之前测试同事提过来一个问题,让帮忙统计项目中总共有多少个接口,在项目中虽然有用到swagger,但是并不是所有的接口都加了swagger需要的注解,这个时候就想象到了通过反射来实现,但是前提是需要获取Spring容器里面所有的Bean,那么如何获取呢,且看分析如下:
我们知道Spring容器在启动的时候会初始化一个默认的BeanFactory,这个BeanFactory就是org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory,也就是在著名的AbstractApplicationContext的refresh方法里面,获取BeanFactory的时候:
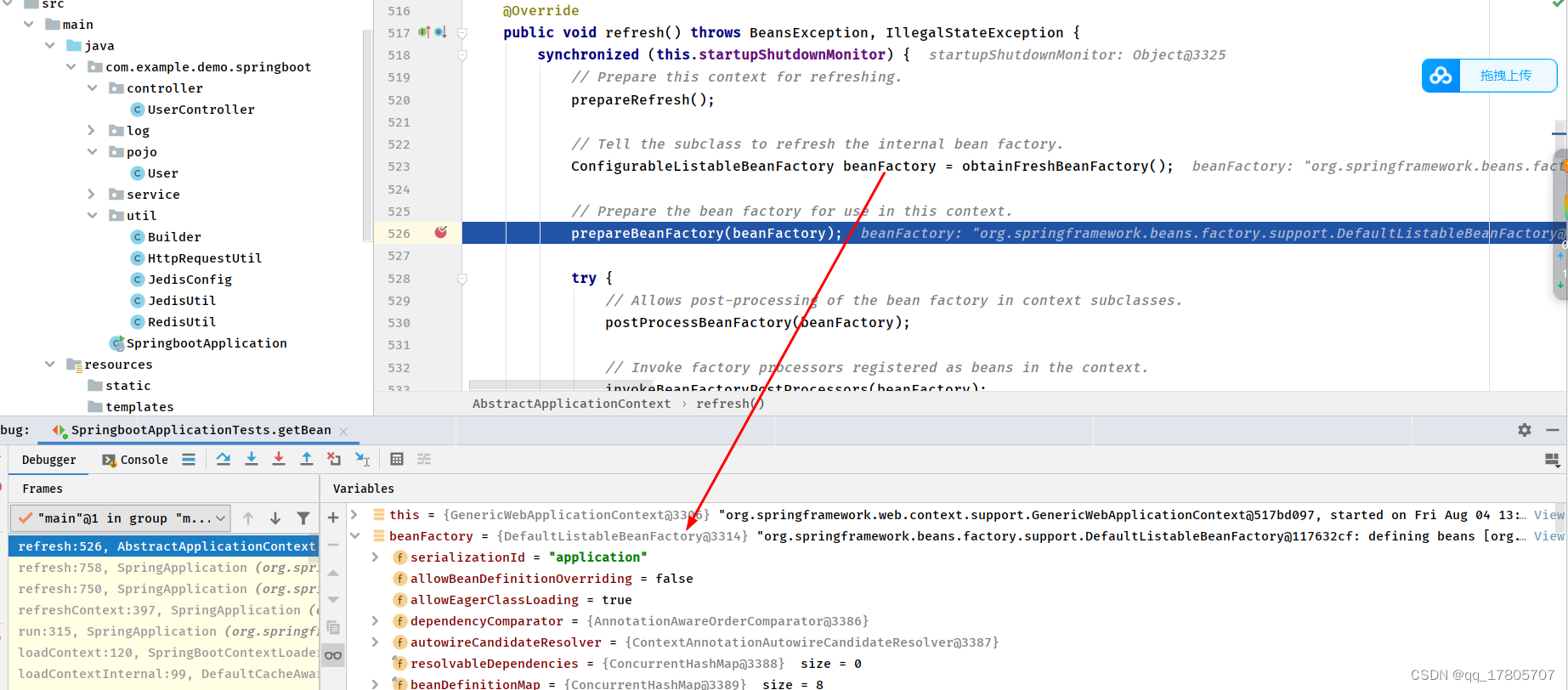
根据类的继承关系图,我们会发现DefaultListableBeanFactory实现了ListableBeanFactory这么一个接口,它里面有个方法可以获取到Srping容器里面所有的Bean名称:
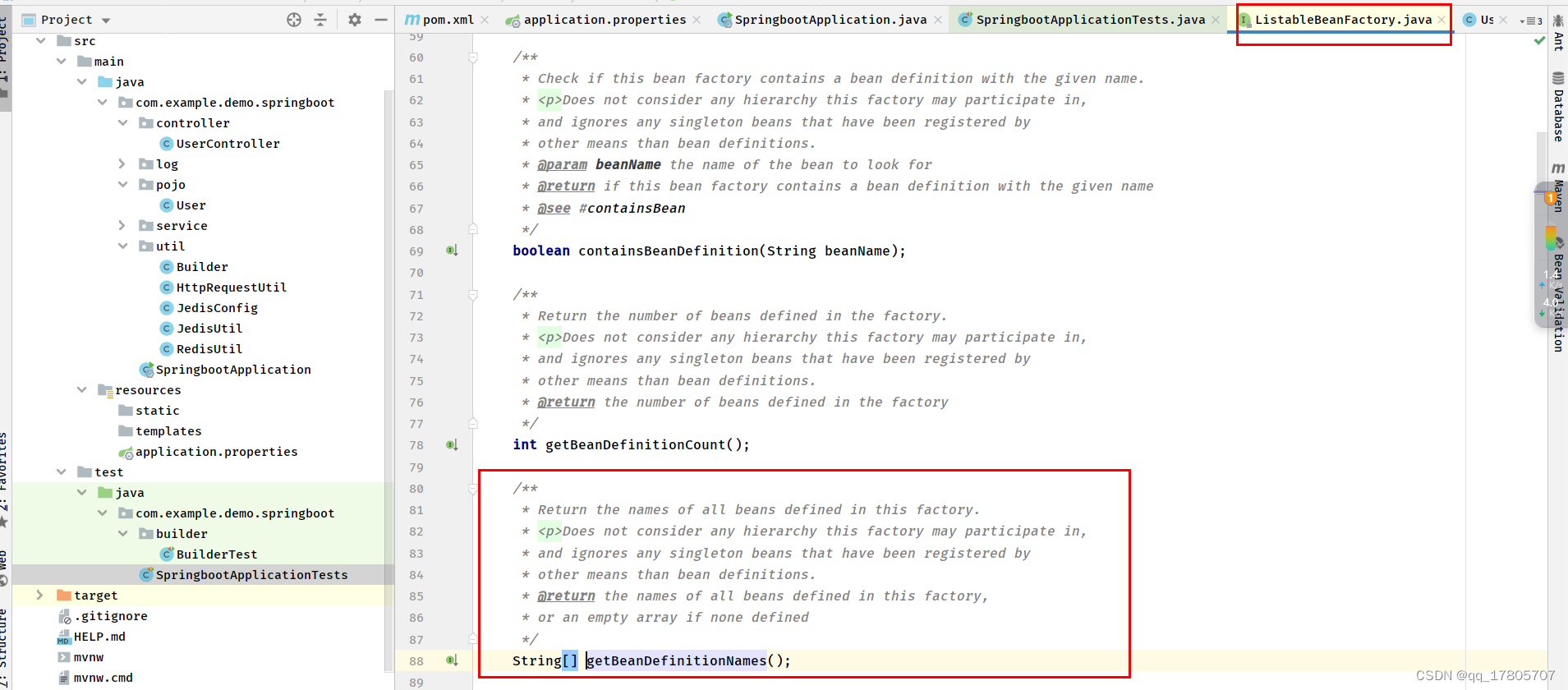
而我们知道我们通常在获取Bean的时候要么通过bean名称,要么通过bean类型,也就是我们通常用的applicationContext.getBean(beanName)和applicationContext.getBean(Class type)这两个方法,那么要获取Spring容器里面所有的bean以及统计有多少个接口就是下面的的代码了:
public void getBean() {
//获取所有的beanName
String[] beans = applicationContext
.getBeanDefinitionNames();
int i = 0;
for (String beanName : beans) {
//根据名称找到所有的bean
System.err.println(applicationContext.getBean(beanName));
//根据Bean名称找到对应的Class,然后通过反射来统计RestController、Controller、RequestMapping的数量
Class<?> beanType = applicationContext
.getType(beanName);
RestController restController = beanType.getAnnotation(RestController.class);
Controller controller = beanType.getAnnotation(Controller.class);
if (restController != null || controller != null) {
Method[] declaredMethods = beanType.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method declaredMethod : declaredMethods) {
if (declaredMethod.getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class) != null) {
