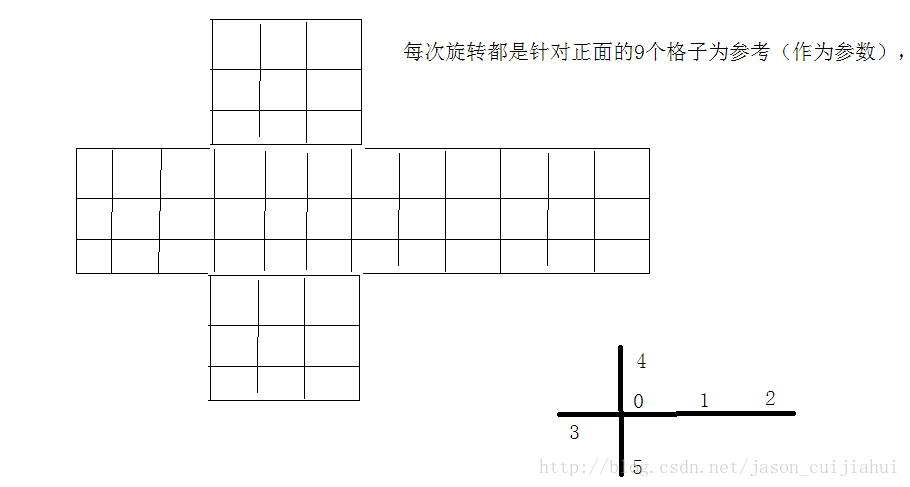
数据结构设计
1.设计一个魔方(六面)的程序
思路:
把魔方从正面看展开成一个平面,如图1所示。设计一个类,其中Spacexy[SPACE][LEN][LEN];中的SPACE为0~5表示六个面,每个数字代表哪一面见图1.LEN为0~2,[LEN][LEN]表示某个面的3*3的9个格子。
类中的方法是根据展开的平面设计的,具体的某个面的某个格子由Spacexy[SPACE][LEN][LEN];定位。
注: [LEN][LEN] = [i][j] ;i, j按照矩阵的方式取
实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class MagicCube{
private:
enum{LEN = 3, SPACE = 6};
enum color{red, yellow, black, blue, green, purple};
enum color Spacexy[SPACE][LEN][LEN];
public:
MagicCube();
~MagicCube(){ };
void LeftRotate(int j);
void UpRoate(int i);
void PrintCube();
};
void MagicCube::UpRoate(int j){
color tmp[LEN];
for(int i=0;i<LEN;i++)
tmp[i] = Spacexy[0][i][j];
// 0
for(int i=0;i<LEN;i++)
Spacexy[0][i][j] = Spacexy[5][i][j];
// 5
for(int i=0;i<LEN;i++)
Spacexy[5]][i][j] = Spacexy[2][LEN-1-i][j];
// 2
for(int i=0;i<LEN;i++)
Spacexy[2][LEN-1-i][j] = Spacexy[4][i][j];
// 4
for(int i=0;i<LEN;i++)
Spacexy[4][i][j] = tmp[i];
}
void MagicCube::LeftRotate(int i)
{
color tmp[LEN];
for(int j=0;j<LEN;j++)
tmp[j] = Spacexy[0][i][j];
// 0
for(int j=0;j<LEN;j++)
Spacexy[0][i][j] = Spacexy[1][i][j];
// 1
for(int j=0;j<LEN;j++)
Spacexy[1][i][j] = Spacexy[2][i][j];
// 2
for(int j=0;j<LEN;j++)
Spacexy[2][i][j] = Spacexy[3][i][j];
// 3
for(int j=0;i<LEN;j++)
Spacexy[3][i][j] = tmp[j];
}
2.Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree
题目:
Serialization is the process of converting a data structure or object into a sequence of bits so that it can be stored in a file or memory buffer, or transmitted across a network connection link to be reconstructed later in the same or another computer environment.
Design an algorithm to serialize and deserialize a binary tree. There is no restriction on how your serialization/deserialization algorithm should work. You just need to ensure that a binary tree can be serialized to a string and this string can be deserialized to the original tree structure.
For example, you may serialize the following tree
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5as “[1,2,3,null,null,4,5]”, just the same as how LeetCode OJ serializes a binary tree. You do not necessarily need to follow this format, so please be creative and come up with different approaches yourself.
实现:
// 我的版本比较蠢
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct Node{
int data;
Node* left;
Node* right;
};
string toString(const int& t) {
ostringstream oss;
oss<<t;
return oss.str();
}
int toInt(const string& str) {
istringstream iss(str);
int num;
iss >> num;
return num;
}
string serialize(Node *root) {
string result = "";
if(root==NULL) return "";
queue<Node*> record;
record.push(root);
while(!record.empty()) {
Node* e = record.front();
if(e==NULL)
result += "null,";
else {
result += toString(e->data)+",";
record.push(e->left);
record.push(e->right);
}
record.pop();
}
return result;
}
Node* CreateBinaryTree(vector<string> &a, int i, int n) {
if(i>n-1 || a[i]=="null") return NULL;
Node *p = new Node;
p->data = toInt(a[i]);
p->left = CreateBinaryTree(a, i*2+1, n);
p->right = CreateBinaryTree(a, i*2+2, n);
return p;
}
void SplitString(const string& s, vector<string>& v, const string& c)
{
string::size_type pos1, pos2;
pos2 = s.find(c);
pos1 = 0;
while(string::npos != pos2)
{
v.push_back(s.substr(pos1, pos2-pos1));
pos1 = pos2 + c.size();
pos2 = s.find(c, pos1);
}
if(pos1 != s.length())
v.push_back(s.substr(pos1));
}
Node* deserialize(string data) {
vector<string> sArr;
SplitString(data, sArr, ",");
Node* root = CreateBinaryTree(sArr, 0, sArr.size());
return root;
}
int main() {
Node *p1 = new Node;
p1->data = 1;
p1->left = NULL;
p1->right = NULL;
Node *p2 = new Node;
p2->data = 2;
p2->left = NULL;
p2->right = NULL;
p1->left = p2;
string sResult = serialize(p1);
cout<<serialize(p1)<<endl;
deserialize(sResult);
cout<<serialize(deserialize(serialize(p1)))<<endl;
return 0;
}// 别人的版本
class Codec {
public:
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return "#";
return to_string(root->val)+","+serialize(root->left)+","+serialize(root->right);
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
return mydeserialize(data);
}
TreeNode* mydeserialize(string& data) {
if (data[0]=='#') {
if(data.size() > 1) data = data.substr(2);
return nullptr;
} else {
TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(helper(data));
node->left = mydeserialize(data);
node->right = mydeserialize(data);
return node;
}
}
private:
int helper(string& data) {
int pos = data.find(',');
int val = stoi(data.substr(0,pos));
data = data.substr(pos+1);
return val;
}
};大数据处理
1.多文件频率排序
题目:
有10个文件,每个文件1G,每个文件的每一行存放的都是用户的query,每个文件的query都可能重复。要求按照query的频度排序。
思路:
a) 方案1
1. 顺序读取10个文件,按照hash(query)的结果将query写入到另外10个文件中。这样新生成的文件每个的大小大约也1G(假设hash函数是随机的)。
2. 找一台内存在2G左右的机器,依次对 用hash_map(query, query_count)来统计每个query出现的次数。利用快速/堆/归并排序按照出现次数进行排序。将排序好的query和对应的query_cout输出到文件中。这样得到了10个排好序的文件。
3. 对 这10个文件进行归并排序(内排序与外排序相结合)。
b) 方案2:
一般query的总量是有限的,只是重复的次数比较多而已,可能对于所有的query,一次性就可以加入到内存了。这样,我们就可以采用trie树/hash_map等直接来统计每个query出现的次数,然后按出现次数做快速/堆/归并排序就可以了。
c) 方案3:
与方案1类似,但在做完hash,分成多个文件后,可以交给多个文件来处理,采用分布式的架构来处理(比如MapReduce),最后再进行合并。
算法
树结构
二叉树
1.二叉树层次遍历
题目:
输入一颗二元树,从上往下按层打印树的每个结点,同一层中按照从左往右的顺序打印。
8
/ \
6 10
/ \ / \
5 79 11输出:
8 6 10 5 7 9 11
思路:
用队列,出队打印,并压入左右儿子。
实现:
struct Node{
int data;
Node* left;
Node* right;
}
void levelPrint(Node* root){
if(root==NULL) return;
queue<Node*> record;
record.push(root);
while(!record.empty()){
cout<<record.front()->data<<' ';
if(record.front()->left!=NULL)
record.push(record.front()->left);
if(record.front()->right!=NULL)
record.push(record.front()->right);
record.pop();
}
cout<<endl;
}2.镜像二叉树
题目:
请完成一个函数,输入一个二叉树,该函数输出它的镜像。
// 原二叉树
8
/ \
6 10
/ \ / \
5 79 11
// 镜像二叉树
8
/ \
10 6
/ \ / \
11 97 5二叉树结点的定义如下:
struct BinaryTreeNode
{
int data;
BinaryTreeNode *Left;
BinaryTreeNode *Right;
}; 思路:
递归思路:
把左子树和右子树变成镜像子树后,在把左右子树的root相互交换。
迭代思路:
类似层次遍历那种思路,不过用的是栈
实现:
// 递归实现
void Mirror(BinaryTreeNode *root){
if(root==NULL) return;
Mirror(root->Left);
Mirror(root->Right);
BinaryTreeNode *tmp = root->Left;
root->Left = root->Right;
root->Right = tmp;
}// 迭代实现
// 这种相当于先序遍历镜像树
void Mirror(BinaryTreeNode *root){
stack<Node*> record;
if(root!=NULL)
record.push(root);
while(!record.empty()){
Node* tmproot = record.top();
record.pop();
if (tmproot->Left!=NULL)
record.push(tmproot->Left);
if (tmproot->Right!=NULL)
record.push(tmproot->Right);
Node* tmp = tmproot->Left;
tmproot->Left = tmproot->Right;
tmproot->Right = tmp;
}
}补充:
这个要写个测试样例。
3.求二叉树中结点的最大距离
题目:
如果我们把二叉树堪称一个图,父子结点之间的连线看成是双向的。我们姑且定义“距离”为两个结点之间的边的个树。求一棵二叉树中相距最远的两个结点之间的边的个树。
思路:
可以用递归的思路去做,设父结点为F,左子树为L,右子树为R,则树F相距最远无非有这三种可能:
- 树L相距最远
- 树R相距最远
- 树L到结点F的最长距离+1+树R到结点F的最长距离
实现:
struct BinaryTreeNode
{
int data;
BinaryTreeNode *Left;
BinaryTreeNode *Right;
};
int TreeMaxLength(BinaryTreeNode *root, int &depth){
int ld, rd;
if(root==NULL){
depth = 0;
return 0;
}
lm = TreeMaxLength(root->Left, ld);
rm = TreeMaxLength(root->Right, rd);
depth = (ld>rd?ld:rd)+1;
// bridge是边的条数而不是结点的个数
int bridge = ld+rd;
int tmp = lm>rm?lm:rm;
return (tmp>bridge?tmp:bridge);
}4.从数组生成一棵二叉树
实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode
{
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
int val;
TreeNode(int x=0)
: val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL){}
};
TreeNode* CreateBinaryTree(int a[], int i, int n){
// 数组中的值-1代表结点null
if(i>n-1 || a[i]==-1) return NULL;
TreeNode *p = new TreeNode(a[i]);
p->left = CreateBinaryTree(a, i*2+1, n);
p->right = CreateBinaryTree(a, i*2+2, n);
return p;
}
void Destory(TreeNode *root){
if(root==NULL) return ;
Destory(root->left);
Destory(root->right);
delete root;
}
5.打印一棵二叉树
实现:
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//using std::vector;
//using std::cout;
//using std::endl;
//using std::max;
void PrintBinaryTree(TreeNode *root);
struct TreeNode
{
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
int val;
TreeNode(int x=0)
: val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL){}
};
static int MaxLevel(TreeNode *root)
{
if(root == NULL) return 0;
return max(MaxLevel(root->left), MaxLevel(root->right)) + 1;
}
// test whether all elements in vector are NULL
static bool IsAllElementsNULL(const vector<TreeNode*> &nodes)
{
vector<TreeNode*>::const_iterator it = nodes.begin();
while(it != nodes.end()){
if(*it) return false;
++it;
}
return true;
}
static void PrintWhiteSpaces(int num)
{
for(int i=0; i<num; ++i)
cout << " ";
}
void PrintNode(vector<TreeNode*> &nodes, int level, int max_level)
{
if(nodes.empty() || IsAllElementsNULL(nodes)) return; // exit
int floor = max_level - level;
int endge_lines = 1 << (max(floor-1, 0));
int first_spaces = (1 << floor) - 1;
int between_spaces = (1 << (floor+1)) - 1;
PrintWhiteSpaces(first_spaces);
// print the 'level' level
vector<TreeNode*> new_nodes;
vector<TreeNode*>::const_iterator it = nodes.begin();
for(; it != nodes.end(); ++it){
if(*it != NULL){
cout << (*it)->val;
new_nodes.push_back((*it)->left);
new_nodes.push_back((*it)->right);
}
else{
new_nodes.push_back(NULL);
new_nodes.push_back(NULL);
cout << " ";
}
PrintWhiteSpaces(between_spaces);
}
cout << endl;
// print the following /s and \s
for(int i=1; i<= endge_lines; ++i){
for(int j=0; j<nodes.size(); ++j){
PrintWhiteSpaces(first_spaces - i);
if(nodes[j] == NULL){
PrintWhiteSpaces(endge_lines + endge_lines + i + 1);
continue;
}
if(nodes[j]->left != NULL)
cout << "/";
else
PrintWhiteSpaces(1);
PrintWhiteSpaces(i+i-1);
if(nodes[j]->right != NULL)
cout << "\\";
else
PrintWhiteSpaces(1);
PrintWhiteSpaces(endge_lines + endge_lines - i);
}
cout << endl;
}
PrintNode(new_nodes, level+1, max_level);
}
// wrapper function
void PrintBinaryTree(TreeNode *root)
{
int max_level = MaxLevel(root);
vector<TreeNode*> nodes;
nodes.push_back(root);
PrintNode(nodes, 1, max_level);
}
int main()
{
TreeNode *root(NULL);
root = new TreeNode(1);
root->left = new TreeNode(2);
root->right = new TreeNode(3);
root->left->left = new TreeNode(4);
root->right->right = new TreeNode(7);
root->left->left->left = new TreeNode(8);
root->left->left->right = new TreeNode(9);
PrintBinaryTree(root);
// root = Destroy(root);
return 0;
} 6.非递归实现二叉树的前序中序后序遍历
实现:
递归前序遍历
void preorderRecursive(TreeNode *node){
if(node == NULL) return;
visit(node);
preorderRecursive(node->left);
preorderRecursive(node->right);
}非递归前序遍历,用栈
void preorderRecursive(TreeNode *node){
stack<TreeNode*> s;
if(node!=NULL) s.push(node);
while(!s.empty()){
TreeNode *tmp = s.top();
s.pop();
visit(tmp);
if(tmp->right!=NULL) s.push(tmp->right);
if(tmp->left!=NULL) s.push(tmp->left);
}
}非递归中序遍历,没有左结点,则对结点进行访问
void inorderRecursive(TreeNode *node){
stack<TreeNode*> s;
TreeNode *tmp = node;
while(!s.empty() || tmp!=NULL){
if(tmp!=NULL){
s.push(tmp);
tmp = tmp->left;
