目录
1--汉明距离(461)

主要思路:
按位异或,统计1的个数;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
class Solution {
public:
int hammingDistance(int x, int y) {
int z = x ^ y; // 按位异或
int res = 0;
while(z){
if((z % 2) == 1) res++;
z = z >> 1; // 右移
}
return res;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
// x = 1, y = 4
int x = 1, y = 4;
Solution S1;
int res = S1.hammingDistance(x, y);
std::cout << res << std::endl;
return 0;
}2--目标和(494)
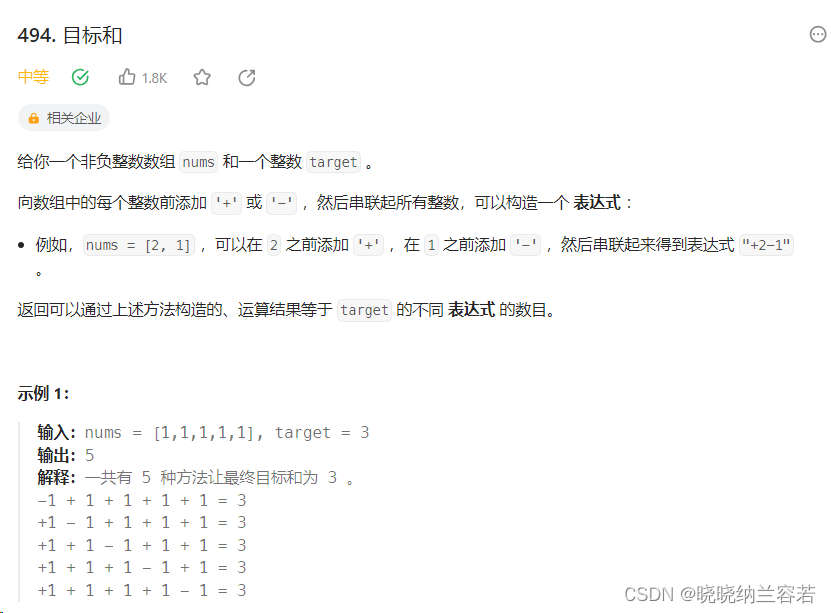
主要思路:
转化为 0-1 背包问题,一部分数值连同 target 转化为背包容量,剩余一部分数值转化为物品,求解恰好装满背包容量的方法数;dp[j] 表示背包容量为 j 时,装满背包的方法数;
状态转移方程:dp[j] += dp[j - nums[i]],其实质是:当背包已经装了nums[i]时,剩余容量为 j - nums[i],此时装满剩余容量的方法数为 dp[j - nums[i]],遍历不同的 nums[i] 将方法数相加即可;
是有点难理解。。。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
class Solution {
public:
int findTargetSumWays(std::vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int sum = 0;
for(int num : nums) sum += num;
if(sum < std::abs(target)) return 0; // 数组全部元素相加相减都不能构成target
if((sum + target) % 2 == 1) return 0; // 不能二等分
int bagsize = (sum + target) / 2;
std::vector<int> dp(bagsize + 1, 0);
dp[0] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){ // 遍历物品
for(int j = bagsize; j >= nums[i]; j--){ // 遍历背包容量
dp[j] += dp[j - nums[i]];
}
}
return dp[bagsize];
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
// nums = [1, 1, 1, 1, 1], target = 3
std::vector<int> test = {1, 1, 1, 1, 1};
int target = 3;
Solution S1;
int res = S1.findTargetSumWays(test, target);
std::cout << res << std::endl;
return 0;
}3--把二叉搜索树转换为累加树(538)
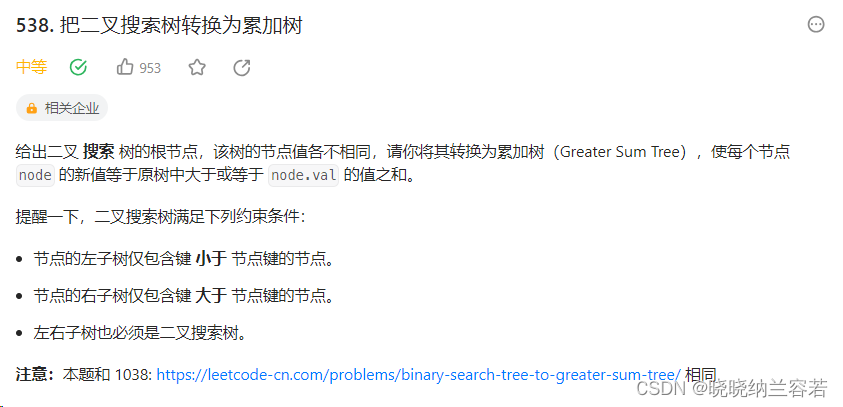
主要思路:
二叉树递归,本题的遍历顺序应该为 右→根→左;逐层向下传递数据,同时回溯逐层向上返回数据;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* convertBST(TreeNode* root){
dfs(root, 0);
return root;
}
int dfs(TreeNode* root, int sum){
if(root == nullptr) return sum;
// 右
int right = dfs(root->right, sum);
// 根
root->val = root->val + right;
// 左
int left = dfs(root->left, root->val);
return left;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
// [4, 1, 6, 0, 2, 5, 7, null, null, null, 3, null, null, null, 8]
TreeNode* Node1 = new TreeNode(4);
TreeNode* Node2 = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode* Node3 = new TreeNode(6);
TreeNode* Node4 = new TreeNode(0);
TreeNode* Node5 = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode* Node6 = new TreeNode(5);
TreeNode* Node7 = new TreeNode(7);
TreeNode* Node8 = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode* Node9 = new TreeNode(8);
Node1->left = Node2;
Node1->right = Node3;
Node2->left = Node4;
Node2->right = Node5;
Node3->left = Node6;
Node3->right = Node7;
Node5->right = Node8;
Node7->right = Node9;
Solution S1;
TreeNode* res = S1.convertBST(Node1);
// 层次遍历打印
std::queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(res);
while(!q.empty()){
TreeNode* top = q.front();
q.pop();
if(top != nullptr){
std::cout << top->val << " ";
}
else{
std::cout << "null" << " ";
}
if(top != nullptr){
q.push(top->left);
q.push(top->right);
}
}
return 0;
}4--二叉树的直径(543)

