Pie()
.add(
"",
[list(z) for z in zip(Faker.choose(), Faker.values())],
radius=["40%", "60%"],
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(
position="outside",
formatter="{a|{a}}{abg|}\n{hr|}\n {b|{b}: }{c} {per|{d}%} ",
background_color="#eee",
border_color="#aaa",
border_width=1,
border_radius=4,
rich={
"a": {
"color": "#999", "lineHeight": 22, "align": "center"},
"abg": {
"backgroundColor": "#e3e3e3",
"width": "100%",
"align": "right",
"height": 22,
"borderRadius": [4, 4, 0, 0],
},
"hr": {
"borderColor": "#aaa",
"width": "100%",
"borderWidth": 0.5,
"height": 0,
},
"b": {
"fontSize": 16, "lineHeight": 33},
"per": {
"color": "#eee",
"backgroundColor": "#334455",
"padding": [2, 4],
"borderRadius": 2,
},
},
),
)
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Pie-富文本示例"))
.render("pie_rich_label.html")
)
运行效果如下:
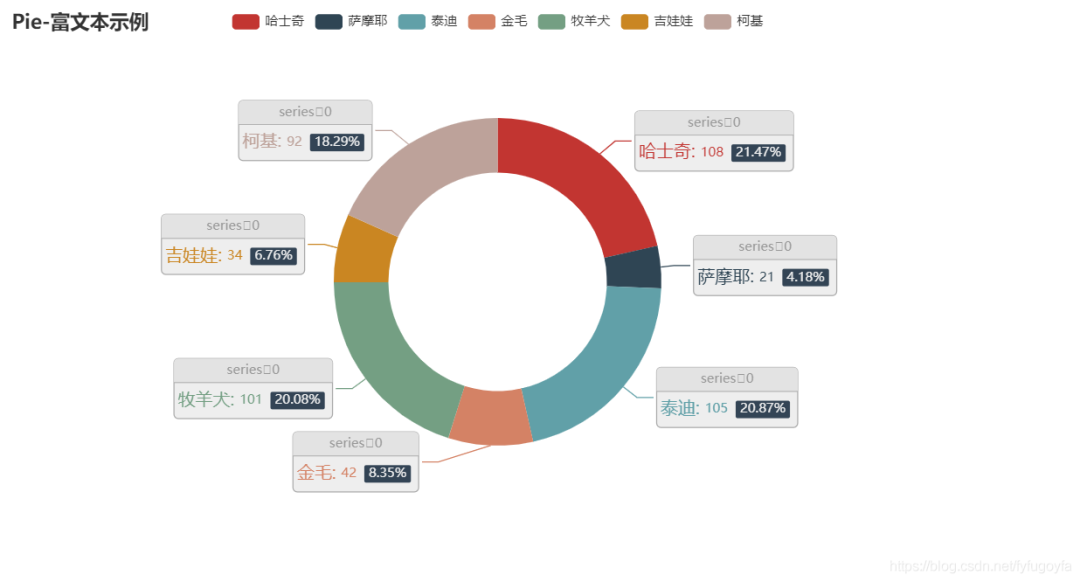
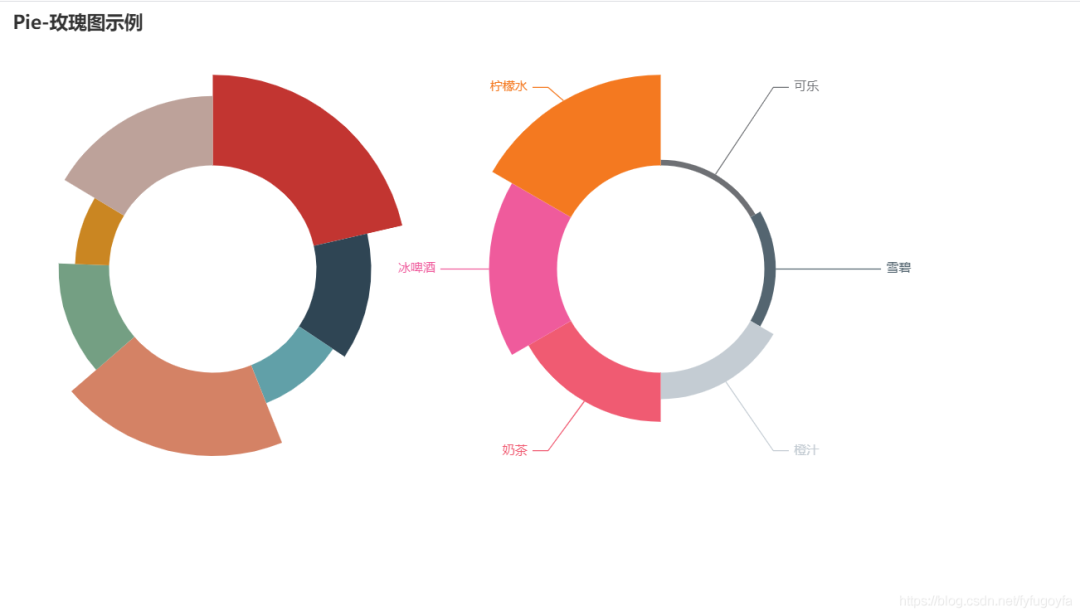
六、玫瑰图
代码如下:
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Pie
from pyecharts.faker import Faker
from pyecharts.globals import CurrentConfig
CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/'
labels = ['可乐', '雪碧', '橙汁', '奶茶', '冰啤酒', '柠檬水']
values = [6, 12, 28, 52, 72, 96]
v = Faker.choose()
c = (
Pie()
.add(
"",
[list(z) for z in zip(v, Faker.values())],
radius=["40%", "75%"],
center=["22%", "50%"],
rosetype="radius",
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False),
)
.add(
"",
[list(z) for z in zip(labels, values)],
radius=["40%", "75%"],
center=["70%", "50%"],
rosetype="area",
)
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Pie-玫瑰图示例"),
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(is_show=False)
)
.render("pie_rosetype.html")
)
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Pie
