计算contigs和genes相对丰度可以提供有关微生物群落结构和功能的信息。以下是计算这两个指标的意义:
1. Contigs的相对丰度:contigs是利用基因组测序技术获得的碎片序列,通过计算contigs的相对丰度可以了解微生物群落中不同菌种的相对丰度。这可以帮助研究者理解微生物群落的物种组成和群落结构。
2. Genes的相对丰度:基因是生物体内功能的基本单位,通过计算基因的相对丰度可以了解不同菌群的功能特征。这可以帮助研究者了解微生物群落的代谢能力、生物合成能力和环境适应性等。
通过同时计算contigs和genes的相对丰度,可以提供全面的微生物群落信息。这些信息对于研究者了解微生物群落的组成和功能、揭示微生物与宿主相互作用等方面具有重要的意义。
第一种方式 基于Bowtie2、samtools、checkm
计算contigs的丰度一般使用assembly的结果,计算基因风度时一般用prodigal的结果,prodigal结果中建议同时输出蛋白序列和核酸序列文件,基因注释是一般使用diamond需要使用蛋白序列,而这里计算丰度需要与原始核酸序列进行比对,所以这里要用核酸序列,prodigal输出的核酸序列和蛋白序列id一样,所以只需要最后以序列id进行mapping就可以了。
首先根据拼接的contigs构建新的Index,如下所示:
bowtie2-build --threads 20 sample1/final_assembly.fasta sample1.contig
# 或 prodigal结果
bowtie2-build --threads 20 sample1.nucle_seq.fa sample1.gene接下来将宏基因组测序的全部reads映射到拼接得到的Contigs上,每个reads至多只能分配到一条Contigs上:
#注意前面步骤的输出文件名,与这里的-x参数对应
# 如果是使用assembly的
bowtie2 -p 20 \
-x sample1.contig \
-1 sample1_clean_reads_1.fq \
-2 sample1_clean_reads_2.fq \
-S sample1.contig.sam \
--fast
# 或 prodigal结果
bowtie2 -p 20 \
-x sample1.gene \
-1 sample1_clean_reads_1.fq \
-2 sample1_clean_reads_2.fq \
-S sample1.gene.sam \
--fast
以下为第二种方式共用
使用samtools工具将sam文件转化为bam文件:
samtools view -bS --threads 20 sample1.contig.sam > sample1.contig.bam
# prodigal
samtools view -bS --threads 20 sample1.gene.sam > sample1.gene.bam对bam文件按照比对的位置坐标对reads进行排序:
samtools sort sample1.contig.bam -o sample1.contig.reads.sorted.bam --threads 20
# prodigal结果
samtools sort sample1.gene.bam -o sample1.gene.reads.sorted.bam --threads 20此bam文件中便储存了reads的mapping结果,接下来一般是自己写脚本来解析。这里我们也可以借助CheckM来实现。要计算coverage首先需要准备bam的index文件,如下所示:
samtools index sample1.contig.reads.sorted.bam
#prodigal 结果
samtools index sample1.gene.reads.sorted.bam运行结束后生成会生成伴随的index文件contig.reads.sorted.bam.bai,其与对应的sorted bam放在同一路径。CheckM是一个宏基因组bins评估工具,这时候我们可以把所有的contigs序列文件当作一个“bin”放到bins文件夹中。接下来使用CheckM计算coverage:
#每个样品一个文件夹,作为一个bin
mkdir sample1
cp sample1.contig.fasta sample1
checkm coverage \
-x fasta \
-m 20 \
-t 20 \
sample1 \
sample1.contigs_coverage.out \
sample1.contig.reads.sorted.bam
### prodigal
cp sample1.nucle_seq.fa sample1
checkm coverage \
-x fasta \
-m 20 \
-t 20 \
sample1 \
sample1.gene_coverage.out \
sample1.gene.reads.sorted.bam结果包含contig序列ID、所在的bin的ID、coverage等信息,如下所示,用excel对齐了看吧:

- Sequence Id: 序列的唯一标识符。
- Bin Id: 该序列所属的Bin(即被分组到哪个类别)。在宏基因组学中,Bin通常指的是组装后相似特征或物种的组集合。
- Sequence length (bp): 序列的长度,以碱基对(bp)计算。
- Bam Id: 对应该序列的测序数据文件。
- Coverage: 覆盖度,指的是这个contig在样品中出现的平均次数。它通常由测序reads的比对情况得出。
- Mapped reads: 映射的reads数量,指的是能够成功比对到这个contig上的测序reads数量。