}
else{
tmp = s.top();
s.pop();
visit(tmp);
tmp = tmp->right;
}
}
}非递归后序遍历,利用非递归前序遍历进行转化
void postorderRecursive(TreeNode *node){
stack<TreeNode *> sTraverse, sVisit;
if(node!=NULL) sTraverse.push(node);
while(!sTraverse.empty()){
Node *tmp = sTraverse.top();
sTraverse.pop();
sVisit.push(tmp);
// 先右结点
if(tmp->right != NULL) tmp = tmp->right;
// 后左结点
if(tmp->left != NULL) tmp = tmp->left;
}
while(!sVisit.empty()){
visit(sVisit.top());
sVisit.pop();
}
}7.二叉树的深度
题目:输入一棵二叉树的根结点,求该树的深度。
实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode
{
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
int val;
TreeNode(int x=0)
: val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL){}
};
// 核心代码
void searchDepth(TreeNode *root, int depth, int &maxDepth){
if(root==NULL){
if(depth>maxDepth)
maxDepth = depth;
return;
}
searchDepth(root->left, depth+1, maxDepth);
searchDepth(root->right, depth+1, maxDepth);
}
// 测试代码
TreeNode* CreateBinaryTree(int a[], int i, int n){
// 数组中的值-1代表结点null
if(i>n-1 || a[i]==-1) return NULL;
TreeNode *p = new TreeNode(a[i]);
p->left = CreateBinaryTree(a, i*2+1, n);
p->right = CreateBinaryTree(a, i*2+2, n);
return p;
}
void Destory(TreeNode *root){
if(root==NULL) return ;
Destory(root->left);
Destory(root->right);
delete root;
}
int main(){
int tree[] = {10, 6, 14, 4, -1, -1, 16, -1, 3};
TreeNode* root = CreateBinaryTree(tree, 0, 9);
int max = 0;
searchDepth(root, 0, max);
cout<<max<<endl;
Destory(root);
return 0;
}
8.二叉树两个结点的最低共同父结点(LCP)
题目:
输入二叉树中的两个结点,输出这两个结点在数中最低的共同父结点。
思路(递归):
1. 在左子树查找目标对象
2. 在右子树查找目标对象
a) 如果在左子树中什么都没找到,则表明都在右子树上,然后LCP是最早查找的目标对象
b) 如果在左子树中什么都没找到,则表明都在右子树上,然后LCP是最早查找的目标对象
c) 如果在左右子树各找到一个,则表明LCP是根结点
实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode
{
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
int val;
TreeNode(int x=0)
: val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL){}
};
TreeNode* CreateBinaryTree(int a[], int i, int n){
// 数组中的值-1代表结点null
if(i>n-1 || a[i]==-1) return NULL;
TreeNode *p = new TreeNode(a[i]);
p->left = CreateBinaryTree(a, i*2+1, n);
p->right = CreateBinaryTree(a, i*2+2, n);
return p;
}
void Destory(TreeNode *root){
if(root==NULL) return ;
Destory(root->left);
Destory(root->right);
delete root;
}
TreeNode* GetLCP(TreeNode *root, TreeNode *n1, TreeNode *n2){
if(root==NULL || n1==NULL || n2==NULL) return NULL;
if(n1==root || n2==root) return root;
// 在左子树上找n1或n2
TreeNode* leftSub = GetLCP(root->left, n1, n2);
// 在右子树上找n1或n2
TreeNode* rightSub = GetLCP(root->right, n1, n2);
if(leftSub==NULL){// n1和n2都不能在左子树找到,则返回右子树中率先遇到n1或n2的结点
return rightSub;
}
else if(rightSub==NULL){
return leftSub;
}
else{// n1和n2分别在左右子树上,所以返回根结点
return root;
}
}
int main(){
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8};
TreeNode *root = CreateBinaryTree(arr, 0, 8);
/*
1
2 3
4 5 6 7
8
*/
TreeNode *n1 = root->left->left->left;
TreeNode *n2 = root->left->right;
TreeNode *result = GetLCP(root, n1, n2);
cout<<result->val<<endl;
Destory(root);
} 9.Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
题目:
Given a binary tree, return the zigzag level order traversal of its nodes’ values. (ie, from left to right, then right to left for the next level and alternate between).
For example:
Given binary tree [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7return its zigzag level order traversal as:
[
[3],
[20,9],
[15,7]
]实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
void zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> r1;
stack<TreeNode*> r2;
r1.push(root);
while(r1.empty()==false || r2.empty()==false) {
while(!r1.empty()) {
TreeNode* e = r1.front();
cout<<e->val<<" ";
if(e->left!=NULL) r2.push(e->left);
if(e->right!=NULL) r2.push(e->right);
r1.pop();
}
cout<<endl;
while(!r2.empty()) {
TreeNode* e = r2.top();
cout<<e->val<<" ";
if(e->left!=NULL) r1.push(e->left);
if(e->right!=NULL) r1.push(e->right);
r2.pop();
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
int main() {
TreeNode *n1 = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode *n2 = new TreeNode(9);
TreeNode *n3 = new TreeNode(20);
TreeNode *n4 = new TreeNode(15);
TreeNode *n5 = new TreeNode(7);
n1->left = n2;
n1->right = n3;
n3->left = n4;
n3->right = n5;
zigzagLevelOrder(n1);
}10.Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
题目:
Given preorder and inorder traversal of a tree, construct the binary tree.
Note:
You may assume that duplicates do not exist in the tree.
For example, given
preorder = [3,9,20,15,7]
inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
Return the following binary tree:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7思路
实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(-1), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
TreeNode* helper(vector<int>& preorder, int preI, int preJ, vector<int>& inorder, int inI, int inJ) {
if(preI > preJ || inI > inJ) return NULL;
int rootVal = preorder[preI];
int rootIndex = 0;
for(int i=inI;i<=inJ;i++) {
if(inorder[i] == rootVal) {
rootIndex = i;
break;
}
}
TreeNode* newNode = new TreeNode(rootVal);
int lLen = rootIndex - inI;
int rLen = inJ - rootIndex;
newNode->left = helper(preorder, preI+1, preI+lLen, inorder, inI, rootIndex-1);
newNode->right = helper(preorder, preI+lLen+1, preJ, inorder, rootIndex+1, inJ);
return newNode;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
return helper(preorder, 0, preorder.size()-1, inorder, 0, inorder.size()-1);
}
// 打印二叉树
TreeNode* Array2BinaryTree(int arr[], int i, int j){
if(i>j) return NULL;
int mid = (i+j)/2;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode;
root->val = arr[mid];
root->left = Array2BinaryTree(arr, i, mid-1);
root->right = Array2BinaryTree(arr, mid+1, j);
return root;
}
// 打印二叉树
void PrintBinaryTree(TreeNode *root);
static int MaxLevel(TreeNode *root)
{
if(root == NULL) return 0;
return max(MaxLevel(root->left), MaxLevel(root->right)) + 1;
}
// test whether all elements in vector are NULL
static bool IsAllElementsNULL(const vector<TreeNode*> &nodes)
{
vector<TreeNode*>::const_iterator it = nodes.begin();
while(it != nodes.end()){
if(*it) return false;
++it;
}
return true;
}
static void PrintWhiteSpaces(int num)
{
for(int i=0; i<num; ++i)
cout << " ";
}
void PrintNode(vector<TreeNode*> &nodes, int level, int max_level)
{
if(nodes.empty() || IsAllElementsNULL(nodes)) return; // exit
int floor = max_level - level;
int endge_lines = 1 << (max(floor-1, 0));
int first_spaces = (1 << floor) - 1;
int between_spaces = (1 << (floor+1)) - 1;
PrintWhiteSpaces(first_spaces);
// print the 'level' level
vector<TreeNode*> new_nodes;
vector<TreeNode*>::const_iterator it = nodes.begin();
for(; it != nodes.end(); ++it){
if(*it != NULL){
cout << (*it)->val;
new_nodes.push_back((*it)->left);
new_nodes.push_back((*it)->right);
}
else{
new_nodes.push_back(NULL);
new_nodes.push_back(NULL);
cout << " ";
}
PrintWhiteSpaces(between_spaces);
}
cout << endl;
// print the following /s and \s
for(int i=1; i<= endge_lines; ++i){
for(int j=0; j<nodes.size(); ++j){
PrintWhiteSpaces(first_spaces - i);
if(nodes[j] == NULL){
PrintWhiteSpaces(endge_lines + endge_lines + i + 1);
continue;
}
if(nodes[j]->left != NULL)
cout << "/";
else
PrintWhiteSpaces(1);
PrintWhiteSpaces(i+i-1);
if(nodes[j]->right != NULL)
cout << "\\";
else
PrintWhiteSpaces(1);
PrintWhiteSpaces(endge_lines + endge_lines - i);
}
cout << endl;
}
PrintNode(new_nodes, level+1, max_level);
}
// wrapper function
void PrintBinaryTree(TreeNode *root)
{
int max_level = MaxLevel(root);
vector<TreeNode*> nodes;
nodes.push_back(root);
PrintNode(nodes, 1, max_level);
}
int main() {
int preArr[] = {3, 9, 20, 15, 7};
int inArr[] = {9, 3, 15, 20, 7};
vector<int> preorder(preArr, preArr+5);
vector<int> inorder(inArr, inArr+5);
TreeNode* root = buildTree(preorder, inorder);
PrintBinaryTree(root);
return 0;
}
二叉查找树
1.把一个有序整数数组转化为二叉查找树
思路:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode
{
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
int val;
TreeNode(int x=0)
: val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL){}
};
TreeNode* Array2BinaryTree(int arr[], int i, int j){
if(i>j) return NULL;
int mid = (i+j)/2;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode;
root->val = arr[mid];
root->left = Array2BinaryTree(arr, i, mid-1);
root->right = Array2BinaryTree(arr, mid+1, j);
return root;
}
// 打印二叉树
void PrintBinaryTree(TreeNode *root);
static int MaxLevel(TreeNode *root)
{
if(root == NULL) return 0;
return max(MaxLevel(root->left), MaxLevel(root->right)) + 1;
}
// test whether all elements in vector are NULL
static bool IsAllElementsNULL(const vector<TreeNode*> &nodes)
{
vector<TreeNode*>::const_iterator it = nodes.begin();
while(it != nodes.end()){
if(*it) return false;
++it;
}
return true;
}
static void PrintWhiteSpaces(int num)
{
for(int i=0; i<num; ++i)
cout << " ";
}
void PrintNode(vector<TreeNode*> &nodes, int level, int max_level)
{
if(nodes.empty() || IsAllElementsNULL(nodes)) return; // exit
int floor = max_level - level;
int endge_lines = 1 << (max(floor-1, 0));
int first_spaces = (1 << floor) - 1;
int between_spaces = (1 << (floor+1)) - 1;
PrintWhiteSpaces(first_spaces);
// print the 'level' level
vector<TreeNode*> new_nodes;
vector<TreeNode*>::const_iterator it = nodes.begin();
for(; it != nodes.end(); ++it){
if(*it != NULL){
cout << (*it)->val;
new_nodes.push_back((*it)->left);
new_nodes.push_back((*it)->right);
}
else{
new_nodes.push_back(NULL);
new_nodes.push_back(NULL);
cout << " ";
}
PrintWhiteSpaces(between_spaces);
}
cout << endl;
// print the following /s and \s
for(int i=1; i<= endge_lines; ++i){
for(int j=0; j<nodes.size(); ++j){
PrintWhiteSpaces(first_spaces - i);
if(nodes[j] == NULL){
PrintWhiteSpaces(endge_lines + endge_lines + i + 1);
continue;
}
if(nodes[j]->left != NULL)
cout << "/";
else
PrintWhiteSpaces(1);
PrintWhiteSpaces(i+i-1);
if(nodes[j]->right != NULL)
cout << "\\";
else
PrintWhiteSpaces(1);
PrintWhiteSpaces(endge_lines + endge_lines - i);
}
cout << endl;
}
PrintNode(new_nodes, level+1, max_level);
}
// wrapper function
void PrintBinaryTree(TreeNode *root)
{
int max_level = MaxLevel(root);
vector<TreeNode*> nodes;
nodes.push_back(root);
PrintNode(nodes, 1, max_level);
}
int main(){
int test1[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int test2[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
TreeNode *root1 = Array2BinaryTree(test1, 0, 4);
PrintBinaryTree(root1);
TreeNode *root2 = Array2BinaryTree(test2, 0, 5);
PrintBinaryTree(root2);
return 0;
} 其他:
非递归实现。
堆
1.队伍晋级
题目:
n 支队伍比赛,分别编号为 0, 1, 2, …, n-1,已知它们之间的实力对比关系,
存储在一个二维数组 w[n][n]中,w[i][j] 的值代表编号为 i,j 的队伍中更强的一支。
所以 w[i][j]=i 或者 j,现在给出它们的出场顺序,并存储在数组 order[n]中,
比如 order[n] = {4, 3, 5, 8, 1……},那么第一轮比赛就是 4 对 3, 5 对 8,…….
