一些业务场景我们需要使用多线程异步执行任务,加快任务执行速度。
比如APP一个用户的登录,可能需要获取这个用户基本信息、订单数据、积分信息等等,这些信息虽然都隶属于这个用户,但是获取过程并不存在顺序上的强关联,如果串行话去获取,就需要逐个等待,因此完全可以将这些数据的获取过程做成并行请求,拿到响应数据之后,整理返回即可,从而提高整个过程的响应速度。
CompletableFuture 是 Java 8 引入的一个类,用于处理异步编程和并发操作。它提供了一种简洁而强大的方式来处理并发任务的结果和异常。
一、一个示例回顾Future
JDK5新增了Future接口,用于描述一个异步计算的结果。虽然 Future 以及相关使用方法提供了异步执行任务的能力,但是对于结果的获取却是很不方便,
我们必须使用 Future.get()的方式阻塞调用线程,或者使用轮询方式判断 Future.isDone 任务是否结束,再获取结果。
这两种处理方式都不是很优雅,相关代码如下:
@Test
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
Future<String> future = executorService.submit(() -> {
Thread.sleep(2000);
return "hello";
});
System.out.println(future.get());
System.out.println("end");
}
与此同时,Future无法解决多个异步任务需要相互依赖的场景,简单点说就是,主线程需要等待子线程任务执行完毕之后在进行执行,这个时候你可能想到了CountDownLatch,
没错确实可以解决,代码如下。这里定义两个Future,第一个通过用户id获取用户信息,第二个通过商品id获取商品信息。
@Test
public void testCountDownLatch() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
CountDownLatch downLatch = new CountDownLatch(2);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Future<String> userFuture = executorService.submit(() -> {
//模拟查询商品耗时500毫秒
Thread.sleep(500);
downLatch.countDown();
return "用户A";
});
Future<String> goodsFuture = executorService.submit(() -> {
//模拟查询商品耗时500毫秒
Thread.sleep(400);
downLatch.countDown();
return "商品A";
});
downLatch.await();
//模拟主程序耗时时间
Thread.sleep(600);
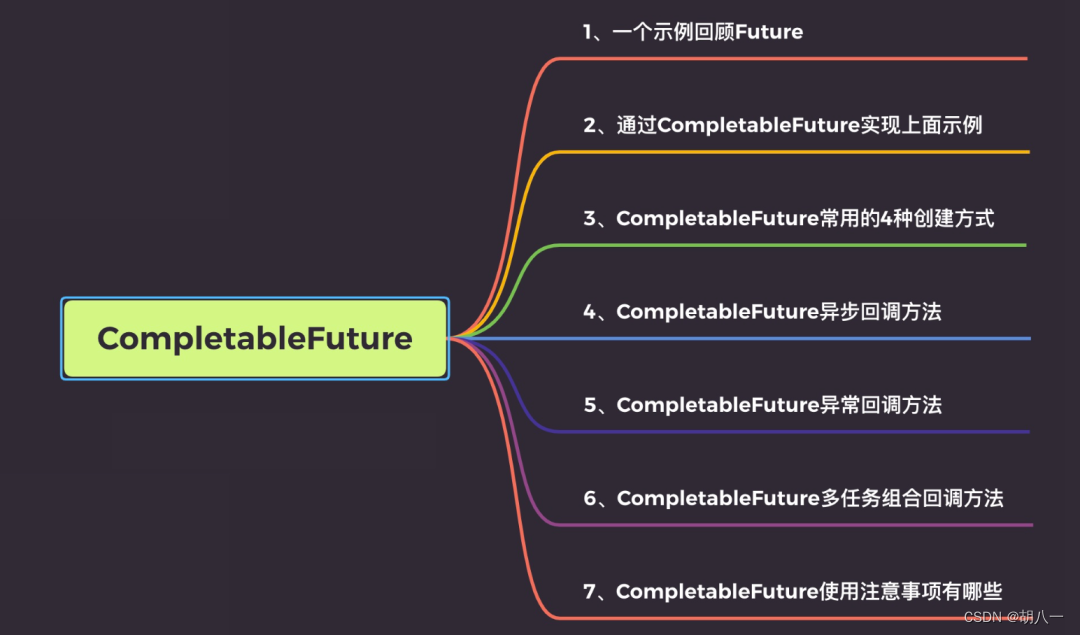
System.out.println("获取用户信息:" + userFuture.get());
System.out.println("获取商品信息:" + goodsFuture.get());
System.out.println("总共用时" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms");
}
运行结果:
从运行结果可以看出结果都已经获取,而且如果我们不用异步操作,执行时间应该是:500+400+600 = 1500,用异步操作后实际只用1146。
但是Java8以后我不在认为这是一种优雅的解决方式,接下来我们来了解下CompletableFuture的使用。
二、通过CompletableFuture实现上面示例
@Test
public void testCompletableInfo() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//调用用户服务获取用户基本信息
CompletableFuture<String> userFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->
//模拟查询商品耗时500毫秒
{
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "用户A";
});
//调用商品服务获取商品基本信息
CompletableFuture<String> goodsFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->
//模拟查询商品耗时500毫秒
{
try {