from pyecharts.globals import CurrentConfig
import pandas as pd
CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/'
provinces = ['北京','上海','黑龙江','吉林','辽宁','内蒙古','新疆','西藏','青海','四川','云南','陕西','重庆',
'贵州','广西','海南','澳门','湖南','江西','福建','安徽','浙江','江苏','宁夏','山西','河北','天津']
num = [1,1,1,17,9,22,23,42,35,7,20,21,16,24,16,21,37,12,13,14,13,7,22,8,16,13,13]
color_series = ['#FAE927','#E9E416','#C9DA36','#9ECB3C','#6DBC49',
'#37B44E','#3DBA78','#14ADCF','#209AC9','#1E91CA',
'#2C6BA0','#2B55A1','#2D3D8E','#44388E','#6A368B'
'#7D3990','#A63F98','#C31C88','#D52178','#D5225B',
'#D02C2A','#D44C2D','#F57A34','#FA8F2F','#D99D21',
'#CF7B25','#CF7B25','#CF7B25']
# 创建DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'provinces': provinces, 'num': num})
# 降序排序
df.sort_values(by='num', ascending=False, inplace=True)
# 提取数据
v = df['provinces'].values.tolist()
d = df['num'].values.tolist()
# 绘制饼图
pie1 = Pie(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(width='1250px', height='750px'))
# 设置颜色
pie1.set_colors(color_series)
pie1.add("", [list(z) for z in zip(v, d)],
radius=["30%", "100%"],
center=["50%", "50%"],
rosetype="area"
)
# 设置全局配置项
pie1.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title='多省区市\n确诊病例连续多日',subtitle='零新增',
title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(font_size=25,color= '#0085c3'),
subtitle_textstyle_opts= opts.TextStyleOpts(font_size=50,color= '#003399'),
pos_right= 'center',pos_left= 'center',pos_top='42%',pos_bottom='center'
),
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(is_show=False),
toolbox_opts=opts.ToolboxOpts())
# 设置系列配置项
pie1.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=True, position="inside", font_size=12,
