为什么要用内存池
避免内存碎片
减少系统调用次数(brk,mmap)
内存碎片
是什么
不可用的空闲内存。这些内存小且不连续
产生原因
内存分配的起始地址需要是4/8/16的倍数(由CPU体系结构决定)
夹在大块内存之间的小块空闲内存不易被使用
可能出现问题
-
服务器程序在长周期或者大量访问的情况后会变得反应迟钝,排查原因发现占用内存会随着请求数量的增多不规律而且不正常地增长,如果使用valgrind等工具发现没有内存泄露,则有可能是内存碎片。
-
程序运行几天乃至几个月出现内存问题:例如malloc返回NULL。
怎么解决
使用开源方案jemallloc/tcmalloc
实现自己的内存池
使用场景
全局内存池
- 生命周期是程序运行期间,小内存需要回收
- 可以直接用jemallloc/tcmalloc
1个连接1个内存池
- 生命周期短,小内存不需要回收
- 1个连接只有1个线程使用的话,不需要加锁
设计内存池需要考虑的问题
- 查找速度慢
- 小块内存回收麻烦
- 为避免小块内存造成内存碎片,结构体定义占用内存和内存块需要是连续的一块内存。
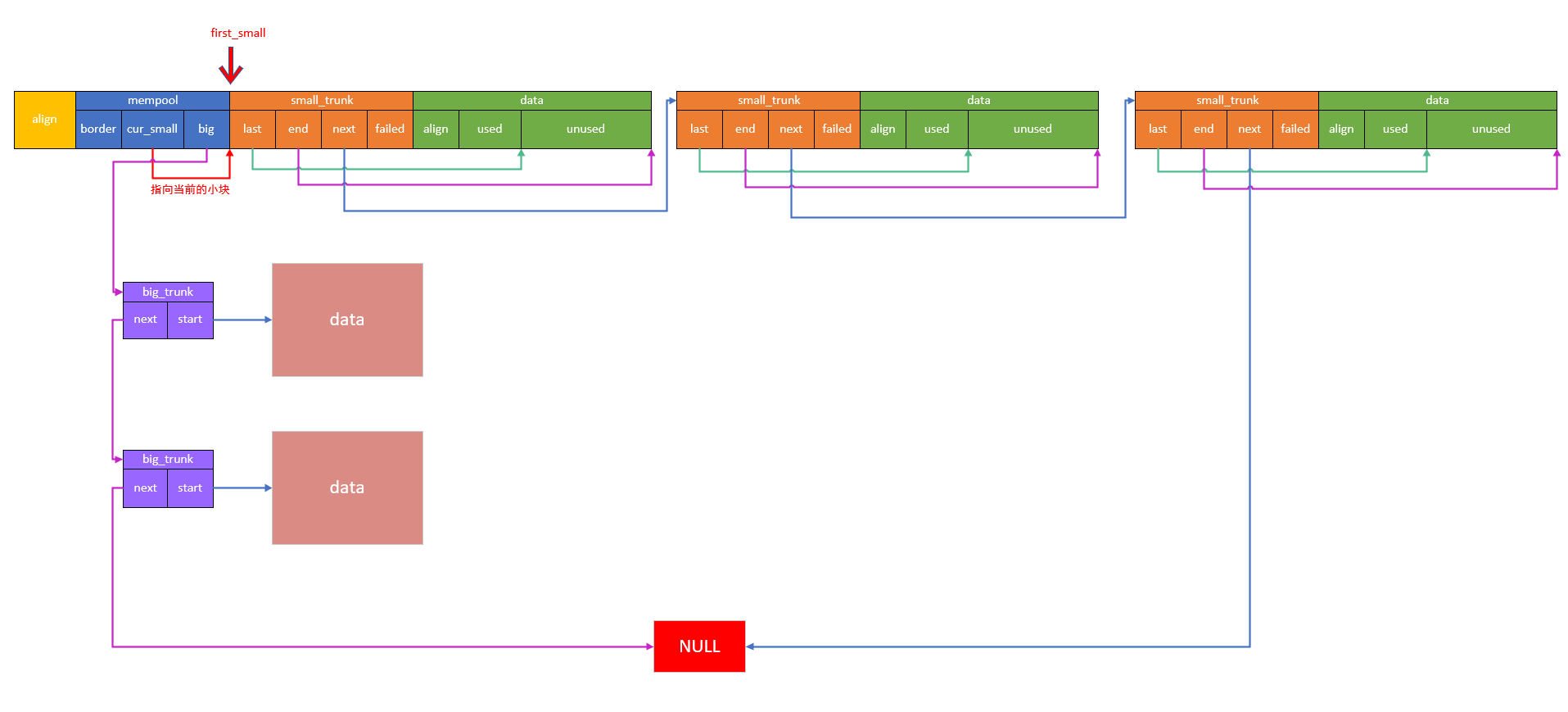
内存布局
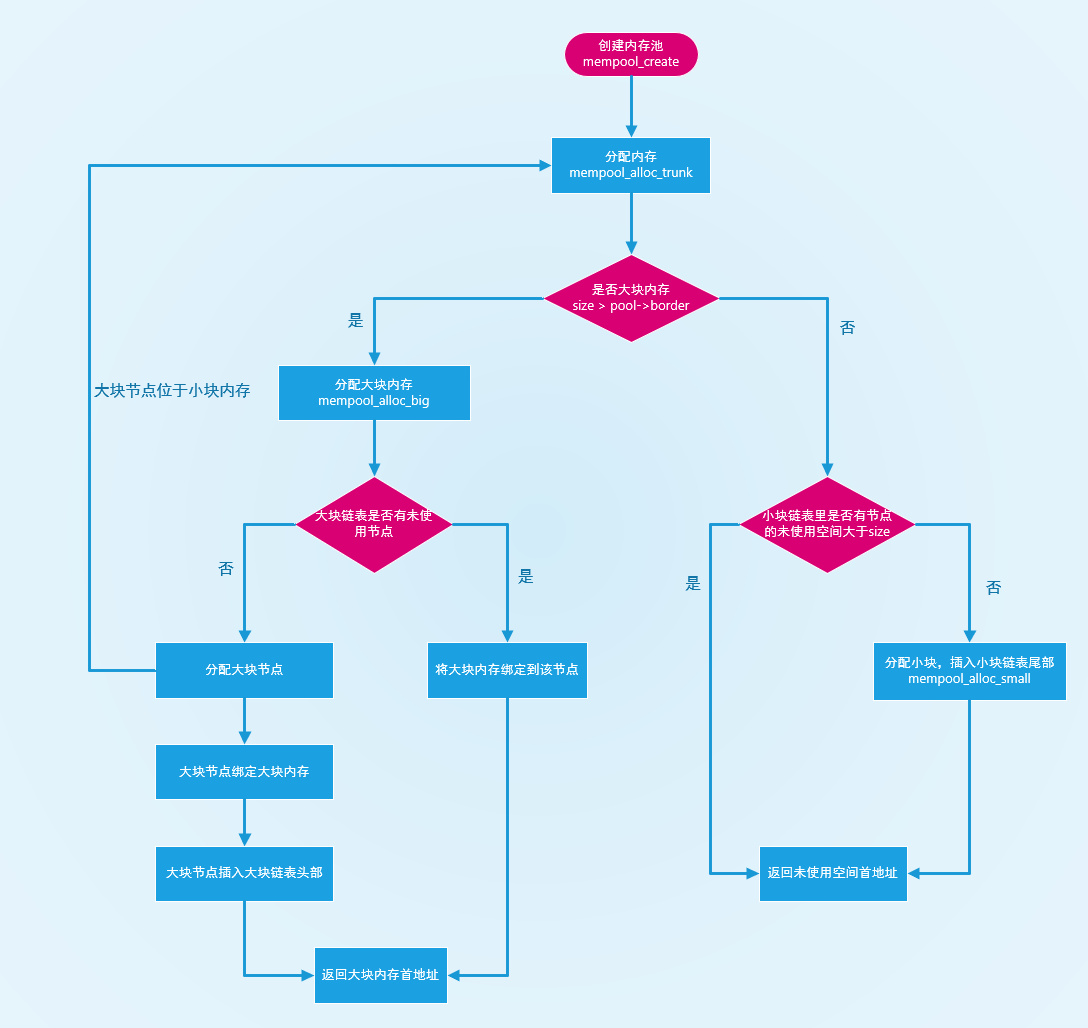
代码流程图
代码实现
本文仿照nginx,基于1个连接1个内存池这种方案实现内存池
- 小块定义
small_trunk - 大块定义
big_trunk - 内存池定义
mempool - 创建内存池
mempool_create - 销毁内存池
mempool_destroy - 重置内存池
mempool_reset - 块分配
mempool_alloc_trunk - 大块分配
mempool_alloc_big - 小块分配
mempool_alloc_small - 释放大块内存
mempool_free_trunk
小块链表用尾插法
大块链表用头插法
大块的节点(不包括data)位于小块内存中
小块内存的大小由用户决定:mempool_create(size_t size)
具体代码
/*
* 内存池结构体定义
* 创建内存池
* 块分配
* 大块分配
* 小块分配
* 大块释放
* 销毁内存池
* 重置内存池
*/
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define ENABLE_LOG
#define MP_ALIGNMENT 32
#define MP_MAX_SMALL_TRUNK 4096
#define MP_MIN_SMALL_TRUNK 16 // 保证big_trunk结构体是小块内存
#define ALIGN_PTR(ptr, align) (void*)(((size_t)(ptr) + ((align) - 1)) & (~((align) - 1)))
/*
* 指针如果定义为void*,如果要进行算数运算(+或-),单位是1,跟unsinged char*一样
* 6.24 Arithmetic on void- and Function-PointersIn GNU C,
* addition and subtraction operations are supported on pointers to void and on pointers to functions.