Thread.sleep(400);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "商品A";
});
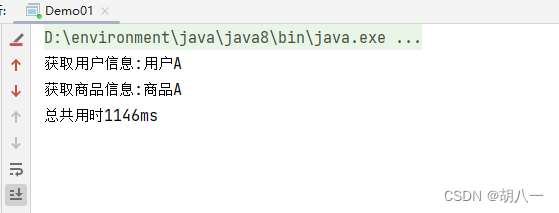
System.out.println("获取用户信息:" + userFuture.get());
System.out.println("获取商品信息:" + goodsFuture.get());
//模拟主程序耗时时间
Thread.sleep(600);
System.out.println("总共用时" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms");
}
运行结果:
通过CompletableFuture可以很轻松的实现CountDownLatch的功能,你以为这就结束了,远远不止,CompletableFuture比这要强多了。
比如可以实现:任务1执行完了再执行任务2,甚至任务1执行的结果,作为任务2的入参数等等强大功能,下面就来学学CompletableFuture的API。
三、CompletableFuture创建方式
1、常用的4种创建方式
CompletableFuture源码中有四个静态方法用来执行异步任务
/**
* Returns a new CompletableFuture that is asynchronously completed
* by a task running in the {@link ForkJoinPool#commonPool()} with
* the value obtained by calling the given Supplier.
*
* @param supplier a function returning the value to be used
* to complete the returned CompletableFuture
* @param <U> the function's return type
* @return the new CompletableFuture
*/
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) {
return asyncSupplyStage(asyncPool, supplier);
}
/**
* Returns a new CompletableFuture that is asynchronously completed
* by a task running in the given executor with the value obtained
* by calling the given Supplier.
*
* @param supplier a function returning the value to be used
* to complete the returned CompletableFuture
* @param executor the executor to use for asynchronous execution
* @param <U> the function's return type
* @return the new CompletableFuture
*/
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier,
Executor executor) {
return asyncSupplyStage(screenExecutor(executor), supplier);
}
/**
* Returns a new CompletableFuture that is asynchronously completed
* by a task running in the {@link ForkJoinPool#commonPool()} after
* it runs the given action.
*
* @param runnable the action to run before completing the
* returned CompletableFuture
* @return the new CompletableFuture
*/
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable) {
return asyncRunStage(asyncPool, runnable);
}
/**
* Returns a new CompletableFuture that is asynchronously completed
* by a task running in the given executor after it runs the given
* action.
