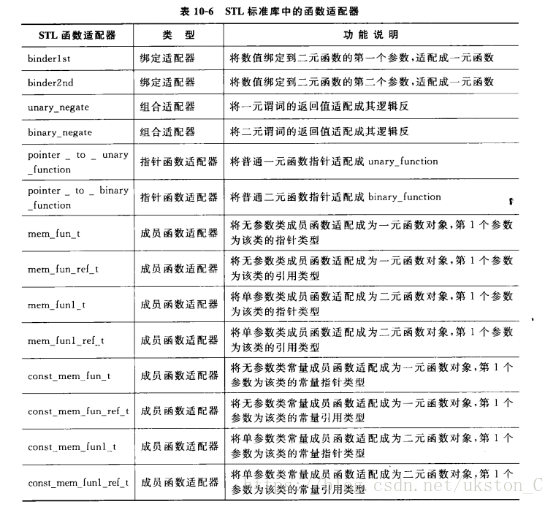
函数适配器
1)函数适配器
2)常用函数适配器
标准库提供一组函数适配器,用来特殊化或者扩展一元和二元函数对象。常用适配器是:
1绑定器(binder): binder通过把二元函数对象的一个实参绑定到一个特殊的值上,将其转换成一元函数对象。C++标准库提供两种预定义的binder适配器:bind1st和bind2nd,前者把值绑定到二元函数对象的第一个实参上,后者绑定在第二个实参上。
2取反器(negator) : negator是一个将函数对象的值翻转的函数适配器。标准库提供两个预定义的ngeator适配器:not1翻转一元预定义函数对象的真值,而not2翻转二元谓词函数的真值。
常用函数适配器列表如下:
bind1st(op, value)
bind2nd(op, value)
not1(op)
not2(op)
mem_fun_ref(op)
mem_fun(op)
ptr_fun(op)
3)常用函数适配器案例
#include"vector"
#include"algorithm"
#include"string"
#include"functional"
#include"iostream"
using namespace std;
class dayu
{
public:
dayu(int i)
{
num = i;
}
bool operator()(int &n)
{
if (n > num)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
private:
int num;
};
int main01()
{
vector<int>v1(15);
for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++)
{
v1[i] = rand() %100;
}
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v1.begin(); it != v1.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";//41 67 34 0 69 24 78 58 62 64 5 45 81 27 61
}
cout << endl;
//求出5的个数;count
/*template<class _InIt,
class _Ty> inline
typename iterator_traits<_InIt>::difference_type
count(_InIt _First, _InIt _Last, const _Ty& _Val)
{ // count elements that match _Val
_DEBUG_RANGE(_First, _Last);
return (_Count_np(_Unchecked(_First), _Unchecked(_Last), _Val));
}*/
int num1 = count(v1.begin(),v1.end(),5);
cout << "5的个数num1=: " << num1 << endl;//1
//////////////求出大于50的数的个数//////////////////
//通过谓词的方式求解
/*template<class _InIt,
class _Pr> inline
typename iterator_traits<_InIt>::difference_type
count_if(_InIt _First, _InIt _Last, _Pr _Pred)
{ // count elements satisfying _Pred
_DEBUG_RANGE(_First, _Last);
_DEBUG_POINTER(_Pred);
return (_Count_if(_Unchecked(_First), _Unchecked(_Last), _Pred));
}*/
int num2 = count_if(v1.begin(),v1.end(),dayu(50));
cout << "dayu(50)num2=: " << num2 << endl;//8
//通过函数适配器的方式求解
/* // TEMPLATE STRUCT greater
template<class _Ty = void>
struct greater
: public binary_function<_Ty, _Ty, bool>
{ // functor for operator>
bool operator()(const _Ty& _Left, const _Ty& _Right) const
{ // apply operator> to operands
return (_Left > _Right);
}
};
*/
int num3 = count_if(v1.begin(),v1.end(),bind2nd(greater<int>(),50));//令_Right=50;
cout << "大于50的个数num3= " << num3 << endl;
//////////////////求奇偶数的个数(能否被2整除)///////////////////////
/* // TEMPLATE STRUCT modulus
template<class _Ty = void>
struct modulus
: public binary_function<_Ty, _Ty, _Ty>
{ // functor for operator%
_Ty operator()(const _Ty& _Left, const _Ty& _Right) const
{ // apply operator% to operands
return (_Left % _Right);
}
};
*/
//左参数来自容器,右参数来自自定义
int num4 = count_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(),bind2nd(modulus<int>(),2));
cout << "奇数个数num4= " << num4 << endl; //8
int num5 = count_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), not1(bind2nd(modulus<int>(), 2)));
cout << "偶数个数num5= " << num5 << endl; //7
return 0;
}
/////////////////////成员函数适配器///////////////
class Student
{public:
string num;
string name;
public:
Student(string num,string name)
{
this->num = num;
this->name = name;
}
bool show()
{
cout << num << ":"<<name << endl;
return true;
}
};
int main02()
{
//mem_fun_ref 当集合是基于对象的
Student s1("1001","liubang");
Student s2("1002", "xiangyu");
vector<Student> v;
v.push_back(s1);
v.push_back(s2);
