前言
MyBatis 包含一个非常强大的查询缓存特性,它可以非常方便地配置和定制。除了局部的 session 缓存,默认情况下是没有二级开启缓存的。那么MyBatis的一级缓存跟二级缓存在它的框架内部是如何实现的?我们去一探究竟吧。
一级缓存
一级缓存是默认开启的。当然你也可以关闭。在SQL 映射文件中,设置语句参数即可:
flushCache 将其设置为 true,任何时候只要语句被调用,都会导致本地缓存和二级缓存都会被清空,默认值:false。
使用
因为,前面我们已经知道,一级缓存是基于SqlSession生命周期的所以,我们使用同一个例子,来看一级缓存的效果。记得开启日志。< setting name=”logImpl” value=”STDOUT_LOGGING” />
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis/conf/mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
BlogMapper mapper = session.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
Blog blog = mapper.selectBlog(1L);
System.out.println(blog);
blog = mapper.selectBlog(1L);
System.out.println(blog);
} finally {
session.close();
}
}
运行结果:
Opening JDBC Connection
Created connection 2050462663.
Setting autocommit to false on JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@7a3793c7]
==> Preparing: select blog_id,blog_title,blog_content,create_time from blog where blog_id = ?
==> Parameters: 1(Long)
<== Columns: blog_id, blog_title, blog_content, create_time
<== Row: 1, 什么是mybatis, MyBatis是支持定制化SQL、存储过程以及高级映射的优秀的持久层框架。
, 2018-05-25 14:28:35.0
<== Total: 1
Blog{blogId=1, blogTitle=’什么是mybatis’, blogContent=’MyBatis是支持定制化SQL、存储过程以及高级映射的优秀的持久层框架。
‘, createTime=Fri May 25 14:28:35 CST 2018}
Blog{blogId=1, blogTitle=’什么是mybatis’, blogContent=’MyBatis是支持定制化SQL、存储过程以及高级映射的优秀的持久层框架。
‘, createTime=Fri May 25 14:28:35 CST 2018}
Resetting autocommit to true on JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@7a3793c7]
Closing JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@7a3793c7]
Returned connection 2050462663 to pool.
在日志中,我们只看到了一次查询。
源码
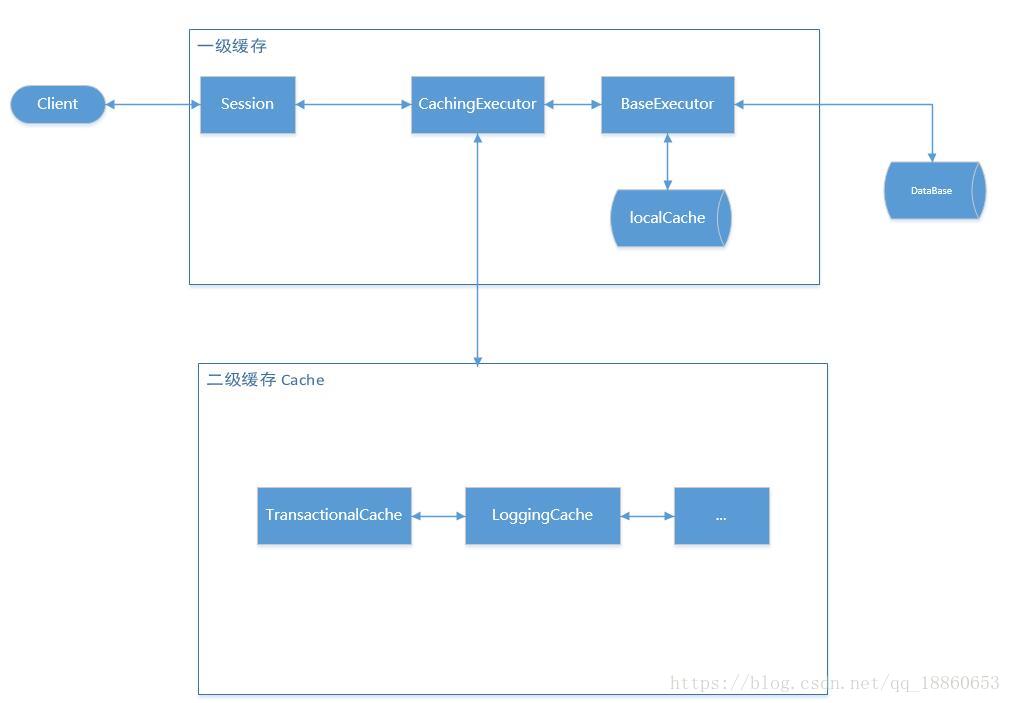
在之前的文章中,我们知道Executor是最终执行者,在实现类BaseExecutor中,有个 PerpetualCache localCache;
这是存放本地缓存(一级缓存的地方),我们看下查询的代码:
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
//首先从缓存中读取
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
//缓存中没有,则从数据库中读取
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