*
* @param runnable the action to run before completing the
* returned CompletableFuture
* @param executor the executor to use for asynchronous execution
* @return the new CompletableFuture
*/
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable,
Executor executor) {
return asyncRunStage(screenExecutor(executor), runnable);
}
一般我们用上面的静态方法来创建CompletableFuture,这里也解释下他们的区别:
- supplyAsync执行任务,支持返回值。
- runAsync执行任务,没有返回值。
supplyAsync方法
//使用默认内置线程池ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),根据supplier构建执行任务
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
//自定义线程,根据supplier构建执行任务
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor
runAsync方法
//使用默认内置线程池ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),根据runnable构建执行任务
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)
//自定义线程,根据runnable构建执行任务
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)
2、结果获取的4种方式
对于结果的获取CompltableFuture类提供了四种方式
//方式一
public T get()
//方式二
public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
//方式三
public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent)
//方式四
public T join()
说明:
get()和get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) => 在Future中就已经提供了,后者提供超时处理,如果在指定时间内未获取结果将抛出超时异常
getNow => 立即获取结果不阻塞,结果计算已完成将返回结果或计算过程中的异常,如果未计算完成将返回设定的valueIfAbsent值
join => 方法里不会抛出异常
示例:
@Test
public void testCompletableGet() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
CompletableFuture<String> cp1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "商品A";
});
// getNow方法测试
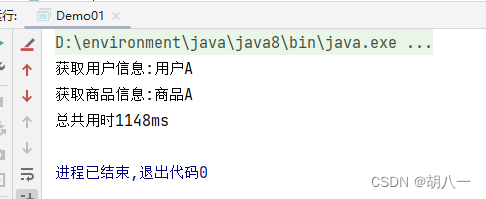
System.out.println(cp1.getNow("商品B"));
//join方法测试
CompletableFuture<Integer> cp2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync((() -> 1 / 0));
System.out.println(cp2.join());
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------");
//get方法测试
CompletableFuture<Integer> cp3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync((() -> 1 / 0));
System.out.println(cp3.get());
}
运行结果:
把System.out.println(cp2.join());注释了再次运行
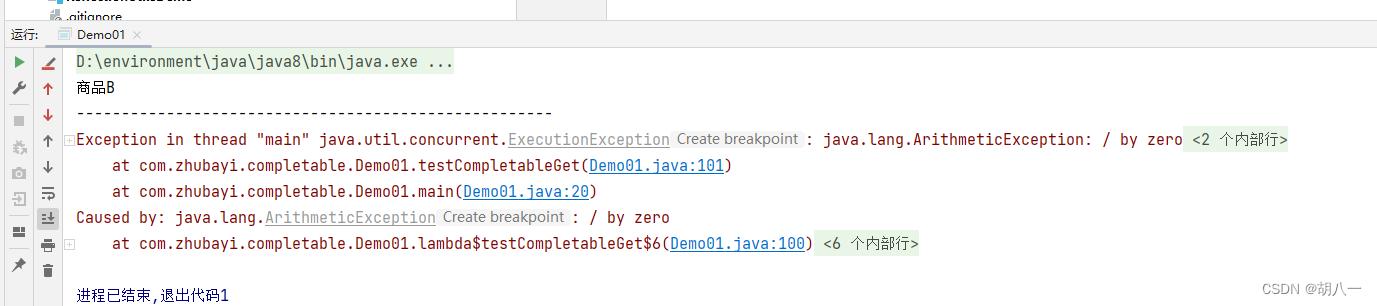
第一个执行结果为 商品B,因为要先睡上1秒结果不能立即获取
join方法获取结果方法里不会抛异常,但是执行结果会抛异常,抛出的异常为CompletionException
get方法获取结果方法里将抛出异常,执行结果抛出的异常为ExecutionException
四、异步回调方法
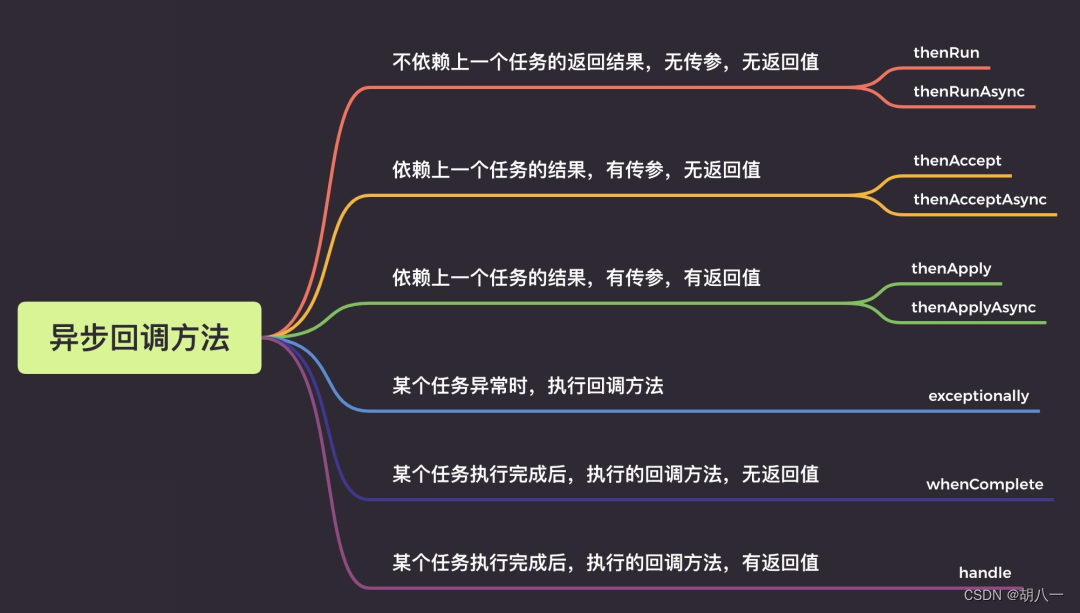
1、thenRun/thenRunAsync
通俗点讲就是,做完第一个任务后,再做第二个任务,这两个任务没有关联关系,第二个任务也没有返回值。
示例:
@Test
public void testCompletableThenRunAsync() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