胜者晋级,败者淘汰,同一轮淘汰的所有队伍排名不再细分,即可以随便排,
下一轮由上一轮的胜者按照顺序,再依次两两比,比如可能是 4 对 5,直至出现第一名
编程实现,给出二维数组 w,一维数组 order 和用于输出比赛名次的数组 result[n],
求出 result。
思路:
就是用target追踪最近的一个空位,把胜利者移动到空位上(与原来target位置的元素交换交换)。然后递归就ok了。
实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void swap(int *target, int i, int j){
if(i==j) return;
int tmp = target[i];
target[i] = target[j];
target[j] = tmp;
}
void finalResult(int *result, int n, int **w){
if(n==1) return;
int trace = 0;
int win;
for(int i=0;i<n;i+=2){
if(i==n-1)
win = i;
else
win = (w[result[i]][result[i+1]]==result[i])? i:i+1;
swap(result, trace, win);
trace++;
}
finalResult(result, trace, w);
}
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
int *test = new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>test[i];
}
int **w = new int*[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
w[i] = new int[n];
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
cin>> w[i][j];
}
}
finalResult(test, n, w);
cout<<"Result:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
cout<<test[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
delete []test;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
delete []w[i];
delete []w;
}其他:
no-copying merge: merge order to result, then merge the first half from order, and so on.
in place matrix rotation: rotate 01, 23, …, 2k/2k+1 to 02…2k, 1, 3, … 2k+1…
2.矩阵逆时针旋转90度(Inplace rotate square matrix by 90 degrees)
题目:
Given an square matrix, turn it by 90 degrees in anti-clockwise direction without using any extra space.
例子:
Input
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
Output:
3 6 9
2 5 8
1 4 7
Input:
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16
Output:
4 8 12 16
3 7 11 15
2 6 10 14
1 5 9 13思路:
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16
First Cycle:
1 (2) 3 4
(5) (8)
9 12
13 14 (15) 16
Second Cycle:
(6) 7
10 (11)
实现:
void rotateMatrix(int **m, int n){
// head代表第几层
for(int head=0;head<n/2;head++){
// round追踪圈上的数
// n/2为那一层的长度
for(int round = head;round<n/2-1;round++){
int tmp = m[head][round];
m[head][round] = m[round][n-1-head];
m[round][n-1-head] = m[n-1-head][n-1-round];
m[n-1-head][n-1-round] = m[n-1-round][head];
m[n-1-round][head] = tmp;
}
}
}3.从数据流中随机去m个数
题目:
有一个很大很大的输入流,大到没有存储器可以将其存储下来,且只输入一次,如何从这个输入流中随机取得m个记录。
思路:
算法(数据流共有n个数据):
If m >= n, just keep it.
For m < n, generate a random number R=rand(n) in [0, n), replace a[R] with new number if R falls in [0, m).
我们可以证明算法的可行性,当m < n时,我们考虑第i个数据被选上的概率
a) i<=m时,概率为i不被第m+1, …, n个数据所替换的概率,即
b) i>m时,概率为i被换进去且不被第i+1, …, n个数据所替换的概率,即
综上,随机性可以保证!
优先队列
1.Top K Frequent Elements
题目:
Given a non-empty array of integers, return the k most frequent elements.
For example,
Given [1,1,1,2,2,3] and k = 2, return [1,2].
Note:
You may assume k is always valid, 1 ≤ k ≤ number of unique elements.
Your algorithm’s time complexity must be better than O(n log n), where n is the array’s size.
思路:
思路1~**时间复杂度:O(n);空间复杂度:O(2*n)**
hash,得到<元素,频次>键值对
因为频次小于n,建散列表,即新建大小为n+1的数组,数组下标为频次,数组内容为有相同频次的键值list,对散列表按下标由大到小遍历,找出k个键值
思路2~**时间复杂度:O(n*log(n-k));空间复杂度:O(n)**
hash map
新建大小为n-k的最大堆,遍历<元素, 频次>,频次大于堆顶的保存到返回列表,频次小于堆顶的入堆,最后最小堆保存的是出现频次最低的n-k个,被“舍弃”的元素则是出现频次最大的k个
实现:
// 思路1
* 求一个数组中,出现次数最多的k个数,利用桶排序的思想,注意这里的桶排序空间
* 复杂度为O(n),桶的下标表示出现的次数,桶的元素是一个List,表示所有出现了
* 这些次数的元素,厉害
* */
public List<Integer> topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
//第一步,还是先统计每个数字出现的次数,这个貌似不可避免,时间复杂度为O(n)
HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>();
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
Integer count = map.get(nums[i]);
if(count==null){
count = 0;
}
map.put(nums[i], count+1);
}
//第二步,构造一个桶,下标表示出现次数,如果nums大小为n,且这n个数相等,那么
//出现次数最大为n,所有桶的大小为n+1
//这个桶实际上是将上面那个map的key value翻转了一下,因为对于同一个value可能有多个
//key,所以buckey的元素应该是个列表,第一次这么用列表
List<Integer>[] bucket = new List[nums.length+1];
for(int key:map.keySet()){
int count = map.get(key);
if(bucket[count]==null){
ArrayList<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
temp.add(key);
bucket[count] = temp;
}else{
bucket[count].add(key);
}
}
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i=bucket.length-1;i>=0&&res.size()<k;i--){
if(bucket[i]!=null){
//这里addAll是因为题目说明了只有一个唯一解,是个特例
res.addAll(bucket[i]);
}
}
return res;
} // 思路2
//返回一个数组中,出现次数最多的k个数
public List<Integer> topKFrequent2(int[] nums, int k) {
//先统计每个数字出现的次数,这个貌似不可避免,时间复杂度为O(n)
HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>();
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
Integer count = map.get(nums[i]);
if(count==null){
count = 0;
}
map.put(nums[i], count+1);
}
//然后应该可以使用优先队列了,
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(k,new Comp(map));
for(int key:map.keySet()){
if(pq.size()<k){
pq.add(key);
continue;
}
int small = pq.peek();
if(map.get(small)<map.get(key)){
pq.poll();
pq.add(key);
}
}
return new ArrayList<Integer>(pq);
}
//注意构造函数,使用map来初始化
class Comp implements Comparator<Integer>{
HashMap<Integer,Integer> map;
public Comp(HashMap<Integer,Integer> map){
this.map = map;
}
@Override //通过key的value来排序
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return map.get(o1)-map.get(o2);
}
} 字典树
Union Find
线段树
线性结构
链表
1.判断两个链表是否相交(链表可能有环),且返回第一个相交节点的指针
题目:
给出两个单向链表的头指针,比如h1、h2,判断链表是否相交,如果不相交返回NULL;如果相交,返回指向第一个相交节点的指针;时间复杂度控制在O(n)的前提下。
两个关键算法:
1.判断两个无环链表是否相交,若相交求出其交点
两个有公共结点而部分重合的链表,拓扑形状看起来像一个Y,而不可能像X。即从公共节点开始之后的所有都相同!求出链表长度差,遍历差数目长的链表,之后同步遍历两链表,第一个相同的节点即是结果。
int GetLength(Node *head){
int length = 0;
while(head){
length++;
head = head->next;
}
return length;
}
// 不相交则返回NULL,相交则返回相交节点指针
Node* AcyclicCommon(Node *h1, Node *h2){
int len1 = GetLength(h1);
int len2 = GetLength(h2);
// 令h1,len1为较长链的头节点,长度
if(len1<len2){
int tmpLen = len1;
len1 = len2;
len2 = tmpLen;
Node *tmpH = h1;
h1 = h2;
h2 = tmpH;
}
// cout<<len1<<"|"<<len2<<endl;
// 跑到同一起跑线
for(int i=0;i<len1-len2;i++)
h1 = h1->next;
while(h1 && h1!=h2){
h1 = h1->next;
h2 = h2->next;
}
return h1;
}2.判断一个链表是否有环并确定环的入口
S1:判断是否有环
设置两个指针(fast, slow),初始值都指向头,slow每次前进一步,fast每次前进二步,如果链表存在环,则fast必定先进入环,而slow后进入环,两个指针必定相遇。(当然,fast先行头到尾部为NULL,则为无环链表)
S2:找出环入口
由S1可知,
设入口环与相遇点距离为
,
,起点到环入口点的距离为
,则
由此可知, 从链表头、与相遇点分别设一个指针,每次各走一步,两个指针必定相遇,且相遇第一点为环入口点。
Node* CyclicEntrance(Node* head){
Node *fast = head;
Node *slow = head;
bool isCyclic = false;
// 先找到相遇点
while(fast && fast->next){
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow==fast){
isCyclic = true;
break;
}
}
if(!isCyclic) return NULL;
// 一个从起点,一个从相遇点重新遍历,步长相同,当再次相遇时,就是环入口
slow = head;
while(slow!=fast){
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return fast;
}
思路:
- 情况1:两个链表无环
- 情况2:两个链表皆有环
- 情况3:一个链表有环,一个链表无环
实现:
truct Node{
int data;
Node* next;
// Node(int x) : data(x){}
};
int GetLength(Node *head){
int length = 0;
while(head){
length++;
head = head->next;
}
return length;
}
// 不相交则返回NULL,相交则返回相交节点指针
Node* AcyclicCommon(Node *h1, Node *h2){
int len1 = GetLength(h1);
int len2 = GetLength(h2);
// 令h1,len1为较长链的头节点,长度
if(len1<len2){
int tmpLen = len1;
len1 = len2;
len2 = tmpLen;
Node *tmpH = h1;
h1 = h2;
h2 = tmpH;
}
// cout<<len1<<"|"<<len2<<endl;
// 跑到同一起跑线
for(int i=0;i<len1-len2;i++)
h1 = h1->next;
while(h1 && h1!=h2){
h1 = h1->next;
h2 = h2->next;
}
return h1;
}
Node* CyclicEntrance(Node* head){
Node *fast = head;
Node *slow = head;
bool isCyclic = false;
// 先找到相遇点
while(fast && fast->next){
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow==fast){
isCyclic = true;
break;
}
}
if(!isCyclic) return NULL;
// 一个从起点,一个从相遇点重新遍历,步长相同,当再次相遇时,就是环入口
slow = head;
while(slow!=fast){
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return fast;
}
// 核心代码
Node* FirstCommonNode(Node *h1, Node *h2){
Node *e1 = CyclicEntrance(h1);
Node *e2 = CyclicEntrance(h2);
Node *pResult = NULL;
if(e1==e2){
if(e1){// 情况2:两个链表皆有环,且相交于环入口前
Node *pTemp1 = e1->next;
Node *pTemp2 = e2->next;
e1->next = NULL;
e2->next = NULL;
pResult = AcyclicCommon(h1, h2);
e1->next = pTemp1;
e2->next = pTemp2;
}
else{// 情况1:两个链表无环
pResult = AcyclicCommon(h1, h2);
}
}
else if(e1==NULL || e2==NULL){// 情况3:一个链表有环,一个链表无环
return NULL;
}
else{// 情况2:两个链表皆有环,或相交或不相交
pResult = e1->next;
// 若两个链表的环相交,则可能在重回到e1前遇到e2
while(pResult != e2 && pResult != e1){
pResult = pResult->next;
}
return pResult == e2 ? pResult : NULL;
}
}
2.逆转单链表
实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node{
int data;
Node* next;
// Node(int x) : data(x){}
};
Node* ReverseLink(Node *head){
if(head==NULL || head->next==NULL) return head;
Node* newHead = ReverseLink(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = NULL;
return newHead;
}
Node* CreateLink(int arr[], int n){
Node* head = new Node;
head->data = arr[0];
head->next = NULL;
Node *tmp = head;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
Node *element = new Node;
element->data = arr[i];
element->next = NULL;
tmp->next = element;
tmp = element;
}
tmp->next = NULL;
return head;
}
void DeleteLink(Node *head){
while(head){
Node *tmp = head;
head = head->next;
delete tmp;
}
}
void PrintLink(Node *head){
while(head){
cout<<head->data<<" ";
head = head->next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main(){
int test[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
Node* head = CreateLink(test, 5);
PrintLink(head);
head = ReverseLink(head);
PrintLink(head);
DeleteLink(head);
}
3.合并两个有序链表
题目:
有两个升序链表h1, h2,返回h1以及h2合并后的有序链表
思路:
递归与非递归实现思路
实现:
// 递归实现
struct Node{
int e;
Node* next;
};
Node *merge(Node *h1, Node *h2){
if(h1 == NULL) return h2;
if(h2 == NULL) return h1;
Node *head;
if(h1->e>h2->e)
head = h2;
else{
head = h1;
h1 = h2;
}
Node *pretmph = head;
Node *tmph = head->next;
Node *tmp1 = h1;
while(tmp1!=NULL){
while(tmph != NULL && tmph->e<tmp1->e){
pretmph = tmph
tmph = tmph->next
}
pretmph->next = tmp1;
// 交换tmp1以及tmph
tmp1 = tmph;
tmph = pretmph->next;
}
return head;
}4.输出链表的倒数第k个结点
题目:
输入一个单向链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。链表的倒数第0个结点为链表的尾指针。
思路:
维护两个间隔为k的指针,k…0,遍历到链表尾结点
实现:
Node* lastK(Node *head, int k){
Node *pre = head;
Node *mark = head;
//保证mark与pre之间间隔k个结点,所以mark为NULL(-1)时,pre(k)刚刚好指向倒数第k个。
for(int i=0; i<k+1; i++){
if(mark==NULL)
return NULL;
mark = mark->next;
}
while(mark!=NULL){
mark = mark->next;
pre = pre->next;
}
return pre;
}5.从尾到头打印单链表
题目:
实现一个函数,输入一个单链表的头结点,从尾到头反过来打印出每个结点的值
思路:
1. 翻转单链表,再进行输出,但链表的结构已经发生了变化