* This is done by treating the size of a void or of a function as 1.
* A consequence of this is that sizeof is also allowed on void and on function types, and returns 1.
* The option -Wpointer-arith requests a warning if these extensions are used.
*
* 定义为unsigned char*更加明确知道单位是1
*
* 注意指针是结构体指针进行算数运算要转为unsigned char*
*/
// 小块
typedef struct _small_trunk {
unsigned char* last; // 未使用内存首地址
unsigned char* end; // 未使用内存尾地址
struct _small_trunk* next; // 指向下一小块
size_t failed; // 申请失败次数
} small_trunk;
// 大块
typedef struct _big_trunk {
struct _big_trunk* next; // 指向下一个大块
void* start; // 大块首地址
} big_trunk;
// 内存池
typedef struct _mempool {
size_t border; // 大小块边界
small_trunk* cur_small; // 当前的小块
big_trunk* big; // 第一个大块
small_trunk first_small[0]; // 指向第一个小块
} mempool;
void* mempool_alloc_trunk(mempool* pool, size_t size);
mempool* mempool_create(size_t size) {
mempool* pool;
int ret = posix_memalign((void**)&pool, MP_ALIGNMENT, sizeof(mempool) + sizeof(small_trunk) + size);
if (0 != ret) {
return NULL;
}
memset(pool, 0, sizeof(mempool) + sizeof(small_trunk) + size);
pool->border = size > MP_MAX_SMALL_TRUNK ? MP_MAX_SMALL_TRUNK : size;
pool->cur_small = pool->first_small;
pool->big = NULL;
// 分配的时候再对齐,这里不需要对齐
// fix bug: 没有转为unsigned char*,导致偏移量计算错误(24x56)
pool->first_small->last = (unsigned char *)pool + sizeof(mempool) + sizeof(small_trunk);
pool->first_small->end = pool->first_small->last + size;
pool->first_small->next = NULL;
pool->first_small->failed = 0;
#if 0
printf("pool:%p\n", pool);
printf("first_small:%p\n", pool->first_small);
printf("last:%p\n", pool->first_small->last);
printf("end:%p\n", pool->first_small->end);
printf("next:%p\n", pool->first_small->next);
printf("failed:%p\n", &pool->first_small->failed);
printf("first_small:%p, &first_small:%p, end:%p, end-first_small:%ld\n",
pool->first_small, &pool->first_small, pool->first_small->end,
pool->first_small->end - (unsigned char*)pool->first_small);
#endif
#ifdef ENABLE_LOG
printf("alloc pool addr:%p, border:%ld\n", pool, pool->border);
#endif
return pool;
}
// 只释放大块内存,小块内存last指针重置
void mempool_reset(mempool* pool) {
big_trunk* cur_big = pool->big;
while (cur_big) {
if (cur_big->start) {
#ifdef ENABLE_LOG
printf("free big trunk addr:%p\n", cur_big->start);
#endif
free(cur_big->start);
cur_big->start = NULL;
}
cur_big = cur_big->next;
}
pool->big = NULL;
small_trunk* cur_small = pool->first_small;
while (cur_small) {
cur_small->last = (unsigned char*)cur_small + sizeof(small_trunk);
cur_small->failed = 0;
cur_small = cur_small->next;
}
}
// 大块结构体位于小块上,先释放大块,再释放小块
void mempool_destroy(mempool* pool) {
big_trunk* cur_big = pool->big;
while (cur_big) {
#ifdef ENABLE_LOG
printf("free big trunk addr:%p\n", cur_big->start);
#endif
free(cur_big->start);
cur_big->start = NULL;
cur_big = cur_big->next;
}
small_trunk* cur_small = pool->first_small->next;
small_trunk* next_small;
while (cur_small) {
next_small = cur_small->next;
#ifdef ENABLE_LOG
printf("free small trunk addr:%p\n", cur_small);
#endif
free(cur_small);
cur_small = next_small;
}
#ifdef ENABLE_LOG
printf("free pool addr:%p\n", pool);
#endif
free(pool);
}
/*
* 分配小块结构体和内存
* 将新的小块插入小块链表尾部(尾插法)
* 如果当前块失败次数超过4,则将内存池当前块指针指向下一块小块
* 返回未使用内存起始地址对齐后的值trunk_last
*/
static void* mempool_alloc_small(mempool* pool, size_t size) {
small_trunk* new_trunk;
