Amr bought a new video game "Guess Your Way Out! II". The goal of the game is to find an exit from the maze that looks like a perfect binary tree of height h. The player is initially standing at the root of the tree and the exit from the tree is located at some leaf node.
Let's index all the nodes of the tree such that
- The root is number 1
- Each internal node i (i ≤ 2h - 1 - 1) will have a left child with index = 2i and a right child with index = 2i + 1
The level of a node is defined as 1 for a root, or 1 + level of parent of the node otherwise. The vertices of the level h are called leaves. The exit to the maze is located at some leaf node n, the player doesn't know where the exit is so he has to guess his way out!
In the new version of the game the player is allowed to ask questions on the format "Does the ancestor(exit, i) node number belong to the range [L, R]?". Here ancestor(v, i) is the ancestor of a node v that located in the level i. The game will answer with "Yes" or "No" only. The game is designed such that it doesn't always answer correctly, and sometimes it cheats to confuse the player!.
Amr asked a lot of questions and got confused by all these answers, so he asked you to help him. Given the questions and its answers, can you identify whether the game is telling contradictory information or not? If the information is not contradictory and the exit node can be determined uniquely, output its number. If the information is not contradictory, but the exit node isn't defined uniquely, output that the number of questions is not sufficient. Otherwise output that the information is contradictory.
The first line contains two integers h, q (1 ≤ h ≤ 50, 0 ≤ q ≤ 105), the height of the tree and the number of questions respectively.
The next q lines will contain four integers each i, L, R, ans (1 ≤ i ≤ h, 2i - 1 ≤ L ≤ R ≤ 2i - 1, 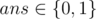 ), representing a question as described in the statement with its answer (ans = 1 if the answer is "Yes" and ans = 0 if the answer is "No").
), representing a question as described in the statement with its answer (ans = 1 if the answer is "Yes" and ans = 0 if the answer is "No").
If the information provided by the game is contradictory output "Game cheated!" without the quotes.
Else if you can uniquely identify the exit to the maze output its index.
Otherwise output "Data not sufficient!" without the quotes.

3 1 3 4 6 0
7
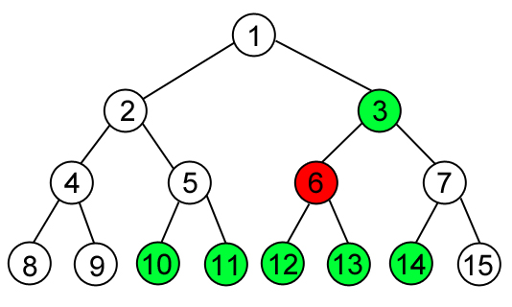
4 3 4 10 14 1 3 6 6 0 2 3 3 1
14
4 2 3 4 6 1 4 12 15 1
Data not sufficient!
4 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 3 1
Game cheated!
Node u is an ancestor of node v if and only if
- u is the same node as v,
- u is the parent of node v,
- or u is an ancestor of the parent of node v.
In the first sample test there are 4 leaf nodes 4, 5, 6, 7. The first question says that the node isn't in the range [4, 6] so the exit is node number 7.
In the second sample test there are 8 leaf nodes. After the first question the exit is in the range [10, 14]. After the second and the third questions only node number 14 is correct. Check the picture below to fully understand.
题意:
给定一棵高度为h的满二叉树,规定根节点的标号和深度均为1,对每个深度小于h的节点i,其左儿子标号为2*i,右儿子标号为2*i+1,儿子的深度为父亲节点的深度+1,深度h的节点为叶子节点,现在恰有1个叶子节点是exit节点,有q个信息(i,L,R,ans),表示询问exit节点的深度为i的祖先的标号是否在区间[L,R]内,ans=1表明“是”,ans=0表明“否”,问能否根据已有信息唯一确定exit节点.
分析:
对于每一个询问,可以利用满二叉树的性质将深度为i的区间[L,R]对应到深度为h的区间[L',R']上,若ans=1,则[L',R']被覆盖,否则[2^(h-1),L'-1]以及[R'+1,2^h-1]被覆盖,若有解,则应该恰好存在1个位置被这q组区间覆盖,利用扫描线维护即可,考虑到q==0的情形,可以加入区间[2^(h-1),2^h-1],考虑被q+1组区间覆盖的位置即可,复杂度O(hq+qlogq)。
代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
vector<pair<ll,int> >Event;
int main()
{
int h,q;
scanf("%d%d",&h,&q);
for(int i=1;i<=q;i++)
{
int x,res;
ll L,R;
scanf("%d%I64d%I64d%d",&x,&L,&R,&res);
for(int j=x+1;j<=h;j++)
{
L=(L<<1);
R=(R<<1|1);
}
if(res==1)
{
Event.push_back(make_pair(L,-1));
Event.push_back(make_pair(R,1));
}
else
{
if(L>(1LL<<(h-1)))
{
Event.push_back(make_pair(1LL<<(h-1),-1));
Event.push_back(make_pair(L-1,1));
}
if(R<(1LL<<h)-1);
{
Event.push_back(make_pair(R+1,-1));
Event.push_back(make_pair((1LL<<h)-1,1));
}
}
}
Event.push_back(make_pair(1LL<<(h-1),-1));
Event.push_back(make_pair((1LL<<h)-1,1));
sort(Event.begin(),Event.end());
int cnt=0;
ll tot=0,la=1LL<<(h-1),loc=0;
for(int i=0;i<Event.size();i++)
{
if(cnt==q+1)tot+=Event[i].first-la+1;
cnt-=Event[i].second;
if(cnt==q+1)la=Event[i].first;
}
if(tot>1)printf("Data not sufficient!");
else if(tot==0)printf("Game cheated!");
else printf("%I64d",la);
return 0;
}