2. 用栈收集顺序遍历结果,再出栈输出
3. 直接递归实现
实现:
// 直接递归实现
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node{
int data;
Node* next;
// Node(int x) : data(x){}
};
// 核心代码
void ReversePrint(Node *head){
if(head==NULL) return;
ReversePrint(head->next);
cout<<head->data<<" ";
}
Node* CreateLink(int arr[], int n){
Node* head = new Node;
head->data = arr[0];
head->next = NULL;
Node *tmp = head;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
Node *element = new Node;
element->data = arr[i];
element->next = NULL;
tmp->next = element;
tmp = element;
}
tmp->next = NULL;
return head;
}
void DeleteLink(Node *head){
while(head){
Node *tmp = head;
head = head->next;
delete tmp;
}
}
void PrintLink(Node *head){
while(head){
cout<<head->data<<" ";
head = head->next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main(){
int test[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
Node* head = CreateLink(test, 5);
PrintLink(head);
ReversePrint(head);
DeleteLink(head);
}
6.在O(1)时间内删除链表结点
题目:
给定单向链表的头指针和一个节点指针,定义一个函数void DeleteNode(Node* head, Node* toBeDeleted)在O(1)时间删除该节点。
思路:
https://www.2cto.com/kf/201408/322311.html
实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node{
int data;
Node* next;
// Node(int x) : data(x){}
};
void DeleteNode(Node* head, Node* toBeDeleted){
if(toBeDeleted==NULL) return;
if(toBeDeleted->next!=NULL){
Node* tmp = toBeDeleted->next;
toBeDeleted->data = tmp->data;
toBeDeleted->next = tmp->next;
delete tmp;
}
else{
if(head==toBeDeleted){
delete head;
return;
}
Node* tmp = head;
while(tmp->next->next!=NULL)
tmp = tmp->next;
delete tmp->next;
tmp->next = NULL;
}
}
Node* CreateLink(int arr[], int n){
Node* head = new Node;
head->data = arr[0];
head->next = NULL;
Node *tmp = head;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
Node *element = new Node;
element->data = arr[i];
element->next = NULL;
tmp->next = element;
tmp = element;
}
tmp->next = NULL;
return head;
}
void DeleteLink(Node *head){
while(head){
Node *tmp = head;
head = head->next;
delete tmp;
}
}
void PrintLink(Node *head){
while(head){
cout<<head->data<<" ";
head = head->next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main(){
int test[] = {1, 2};
Node* head = CreateLink(test, 2);
DeleteNode(head, head->next);
PrintLink(head);
DeleteLink(head);
}
7.复杂链表的复制
题目:
请实现函数ComplexListNode* Clone(ComplexListNode* pHead),复制一个复杂链表。
在复杂链表中,每个结点除了有一个pNext指针指向下一个结点之外,还有一个pSibling指向链表中的任意结点或者NULL。
结点的定义如下:
struct ComplexListNode{
int val;
ComplexListNode* pNext;
ComplexListNode* pSibling;
};思路:
用map记录,原结点指针到拷贝结点指针的映射。
实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
struct ComplexListNode{
int val;
ComplexListNode *pNext;
ComplexListNode *pSibling;
};
typedef map<ComplexListNode*, ComplexListNode*> Node2node;
ComplexListNode* CloneNodes(ComplexListNode* head, Node2node &record){
if(head==NULL) return NULL;
ComplexListNode* chead = new ComplexListNode;
ComplexListNode* tmp = chead;
while(head!=NULL){
record[head] = tmp;
tmp->val = head->val;
if(head->pNext==NULL)
tmp->pNext = NULL;
else
tmp->pNext = new ComplexListNode;
head = head->pNext;
tmp = tmp->pNext;
}
return chead;
}
void SetSiblings(ComplexListNode* head,ComplexListNode* chead, Node2node &record){
while(head!=NULL){
if(head->pSibling!=NULL)
chead->pSibling = record[head->pSibling];
else
chead->pSibling = NULL;
chead = chead->pNext;
head = head->pNext;
}
}
ComplexListNode* ComplexListCopy(ComplexListNode* head){
Node2node record;
ComplexListNode* chead = CloneNodes(head, record);
SetSiblings(head, chead, record);
return chead;
}更多:
在不使用辅助空间的情况下实现O(N)的时间效率,即空间复杂度为O(1)。
https://www.cnblogs.com/AndyJee/p/4654545.html
8.链表相加
题目:
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order and each of their nodes contain a single digit. Add the two numbers and return it as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example
Input: (2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
Output: 7 -> 0 -> 8
Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int element;
Node* next;
};
Node* AddLink(Node *h1, Node *h2) {
Node *result = NULL;
Node *tmp = NULL;
int preIn = 0;
while(h1!=NULL || h2!=NULL) {
int num1 = 0;
if(h1!=NULL) num1 = h1->element;
int num2 = 0;
if(h2!=NULL) num2 = h2->element;
int num = (num1 + num2 + preIn) % 10;
int in = (num1 + num2 + preIn) / 10;
if(num==0 && in==0) break;
if(tmp == NULL) {
tmp = new Node;
tmp->element = num;
tmp->next = NULL;
result = tmp;
} else {
Node *newNode = new Node;
newNode->element = num;
newNode->next = NULL;
tmp->next = newNode;
tmp = newNode;
}
preIn = in;
if (h1!=NULL) h1 = h1->next;
if (h2!=NULL) h2 = h2->next;
}
return result;
}
int main() {
Node *h1 = new Node;
h1->element = 2;
Node *h2 = new Node;
h2->element = 4;
Node *h3 = new Node;
h3->element = 3;
h1->next = h2;
h2->next = h3;
h3->next = NULL;
Node *h4 = new Node;
h4->element = 5;
Node *h5 = new Node;
h5->element = 6;
Node *h6 = new Node;
h6->element = 4;
h4->next = h5;
h5->next = h6;
h6->next = NULL;
Node *result = AddLink(h1, h4);
cout<<result->element<<result->next->element<<result->next->next->element<<endl;
}9.Odd Even Linked List
题目:
Given a singly linked list, group all odd nodes together followed by the even nodes. Please note here we are talking about the node number and not the value in the nodes.
You should try to do it in place. The program should run in O(1) space complexity and O(nodes) time complexity.
Example:
Given 1->2->3->4->5->NULL,
return 1->3->5->2->4->NULL.
Note:
The relative order inside both the even and odd groups should remain as it was in the input.
The first node is considered odd, the second node even and so on …
实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};
ListNode* oddEvenList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode *oHead = head;
if(head==NULL) return head;
ListNode *eHead = head->next;
ListNode *oTmp = oHead;
ListNode *eTmp = eHead;
ListNode *mTmp = oHead;
while(oTmp!=NULL && eTmp!=NULL) {
oTmp->next = eTmp->next;
if(oTmp->next != NULL)
eTmp->next = oTmp->next->next;
else
eTmp->next = NULL;
oTmp = oTmp->next;
if(oTmp!=NULL) mTmp = oTmp;
eTmp = eTmp->next;
}
mTmp->next = eHead;
return head;
}
int main() {
ListNode* n1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode* n2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode* n3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode* n4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode* n5 = new ListNode(5);
n1->next = n2;
n2->next = n3;
n3->next = n4;
n4->next = n5;
ListNode *h = oddEvenList(n1);
while(h!=NULL) {
cout<<h->val<<" ";
h = h->next;
}
cout<<endl;
}哈希表
1.判断数组中是否存在两数之和相等的情况
题目:
Given an array a[] of n integers, the 4-SUM problem is to determine if there exist distinct indices i, j, k, and l such that a[i]+a[j] = a[k]+a[l]. Design an algorithm for the 4-SUM problem that takes time proportional to
(under suitable technical assumptions).
思路:
把数组的两两和存在哈希表中(共
种可能)
实现:
#include<unordered_set>
using namespace std;
bool isExist(int a[], int n){
unordered_set<int> record;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++){
//判断set中是否包含值i+j
if(record.find(i+j) != record.end())
return true;
else
record.insert(i+j);
}
return false;
}2.Given an array of integers, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to a specific target.
Example:
Given nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9,
Becasuse nums[0]+nums[1] = 2 + 7 =9,
return [0, 1].
思路:
遇到num(2)就把key = target-num(7), value = 0插入字典,遇到num(7)发现字典中有key = 7的项,所以return [0, 1]
实现:
def twoSum(nums, target):
diff = {}
for i, num in enumerate(nums):
if num in diff:
return (diff[num], i)
else:
diff[target-num] = i
return ()3.Suppose that cows of the same breed get into an argument …..
题目:
Example: If we write a function crowded_cows(cow_list, k), we have
crowded_cows([7, 3, 4, 2, 3, 4], 3) == 4 (3和另外一个3间隔少于等于4头牛,所以牛3的群有2个;牛4同理,但它出现比较后,所以输出的是牛4)
crowded_cows([7, 3, 4, 2, 3, 10, 4], 3) == 4 (3和另外一个3间隔少于等于3头牛,所以牛3的群有2个;牛4同理,但它出现比较后,所以输出的是牛4)
crowded_cows([7, 3, 1, 0, 4, 2, 16, 28, 3, 4], 3) == -1
思路:
实现:
def crowded_cows(cows, interval):
# record[cowId] = [index, num]
record = {}
# maxcow: [maxIndex, maxNum]
maxcow = [-1, 1]
for i, cow in enumerate(cows):
if cow in record:
# <= interval不对,因为index2-index1 = 1,中间间隔元素为0
if i-record[cow][0] < interval:
record[cow] = [i, record[cow][1]+1]
if record[cow][1] > maxcow[1]:
maxcow = record[cow]
else:
record[cow] = [i, 1]
else:
record[cow] = [i, 1]
if maxcow[0] == -1:
return -1
else:
return cows[maxcow[0]] 4.URL去重
题目:
有大量的字符串格式的URL,如何从中去除重复的,优化时间空间复杂度
思路:
将URL存入hash链表,每个URL读入到hash链表中,遇到重复的就舍弃,否则加入到链表里面,最后遍历得到所有不重复的URL。空间复杂度M,时间复杂度为O(N+N/M),M为不重复的URL,N为总URL数,但是M无法预测,所以存在风险,可能内存不足以存储所有的不重复URL。 (我搞不大懂时间复杂度怎么来的?)
为了解决内存可能不足的问题,需要把hash链表变化成普通的hash表,每个hash表元素指向一个文件文件,这个文件记录了所有该hash值对应的无重复的URL,那么在加入URL的时候就遍历对应文件中的URL,没有重复则加入到文件中。这样做时间复杂度没有提升,但是每次都要读写文件,消耗的时间应该是上一种方式的三倍,而对内存的要求比较小。一个改进是加入URL的时候进行排序,这样能减少比对的次数(B树/红黑树还是什么其他数据结构?!)。
其他:
复习好哈希表的章节,再好好思考。
5.设计一个系统处理词语搭配问题
题目:
设计一个系统处理词语搭配问题,比如说中国和人民可以搭配,
则中国人民人民中国都有效。要求:
*系统每秒的查询数量可能上千次;
*词语的数量级为10W;
*每个词至多可以与1W 个词搭配
当用户输入中国人民的时候,要求返回与这个搭配词组相关的信息。
思路:
This problem can be solved in three steps:
- identify the words
- recognize the phrase
- retrieve the information
Solution of 1: The most trivial way to efficiently identify the words is hash table or BST. A balanced BST with 100 words is about 17 levels high. Considering that 100k is not a big number, hashing is enough. (存储所有的词)
Solution of 2: Since the phrase in this problem consists of only 2 words, it is easy to split the words. There won’t be a lot of candidates. To find a legal combination, we need the “matching” information. So for each word, we need some data structure to tell whether a word can co-occur with it. 100k is a bad number – cannot fit into a 16bit digit. However, 10k*100k is not too big, so we can simply use array of sorted array to do this. 1G integers, or 4G bytes is not a big number, We can also use something like VInt to save a lot of space. To find an index in a 10k sorted array, 14 comparisons are enough. (分词和匹配检索)
Above operation can be done in any reasonable work-station’s memory very fast, which should be the result of execution of about a few thousands of simple statements.