formatter="{b}:{c}天", font_style="italic",
font_weight="bold", font_family="SimHei"
),
)
# 渲染在html页面上
pie1.render('南丁格尔玫瑰图示例.html')
运行效果如下:

七、词云图
词云就是通过形成关键词云层或关键词渲染,过滤掉大量的文本信息,对网络文本中出现频率较高的关键词的视觉上的突出。
import jieba
import collections
import re
from pyecharts.charts import WordCloud
from pyecharts.globals import SymbolType
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.globals import ThemeType, CurrentConfig
CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/'
with open('barrages.txt') as f:
data = f.read()
# 文本预处理 去除一些无用的字符 只提取出中文出来
new_data = re.findall('[\u4e00-\u9fa5]+', data, re.S) # 只要字符串中的中文
new_data = " ".join(new_data)
# 文本分词--精确模式
seg_list_exact = jieba.cut(new_data, cut_all=False)
result_list = []
with open('stop_words.txt', encoding='utf-8') as f:
con = f.readlines()
stop_words = set()
for i in con:
i = i.replace("\n", "") # 去掉读取每一行数据的\n
stop_words.add(i)
for word in seg_list_exact:
# 设置停用词并去除单个词
if word not in stop_words and len(word) > 1:
result_list.append(word)
print(result_list)
# 筛选后统计
word_counts = collections.Counter(result_list)
# 获取前100最高频的词
word_counts_top100 = word_counts.most_common(100)
# 打印出来看看统计的词频
print(word_counts_top100)
# 链式调用
c = (
WordCloud(
init_opts=opts.InitOpts(width='1350px', height='750px', theme=ThemeType.MACARONS)
)
.add(
series_name="词频", # 系列名称
data_pair=word_counts_top100, # 系列数据项 [(word1, count1), (word2, count2)]
word_size_range=[15, 108], # 单词字体大小范围
textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts( # 词云图文字的配置
font_family='KaiTi',
),
shape=SymbolType.DIAMOND, # 词云图轮廓,有 'circle', 'cardioid', 'diamond', 'triangle-forward', 'triangle', 'pentagon', 'star' 可选
pos_left='100', # 距离左侧的距离
pos_top='50', # 距离顶部的距离
)
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts( # 标题配置项