i++;
}
}
}
}
System.err.println("接口数量:" + i);
}第二种方法:spring已经提供了方便获取指定注解的所有的bean和方法:,比如下面的代码就可以获取所有带有@RequestMapping的注解的方法
public void getRequestMappingMethods() {
String[] beanDefinitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(Object.class, false, true);
for (String beanDefinitionName : beanDefinitionNames) {
Object bean = null;
Lazy onBean = applicationContext.findAnnotationOnBean(beanDefinitionName, Lazy.class);
if (onBean != null) {
continue;
} else {
bean = applicationContext.getBean(beanDefinitionName);
}
Map<Method, RequestMapping> annotatedMethods = null; // referred to :org.springframework.context.event.EventListenerMethodProcessor.processBean
try {
annotatedMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(bean.getClass(),
new MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<RequestMapping>() {
@Override
public RequestMapping inspect(Method method) {
return AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method, RequestMapping.class);
}
});
} catch (Throwable ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
if (annotatedMethods == null || annotatedMethods.isEmpty()) {
continue;
}
for (Map.Entry<Method, RequestMapping> methodXxlJobEntry : annotatedMethods.entrySet()) {
Method executeMethod = methodXxlJobEntry.getKey();
RequestMapping xxlJob = methodXxlJobEntry.getValue();
// regist
System.err.println("executeMethod:"+executeMethod);
}
}
}