localCache的作用域是BaseExecutor,而SqlSession的产生是独立的,且每次都是自己new了一个Executor
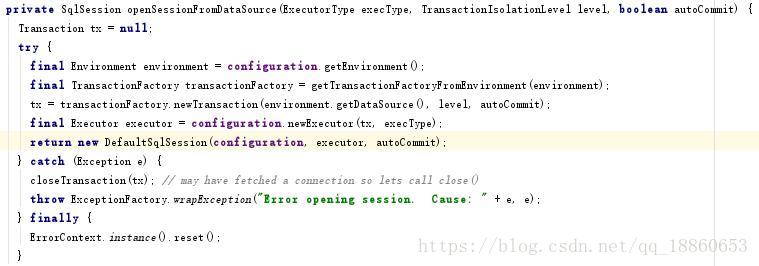
故,这个localCache缓存只在同一session下产生作用。
一级缓存在update等操作时,会清空缓存。
public void clearLocalCache() {
if (!closed) {
localCache.clear();
localOutputParameterCache.clear();
}
}
二级缓存
使用
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
要开启二级缓存,在配置中开启的清空下,你还需要在你的 SQL 映射文件中添加一行:
<cache/>
现在,我们写个demo看下其作用:
public class Demo3CacheSecond {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis/conf/mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession session1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
BlogMapper mapper1 = session1.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
Blog blog1 = mapper1.selectBlog(1L);
System.out.println("blog1:" + blog1);
session1.commit();
} finally {
session1.close();
}
SqlSession session2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
BlogMapper mapper2 = session2.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
Blog blog2 = mapper2.selectBlog(1L);
System.out.println("blog2:" + blog2);
session2.commit();
} finally {
session2.close();
}
}
}
运行结果:
Cache Hit Ratio [top.yuyufeng.learn.mybatis.mapper.BlogMapper]: 0.0
Opening JDBC Connection
Created connection 1241569743.
Setting autocommit to false on JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@4a00d9cf]
==> Preparing: select blog_id,blog_title,blog_content,create_time from blog where blog_id = ?
==> Parameters: 1(Long)
<== Columns: blog_id, blog_title, blog_content, create_time
<== Row: 1, 什么是mybatis, MyBatis是支持定制化SQL、存储过程以及高级映射的优秀的持久层框架。
, 2018-05-25 14:28:35.0
<== Total: 1
blog1:Blog{blogId=1, blogTitle=’什么是mybatis’, blogContent=’MyBatis是支持定制化SQL、存储过程以及高级映射的优秀的持久层框架。
‘, createTime=Fri May 25 14:28:35 CST 2018}
Resetting autocommit to true on JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@4a00d9cf]
Closing JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@4a00d9cf]
Returned connection 1241569743 to pool.