相对丰度计算公式:
要计算基因在样品中的相对丰度,您可以使用覆盖度和Mapped reads。通常情况下,丰度可以用覆盖度和测序reads的总数来估算。例如,可以使用以下公式计算相对丰度:
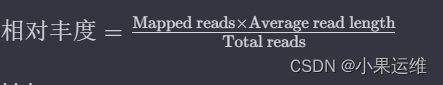
其中:
- Mapped reads 是该contig的映射reads数量。
- Average read length 是测序reads的平均长度。
- Total reads 是所有测序reads的总数。
Total reads统计:
python脚本:
def count_reads_fastq(fastq_file):
with open(fastq_file, 'r') as f:
count = sum(1 for line in f) // 4 # 每4行代表一个read,因此除以4得到reads数量
return count
# 替换为您的FASTQ文件路径
file_path = 'path/to/your/fastq_file.fastq'
# 调用函数计算reads数量
reads_count = count_reads_fastq(file_path)
print(f"FASTQ文件中的reads数量为: {reads_count}")
bash脚本:
# 统计FASTQ文件中reads的数量
grep -c "^@" your_fastq_file.fastq
这里需要注意第一列的sequence id,后续需要mapping到基因注释结果中对应的seq id,除此外,我们只需要reads的mapping信息即可。接下来可以根据map的reads数计算相对丰度,也即除以contig长度和总得reads数,类似于RNA-seq中的RPKM标准化方法。假如是多样品混合拼接,只需要将每一个样品的reads数据重复上面操作,最后根据contig id进行整合。
第二种方式:BWA(推荐)、samtools、CheckM
#首先对参考序列构建index:
bwa index -p sample1_gene sample1.nucle_seq.fa
#使用BWA-MEM进行比对:
bwa mem \
-t 20 \
sample1_gene \
sample1_clean_1.fastq \
sample1_clean_2.fastq \
>sample1_gene.sam从这里开始与第一种方式samtools步骤开始相同
第三种方式: bedtools计算
# 步骤1:比对测序reads到参考基因组
# 假设使用Bowtie2进行比对
bowtie2-build your_genome.fa your_genome_index # 如果尚未构建索引
bowtie2 -x your_genome_index -U your_reads.fastq -S aligned.sam
# 步骤2:将比对结果转换为BAM格式
samtools view -S -b aligned.sam > aligned.bam
# 再sort排序一下
samtools sort aligned.bam -o aligned.sorted.bam --threads 20
samtools index aligned.sorted.bam
# 步骤3:提取覆盖度信息
# 假设使用bedtools进行提取覆盖度信息
bedtools genomecov -ibam aligned.sorted.bam > coverage.bed
# 步骤4:计算基因长度
# 假设已经有基因长度信息的文件,如genes_lengths.txt
# 步骤5:计算相对丰度
awk 'BEGIN {OFS="\t"} NR==FNR {len[$1]=$2; next} {print $1, $2/len[$1]}' genes_coverage.txt genes_lengths.txt > relative_abundance.txt
全流程计算脚本
多样品请自己做for循环操作
自动分析脚本1
用于计算基于 bwa-mem、samtools 和 CheckM 的Contigs相对丰度。该脚本假设你已经有参考基因组和测序数据,并安装了相应的软件。
#!/bin/bash
# 定义文件路径
reference_genome="your_reference_genome.fa"
reads="your_reads.fastq"
# 步骤1:用bwa-mem比对测序reads到参考基因组
bwa index $reference_genome # 如果尚未构建索引
bwa mem -t 4 $reference_genome $reads > aligned.sam
# 步骤2:将比对结果转换为BAM格式
samtools view -bS aligned.sam > aligned.bam
samtools sort -o aligned_sorted.bam aligned.bam
samtools index aligned_sorted.bam
# 步骤3:使用CheckM估算Contigs的丰度
checkm lineage_wf -f checkm_output.txt -x fa $reference_genome contigs_dir/ checkm_results/
# 步骤4:提取覆盖度信息
checkm qa -o 2 -f checkm_coverage.txt checkm_results/lineage.ms contigs_dir/ coverage.txt
自动分析脚本2
基于bowtie2、samtools和bedtools计算Contigs或Genes在样品中相对丰度的流程自动分析脚本。请注意,这个脚本仅供参考,并不能直接运行,因为其中的文件路径、参数和具体数据可能需要根据实际情况进行调整。