title='弹幕词云图',
title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(
font_family='SimHei',
font_size=25,
color='black'
),
pos_left='500',
pos_top='10',
),
tooltip_opts=opts.TooltipOpts( # 提示框配置项
is_show=True,
background_color='red',
border_color='yellow',
),
toolbox_opts=opts.ToolboxOpts( # 工具箱配置项
is_show=True,
orient='vertical',
)
)
.render('弹幕词云图.html')
)
运行效果如下:

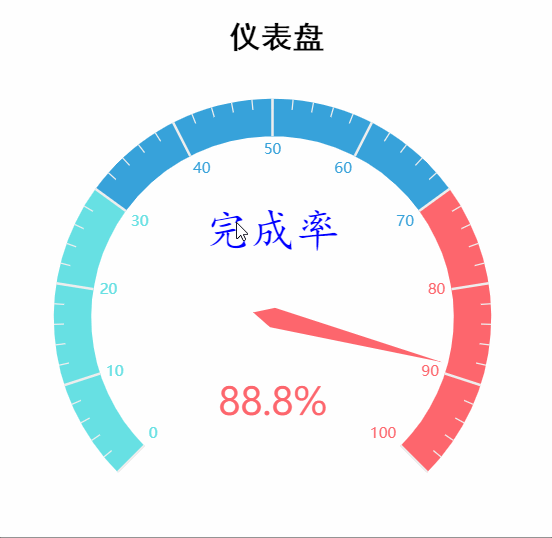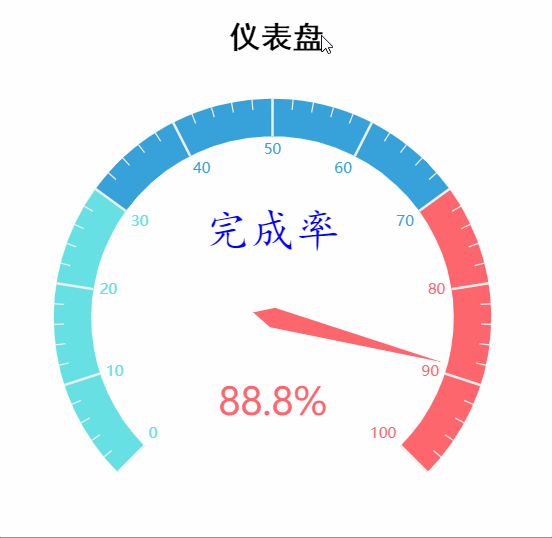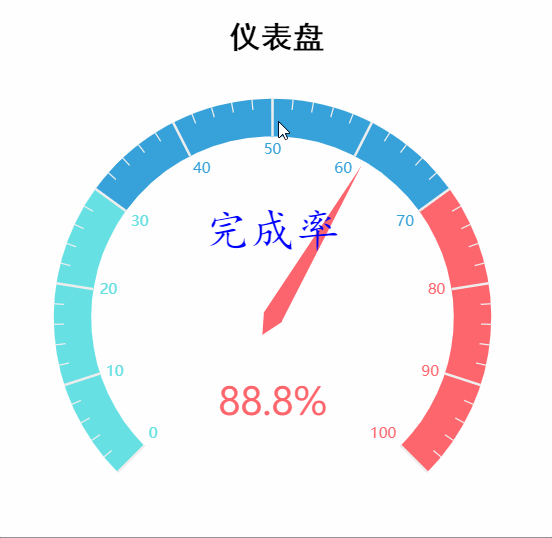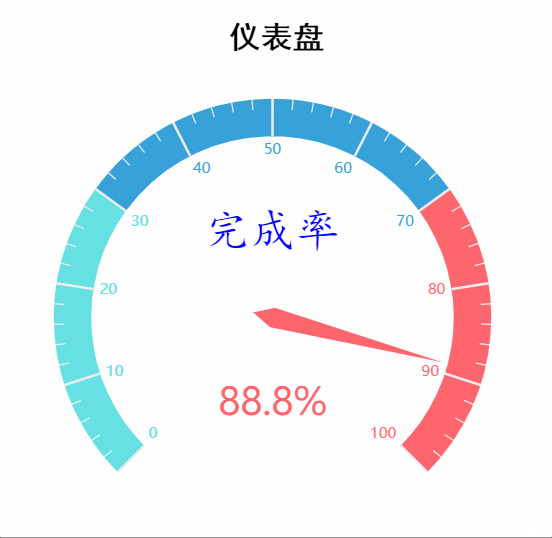
八、仪表盘
from pyecharts.charts import Gauge
from pyecharts.globals import CurrentConfig
from pyecharts import options as opts
CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/'
c = (
Gauge()
.add(
series_name='业务指标', # 系列名称,用于 tooltip 的显示,legend 的图例筛选。
data_pair=[['完成率', 88.8]], # 系列数据项,格式为 [(key1, value1), (key2, value2)]
radius='70%', # 仪表盘半径,可以是相对于容器高宽中较小的一项的一半的百分比,也可以是绝对的数值。
axisline_opts=opts.AxisLineOpts(
linestyle_opts=opts.LineStyleOpts( # 坐标轴轴线配置项
color=[(0.3, "#67e0e3"), (0.7, "#37a2da"), (1, "#fd666d")],
width=30,
)
),
title_label_opts=opts.LabelOpts( # 轮盘内标题文本项标签配置项
font_size=25, color='blue', font_family='KaiTi'
)
)
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts( # 标题配置项
title='仪表盘',
title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(
font_size=25, font_family='SimHei',
color='black', font_weight='bold',
),
pos_left="410", pos_top="8",
),
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts( # 图例配置项
is_show=False
),
tooltip_opts=opts.TooltipOpts( # 提示框配置项
is_show=True,
formatter="{a} <br/>{b} : {c}%",
)
)
.render('gauge.html')
)
运行效果如下:
九、水球图
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Grid, Liquid