CompletableFuture<Void> cp1 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
//执行任务A
Thread.sleep(600);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
CompletableFuture<Void> cp2 = cp1.thenRun(() -> {
try {
//执行任务B
Thread.sleep(400);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
// get方法测试
System.out.println(cp2.get());
//模拟主程序耗时时间
Thread.sleep(600);
System.out.println("总共用时" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms");
}
运行结果
thenRun 和thenRunAsync有什么区别呢?
如果你执行第一个任务的时候,传入了一个自定义线程池:
- 调用
thenRun方法执行第二个任务时,则第二个任务和第一个任务是共用同一个线程池。 - 调用
thenRunAsync执行第二个任务时,则第一个任务使用的是你自己传入的线程池,第二个任务使用的是ForkJoin线程池。
说明: 后面介绍的
thenAccept和thenAcceptAsync,thenApply和thenApplyAsync等,它们之间的区别也是这个。
2、thenAccept/thenAcceptAsync
第一个任务执行完成后,执行第二个回调方法任务,会将该任务的执行结果,作为入参,传递到回调方法中,但是回调方法是没有返回值的。
示例
@Test
public void testCompletableThenAccept() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
CompletableFuture<String> cp1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return "dev";
});
CompletableFuture<Void> cp2 = cp1.thenAccept((a) -> {
System.out.println("上一个任务的返回结果为: " + a);
});
cp2.get();
}
运行结果
3、 thenApply/thenApplyAsync
表示第一个任务执行完成后,执行第二个回调方法任务,会将该任务的执行结果,作为入参,传递到回调方法中,并且回调方法是有返回值的。
示例
@Test
public void testCompletableThenApply() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> cp1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return "dev";
}).thenApply((a) -> {
if(Objects.equals(a,"dev")){
return "dev";
}
return "prod";
});
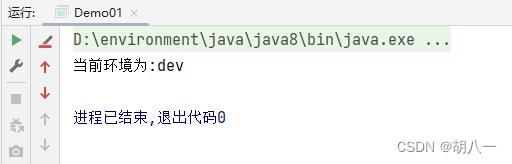
System.out.println("当前环境为:" + cp1.get());
运行结果
五、异常回调
当CompletableFuture的任务不论是正常完成还是出现异常它都会调用whenComplete这回调函数。
- 正常完成:
whenComplete返回结果和上级任务一致,异常为null; - 出现异常:
whenComplete返回结果为null,异常为上级任务的异常;
即调用get()时,正常完成时就获取到结果,出现异常时就会抛出异常,需要你处理该异常。
示例
1、只用whenComplete
@Test
public void testCompletableWhenComplete() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Double> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
if (Math.random() < 0.5) {
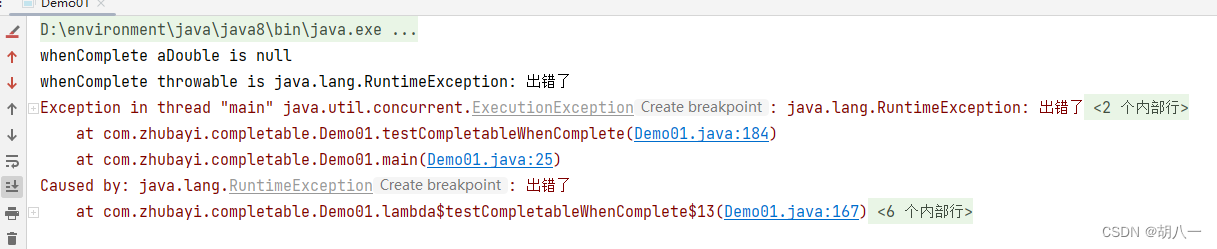
throw new RuntimeException("出错了");
}
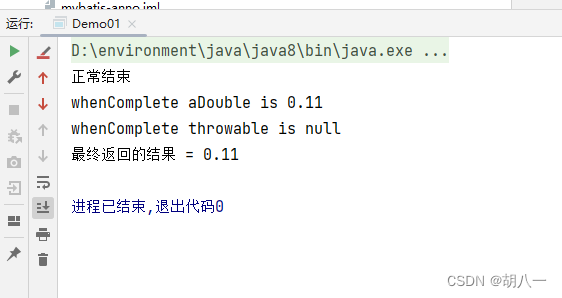
System.out.println("正常结束");
return 0.11;
}).whenComplete((aDouble, throwable) -> {
if (aDouble == null) {
System.out.println("whenComplete aDouble is null");
} else {
System.out.println("whenComplete aDouble is " + aDouble);
}
if (throwable == null) {
System.out.println("whenComplete throwable is null");