#!/bin/bash
# 假设有参考基因组文件your_genome.fa,测序reads文件your_reads.fastq和基因注释文件genes_annotation.gff
# 步骤1:构建参考基因组索引
bowtie2-build your_genome.fa your_genome_index
# 步骤2:将测序reads比对到参考基因组
bowtie2 -x your_genome_index -U your_reads.fastq -S aligned.sam
# 步骤3:将比对结果转换为BAM格式
samtools view -S -b aligned.sam > aligned.bam
# 步骤4:生成基因覆盖度文件
bedtools genomecov -ibam aligned.bam -g your_genome.fa.fai > coverage.txt
# 步骤5:根据基因注释文件提取基因长度信息
awk '{if($3=="gene") print $0}' genes_annotation.gff | cut -f 1,4,5 > genes_lengths.txt
# 步骤6:根据覆盖度和基因长度信息计算相对丰度
awk 'BEGIN {OFS="\t"} NR==FNR {len[$1]=$3-$2; next} {print $1, $2/len[$1]}' coverage.txt genes_lengths.txt > relative_abundance.txt
# 输出结果
echo "相对丰度计算完成。结果保存在 relative_abundance.txt 文件中。"
自动分析脚本3
# python
import subprocess
import os
# 定义文件路径
ref_genome = 'path/to/your_reference_genome.fasta'
sample_reads = 'path/to/your_sample_reads.fastq'
gene_lengths = 'path/to/your_gene_lengths.txt'
# 步骤1:比对测序reads到参考基因组
# 使用Bowtie2进行比对
bowtie_index = 'your_genome_index'
subprocess.run(['bowtie2-build', ref_genome, bowtie_index])
subprocess.run(['bowtie2', '-x', bowtie_index, '-U', sample_reads, '-S', 'aligned.sam'])
# 步骤2:将比对结果转换为BAM格式
subprocess.run(['samtools', 'view', '-S', '-b', 'aligned.sam', '-o', 'aligned.bam'])
# 步骤3:提取覆盖度信息
subprocess.run(['bedtools', 'genomecov', '-ibam', 'aligned.bam', '-g', ref_genome + '.fai', '>', 'coverage.bed'])
# 步骤4:计算基因长度
# 假设已经有基因长度信息的文件
# 步骤5:计算相对丰度
with open('genes_coverage.txt', 'r') as cov_file, open(gene_lengths, 'r') as len_file, open('relative_abundance.txt', 'w') as output:
for cov_line, len_line in zip(cov_file, len_file):
contig_id, coverage = cov_line.strip().split('\t')
gene_id, length = len_line.strip().split('\t')
rel_abundance = float(coverage) / float(length)
output.write(f"{gene_id}\t{rel_abundance}\n")
# 清理临时文件(可选)
os.remove('aligned.sam')
os.remove('aligned.bam')
os.remove('coverage.bed')
自动分析脚本4
NGless 是一个用于分析宏基因组数据的领域特定语言(DSL)。
安装和使用参考:生物信息学分析领域领先的特制语言环境NGLess(Next Generation Less)介绍、安装配置和详细使用方法-CSDN博客
以下是一个使用 NGless 的示例脚本,用于计算 contigs 或 genes 在样品中的相对丰度。请注意,这只是一个简化的示例,实际的分析脚本可能需要根据具体的数据和需求进行调整。
# 加载所需模块
ngless "0.11"
import "mapped"
# 定义输入文件
input = paired('sample_R1.fastq.gz', 'sample_R2.fastq.gz') using |read|:
read = read.subsample(percent=10) # 使用10%的数据进行演示
# 比对reads到Contigs或Genes
mapped = map(input, reference='contigs.fasta.gz', fafile=True) using |read|:
read = read.subsample(percent=10) # 使用10%的数据进行演示
# 计算覆盖度
cov = coverage(mapped)