for_each(v.begin(),v.end(),mem_fun_ref(&Student::show));
//mem_fun 当集合是基于对象指针的
Student *ps1=new Student("1001", "liubang");
Student *ps2=new Student("1002", "xiangyu");
vector<Student*> pv;
pv.push_back(ps1);
pv.push_back(ps2);
for_each(pv.begin(), pv.end(), mem_fun(&Student::show));
return 0;
}
///////////////////////普通函数适配器的基本用法(ptr_fun)//////////////
/*template<class _Arg,
class _Result> inline
pointer_to_unary_function<_Arg, _Result,
_Result (__cdecl *)(_Arg)>
ptr_fun(_Result (__cdecl *_Left)(_Arg))
{ // return pointer_to_unary_function functor adapter
return (pointer_to_unary_function<_Arg, _Result,
_Result (__cdecl *)(_Arg)>(_Left));
*/
bool f(int x)
{
return x > 3;
}
bool g(int x,int y)
{
return x > y;
}
int main03()
{
int a[] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
int nsize = sizeof(a) / sizeof(int);
int numf3 = count_if(a, a + nsize, f);
cout << "numf>3: "<<numf3 << endl; //6 对一个参数的普通函数而言,ptr_fun无太大优势;
int numf4 = count_if(a, a + nsize, ptr_fun(f));
cout << "numptr_fun(f): " << numf4 << endl; //6
int numg = count_if(a, a + nsize, bind2nd(ptr_fun(g),5));
cout << "numptr_fun(g): " << numg << endl; //4
return 0;
}
int main()
{
//main01();
//main02();
main03();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//综合案例1
//////////编程求圆和长方形的面积////////////////////
#include"iostream"
#include"vector"
#include"algorithm"
#include"functional"
using namespace std;
class Shape
{
public:
virtual bool showarea() = 0;
};
class Circle:public Shape
{
private:
float r;
public:
Circle(float r)
{
this->r = r;
}
bool showarea()
{
cout << "Area of The Circle is: " << 3.14*r*r << endl;
return true;
}
};
class Rectangle :public Shape
{
private:
float length;
float width;
public:
Rectangle(float length,float width)
{
this->length = length;
this->width = width;
}
bool showarea()
{
cout << "Area of The Rectangle is: " << length*width << endl;
return true;
}
};
class Shapemanager
{private:
vector<Shape*>v;//多态,所以采用基类指针
public:
bool add(Shape* s)
{
v.push_back(s);//添加形状指针;
return true;
}
bool showEACHarea()
{
for_each(v.begin(),v.end(),mem_fun(&Shape::showarea));
return true;
}
};
int main()
{
Shapemanager spm;
Shape *obj1 = new Circle(5);
Shape *obj2 = new Rectangle(5,15);
spm.add(obj1);
spm.add(obj2);
spm.showEACHarea();//78.5 , 75
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//综合案例2
//假设学生对象的集合的索引从0开始,依次增1,
//要求不改变学生成绩集合中学生对象的顺序,依据成绩升序输出索引
#include"iostream"
#include"vector"
#include"algorithm"
#include"functional"
#include"string "
#include"iterator"
using namespace std;
class Student
{
public:
string num;
int grade;
public:
Student( string num,int grade)
{
this->num = num;
this->grade = grade;
}
};
class Studmanager
{
private:
vector<Student> &v;//学生集合对象de引用
public:
Studmanager(vector<Student> &v): v(v){ }
bool operator()(int a,int b)//a,b表示学生对象的序号
{
return v[a].grade < v.at(b).grade;//按成绩从小到大排序
}
};
int main()
{
Student s1("1001",70);
Student s2("1002", 76);
Student s3("1003", 90);
Student s4("1004", 87);
vector<Student>vStudent;
vStudent.push_back(s1);
vStudent.push_back(s2);
vStudent.push_back(s3);
vStudent.push_back(s4);
vector<int>v1;
v1.push_back(0);
v1.push_back(1);
v1.push_back(2);
v1.push_back(3);
sort(v1.begin(), v1.end(), Studmanager(vStudent));//序号按照成绩的大小排序
copy(v1.begin(),v1.end(),ostream_iterator<int>(cout," "));//0132
system("pause");
return 0;
}