from pyecharts.commons.utils import JsCode
from pyecharts.globals import CurrentConfig, ThemeType
CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/'
lq_1 = (
Liquid()
.add(
series_name='电量', # 系列名称,用于 tooltip 的显示,legend 的图例筛选。
data=[0.25], # 系列数据,格式为 [value1, value2, ....]
center=['60%', '50%'],
# 水球外形,有' circle', 'rect', 'roundRect', 'triangle', 'diamond', 'pin', 'arrow' 可选。
# 默认 'circle' 也可以为自定义的 SVG 路径
shape='circle',
color=['yellow'], # 波浪颜色 Optional[Sequence[str]] = None,
is_animation=True, # 是否显示波浪动画
is_outline_show=False, # 是否显示边框
)
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title='多个Liquid显示'))
)
lq_2 = (
Liquid()
.add(
series_name='数据精度',
data=[0.8866],
center=['25%', '50%'],
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(
font_size=50,
formatter=JsCode(
"""function (param) {
return (Math.floor(param.value * 10000) / 100) + '%';
}"""
),
position='inside'
)
)
)
grid = Grid(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(theme=ThemeType.DARK)).add(lq_1, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts()).add(lq_2, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts())
grid.render("multiple_liquid.html")
运行效果如下:

数据获取
数据来源:http://www.tianqihoubao.com/aqi/chengdu-201901.html
爬取2019年全年成都空气质量数据
import pandas as pd
dates = pd.date_range('20190101', '20191201', freq='MS').strftime('%Y%m') # 构造出日期序列 便于之后构造url
for i in range(len(dates)):
df = pd.read_html(f'http://www.tianqihoubao.com/aqi/chengdu-{dates[i]}.html', encoding='gbk', header=0)[0]
if i == 0:
df.to_csv('2019年成都空气质量数据.csv', mode='a+', index=False) # 追加写入
i += 1
else:
df.to_csv('2019年成都空气质量数据.csv', mode='a+', index=False, header=False)
查看爬取的数据
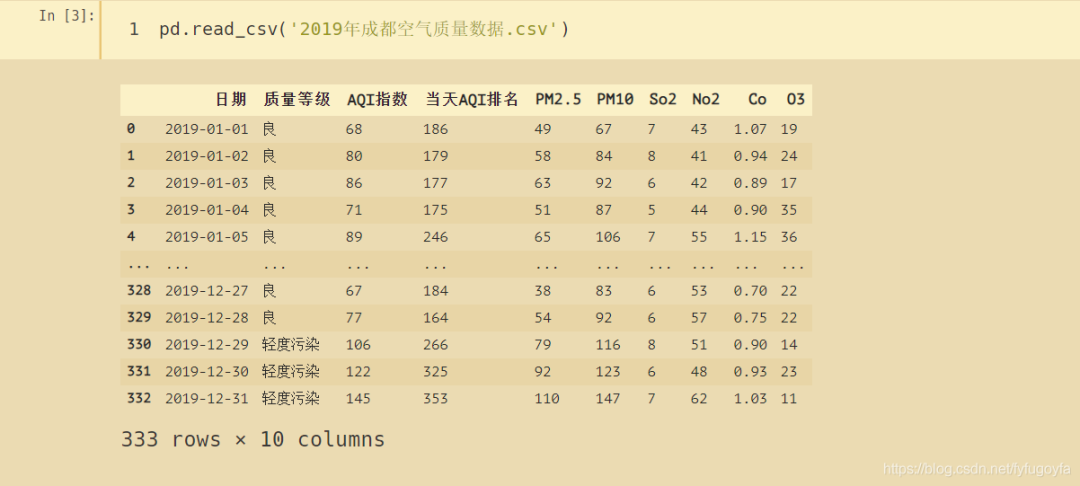
十、折线图