Solution of 3: The information could be to big to fit in the memory. So a B-tree may be adopted to index the contents. Caching techniques is also helpful. Considering there are at most 10^9 entries, a 3 or 4 level of B-tree is okay, so it will be at most 5 disk access. However, there are thousands of requests and we can only do hundreds of disk seeking per second. It could be necessary to dispatch the information to several workstations. (返回每个词的相关信息)
其他:
细节待完善。
6.有一千万条短信,有重复,以文本文件的形式保存,一行一条,有重复。
请用5分钟时间,找出重复出现最多的前10条
思路:
1. 用哈希表对短信进行存储计数
2. 对哈希表进行遍历,并用大小为10的小根堆,找出重复出现最多的前10条。
其它:
1. 用有序的红黑树,效果会不会更好。
2. 哈希函数的设计
3. 应该是等计数结束后再遍历构造小根堆会比较好
4. 对新进入的url,更新哈希表,然后直接更新小根堆(要判断新进入的url是否本来就在小根堆中),不需要遍历。
7.收藏了1万条 url,现在给你一条url,如何找出相似的url
思路:
用字典树对url进行存储,看对相似程度的需求,找到某棵子树,这颗子树包含了所有所需的相似url。
8.一个文件,内含一千万行字符串,每个字符串在1K以内,要求找出所有相反的串对,如abc和cba。
思路:
文件的大小上限是10G,不可能在内存操作了。
考虑设计一种hash使得如果两个字符串维相反串能得出相同的hash值,然后用该hash将文件中的字符串散列到不同的文件中,再在各文件中进行匹配。比如这样的hash函数对字符串上所有字符的ascii求和,因为长度在1K以内,因此范围在int之内。更进一步,可以在上面那个hash后面再加一个字符串长度,可以得到更好的散列效果。
然后对每个hash对应的文件进行处理,遇到abc则先查询是否命中哈希表中的已有值,若有则找到一对(abc, cba),否则把cba写入哈希表。下一个字符串继续。
9.在一个数组中找到三元组,使得三元组内的三个元素加和为0
思路:
先排序
然后对于有相同元素s时要进行分类(为了防止重复输出),{s, s, s, o1, o2, o3}
1. 只用一个s,则后面两个元素在{o1, o2, o3}上找(算法是首位向内扫描)
2. 只用两个s,则后面一个元素在{o1, o2, o3}上找
3. 只用三个s
实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
void threeSum0(int arr[], int len) {
int i=0;
sort(arr, arr+len);
while(i<=len-3) {
int index = i+1;
while(index<=len-1 && arr[i]==arr[index]) index++;
int indexLen = index-i;
// 只用一个arr[i]
int j=index;
int k=len-1;
while(j<k) {
if(arr[j]+arr[k]==-arr[i]) {
cout<<"("<<arr[i]<<", "<<arr[j]<<", "<<arr[k]<<")"<<endl;
int tmpJ = j;
j++;
while(j<=len-1 && arr[j]==arr[tmpJ]) j++;
int tmpK = k;
k--;
while(k>=0 && arr[k]==arr[tmpK]) k--;
}
else if(arr[j]+arr[k]>-arr[i]) {
k--;
}
else {
j++;
}
}
// 只用两个arr[i]
if(indexLen>=2) {
for(int k=index;k<len;k++) {
if(2*arr[i]+arr[k]==0) {
cout<<"("<<arr[i]<<", "<<arr[i]<<", "<<arr[k]<<")"<<endl;
break;
}
}
}
// 只用三个arr[i]
if(indexLen>=3) {
if(3*arr[i]==0) {
cout<<"("<<arr[i]<<", "<<arr[i]<<", "<<arr[i]<<")"<<endl;
}
}
i = index;
}
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {1, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1};
//int arr[] = {-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4};
threeSum0(arr, 6);
return 0;
}
其他:
其实用集合的方式也是可以做的。
10.Group Anagrams
题目:
Given an array of strings, group anagrams together.
For example, given: [“eat”, “tea”, “tan”, “ate”, “nat”, “bat”],
Return:
[
["ate", "eat","tea"],
["nat","tan"],
["bat"]
]Note: All inputs will be in lower-case.
实现:
// 思路1
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
vector<vector<string> > groupAnagrams(vector<string> &strs) {
vector<vector<string> > result;
unordered_map<string, vector<string> > record;
for(string str : strs) {
string t = str;
sort(t.begin(), t.end());
record[t].push_back(str);
}
for(auto a : record) {
result.push_back(a.second);
}
return result;
}
int main() {
vector<string> strs;
strs.push_back("eat");
strs.push_back("tea");
strs.push_back("tan");
strs.push_back("ate");
strs.push_back("nat");
strs.push_back("bat");
vector<vector<string> > result = groupAnagrams(strs);
for(vector<string> r : result) {
for(string e : r) {
cout<<e<<", ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
// 思路2 略11.Insert Delete GetRandom O(1)
题目:
Design a data structure that supports all following operations in average O(1) time.
insert(val): Inserts an item val to the set if not already present.
remove(val): Removes an item val from the set if present.
getRandom: Returns a random element from current set of elements. Each element must have the same probability of being returned.Example:
// Init an empty set.
RandomizedSet randomSet = new RandomizedSet();
// Inserts 1 to the set. Returns true as 1 was inserted successfully.
randomSet.insert(1);
// Returns false as 2 does not exist in the set.
randomSet.remove(2);
// Inserts 2 to the set, returns true. Set now contains [1,2].
randomSet.insert(2);
// getRandom should return either 1 or 2 randomly.
randomSet.getRandom();
// Removes 1 from the set, returns true. Set now contains [2].
randomSet.remove(1);
// 2 was already in the set, so return false.
randomSet.insert(2);
// Since 2 is the only number in the set, getRandom always return 2.
randomSet.getRandom();思路:
这道题让我们在常数时间范围内实现插入删除和获得随机数操作,如果这道题没有常数时间的限制,那么将会是一道非常简单的题,我们直接用一个set就可以搞定所有的操作。但是由于时间的限制,我们无法在常数时间内实现获取随机数,所以只能另辟蹊径。
此题的正确解法是利用到了一个一维数组和一个哈希表,其中数组用来保存数字,哈希表用来建立每个数字和其在数组中的位置之间的映射,对于插入操作,我们先看这个数字是否已经在哈希表中存在,如果存在的话直接返回false,不存在的话,我们将其插入到数组的末尾,然后建立数字和其位置的映射。删除操作是比较tricky的,我们还是要先判断其是否在哈希表里,如果没有,直接返回false。由于哈希表的删除是常数时间的,而数组并不是,为了使数组删除也能常数级,我们实际上将要删除的数字和数组的最后一个数字调换个位置,然后修改对应的哈希表中的值,这样我们只需要删除数组的最后一个元素即可,保证了常数时间内的删除。而返回随机数对于数组来说就很简单了,我们只要随机生成一个位置,返回该位置上的数字即可
实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
class RandomizedSet {
public:
RandomizedSet() {}
bool insert(int val) {
if(num2pos.count(val)) return false;
nums.push_back(val);
num2pos[val] = nums.size() - 1;
return true;
}
bool remove(int val) {
if(!num2pos.count(val)) return false;
int last = nums.back();
num2pos[last] = num2pos[val];
nums[num2pos[val]] = last;
nums.pop_back();
num2pos.erase(val);
return true;
}
int getRandom() {
return nums[rand() % nums.size()];
}
private:
vector<int> nums;
unordered_map<int, int> num2pos;
};
int main() {
RandomizedSet obj;
bool param_1 = obj.insert(1);
bool param_2 = obj.remove(1);
bool param_4 = obj.insert(2);
int param_3 = obj.getRandom();
cout<<param_3<<endl;
return 0;
}
栈
1.栈的push/pop序列
题目:
输入两个整数序列。其中一个序列表示栈的push顺序,判断另一个序列有没有可能是对应的pop顺序。为了简单起见,我们假设push序列的任意两个整数都是不相等的。
比如输入的push序列是1、2、3、4、5,那么4、5、3、2、1就有可能是一个pop系列。因为可以有如下的push和pop序列:push 1,push 2,push 3,push 4,pop,push 5,pop,pop,pop,pop,这样得到的pop序列就是4、5、3、2、1。但序列4、3、5、1、2就不可能是push序列1、2、3、4、5的pop序列。
思路:
实现:
bool isPopSeries(int push[], int pop[], int n){
stack<int> helper;
int i=0;
int j=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
helper.ppush[i]);
if(push[i]==pop[j]){
helper.pop();
j++;
}
}
while(!stack.empty()&&stack.top()==pop[j]){
if(j==n-1) return true;
stack.pop();
j++;
}
return false;
}2.设计⼀个min函数的栈
题⽬:
定义栈的数据结构,要求添加⼀个min函数,能够得到栈的最⼩元素。
要求函数min,push,pop的时间复杂度都是O(1).
思路:
维护两个stack,其中一个维护min。
实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
class MinStack{
public:
// empty()不应该整合于push, pop, min方法上
bool empty(){ return elements.empty();}
void push(int e){
if(empty() || e<=mins.top()) mins.push(e);
elements.push(e);
}
void pop(){
if(elements.top()==mins.top()) mins.pop();
elements.pop();
}
int min(){ return mins.top();}
private:
stack<int> elements;
stack<int> mins;
};
3.用两个栈(Stack)实现一个队列(Queue)
题目:
某队列的声明如下:
template<typename T>
class CQueue{
public:
CQueue(){}
~CQueue(){}
void appendTail(const T& node);
T deleteHead();
private:
Stack<T> m_stack1;
Stack<T> m_stack2;
};实现:
template<typename T>
class CQueue{
public:
CQueue(){}
~CQueue(){}
void appendTail(const T& node);
T deleteHead();
private:
Stack<T> m_stack1;
Stack<T> m_stack2;
};
template<typename T>
void CQueue::appendTail(const T& node){
m_stack1.push(node);
}
template<typename T>
T deleteHead(){
if(!m_stack2.isEmpty())
return m_stack2.pop();
if(m_stack1.isEmpty())
erorr("delete from empty queue");
while(!m_stack.isEmpt())
m_stack2.push(m_stack1.pop());
return m_stack2.pop();
}4.使用递归颠倒栈
题目:
用递归颠倒一个栈。例如输入栈{1, 2, 3, 4, 5},1 在栈顶。颠倒之后的栈为{5, 4, 3, 2, 1},5 处在栈顶
思路:
- 弹出并保存栈顶元素
- 递归,颠倒剩余的栈
- 将栈顶元素保存至栈底
注意:使用函数PutDataBottom的实现
实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
void PutDataBottom(stack<int> &data, int e){
if(data.empty()){
data.push(e);
return;
}
int lowE = data.top();
// 把lowE提出来主要是为了递归
data.pop();
PutDataBottom(data, e);
data.push(lowE);
}
void Reverse(stack<int> &data){
if(data.size()==1) return;
int e = data.top();
data.pop();
Reverse(data);
PutDataBottom(data, e);
}
int main(){
stack<int> data;
data.push(1);
data.push(2);
data.push(3);
Reverse(data);
cout<<"After Reverse:"<<endl;
while(!data.empty()){
cout<<data.top()<<", ";
data.pop();
}
cout<<endl;
}
5.Evaluate Reverse Polish Notation
题目:
Evaluate the value of an arithmetic expression in Reverse Polish Notation.
Valid operators are +, -, *, /. Each operand may be an integer or another expression.