主要思路:
递归二叉树,对于每一个节点,递归求解左子树的结点数,右子树的结点数,向上返回最大的节点树;
二叉树的直径等于某一个节点左右子树最大路径的总结点数,例如上图中[4, 2, 1, 3]可以理解为以 1 为根节点,其左子树路径的最大结点数为[4, 2],右子树路径的最大结点数为[3];
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
int res = 1; // 路径经过的最大结点数
dfs(root, res);
return res - 1; // res - 1 即为直径
}
int dfs(TreeNode* root, int &res){
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
int left = dfs(root->left, res);
int right = dfs(root->right, res);
res = std::max(res, left + right + 1);
return std::max(left, right) + 1;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
// root = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
TreeNode* Node1 = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode* Node2 = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode* Node3 = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode* Node4 = new TreeNode(4);
TreeNode* Node5 = new TreeNode(5);
Node1->left = Node2;
Node1->right = Node3;
Node2->left = Node4;
Node2->right = Node5;
Solution S1;
int res = S1.diameterOfBinaryTree(Node1);
std::cout << res << std::endl;
return 0;
}5--和为L的子数组(560)

主要思路:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
class Solution {
public:
int subarraySum(std::vector<int>& nums, int k){
std::unordered_map<int, int> hash_map;
hash_map[0] = 1;
int pre = 0; // 前缀和
int res = 0; // 返回的数目
for(auto num : nums){
pre += num; // 截止到当前节点的累加和
if(hash_map.find(pre - k) != hash_map.end()){ // 存在hash_map[pre - k]的节点j,即从节点j开始到当前节点的累加和为k,匹配
res += hash_map[pre - k];
}
hash_map[pre]++; // 累加和为pre的节点数+1
}
return res;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
// nums = [1, 1, 1], k = 2
std::vector<int> test = {1, 1, 1};
int k = 2;
Solution S1;
int res = S1.subarraySum(test, k);
std::cout << res << std::endl;
return 0;
}6--最短无序连续子数组(581)

主要思路:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <limits.h>
class Solution {
public:
int findUnsortedSubarray(std::vector<int>& nums) {
int left_max = INT_MIN, right_min = INT_MAX;
int l = -1, r = -1; // 初始化左右边界
int n = nums.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(nums[i] >= left_max){
left_max = nums[i]; // 更新左边最大值
}
else{
r = i; // 更新右边界
}
if(nums[n - i - 1] <= right_min){
right_min = nums[n - i - 1];
}
else{
l = n - i - 1; // 更新左边界
}
}
return r == -1? 0 : r - l + 1;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
// nums = [2, 6, 4, 8, 10, 9, 15]
std::vector<int> test = {2, 6, 4, 8, 10, 9, 15};
Solution S1;
int res = S1.findUnsortedSubarray(test);
std::cout << res << std::endl;
return 0;
}7--合并二叉树(617)