} else {
System.out.println("whenComplete throwable is " + throwable.getMessage());
}
});
System.out.println("最终返回的结果 = " + future.get());
}
运行结果:
正常完成,没有异常时:
出现异常时:get()会抛出异常
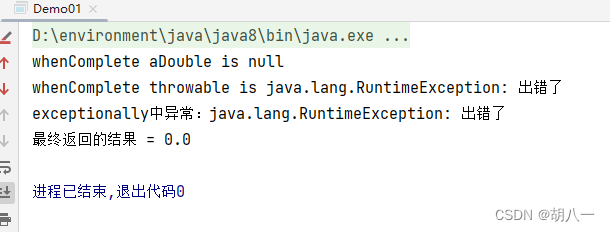
2、whenComplete + exceptionally示例
示例
@Test
public void testWhenCompleteExceptionally() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Double> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
if (Math.random() < 0.5) {
throw new RuntimeException("出错了");
}
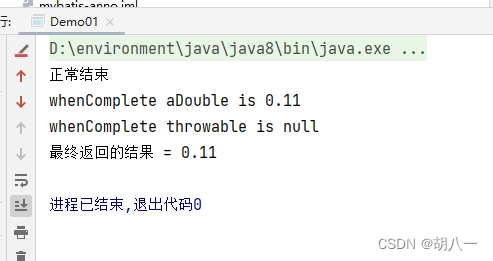
System.out.println("正常结束");
return 0.11;
}).whenComplete((aDouble, throwable) -> {
if (aDouble == null) {
System.out.println("whenComplete aDouble is null");
} else {
System.out.println("whenComplete aDouble is " + aDouble);
}
if (throwable == null) {
System.out.println("whenComplete throwable is null");
} else {
System.out.println("whenComplete throwable is " + throwable.getMessage());
}
}).exceptionally((throwable) -> {
System.out.println("exceptionally中异常:" + throwable.getMessage());
return 0.0;
});
System.out.println("最终返回的结果 = " + future.get());
}
运行结果
正常完成,没有异常时:
当出现异常时,exceptionally中会捕获该异常,给出默认返回值0.0。
六、多任务组合回调
1、AND组合关系
thenCombine / thenAcceptBoth / runAfterBoth 都表示:当任务一和任务二都完成再执行任务三。
区别在于:
runAfterBoth不会把执行结果当做方法入参,且没有返回值thenAcceptBoth:会将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且无返回值thenCombine:会将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且有返回值
示例
@Test
public void testCompletableThenCombine() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//创建线程池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
//开启异步任务1
CompletableFuture<Integer> task = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("异步任务1,当前线程是:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int result = 1 + 1;
System.out.println("异步任务1结束");
return result;
}, executorService);
//开启异步任务2
CompletableFuture<Integer> task2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("异步任务2,当前线程是:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int result = 1 + 1;
System.out.println("异步任务2结束");
return result;
}, executorService);
//任务组合
CompletableFuture<Integer> task3 = task.thenCombineAsync(task2, (f1, f2) -> {
System.out.println("执行任务3,当前线程是:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
System.out.println("任务1返回值:" + f1);
System.out.println("任务2返回值:" + f2);
return f1 + f2;
}, executorService);