折线图是排列在工作表的列或行中的数据可以绘制到折线图中。折线图可以显示随时间(根据常用比例设置)而变化的连续数据,因此非常适用于显示在相等时间间隔下数据的趋势。
绘制2019年成都AQI指数走势图
import pandas as pd
import pyecharts.options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Line
from pyecharts.globals import CurrentConfig
CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/'
df = pd.read_csv('2019年成都空气质量数据.csv')
date = [x for x in range(len(df['日期']))]
value = [int(i) for i in df['AQI指数']]
# 绘制折线图
line = Line()
line.add_xaxis(xaxis_data=date)
line.add_yaxis(
"AQI指数", # 系列数据项
value, # y轴数据
areastyle_opts=opts.AreaStyleOpts(opacity=0.5, color='#00FFFF'), # 设置图形透明度 填充颜色
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False), # 标签配置项
markpoint_opts=opts.MarkPointOpts( # 标记点配置项
data=[
opts.MarkPointItem(type_="max", name="最大值"),
opts.MarkPointItem(type_="min", name="最小值"),
opts.MarkPointItem(type_="average", name="平均值")
]
),
markline_opts=opts.MarkLineOpts( # 标记线配置项
data=[opts.MarkLineItem(type_="average", name="平均值")])
)
line.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title='2019成都AQI指数走势图(按日统计)')
)
line.render('2019成都AQI指数走势图(按日统计).html')
运行效果如下:
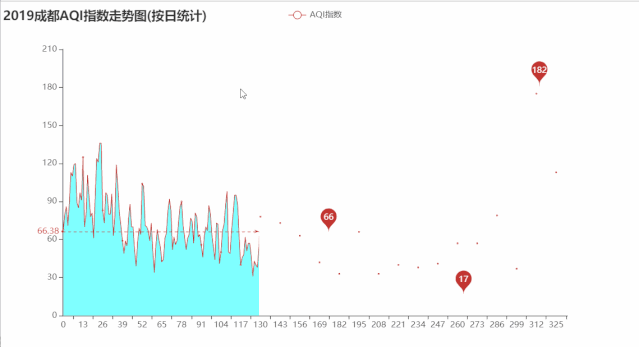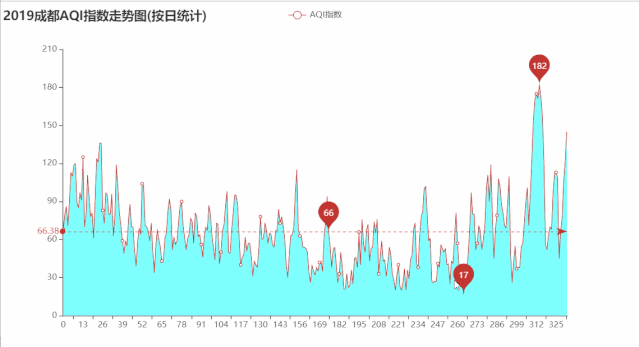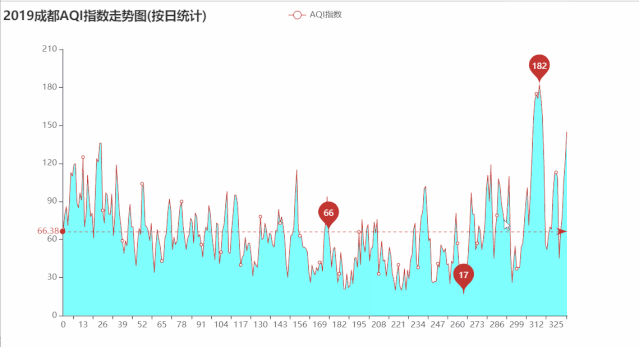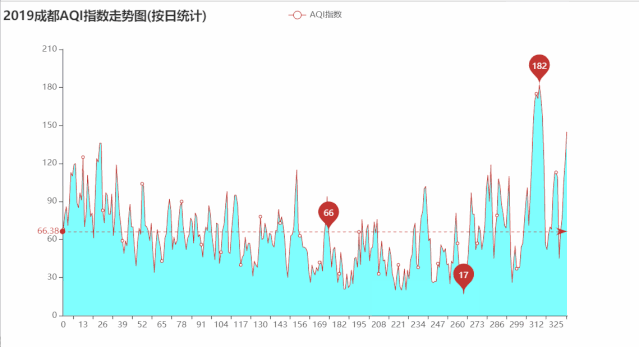
import pandas as pd
import pyecharts.options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Line
from pyecharts.globals import CurrentConfig, ThemeType
import math
CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/'
df = pd.read_csv('2019年成都空气质量数据.csv')[['日期', 'AQI指数']]
data = df['日期'].str.split('-', expand=True)[1]
df['月份'] = data
# 按月份分组 聚合 统计每月AQI指数平均值
counts = df.groupby('月份').agg({
'AQI指数': 'mean'})
date = [f'{x}月' for x in range(1, 13)]
value = [math.ceil(i) for i in counts['AQI指数']]