Some examples:
["2", "1", "+", "3", "*"] -> ((2 + 1) * 3) -> 9
["4", "13", "5", "/", "+"] -> (4 + (13 / 5)) -> 6实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
bool isOp(string op) {
return op.length()==1 && (op=="+" || op=="-" || op=="*" || op=="/");
}
int evalRPN(vector<string> &tokens) {
stack<int> al;
int res = 0;
for(int i=0;i<tokens.size();i++) {
string e = tokens[i];
if(!isOp(tokens[i])) {
al.push(atoi(e.c_str()));
}
else {
int op1, op2;
op2 = al.top();
al.pop();
op1 = al.top();
al.pop();
if(e=="+") {
res = op1 + op2;
} else if(e=="-") {
res = op1 - op2;
} else if(e=="*") {
res = op1 * op2;
} else if(e=="/") {
res = op1 / op2;
}
al.push(res);
}
}
return res;
}
int main() {
vector<string> strs;
strs.push_back("4");
strs.push_back("13");
strs.push_back("5");
strs.push_back("/");
strs.push_back("+");
cout<<evalRPN(strs)<<endl;
return 0;
}数组
队列
区间
矩阵
数据结构
动态规划
最长公共子序列(LCS)
1.数列s1与s2最长公共子序列(LCS)
题目:
⼦串(Substring):串的⼀个连续的部分
⼦序列(Subsequence):从不改变序列的顺序,⽽从序列中去掉任
意的元素⽽获得的新序列;
例子:
字符串acdfg同akdfc的最⻓公共⼦串为df,⽽他们的最⻓公共⼦序列是adf。
思路:
- c[i, j]: s1取长度为i的部分与s2取长度为j的部分的最长公共子序列的长度;
- 可以从矩阵c得到最长公共子串的内容
实现:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void lcs(const string &s1, const string &s2, string &result){
int len1 = s1.length();
int len2 = s2.length();
// vector<int>后面一定要加空格,不然会当成>>,出现编译错误
vector<vector<int> > matrix(len1+1, vector<int>(len2+1));
for(int i=0;i<=len1;i++)
matrix[i][0] = 0;
for(int j=1;j<=len2;j++)
matrix[0][j] = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=len1;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=len2;j++){
if(s1[i-1]==s2[j-1])
matrix[i][j] = matrix[i-1][j-1] + 1;
else
matrix[i][j] = matrix[i-1][j] > matrix[i][j-1] ? matrix[i-1][j] : matrix[i][j-1];
}
// 最长公共子串的长度为matrix[len1][len2]
// 下面打印最长公共子串
int i = len1;
int j = len2;
while(i!=0 && j!=0){
if(s1[i-1] == s2[j-1]){
result.push_back(s1[i-1]);
i--;
j--;
}
else{
if(matrix[i-1][j]>matrix[i][j-1])
i--;
else
j--;
}
}
// 翻转字符串
reverse(result.begin(), result.end());
}复杂度:
时间复杂度O(len1*len2),空间复杂度O(len1*len2)
拓展:
2.LCS的应用:最长递增子序列LIS
题目:
找出给定数组最⻓且单调递增的⼦序列。
如:给定数组A{5,6,7,1,2,8},则其最⻓的单调递增⼦序列为{5,6,7,8},⻓度为4
思路:
a) 思路1:
其实此问题可以转换成最⻓公共⼦序列问题只需要将原始数组进⾏排序A’{1,2,5,6,7,8}
因为,原始数组A的⼦序列顺序保持不变,⽽且排序后A’本⾝就是递增的,这样,就保证了两个序列的最⻓公共⼦序列的递增特性。如此,若想求数组A的最⻓递增⼦序列,其实就是求数组A与它的排序数组A’的最⻓公共⼦序列 。
b) 思路2:
动态规划的思路,F(i)是以下标为i的元素最长递增子串的长度
c) 思路3:
https://www.cnblogs.com/sasuke-/p/5396843.html
实现:
a) 实现1
1. 先把数组A整成有序数组B
2. 再求数组A和数组B的最长公共子序列
b) 实现2:动态规划
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int LIS(int arr[], int n) {
int *record = new int[n];
record[0] = 1;
int rIndex = 0;
int result = 1;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++) {
int max = 1;
for(int j=0;j<i;j++) {
if(arr[j]<arr[i] && record[j]+1>max) {
max = record[j]+1;
}
record[i] = max;
if(max>result) {
rIndex = i;
result = max;
}
}
}
int count = 0;
int trace = rIndex;
while(trace>=0 && count<result) {
while(record[trace]!=result-count) trace--;
cout<<arr[trace]<<" ";
count++;
}
cout<<endl;
cout<<endl;
delete[] record;
return result;
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {1, 4, 3, 2, 6, 5, 0};
cout<<"Max Len: "<<LIS(arr, sizeof(arr)/sizeof(int))<<endl;
return 0;
}其他:
其实可以直接使用贪心算法去做。
最长公共子串
1.数列s1与s2最长公共子串(LCS)
题目:
⼦串(Substring):串的⼀个连续的部分
⼦序列(Subsequence):从不改变序列的顺序,⽽从序列中去掉任
意的元素⽽获得的新序列;
例子:
字符串acdfg同akdfc的最⻓公共⼦串为df,⽽他们的最⻓公共⼦序列是adf。
思路:
- 动态规划最重要的是定义出状态转移方程:
下面是最长公共子序列的定义,显然不适合于最长公共子串:
c[i, j]: s1取长度为i的部分与s2取长度为j的部分的最长公共子串的长度;
下面是最长公共子串的状态转移方程的定义:
c[i, j]: s1取长度为i的部分,s2取长度为j的部分,这两部分尾部重合的长度为c[i, j],如abcdef与kbfffffdef的值为3 (def);
用maxInfo最最长公共子串进行追踪
实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct Info{
int i;
int j;
int value;
};
void lcs(const string &s1, const string &s2, string &result){
int len1 = s1.length();
int len2 = s2.length();
Info maxInfo = {0, 0, 0};
vector<vector<int> > matrix = (len1+1, vector<int>(len2+1));
for(int i=0;i<=len1;i++)
matrix[i][0] = 0;
for(int j=1;j<=len2;j++)
matrix[0][j] = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=len1;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=len2;j++){
if(s1[i-1]==s2[j-1]){
matrix[i][j] = matrix[i-1][j-1] + 1;
if(matrix[i][j]>maxInfo.value){
maxInfo.i = i;
maxInfo.j = j;
maxInfo.value = value;
}
}
else
matrix[i][j] = 0;
}
result = s1.substr(maxInfo.i-maxInfo.value, maxInfo.value);
}复杂度:
时间复杂度O(len1*len2),空间复杂度O(len1*len2)
背包问题
1.01背包问题
http://blog.csdn.net/mu399/article/details/7722810
http://blog.csdn.net/kangroger/article/details/38864689
2.完全背包问题
http://blog.csdn.net/kangroger/article/details/38864689
3.和等于m的所有的可能的组合
题目:
输入两个整数n和m,从数列1, 2, 3, …, n中随意取几个数,使其和等于m,要求将其中所有的可能组合列出来。
思路:
set[i][sum]:代表利用前i个数字得到和为sum的组合
set[i-1][sum]:代表利用前i-1个数字得到和为sum的组合
set[i-1][sum-1]:代表利用前i-1个数字得到和为sum-i的组合
很明显有以下的等式:
set[i][sum] = set[i-1][sum] V set[i-1][sum-i]
实现:
// 递归
//利用标记数组进行打印
void Print(bool *record, int length){
for(int i=1;i<=length;i++){
if(record[i])
cout<<i<<' ';
}
cout<<endl;
}
// 打印的时候需要引入一个数组进行元素选择的标记
void AllCombination(int num, int sum, bool *record, int length){
// 考虑到(1, 1, record, length)的情况,sum==0的判断必须放前面
if(sum == 0){
Print(record, length);
return;
}
if(sum < 0 || num <= 0) return;
// set[i-1][sum-i]
record[num] = true;
AllCombination(num-1, sum-num, record, length);
// set[i-1][sum]
record[num] = false;
AllCombination(num-1, sum, record, length);
}
/*
// set[i-1][sum-i]
record[num] = true;
AllCombination(num-1, sum-num, record, length);
// set[i-1][sum]
record[num] = false;
AllCombination(num-1, sum, record, length);
变成下面这样可不行,因为record[num]最终置为true了:
// set[i-1][sum]
record[num] = false;
AllCombination(num-1, sum, record, length);
// set[i-1][sum-i]
record[num] = true;
AllCombination(num-1, sum-num, record, length);
要进行修改:
// set[i-1][sum]
record[num] = false;
AllCombination(num-1, sum, record, length);
// set[i-1][sum-i]
record[num] = true;
AllCombination(num-1, sum-num, record, length);
// 把num算进去的情况,已经考虑完了,所以要把record[num]重置
// 想一下5, 5, 10要求sum=10
record[num] = false;
*/
4.有两个序列 a,b,大小都为 n,序列元素的值任意整数,无序
题目:
要求通过交换 a,b 中的元素,使[序列 a 元素的和]与[序列 b 元素的和]之间的差最小。
例如:
var a=[100,99,98,1,2,3];
var b=[1,2,3,4,5,40];
思路(递归):
令
1. input[] = [a, b]
2. len为考虑input数组的第0位到第len-1位
3. n为考虑从input数组中挑选的数的个数
4. target为目前挑选出来的数组成的集合和剩下的集合之间的差
首先:
要令abs(target) = abs(sum(a)-sum(b))最小相当于abs(target) = abs(sum(input)-2*sum(b))最小。
minDiff(input, len, n, target) 等价于下面两种情况:
1.挑选第len-1个元素: minDiff(input, len-1, n-1, target-2*input[len-1]);
2.不挑选第len-1个元素: minDiff(input, len-1, n, target);
minDiff(input, len, n, target) = abs(situation1) < abs(situation2) ? situation1:situation2
上面的做法只能求得minDiff的值,但不能把a, b集合打印出来,所以要用mark数组,追踪每条路径。用path数组,追踪拥有最小Diff的路径。
思路(动态规划):
就是把matrix[i][j][sum]搞出来,其实就是把matrix[len][n]的sum的所有可能通过动态规划搞出来,然后看哪个sum令abs(target-2*sum)最小。
实现:
// 大功告成,递归
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int findMax(int input[], int len){
int max = 1 << 31;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(input[i]>max)
max = input[i];
}
return max;
}
int abs(int num){
return num >= 0 ? num : -num;
}
int sum(int input[], int len){
int result = 0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
result += input[i];
return result;
}
void printPath(int input[], int len, bool *mark){
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(mark[i])
cout<<input[i]<<", ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
int minDiff(int input[], int len, int n, int target, bool *mark, int& markLen, bool *path, int& minResult){
if(len < n){
return ~(1<<31);
}
if(n==0){
if(abs(target)<abs(minResult)){
minResult = target;
for(int i=0;i<markLen;i++)
path[i]=mark[i];
}
return target;
}
mark[len-1] = true;
int min2 = minDiff(input, len-1, n-1, target-2*input[len-1], mark, markLen, path, minResult);
mark[len-1] = false;
int min1 = minDiff(input, len-1, n, target, mark, markLen, path, minResult);
bool test = abs(min1) < abs(min2);
return test? min1 : min2;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
int test[] = {-3, 9, 10, 65, 5, 6, 13, 55};
int len = 8;
bool *mark = new bool[len];
bool *path = new bool[len];
int minResult = ~(1<<31);
//cout<<sum(test, len)<<endl;
cout<<"minDiff: "<<minDiff(test, len, 3, sum(test, len), mark, len, path, minResult)<<endl<<endl;
cout<<"set1: (";
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(path[i])
cout<<test[i]<<",";
}
cout<<")"<<endl<<endl;
cout<<"set2: (";
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(!path[i])
cout<<test[i]<<",";
}
cout<<")"<<endl<<endl;
return 0;
delete []mark;
delete []path;
}// 大功告成,动态规划
/*
To do:
1. 首先Record类写得很烂,怎么才能让外部迭代Record内的record,还想不到怎么弄,所以搞了很丑getSum, size这种成员函数
2. 然后对于看是否是合适的subsum,我是把整个record遍历来找的,是否还有其他方法呢?
3. 如果只是为了求最小差的话,其实matrix[i][j]的空间复杂度可以降低很多,首先在算的过程中如果只保存matrix[j] = matrix[1~len][j] = matrix[len][j],因为matrix[i-1][j]的所有subsum会作为一种情况被append到matrix[i][j]中,相当于把前面的拷贝一次到后面,不如不拷贝而直接维护一个vector<Record>就ok了,不过这就不能区分这j个元素的具体组成;再进一步,其实我们利用matrix[j]时只用两列来迭代运算就好;不过,注意的是如果需要得到集合的具体内容而非最小差一个值的话,matrix[i][j]必不可少!