Integer res = task3.get();
System.out.println("最终结果:" + res);
}
运行结果

2、OR组合关系
applyToEither / acceptEither / runAfterEither 都表示:两个任务,只要有一个任务完成,就执行任务三。
区别在于:
runAfterEither:不会把执行结果当做方法入参,且没有返回值acceptEither:会将已经执行完成的任务,作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且无返回值applyToEither:会将已经执行完成的任务,作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且有返回值
示例
@Test
public void testCompletableEitherAsync() {
//创建线程池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
//开启异步任务1
CompletableFuture<Integer> task = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("异步任务1,当前线程是:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int result = 1 + 1;
System.out.println("异步任务1结束");
return result;
}, executorService);
//开启异步任务2
CompletableFuture<Integer> task2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("异步任务2,当前线程是:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int result = 1 + 2;
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("异步任务2结束");
return result;
}, executorService);
//任务组合
task.acceptEitherAsync(task2, (res) -> {
System.out.println("执行任务3,当前线程是:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
System.out.println("上一个任务的结果为:"+res);
}, executorService);
}
运行结果
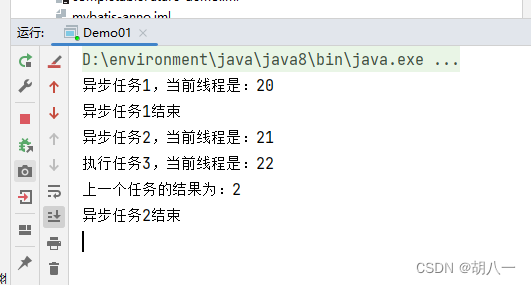
通过结果可以看出,异步任务2都没有执行结束,任务3获取的也是1的执行结果
注意
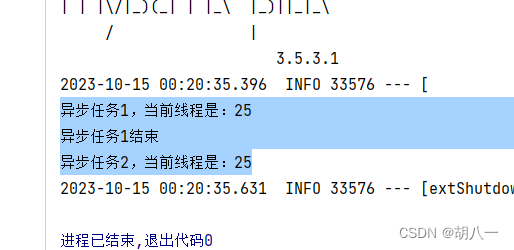
如果把上面的核心线程数改为1也就是
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
运行结果就是下面的了,会发现根本没有执行任务3,显然是任务3直接被丢弃了。
3、多任务组合
allOf:等待所有任务完成anyOf:只要有一个任务完成
示例
allOf:等待所有任务完成
示例
@Test
public void testCompletableAallOf() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//创建线程池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
//开启异步任务1
CompletableFuture<Integer> task = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("异步任务1,当前线程是:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int result = 1 + 1;
System.out.println("异步任务1结束");
return result;
}, executorService);
//开启异步任务2
CompletableFuture<Integer> task2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("异步任务2,当前线程是:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int result = 1 + 2;
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("异步任务2结束");
return result;
}, executorService);
//开启异步任务3
CompletableFuture<Integer> task3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("异步任务3,当前线程是:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int result = 1 + 3;
try {
