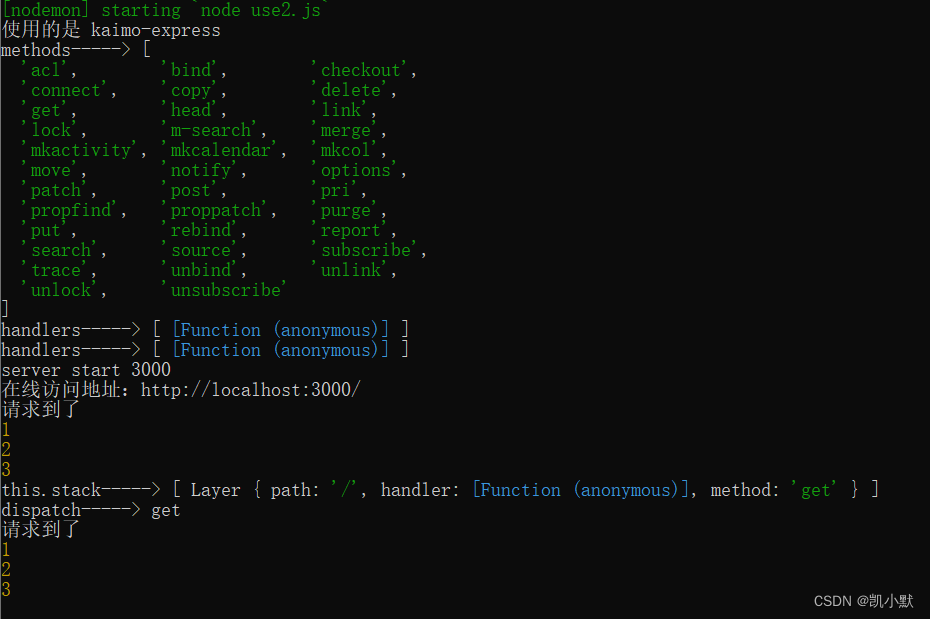
上一节实现 express 的优化处理,这一节来实现 express 的中间件
中间件的特点:
- 可以决定是否向下执行
- 可以拓展属性和方法
- 可以权限校验
- 中间件的放置顺序在路由之前
中间件基于路由,只针对路径拦截,下面是中间件的匹配规则:
- 路径为
/表示任何路径都能匹配到 - 如果以这个路径开头,则匹配
- 和路由的路径一样,也可以匹配
先看 express 的中间件 demo
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
app.use("/", (req, res, next) => {
if (req.query.kaimo == "313") {
next();
} else {
res.send("没有权限访问");
}
});
app.get("/", (req, res, next) => {
res.end("get okk end");
});
app.post("/", (req, res, next) => {
res.end("post okk end");
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log(`server start 3000`);
console.log(`在线访问地址:http://localhost:3000/`);
});
控制台执行下面命令:
curl -v -X POST http://localhost:3000/
然后去访问:http://localhost:3000/
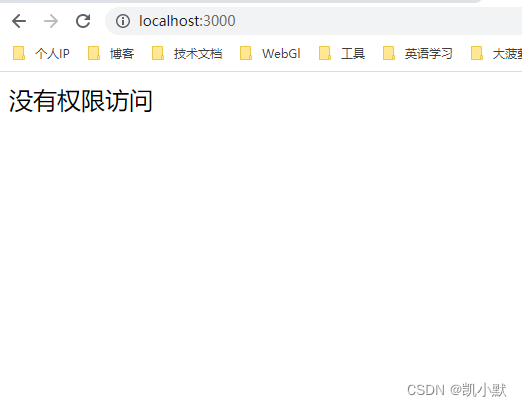
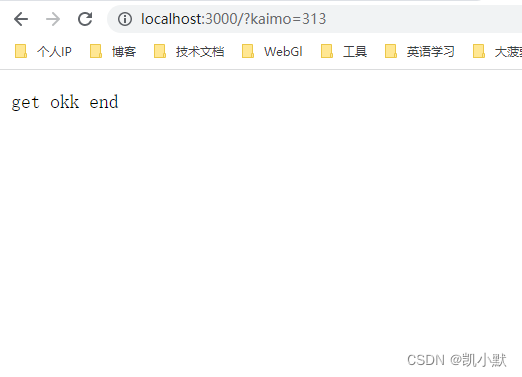
下面实现 express 中间件如图:我们需要在 Router 的前面添加中间件,它没有 route 属性,有路径跟 handler

application.js
const http = require("http");
const Router = require("./router");
const methods = require("methods");
console.log("methods----->", methods);
function Application() {
}
// 调用此方法才开始创建,不是创建应用时直接装载路由
Application.prototype.lazy_route = function () {
if (!this._router) {
this._router = new Router();
}
};
methods.forEach((method) => {
Application.prototype[method] = function (path, ...handlers) {
this.lazy_route();
this._router[method](path, handlers);
};
});
Application.prototype.use = function () {
this.lazy_route();
this._router.use(...arguments);
};
Application.prototype.listen = function () {
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
function done() {
res.end(`kaimo-express Cannot ${
req.method} ${
req.url}`);
}
this.lazy_route();
this._router.handle(req, res, done);
});
server.listen(...arguments);
};
module.exports = Application;
router/index.js
const url = require("url");
const Route = require("./route");
const Layer = require("./layer");
const methods = require("methods");
function Router() {
// 维护所有的路由
this.stack = [];
}
Router.prototype.route = function (path) {
// 产生 route
let route = new Route();
// 产生 layer 让 layer 跟 route 进行关联
let layer = new Layer(path, route.dispatch.bind(route));
// 每个路由都具备一个 route 属性,稍后路径匹配到后会调用 route 中的每一层
layer.route = route;
// 把 layer 放到路由的栈中
this.stack.push(layer);
return route;
};
methods.forEach((method) => {