4. 有人不用vector<vector<Record> >,直接用matrix[i][j][subsum],这样的话索引起来会非常快,但是subsum可能是负数,而且作为一个稀疏矩阵有点浪费空间,我觉得应该用vector<vector<map<int> > > record这样会比较好,map<int>存储了相应i, j的所有subsum,首先map不会大(可以用哈希map会大一点,但红黑map会比较小,这里要考证一下),索引快(哈希map会比红黑map快一点)。最后,在搜索最接近的subsum时显然是红黑map会比较好,因为它是一种BST
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int min(int a, int b){
return a<b ? a : b;
}
int abs(int num){
return num >= 0 ? num : -num;
}
int sum(int input[], int len){
int result = 0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
result += input[i];
return result;
}
class Record{
public:
void append(int subs, bool sele){
Node newElement = {subs, sele};
record.push_back(newElement);
}
bool isEmpty(){
return record.empty();
}
bool isSelected(int sum){
for(int i=0;i<record.size() && record[i].selected;i++){
if(record[i].subsum==sum)
return true;
}
return false;
}
int size(){
return record.size();
}
void closest(int target, int &subs, bool &sele){
int index = -1;
int min = ~(1<<31);
for(int i=0;i<=record.size();i++){
int tmp = abs(target-2*record[i].subsum);
if(min>tmp){
min = tmp;
index = i;
if(min == 0) break;
}
}
subs = record[index].subsum;
sele = record[index].selected;
}
int getSum(int index){
return record[index].subsum;
}
private:
struct Node{
int subsum;
bool selected;
};
vector<Node> record;
};
void minDiff(int input[], int len, int n, int target, vector<int> &result){
vector<vector<Record> > matrix(len+1, vector<Record>(n+1));
for(int i=1;i<=len;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=min(i, n);j++){
if(matrix[i-1][j-1].isEmpty()){
matrix[i][j].append(input[i-1], true);
}
else{
for(int k=0;k<matrix[i-1][j-1].size();k++){
matrix[i][j].append(input[i-1]+matrix[i-1][j-1].getSum(k), true);
}
}
for(int k=0;k<matrix[i-1][j].size();k++){
matrix[i][j].append(matrix[i-1][j].getSum(k), false);
}
}
}
int tmpTarget = target;
int i = len;
int j = n;
cout<<"begin: "<<tmpTarget<<endl;
while(j>=1 && i>=j){
bool sele;
int subs;
matrix[i][j].closest(tmpTarget, subs, sele);
if(sele){
result.push_back(input[i-1]);
tmpTarget = 2*subs - 2*input[i-1];
i--;
j--;
}
else
i--;
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
int test[] = {-3, 9, 10, 65, 5, 6, 13, 55};
int len = 8;
int countSet1 = 3;
int target = sum(test, len);
vector<int> result;
minDiff(test, len, countSet1, target, result);
for(int i=0;i<result.size();i++)
cout<<result[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}5.多米诺骨牌
9.求每一对顶点之间的最短路径: Floyd-Warshall算法
10.子数组的最大等和划分
题目:
一个整数数组,长度为n,将其分为m 份,使各份的和相等,求m 的最大值
比如{3,2,4,3,6} 可以分成{3,2,4,3,6} m=1;
{3,6}{2,4,3} m=2
{3,3}{2,4}{6} m=3 所以m 的最大值为3
思路:
划分为m块时,需要具备的条件:
m的取值为1~n
每一部分之和为 sum/m; (sum为数组元素之和)
sum % m == 0,否则不可能平分
递归思想(简单的背包问题):
假设分为m块,每一块之和即为subSum = sum / m。subSum即为每一块元素之和。
如果array[i]在某一个块中,则需要在数组的其中元素中找出和值为(subSum - array[i])的组合。
利用bool数组标记元素是否已分配到每一块中。
实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
// 从数组中找出和为sum的组合(背包问题)
bool findSum(int arr[], bool tags[], int size, int sum){
if(sum<0) return false;
if(sum==0) return true;
for(int i=size-1;i>=0;i--){
if((!tags[i]) && (arr[i]<=sum)){
tags[i] = true;
if(findSum(arr, tags, size, sum-arr[i]))
return true;
else
tags[i] = false;
}
}
return false;
}
int maxDivide(int arr[], int size){
if(size<=1) return (size>=0 ? size : 0);
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++) sum += arr[i];
cout<<"size: "<<size<<" sum: "<<sum<<endl;
bool *tags = new bool[size];
int m;
for(m=size;m>1;m--){
if(sum%m!=0) continue;
memset(tags, 0, sizeof(bool)*size);
int i;
for(i=0;i<size;i++){
if(!tags[i]){
tags[i] = true;
if(!findSum(arr, tags, size, sum/m-arr[i])) break;
}
}
if(i==size) break;
}
delete []tags;
return m;
}
int main(){
int arr[] = {1, 2, 2, 7, 8};
cout<<maxDivide(arr, sizeof(arr)/sizeof(int))<<endl;
return 0;
}11.数组中最长递减子序列
题目:
求一个数组的最长递减子序列比如{9,4,3,2,5,4,3,2}的最长递减子序列为{9,5,4,3,2}
思路:
令C[i]为数组arr从index i开始的最长递减子序列的长度,则
再根据得到的C数组,递减且C数组对应,得到最长递减子序列。
实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void findDecreasing(int *src, int ls){
int ld = 0;
int *cHelper = new int[ls];
int maxIndex = ls - 1;
int max = 1;
cHelper[ls-1] = 1;
for(int i=ls-2;i>=0;i--){
int tmpMax = 1;
for(int j=i+1;j<ls;j++){
if(src[i]>src[j] && (cHelper[j]+1)>tmpMax)
tmpMax = cHelper[j] + 1;
}
cHelper[i] = tmpMax;
if(cHelper[i]>max){
max = cHelper[i];
maxIndex = i;
}
}
cout<<src[maxIndex]<<" ";
int preIndex = maxIndex;
for(int i=maxIndex+1;i<ls;i++){
if(src[i]<src[preIndex] && cHelper[i]==cHelper[preIndex]-1){
preIndex = i;
cout<<src[i]<<" ";
}
}
cout<<endl;
delete []cHelper;
}
int main(){
int test[] = {9, 4, 3, 2, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
findDecreasing(test, 9);
}
讨论:
12.数组中的最长等差数列
题目:
给定一个未排序数组,找出其中最长的的等差数列。如{1, 6, 3, 5, 9, 7}中的{1, 3, 5, 7, 9}
思路:
records记录的是d与record的映射,record记录的是等差数列最后一个数到等差数列长度的映射。
如{1, 2, 3}
第一次外循环后有:
records[1(d)][2(lastnum)] = 2
records[2(d)][3(lastnum)] = 2
第二次外循环后有:
records[1(d)][2(lastnum)] = 2 -> records[1(d)][3(lastnum)] = 3
records[2(d)][3(lastnum)] = 2
注意d为0时要特殊讨论,因为不进行讨论的话,
如{1, 1, 1}
第一次外循环后有:
records[0(d)][1(lastnum)] = 3
第二次外循环后有:
records[0(d)][1(lastnum)] = 4
实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
typedef map<int, int> Record;
class MaxInfo {
public:
MaxInfo() {
lastNum = 0;
d = 0;
len = 0;
}
void Set(int arg1, int arg2, int arg3) {
lastNum = arg1;
d = arg2;
len = arg3;
}
void Print() {
for(int i=0;i<len;i++) {
cout<< lastNum-(len-i-1)*d << ' ';
}
cout<<endl;
}
int lastNum;
int d;
int len;
};
void FindLongestSeq(int arr[], int n) {
sort(arr, arr+n);
map<int, Record> records;
map<int, Record>::iterator iters;
Record::iterator iter;
MaxInfo max;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
int count = ++records[0][arr[i]];
// d等于0时要单独处理
if(max.len<count) {
max.Set(arr[i], 0, count);
}
for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++) {
int d = arr[j] - arr[i];
if(d!=0) {
count = 2;
iters = records.find(d);
if(iters == records.end()) {
Record e;
e[arr[j]] = count;
records[d] = e;
} else {
iter = records[d].find(arr[j]-d);
if (iter!=records[d].end()) {
count = records[d][arr[j]-d] + 1;
records[d].erase(iter);
}
records[d][arr[j]] = count;
}
if(count>max.len) {
max.Set(arr[j], d, count);
}
}
}
}
max.Print();
}
int main(){
int arr[] = {1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
FindLongestSeq(arr, 8);
return 0;
}时间复杂度:
其他:
可以用动态规划来做,时间复杂度为
。具体实现
13.Jump Game
题目:
Given an array of non-negative integers, you are initially positioned at the first index of the array.
Each element in the array represents your maximum jump length at that position.
Determine if you are able to reach the last index.
For example:
A = [2,3,1,1,4], return true.
A = [3,2,1,0,4], return false.
思路:
实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
bool canJump2Last(int arr[], int n) {
bool *result = new bool[n];
result[0] = true;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++) {
result[i] = false;
for(int j=0;j<i;j++) {
if(result[j] && arr[j]>=i-j) {
result[i] = true;
break;
}
}
}
bool ans = result[n-1];
delete []result;
return ans;
}
int main() {
int arr1[] = {2, 3, 1, 1, 4};
int arr2[] = {3, 2, 1, 0, 4};
cout<<canJump2Last(arr1, 6)<<endl;
cout<<canJump2Last(arr2, 6)<<endl;
return 0;
} 14.Unique Paths
题目:
A robot is located at the top-left corner of a m x n grid (marked ‘Start’ in the diagram below).
The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time. The robot is trying to reach the bottom-right corner of the grid (marked ‘Finish’ in the diagram below).
How many possible unique paths are there?
Above is a 3 x 7 grid. How many possible unique paths are there?
Note: m and n will be at most 100.
思路:
注意:
因为m与n可取100,那么直接用递归会超时,应该要把递归改为动态规划。
其他:
动态规划的空间复杂度可以优化
15.凑零钱
题目:
人民币有1角,5角,1元,5元,10元,20元,50元,100元几种币值,请写一个程序,任意给一个货币金额(精确到小数点后1位),输出最少的货币个数
思路:
1. 去掉无效情况 if(remain/units[j]+num>minNum) return;
2. 一般情况来说,贪心算法会获得较佳的结果,所以count从大到小进行遍历,通过sample跟踪,然后通过1剪去很多无效的情况
实现:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int units[] = {1, 5, 10, 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000};
// 直接用了递归的思路,所以效率有点低
// 其实可以转化为动态规划
void Bag(int units[], int j, int remain, int num, int& minNum) {
// cout<<j<<" "<<remain<<" "<<num<<" "<<minNum<<endl;
if(remain == 0) {
if(num < minNum) {
minNum = num;
}
return;
}
if(remain < 0 || j < 0) return;
// 去掉无效情况
if(remain/units[j]+num>minNum) return;
int sample = minNum;
// count从大到小
for(int count=remain/units[j];count>=0;count--) {
// 一直追踪sample
Bag(units, j-1, remain-count*units[j], num+count, sample);
}
minNum = sample;
}
int main() {
float money;
cin >> money;
int remain = int(money*10);
int result = remain/units[0]+1;
int n = sizeof(units)/sizeof(int);
Bag(units, n-1, remain, 0, result);
if(result==remain/units[0]+1)
cout<<"No Such Combination!"<<endl;
else
cout<<"Min Num: "<<result<<endl;
}图论
1.判断有向图是否强连通/无向图是否连通
2.判断有向图/无向图是否有环
思路:
3.求一个有向图的割点
题目:
求⼀个有向连通图的割点。割点的定义是,如果除去此结点和与其相关的边,有向图不再连通,描述算法。(有向图的连通指的是弱连通)
思路:
通过深搜优先生成树来判定。从任一点出发深度优先遍历得到优先生成树,对于树中任一顶点V而言,其孩子节点为邻接点。由深度优先生成树可得出两类割点的特性:
- 若生成树的根有两棵或两棵以上的子树,则此根顶点必为割点。因为图中不存在连接不同子树顶点的边(深搜可以保证此特性),若删除此节点,则树便成为森林;
- 若生成树中某个非叶子顶点V,其某棵子树的根和子树中的其他节点均没有指向V的祖先的回边,则V为割点。因为删去v,则其子树和图的其它部分被分割开来。
利用深搜算法并定义:
任务一:求顶点v的low值
定义:
1. visited[v](圈内序号):深度优先搜索遍历图时访问顶点v的次序号
2. low[v](圈外序号)=Min{visited[v],low[w],visited[k]},其中w是顶点v在深度优先生成树上的孩子节点;k是顶点v在深度优先生成树上由回边联结的祖先节点。
low[v]可以看作v在w分支上可以联结的最早序号:若low[v]=visited[v],则v不能向上追溯 | 若low[v]=low[w],则v通过子节点w向上追溯 | 若low[v]=visited[k],则v通过自身向上追溯到k
任务二:顶点v是否为割点(绿色)判定条件:
如果对于某个顶点v,存在孩子节点w(注意是存在)且low[w]>=visited[v],则该顶点v必为关节点。因为当w是v的孩子节点时low[w]>=visited[v],表明w及其子孙均无指向v的祖先的回边,那么当删除顶点v后,v的孩子节点将于其他节点被分割开来,从来形成新的连通分量。
实现:
// c++实现
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX_NUM_0 11
using namespace std;
const int MAX_NUM = MAX_NUM_0+1;
int count = 0;
// visited记录结点对应的访问序号
int visited[MAX_NUM];
bool cut[MAX_NUM];
// g[][MAX_NUM] g[i][] is the out edges
// g[i][0] is number of out edges
// g[i][j] is j st out edges of i
// s: 当前搜索结点
// low: s本身能向前追溯到的序号
int dfs(int g[][MAX_NUM], int s){
visited[s] = ++count;
// 任务1:计算s的low
int low = visited[s];
for(int j=1;j<=g[s][0];j++){
if(visited[g[s][j]]==0){
int childLow = dfs(g, g[s][j]);
// 任务1:计算s的low
if(childLow<low){
low = childLow;
}
// 任务2:计算s是否为割点
if(childLow>=visited[s]){
cut[s] = true;
}
}
// 任务1:计算s的low
else if(visited[g[s][j]]<low){
low = visited[g[s][j]];
}
}
return low;
}
void PrintCutPoints(int g[][MAX_NUM], int n){
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(int)*MAX_NUM);
memset(cut, 0, sizeof(bool)*MAX_NUM);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(visited[i]==0)
dfs(g, i);
}
int num = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(cut[i]){
cout<< i <<" ";
num++;
}
cout<<endl<<"Total cut points : "<<num<<endl;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
// 因为是由g[1][]开始的,所以g[0][]没有实际意义
// 对应上述示例图
int g[][MAX_NUM] = {
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{2, 2, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 5, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 6, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{3, 7, 8, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 9, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{2, 6, 10, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
};
int n = 11;
PrintCutPoints(g, n);
return 0;
}其他:
有向图强连通分支算法
1. Kosaraju算法
2. Tarjan算法
3. Gabow算法
搜索/递归/回溯
回溯
1.输出映射组合
题目:
Given a digit string, return all possible letter combinations that the number could represent.