# 计算Contigs或Genes的相对丰度
geneabundance = abundance(cov)
# 输出结果
write(geneabundance, ofile='gene_relative_abundance.txt', format="tsv")
NGless 脚本说明:
-
模块导入和输入定义: 使用
ngless版本 0.11,并导入mapped模块。定义输入文件为样品的 paired-end 测序 reads。 -
比对 reads 到 Contigs 或 Genes: 使用
map函数将测序 reads 比对到 Contigs 或 Genes 的参考序列文件(这里是示意性的文件名contigs.fasta.gz,实际需根据具体文件名修改)。 -
计算覆盖度: 使用
coverage函数从比对结果中计算覆盖度信息。 -
计算相对丰度: 使用
abundance函数从覆盖度信息中计算Contigs或Genes的相对丰度。 -
输出结果: 使用
write函数将相对丰度结果写入文件gene_relative_abundance.txt,并以制表符分隔的文本格式保存。
自动分析脚本5
# R
# 加载所需的R包
library("GenomicRanges")
## ######################获取contigs或者genes覆盖度数据
# 假设你有参考基因组文件为 genome.fa,测序 reads 文件为 reads.fastq
# 步骤1:比对测序 reads 到参考基因组
# 这里假设使用Bowtie2进行比对,需要Bowtie2已安装
system("bowtie2-build genome.fa genome_index") # 构建索引
system("bowtie2 -x genome_index -U reads.fastq -S aligned.sam") # 进行比对
# 步骤2:将比对结果转换为BAM格式
# 需要安装samtools
system("samtools view -S -b aligned.sam > aligned.bam")
# 步骤3:使用GenomicRanges包计算覆盖度
# 安装GenomicRanges包:install.packages("GenomicRanges")
library(GenomicRanges)
# 读取 BAM 文件
bam <- readGAlignments("aligned.bam", use.names=TRUE, param=ScanBamParam(what="pos"))
# 计算覆盖度
coverage <- coverage(bam)
# 将覆盖度信息写入文件
write.table(coverage, file="coverage_data.txt", sep="\t", quote=FALSE, col.names=TRUE, row.names=TRUE)
##############获取 contigs和genes 的长度数据
# 加载所需的R包
library("data.table")
# 步骤1:从组装结果文件中获取Contigs的长度
# 假设有一个示意的组装结果文件(示意数据)
assembly_data <- fread("assembly_results.csv") # 读取组装结果文件
# 计算Contigs的长度
contigs_lengths <- nchar(assembly_data$Contig_Sequence) # 假设Contig_Sequence列包含Contig序列
contigs_data <- data.frame(Contig = assembly_data$Contig_ID, Length = contigs_lengths)
# 步骤2:从基因预测结果文件中获取Genes的长度
# 假设有一个示意的基因预测结果文件(示意数据)
gene_prediction_data <- fread("gene_prediction_results.csv") # 读取基因预测结果文件
# 计算Genes的长度
genes_lengths <- gene_prediction_data$Gene_End - gene_prediction_data$Gene_Start + 1
genes_data <- data.frame(Gene = gene_prediction_data$Gene_ID, Length = genes_lengths)
# 显示Contigs和Genes的长度信息
print("Contigs长度信息:")
print(contigs_data)
print("Genes长度信息:")
print(genes_data)
############# 计算丰度
# 步骤1:读取数据
# 假设有Contigs或Genes的覆盖度数据和长度数据文件(示意)
coverage_data <- read.table("coverage_data.txt", header=TRUE) # Contigs或Genes的覆盖度数据文件
gene_lengths <- read.table("gene_lengths.txt", header=TRUE) # Contigs或Genes的长度数据文件
# 步骤2:计算相对丰度
# 合并覆盖度数据和基因长度数据
merged_data <- merge(coverage_data, gene_lengths, by="Gene")
# 计算相对丰度(示意:使用简单的覆盖度除以长度)
merged_data$Relative_Abundance <- merged_data$Coverage / merged_data$Length
# 显示计算结果
print(merged_data)