Router.prototype[method] = function (path, handlers) {
// 1.用户调用 method 时,需要保存成一个 layer 当道栈中
// 2.产生一个 Route 实例和当前的 layer 创造关系
// 3.要将 route 的 dispatch 方法存到 layer 上
let route = this.route(path);
// 让 route 记录用户传入的 handler 并且标记这个 handler 是什么方法
route[method](handlers);
};
});
Router.prototype.use = function (path, ...handlers) {
// 默认第一个是路径,后面是一个个的方法,路径可以不传
if (typeof path === "function") {
handlers.unshift(path);
path = "/";
}
// 如果是多个函数需要循环添加层
for (let i = 0; i < handlers.length; i++) {
let layer = new Layer(path, handlers[i]);
// 中间件不需要 route 属性
layer.route = undefined;
this.stack.push(layer);
}
};
Router.prototype.handle = function (req, res, out) {
console.log("请求到了");
// 需要取出路由系统中 Router 存放的 layer 依次执行
const {
pathname } = url.parse(req.url);
let idx = 0;
let next = () => {
// 遍历完后没有找到就直接走出路由系统
if (idx >= this.stack.length) return out();
let layer = this.stack[idx++];
// 需要判断 layer 上的 path 和当前请求路由是否一致,一致就执行 dispatch 方法
if (layer.match(pathname)) {
// 中间件没有方法可以匹配
if (!layer.route) {
layer.handle_request(req, res, next);
} else {
// 将遍历路由系统中下一层的方法传入
// 加速匹配,如果用户注册过这个类型的方法在去执行
if (layer.route.methods[req.method.toLowerCase()]) {
layer.handle_request(req, res, next);
} else {
next();
}
}
} else {
next();
}
};
next();
};
module.exports = Router;
layer.js
function Layer(path, handler) {
this.path = path;
this.handler = handler;
}
Layer.prototype.match = function (pathname) {
if (this.path === pathname) {
return true;
}
// 如果是中间件,进行中间件的匹配规则
if (!this.route) {
if (this.path == "/") {
return true;
}
// /aaaa/b 需要 /aaaa/ 才能匹配上
return pathname.startsWith(this.path + "/");
}
return false;
};
Layer.prototype.handle_request = function (req, res, next) {
this.handler(req, res, next);
};
module.exports = Layer;
测试demo
const express = require("./kaimo-express");
const app = express();
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log(1);
next();
});
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log(2);
next();
});
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log(3);
next();
});
app.get("/", (req, res, next) => {
res.end("get okk end");
});
app.post("/", (req, res, next) => {
res.end("post okk end");
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log(`server start 3000`);
console.log(`在线访问地址:http://localhost:3000/`);
});