Thread.sleep(4000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("异步任务3结束");
return result;
}, executorService);
//任务组合
CompletableFuture<Void> allOf = CompletableFuture.allOf(task, task2, task3);
//等待所有任务完成
allOf.get();
//获取任务的返回结果
System.out.println("task结果为:" + task.get());
System.out.println("task2结果为:" + task2.get());
System.out.println("task3结果为:" + task3.get());
}
运行结果
异步任务1,当前线程是:20
异步任务1结束
异步任务2,当前线程是:21
异步任务3,当前线程是:22
异步任务2结束
异步任务3结束
task结果为:2
task2结果为:3
task3结果为:4
anyOf: 只要有一个任务完成
示例
@Test
public void testCompletableAnyOf() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//创建线程池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
//开启异步任务1
CompletableFuture<Integer> task = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int result = 1 + 1;
return result;
}, executorService);
//开启异步任务2
CompletableFuture<Integer> task2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int result = 1 + 2;
return result;
}, executorService);
//开启异步任务3
CompletableFuture<Integer> task3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int result = 1 + 3;
return result;
}, executorService);
//任务组合
CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf = CompletableFuture.anyOf(task, task2, task3);
//只要有一个有任务完成
Object o = anyOf.get();
System.out.println("完成的任务的结果:" + o);
}
运行结果
完成的任务的结果:2
七、CompletableFuture使用有哪些注意点
CompletableFuture 使我们的异步编程更加便利的、代码更加优雅的同时,我们也要关注下它,使用的一些注意点。
1、Future需要获取返回值,才能获取异常信息
@Test
public void testWhenCompleteExceptionally() {
CompletableFuture<Double> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
if (1 == 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("出错了");
}
return 0.11;
});
//如果不加 get()方法这一行,看不到异常信息
//future.get();
}
Future需要获取返回值,才能获取到异常信息。如果不加 get()/join()方法,看不到异常信息。
小伙伴们使用的时候,注意一下哈,考虑是否加try...catch...或者使用exceptionally方法。
2、CompletableFuture的get()方法是阻塞的。
CompletableFuture的get()方法是阻塞的,如果使用它来获取异步调用的返回值,需要添加超时时间。
//反例
CompletableFuture.get();
//正例
CompletableFuture.get(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
3、不建议使用默认线程池
CompletableFuture代码中又使用了默认的ForkJoin线程池,处理的线程个数是电脑CPU核数-1。在大量请求过来的时候,处理逻辑复杂的话,响应会很慢。一般建议使用
自定义线程池,优化线程池配置参数。
4、自定义线程池时,注意饱和策略
CompletableFuture的get()方法是阻塞的,我们一般建议使用future.get(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)。并且一般建议使用自定义线程池。
但是如果线程池拒绝策略是DiscardPolicy或者DiscardOldestPolicy,当线程池饱和时,会直接丢弃任务,不会抛弃异常。因此建议,CompletableFuture线程池策略最好
使用AbortPolicy,然后耗时的异步线程,做好线程池隔离哈。