主要思路:
经典二叉树递归;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
struct TreeNode{
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right){}
};
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* mergeTrees(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {
if(root1 == nullptr) return root2;
if(root2 == nullptr) return root1;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(root1->val + root2->val);
root->left = mergeTrees(root1->left, root2->left);
root->right = mergeTrees(root1->right, root2->right);
return root;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
// root1 = [1,3,2,5], root2 = [2,1,3,null,4,null,7]
TreeNode *Node1 = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode *Node2 = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode *Node3 = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode *Node4 = new TreeNode(5);
Node1->left = Node2;
Node1->right = Node3;
Node2->left = Node4;
TreeNode *Node5 = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode *Node6 = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode *Node7 = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode *Node8 = new TreeNode(4);
TreeNode *Node9 = new TreeNode(7);
Node5->left = Node6;
Node5->right = Node7;
Node6->right= Node8;
Node7->right = Node9;
Solution S1;
TreeNode *res = S1.mergeTrees(Node1, Node5);
std::queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(res);
while(!q.empty()){
TreeNode* cur = q.front();
q.pop();
if(cur != nullptr){
std::cout << cur->val << " ";
q.push(cur->left);
q.push(cur->right);
}
else{
std::cout << "null" << " ";
}
}
return 0;
}8--任务调度器(621)

主要思路:
视频讲解参考:任务调度器
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
class Solution {
public:
int leastInterval(std::vector<char>& tasks, int n) {
using pii = std::pair<int, int>;
// 就绪队列: <任务对应的数量, 任务类型> 大顶堆
std::priority_queue<pii> pq2;
// 冷冻队列: <上次执行时间, 任务类型> 小顶堆
std::priority_queue<pii, std::vector<pii>, std::greater<pii>> pq1;
std::vector<int> cnt(26); // 每种任务剩余的数量
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
std::vector<int> last(26, -INF); // 每种任务上次执行完的时间
for(char c : tasks) cnt[c - 'A']++; // 初始化任务数量
for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++) if(cnt[i]) pq2.push({cnt[i], i}); // 一开始全部处于就绪队列
int time = 0;
while(!pq1.empty() || !pq2.empty()){
// 先把冷冻队列当中已就绪的任务放到就绪队列中
while(!pq1.empty() && pq1.top().first + n < time){
auto item = pq1.top();
pq1.pop();
pq2.push({cnt[item.second], item.second});
}
// 此时冷冻队列中的任务都非就绪,只能从就绪队列中选取任务执行
if(!pq2.empty()){
// 选取数量最多的任务
auto item = pq2.top();
pq2.pop();
cnt[item.second]--; // 数量减1
if(cnt[item.second]){
// 执行完后,将任务放到冷冻队列
pq1.push({time, item.second});
}
}
time++;
}
return time;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
// tasks = ["A","A","A","B","B","B"], n = 2
std::vector<char> test = {'A', 'A', 'A', 'B', 'B', 'B'};
int n = 2;
Solution S1;
int res = S1.leastInterval(test, n);
std::cout << res << std::endl;
return 0;
}9--回文子串(647)

主要思路:
经典思路是基于滑动窗口,另一个思路是基于动态规划;
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
class Solution {
public:
int countSubstrings(std::string s) {
// dp[i][j] 表示区间[i, j]构成的字符串是否是回文串
std::vector<std::vector<bool>> dp(s.length(), std::vector<bool>(s.length(), false));
// 初始化单个字符为回文字符串
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
dp[i][i] = true;
}
int ret = s.length(); // 初始化返回结果
// 递推
for(int len = 2; len <= s.length(); len++){ // 遍历区间长度
for(int l = 0; l + len - 1 < s.length(); l++){ // 枚举左边界
int r = l + len - 1;
if(s[l] != s[r]) continue;
// s[l] == s[r]
if(len == 2 || dp[l+1][r-1] == true){
dp[l][r] = true;
ret++;
}
}
}
return ret;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
// s = "abc"
std::string test= "abc";
Solution S1;
int res = S1.countSubstrings(test);
std::cout << res << std::endl;
return 0;
}10--每日温度(739)

主要思路:
经典单调栈,维护一个单调栈存储索引,通过索引比较温度并记录对应的天数;
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
class Solution {
public:
std::vector<int> dailyTemperatures(std::vector<int>& temperatures) {
std::stack<int> stk; // 存储索引
std::vector<int> res(temperatures.size(), 0);
for(int i = 0; i < temperatures.size(); i++){
while(!stk.empty() && temperatures[i] > temperatures[stk.top()]){ // 通过索引比较温度
res[stk.top()] = i - stk.top();
stk.pop();
}
stk.push(i);
}
return res;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
// temperatures = [73, 74, 75, 71, 69, 72, 76, 73]
std::vector<int> test = {73, 74, 75, 71, 69, 72, 76, 73};
Solution S1;
std::vector<int> res = S1.dailyTemperatures(test);
for(int num : res) std::cout << num << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}Leetcode Hot 100 end in 2023.11.04 !!!