line = Line(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(theme=ThemeType.DARK))
line.set_colors(['red'])
line.add_xaxis(xaxis_data=date)
line.add_yaxis(
"AQI指数均值", # 系列数据项 用于图例筛选
value, # y轴数据
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False),
markpoint_opts=opts.MarkPointOpts( # 标记点配置项
data=[
opts.MarkPointItem(type_="max", name="最大值"),
opts.MarkPointItem(type_="min", name="最小值"),
opts.MarkPointItem(type_="average", name="平均值")
]
),
markline_opts=opts.MarkLineOpts( # 标记线配置项
data=[opts.MarkLineItem(type_="average", name="平均值")])
)
line.set_global_opts( # 全局配置项
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(
title='2019成都AQI全年走势图(按月统计)',
pos_left='32%', pos_top='3%',
title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(
font_family='SimHei', font_size=20, color='#F0FFF0'
)
),
xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(name='月份'), # x轴标签
yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(name='AQI指数均值') # y轴标签
)
line.render('2019成都AQI指数走势图(按月统计).html')
运行效果如下:
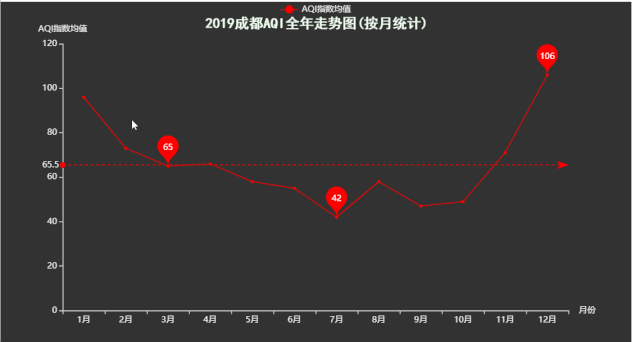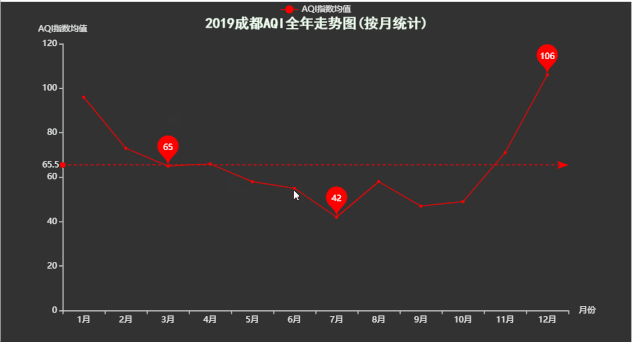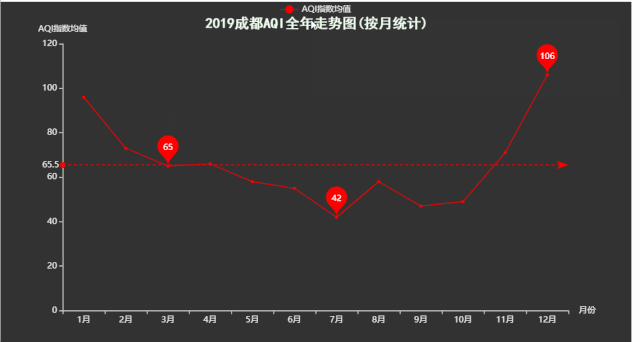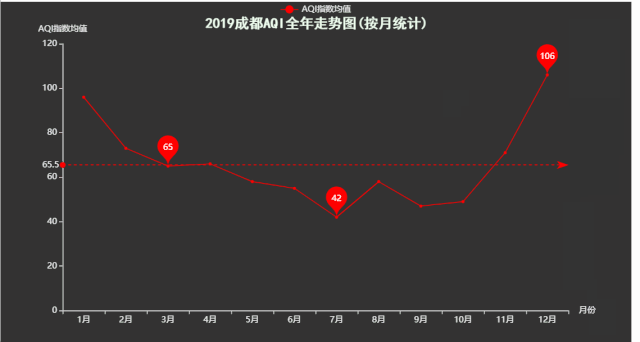
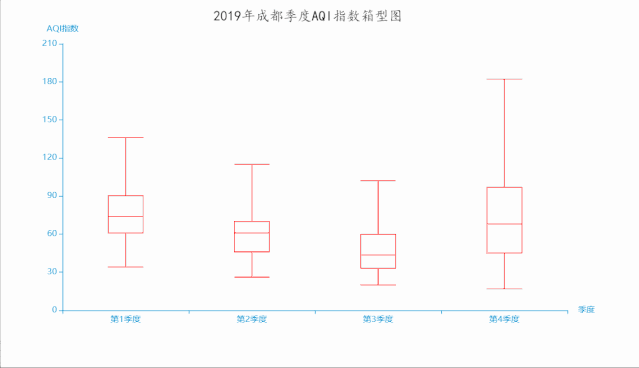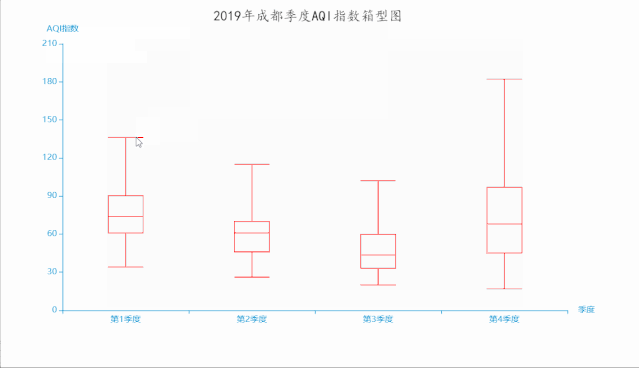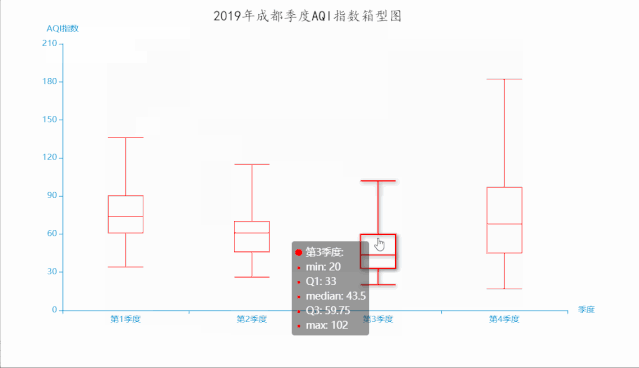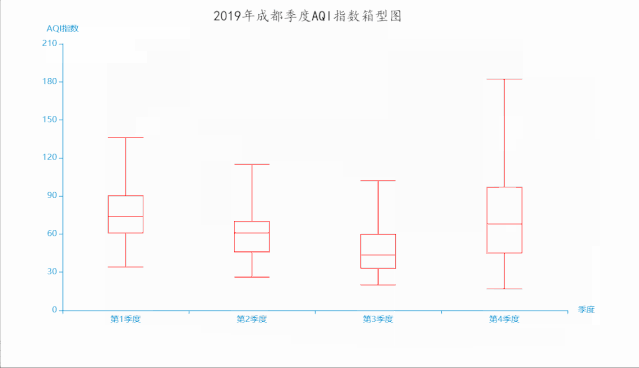
十一、箱形图
箱形图(Box-plot)又称为盒须图、盒式图或箱线图,是一种用作显示一组数据分散情况资料的统计图。因形状如箱子而得名。在各种领域也经常被使用,常见于品质管理。它主要用于反映原始数据分布的特征,还可以进行多组数据分布特征的比 较。箱线图的绘制方法是:先找出一组数据的上边缘、下边缘、中位数和两个四分位数;然后, 连接两个四分位数画出箱体;再将上边缘和下边缘与箱体相连接,中位数在箱体中间。
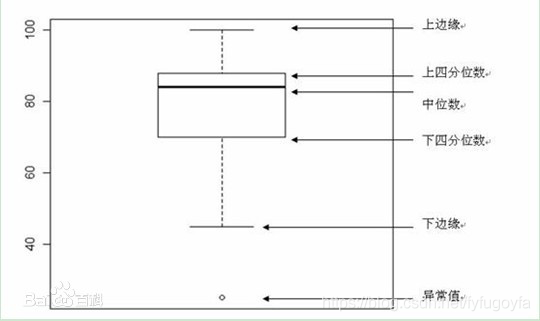
import pandas as pd
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Boxplot
from pyecharts.globals import CurrentConfig, ThemeType