size_t trunk_size = pool->first_small->end - (unsigned char*)pool->first_small;
int ret = posix_memalign((void**)&new_trunk, MP_ALIGNMENT, trunk_size);
if (0 != ret) {
return NULL;
}
#ifdef ENABLE_LOG
printf("alloc small trunk addr:%p\n", new_trunk);
#endif
memset(new_trunk, 0, trunk_size);
unsigned char* trunk_start = (unsigned char*)new_trunk + sizeof(small_trunk);
unsigned char* trunk_last = ALIGN_PTR(trunk_start, MP_ALIGNMENT);
new_trunk->last = trunk_last + size;
new_trunk->end = (unsigned char*)new_trunk + trunk_size;
new_trunk->next = NULL;
new_trunk->failed = 0;
small_trunk* it;
small_trunk* cur_small = pool->cur_small;
for (it = pool->first_small; it->next; it = it->next) {
if (++it->failed > 4) {
cur_small = it->next;
}
}
it->next = new_trunk;
pool->cur_small = cur_small ? cur_small : new_trunk;
return trunk_last;
}
/*
* 分配大块内存
* 判断大块链表是否有未使用节点,有则将大块内存绑定到该节点
* 没有则分配大块节点,然后绑定大块内存,大块节点插入大块链表头部(头插法)
* 返回大块内存首地址ret
*/
static void* mempool_alloc_big(mempool* pool, size_t size) {
void* ret = malloc(size);
if (!ret) {
NULL;
}
memset(ret, 0, size);
int n = 0;
big_trunk* cur;
for (cur = pool->big; cur && ++n > 3; cur = cur->next) {
if (!cur->start) {
cur->start = ret;
return ret;
}
}
big_trunk* new_node = mempool_alloc_trunk(pool, sizeof(big_trunk));
if (!new_node) {
free(ret);
return NULL;
}
new_node->start = ret;
new_node->next = pool->big;
pool->big = new_node;
#ifdef ENABLE_LOG
printf("get big trunk %p\n", ret);
#endif
return ret;
}
/*
* size大于边界值分配大块,否则分配小块
* 分配小块时,从当前小块开始遍历小块链表,找到大于size的未使用空间时直接返回,
* 找不到则创建小块并返回
*/
void* mempool_alloc_trunk(mempool* pool, size_t size) {
if (size > pool->border) {
return mempool_alloc_big(pool, size);
}
small_trunk* cur;
for (cur = pool->cur_small; cur; cur = cur->next) {
cur->last = ALIGN_PTR(cur->last, MP_ALIGNMENT);
printf("end-last:%ld, last:%p, end:%p\n", cur->end - cur->last, cur->last, cur->end);
if (cur->end - cur->last >= size) {
void *ret = cur->last;
cur->last = cur->last + size;
#ifdef ENABLE_LOG
printf("get smaller trunk %p size %ld from small trunk %p\n", ret, size, cur);
#endif
return ret;
}
}
return mempool_alloc_small(pool, size);
}
// 释放大块,小块不能用该函数释放
void mempool_free_trunk(mempool* pool, void* trunk) {
big_trunk* big = pool->big;
while (big) {
if (big->start == trunk) {
#ifdef ENABLE_LOG
printf("free big trunk addr:%p\n", big->start);
#endif
free(big->start);
big->start = NULL;
return;
}
big = big->next;
}
}
int main() {
mempool* pool = mempool_create(5000);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
void* trunk = mempool_alloc_trunk(pool, 1024);
if (!trunk) {
printf("alloc small failed\n");
return -1;
}
// printf("alloc small success\n");
}
printf("\nalloc 10 big trunk\n");
void* arr[10];
for (i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
void* trunk = mempool_alloc_trunk(pool, 8000);
if (!trunk) {
printf("alloc big failed\n");
return -1;
}
arr[i] = trunk;
}
printf("\nfree 10 big trunk\n");
for (i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
mempool_free_trunk(pool, arr[i]);
}
printf("\nreset pool\n");
mempool_reset(pool);
for (i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
void* trunk = mempool_alloc_trunk(pool, 1024);
if (!trunk) {
printf("2 alloc small failed\n");
return -1;
}
}
printf("\ndestory pool\n");
mempool_destroy(pool);
pool = NULL;
return 0;
}