Cache Hit Ratio [top.yuyufeng.learn.mybatis.mapper.BlogMapper]: 0.5
blog2:Blog{blogId=1, blogTitle=’什么是mybatis’, blogContent=’MyBatis是支持定制化SQL、存储过程以及高级映射的优秀的持久层框架。
‘, createTime=Fri May 25 14:28:35 CST 2018}
从日志中分析,在第二次查询过程中,是从缓存中读取的。现在是两个session,所以是从二级缓存中读取的。
源码
开启二级缓存后,执行器Executor会被CachingExecutor包装一层。(这里用到了装饰器模式)
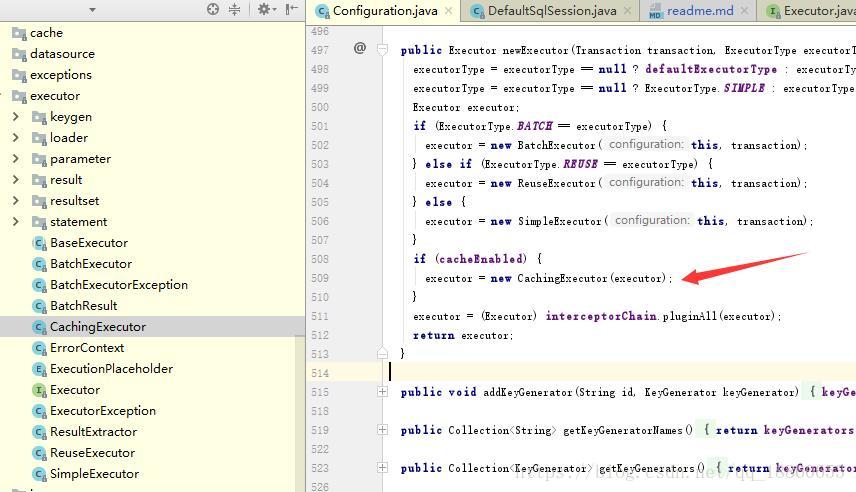
那么,我们看下它是如何用 CachingExecutor来进行二级缓存的操作的:
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
//从MappedStatement 拿到Cache
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, parameterObject, boundSql);
//首先从二级缓存中获取
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
//二级缓存中没有,则跟原来一样获取。
list = delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
//存入二级缓存中
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
在代码中,tcm(TransactionalCacheManager )是二级缓存的关键点。它是缓存存放的地方。二级缓存是Mapper域共享的,就会涉及到线程安全问题更多,所以需要更好的去维护。
public class CachingExecutor implements Executor {
private Executor delegate;
private TransactionalCacheManager tcm = new TransactionalCacheManager();
}
而二级缓存是如何起作用的呢?看下如下源码:
public class TransactionalCache implements Cache {
private Cache delegate;
private boolean clearOnCommit;
private Map<Object, Object> entriesToAddOnCommit;
private Set<Object> entriesMissedInCache;
public TransactionalCache(Cache delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
this.clearOnCommit = false;
this.entriesToAddOnCommit = new HashMap<Object, Object>();
this.entriesMissedInCache = new HashSet<Object>();
}
@Override
public Object getObject(Object key) {
// issue #116
Object object = delegate.getObject(key);
if (object == null) {
//如果没拿到,那么加入失效缓存SET中
entriesMissedInCache.add(key);
}
// issue #146
if (clearOnCommit) {
return null;
} else {
return object;
}
}
@Override
public ReadWriteLock getReadWriteLock() {
return null;
}
@Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object object) {
entriesToAddOnCommit.put(key, object);
}
@Override
public Object removeObject(Object key) {
return null;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
clearOnCommit = true;
entriesToAddOnCommit.clear();
}
public void commit() {
if (clearOnCommit) {
delegate.clear();
}
//刷新缓存
flushPendingEntries();
reset();
}
public void rollback() {
unlockMissedEntries();
reset();
}
private void reset() {
clearOnCommit = false;
entriesToAddOnCommit.clear();
entriesMissedInCache.clear();
}
//刷新缓存的具体操作
private void flushPendingEntries() {
for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry : entriesToAddOnCommit.entrySet()) {
delegate.putObject(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
for (Object entry : entriesMissedInCache) {
if (!entriesToAddOnCommit.containsKey(entry)) {
delegate.putObject(entry, null);
}
}
}
//移除缓存
private void unlockMissedEntries() {
for (Object entry : entriesMissedInCache) {
try {
delegate.removeObject(entry);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("Unexpected exception while notifiying a rollback to the cache adapter."
+ "Consider upgrading your cache adapter to the latest version. Cause: " + e);
}
}
}
}
因为Cache是从MappedStatement 拿到的,而这个是在初始化的时候从xml或者注解中加载的,是全局共享的,所以二级缓存可以在不同的session的生效。
Cache是如何包装的
查看org.apache.ibatis.mapping.CacheBuilder中源码 即可知道。
public Cache build() {
setDefaultImplementations();
Cache cache = newBaseCacheInstance(implementation, id);
setCacheProperties(cache);
// issue #352, do not apply decorators to custom caches
//加上一些装饰
if (PerpetualCache.class.equals(cache.getClass())) {
for (Class<? extends Cache> decorator : decorators) {
cache = newCacheDecoratorInstance(decorator, cache);
setCacheProperties(cache);
}
cache = setStandardDecorators(cache);
} else if (!LoggingCache.class.isAssignableFrom(cache.getClass())) {
cache = new LoggingCache(cache);
}
return cache;
}