CurrentConfig.ONLINE_HOST = 'D:/python/pyecharts-assets-master/assets/'
df = pd.read_csv('2019年成都空气质量数据.csv')[['日期', 'AQI指数']]
df.sort_values(by='AQI指数', inplace=True) # 按AQI指数大小排序 升序
data = df['日期'].str.split('-', expand=True)[1]
df['月份'] = data
item1, item2, item3, item4 = [], [], [], []
# 分为4个季度
for i, j in zip(df['月份'], df['AQI指数']):
if i in ['01', '02', '03']:
item1.append(j)
elif i in ['04', '05', '06']:
item2.append(j)
elif i in ['07', '08', '09']:
item3.append(j)
elif i in ['10', '11', '12']:
item4.append(j)
x_data = [f'第{i}季度' for i in range(1, 5)]
y_data = [item1, item2, item3, item4]
boxplot = Boxplot(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(theme=ThemeType.MACARONS))
boxplot.set_colors(['red'])
boxplot.add_xaxis(xaxis_data=x_data)
boxplot.add_yaxis(series_name='', y_axis=boxplot.prepare_data(y_data))
boxplot.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(
title='2019年成都季度AQI指数箱型图',
pos_left='300', pos_top='5',
title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(
font_family='KaiTi', font_size=20, color='black'
)
),
xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(name='季度'),
yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(name='AQI指数')
)
boxplot.render('2019年成都季度AQI指数箱型图.html')
运行效果如下:
感兴趣的小伙伴,赠送全套Python学习资料,包含面试题、简历资料等具体看下方。

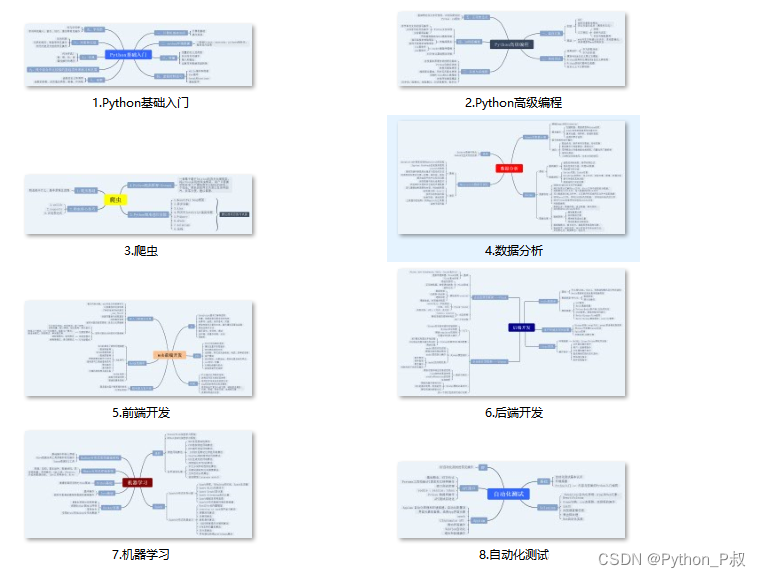
一、Python所有方向的学习路线
Python所有方向的技术点做的整理,形成各个领域的知识点汇总,它的用处就在于,你可以按照下面的知识点去找对应的学习资源,保证自己学得较为全面。
二、Python必备开发工具
工具都帮大家整理好了,安装就可直接上手!
三、最新Python学习笔记
当我学到一定基础,有自己的理解能力的时候,会去阅读一些前辈整理的书籍或者手写的笔记资料,这些笔记详细记载了他们对一些技术点的理解,这些理解是比较独到,可以学到不一样的思路。
四、Python视频合集
观看全面零基础学习视频,看视频学习是最快捷也是最有效果的方式,跟着视频中老师的思路,从基础到深入,还是很容易入门的。
五、实战案例
纸上得来终觉浅,要学会跟着视频一起敲,要动手实操,才能将自己的所学运用到实际当中去,这时候可以搞点实战案例来学习。
六、面试宝典
简历模板
 若有侵权,请联系删除
若有侵权,请联系删除