A mapping of digit to letters (just like on the telephone buttons) is given below.
Input:Digit string "23"
Output: ["ad", "ae", "af", "bd", "be", "bf", "cd", "ce", "cf"].思路很简单,看看代码就懂。
实现:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
string keyboard[] = {" ", "", "abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"};
void DFS(string digits, int level, string path, vector<string> &result) {
if(level==digits.length()) {
result.push_back(path);
return;
}
int len = keyboard[digits[level]-'0'].length();
for(int i=0;i<len;i++) {
char addChar = keyboard[digits[level]-'0'][i];
DFS(digits, level+1, path+addChar, result);
}
}
vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) {
vector<string> result;
DFS(digits, 0, "", result);
return result;
}
int main() {
vector<string> result = letterCombinations("23");
int len = result.size();
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
cout<<result[i]<<", ";
cout<<endl;
return 0;
} 递归
分治法
排列
非递归
排序
快速排序
归并排序
1.寻找逆序对的个数
题目:
多人排成一个队列,我们认为从低到高是正确的序列,但是总有部分人不遵守秩序。如果说,前面的人比后面的人高(两人身高一样认为是合适的),那么我们就认为这两个人是一对“捣乱分子”。
比如说,现在存在一个序列:176, 178, 180, 170, 171
这些捣乱分子对为<176, 170>, <176, 171>, <178, 170>, <178, 171>, <180, 170>, <180, 171>,那么,现在给出一个整型序列,请找出这些捣乱分子对的个数(仅给出捣乱分子对的数目即可,不用具体的对)
思路:
1.插入排序 时间复杂度
| 空间复杂度
f(n) = f(n-1) + 第n个元素的逆序个数
2.归并排序 时间复杂度
| 空间复杂度
f(n) = f(n/2) (有序左子序列)+ f(n/2) (有序右子序列) + 两个子序列的逆序个数
实现:
// 思路1
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int FindBadGuy(int arr[], int n) {
if(n<=1) return 0;
int count = 0;
for(int i=0;i<=n-2;i++){
if(arr[i]>arr[n-1])
count++;
}
return FindBadGuy(arr, n-1) + count;
}
int main(){
int arr[] = {176, 178, 180, 170, 171};
int result = FindBadGuy(arr, 5);
cout<<result<<endl;
return 0;
}// 思路2其他排序
1.如何对n个数进行排序,要求时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(1)
思路:
看上去似乎任何已知的算法都无法做到,如果谁做到了,那么所有的排序方法:QuickSort,ShellSort,HeapSort,BubbleSort等等等等,都可以扔掉了,还要这些算法干吗阿,呵呵。不过实际上,在数字范围有限制的情况下,是有一个这样的算法的,只需要用一个数组记录每个数字出现次数就可以了。
假定你的数字范围在0到65535范围之内,定义一个数组count[65536](这个空间是常量,和n无关,所以是O(1) ),初值全部为0。
那么假设有下面这些数字:
100
200
300
119
0
6
…
那么对于每个这个数字,都做在count中记录一下:
100 => count[100]++
200 => count[200]++
300 => count[300]++
119 => count[119]++
0 => count[0]++
6 => count[6]++
…
最后,遍历一边所有这些数字就可得到0~65535每个数字的个数(在count数组中),然后再顺序遍历count数组,count[n] = m,则输出m个n,(比如说有count[3] = 2, 那么说明有2个数字3),依次输出,最后可得结果。第一次遍历是O(n),第二次遍历是O(1),为常量,所以最后的时间复杂度为O(n),而空间复杂度为O(1)
数学
卡特兰数
1.n对括号正确匹配数目
题目:
给定n对括号,求括号正确配对的字符串数,例如:
0对括号:[空序列] 1种可能
1对括号:() 1种可能
2对括号:()() (()) 2种可能
3对括号:((())) ()(()) ()()() (())() (()()) 5种可能
那么问题来了,n对括号有多少种正确配对的可能呢?
思路:
对于n+1对括号,只有以下的形式
,令S(n)为n对括号的正确配对的可能个数,则
根据卡特兰数的定义,该数列为卡特兰数的序列。卡特兰数有以下递推公式:
实现:
// 只是计算组合个数
unsigned long long catalannumber1(int n)
{
if(n == 0)
return 1;
else
return (4 * n - 2) * catalannumber1(n-1) / (n + 1);
}
unsigned long long catalannumber2(int n)
{
unsigned long long cn = 1;
int i;
for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
cn = (4 * i - 2) * cn / (i + 1);
return cn;
} // 打印所有可能的组合
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void printHelper(string collection, int leftRemain, int rightNeed){
if(leftRemain==0 && rightNeed==0){
cout<<collection<<endl;
return;
}
if(leftRemain>0)
printHelper(collection+"(", leftRemain-1, rightNeed+1);
if(rightNeed>0)
printHelper(collection+")", leftRemain, rightNeed-1);
}
int main(){
printHelper("", 3, 0);
return 0;
} 卡特兰数的典型应用:
- 括号化问题 矩阵链乘: P=a1×a2×a3×……×an,依据乘法结合律,不改变其顺序,只用括号表示成对的乘积,试问有几种括号化的方案?(h(n)种)
- 出栈次序问题 一个无穷大堆栈的进栈序列为1,2,3,..n,有多少个不同的出栈序列?
- 凸多边形三角划分问题 将一个凸多边形区域分成三角形区域的方法数?
- 给定节点组成二叉树 给定N个节点,能构成多少种不同的二叉树?
2.12个高矮不同的人,排成两排
题目:
12个高矮不同的人,排成2排,每排必须是从矮到高排列,而且第二排比对应的第一排的人高,问排列方式有多少种?
思路:
把12个人从低到高排列,编号为1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, …, 12
若编号i处于第一排则标为0,处于第二排则标为1。
一种合法的安排:
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1
等价于
第一排:1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
第二排:7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12
我们再看另一种合法的安排:
0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1
等价于
第一排:1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11
第二排:2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12
经过分析得,合法的安排有以下规律:0相当于括号匹配中的(,而1相当于括号匹配中的),经过之前的分析,合法的安排个数为卡特兰数。
对于n+1对括号,只有以下的形式
,令S(n)为n对括号的正确配对的可能个数,则
根据卡特兰数的定义,该数列为卡特兰数的序列。卡特兰数有以下递推公式:
随机数
1.随机概率发生器
题目:
a) 有一个随机数发生器,能以概率p生成0,以概率1-p生成1,问如何做一个随机数发生器 使得生成0和1的概率相等。
b) 用上面那个生成0和1的概率相等的随机数发生器,怎样做一个随机数发生器使得它生成 的数在1…N之间均匀分布。
思路:
a) 生成01和10是等概率的(p*(1-p)),因此我们遇到00和11就丢弃,只记录01和10。然后令(01表示0;10表示1),则等概率1/2产生0和1了。
b) 利用a中得到的等概率01生成器,生成长度为log(N-1)长度的01序列:
如 N=3,则00->抛弃; 01->1; 10->2; 11->3
如 N=4,则00->4; 01->1; 10->2; 11->3
离散数学
1.根据上排给出十个数,在其下排填出对应的十个数*(网上没有正确的解答,我算是把它给终结了)
题目:
要求下排每个数都是先前上排那十个数在下排出现的次数。上排的十个数如下:
【0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9】
举一个例子,
数值: 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9
分配: 6,2,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0
0 在下排出现了6 次,1 在下排出现了2 次,
2 在下排出现了1 次,3 在下排出现了0 次….
以此类推..
思路:
关键是下排每个数都是先前上排那十个数在下排出现的次数,即隐含着(角度1)在上排中挑选十个数,这十个数可以重复,然后放到下排的位置。(角度2)所以总的出现次数就等于下排有多少个位置要放。
假设:设总共有n个数,上排a[0…n-1],下排b[0…n-1]
1)下排n个数的累加和为n,即b[0]+b[1]+…+b[n-1] = n
2)ai*bi的累加和也为n,即a[0]*b[0]+a[1]*b[1]+…+a[n-1]*b[n-1] = n
3)对于b中任意一个元素b[j], 都存在i,a[i] = b[j].
4)对于b中任意一个元素b[j],都有b[j] >= 0
5)如果a中存在负数,其在b中出现的次数一定为0. 如果a中数值大于n,则其出现次数也为0.
6)考察等式
等价于
。若a中没有0,则b中元素全为0;若a中含有0,则b[0]=k>=1,然后b[k]>=1。
讨论:
1. 如果a中存在负数,其在b中出现的次数一定为0. 如果a中数值大于n,则其出现次数也为0.
2.* 若a中没有0,则b中元素全为0;*
3. 如果a中有0,则a中至少有1个或者以上非0数值在b中出现次数非0;(下面进行分类讨论)
a中只有1个非0数值在b中出现的次数非0 (1)
a 0 b[0]
b b[0] x
由(1)得,x = b[0]
b[0] + b[0] = b[0] *b[0];b[0] = 2 或 b[0] = 0 (舍去);b[0] = 2
a 0 2
b 2 2
-> 结论
a 0 2
b 2 2 0 0a中有2个或者以上非0数值在b中出现的次数非0 (2)
由(2)得,任意i,有a[i]*b[i] < n(注意不等式不能取等)
考虑任意n/2<=a[i] < n,有b[i] < 2;b[i] = 1 或 b[i] = 0;在此范围内只能有一个数值出现1次(否则和会大于n)或者在此范围内任何一个数值出现为0次;考虑在此范围内任何一个数值出现为0次的情况,则在范围1 <= a[i] <= n/2-1中,最多有n/2-1个位置可以放非零的数,所以n个位置中至少有n/2+1个位置要放上零,所以b[0] >= n/2+1,所以与在范围n/2 <= a[i] < n内任何一个数值出现为0次的情况矛盾。因此结论为在范围n/2 <= a[i] < n内必有有且只有一个数值,其出现次数必为1次。(3)
由(3)得,b[1]>=1;若b[1] = 1,则b[1]应该为2(矛盾);因此b[1]>1;
若b[1]=w>1,则b[w]>=1;若b[w]>1,则为了满足对应关系,需要找到另外的b[v] = w,如此类推为了一一对应而进行填坑,反而导致了更多的坑,最终不能满足一一对应关系(矛盾),所以b[w]必为1。此时情况如下:
1 w
w 1
若w=1(显然不成立);若w>2,则也是上面的道理,需要借助他人,导致坑越来越大,显然也是不成立的;因此,w必然为2。此时情况如下:
0 1 2 … n-4 …
n-4 2 1 0 1 0
结论(只有下面3种情况):
1.
a 0 2
b 2 2 0 0
2.
a 0 1 2 … n-4 …
b n-4 2 1 0 1 0
3.a中没有0元素
a …
b 0
2.全排列
题目:
字符串之全排列
思路:
1. https://www.jianshu.com/p/f051a4ae6e93
2. isSwap函数的思路
实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(string &l, int i, int j){
if(i==j) return;
int tmp = l[i];
l[i] = l[j];
l[j] = tmp;
}
bool isSwap(string &l, int i, int j){
for(int k=i;k<j;k++){
if(l[k]==l[j])
return false;
}
return true;
}
void perm(string l, int i){
int n = l.length();
if(i==n){
for(int k=0;k<n;k++)
cout<<l[k];
cout<<endl;
return;
}
for(int j=i;j<n;j++){
if(isSwap(l, i, j)){
swap(l, i, j);
perm(l, i+1);
swap(l, i, j);
}
}
}
int main(){
string src = "haha";
perm(src, 0);
return 0;
}3.组合算法 - 从n中选m个数
http://blog.csdn.net/garrison_Z/article/details/44950027
http://blog.csdn.net/garrison_Z/article/details/44950027
4.A说不知道,B说不知道,C说不知道,然后A说知道了
题目:
有4张红色的牌和4张蓝色的牌,主持人先拿任意两张,再分别在A、B、C三人额头上贴任意两张牌,
A、B、C三人都可以看见其余两人额头上的牌,看完后让他们猜自己额头上是什么颜色的牌,
A说不知道,B说不知道,C说不知道,然后A说知道了。
请教如何推理,A是怎么知道的。
如果用程序,又怎么实现呢?
思路:
从A的角度看,B/C两者是对称的,只考虑下面三种的情况即可
1. (B, C)=(RR, BB) -> A = RB
2. (B, C)=(RB, RB) -> A = RB
若A=RR,则B判断不了,代表了C最多只有一个R;若C为BB,又因为A不能判断,所以B就知道自己不可能是BB,所以B就知道自己为RB了;
3. (B, C)=(RR, RB)-> A
若A=BB,又因为C不能为BB或RR,所以C知道自己是RB了;
5.寻找丑数
题目:
一个数的因子只包含2,3,5的数称为丑数。数字1特别对待也看作是丑数,所以从1开始的10个丑数分别为1,2,3,4,5,6,8,9,10,12。寻找第n个丑数。
思路:
因为丑数只有以上三个因子,所以在排序的丑数列表中,后面的某个丑数一定是前面某个丑数乘以2或3或5的结果,所以我们可以以这三个因子得到不同的丑数,然后把乘以2或3或5的得到的丑数进行排序,把最小的丑数更新到丑数列表中;如果列表的某个丑数乘以2或3或5的结果刚好是丑数中的最小值,那么就继续把该数对应的下标增加1,表示继续寻找下一个新的丑数。
实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int Min3(int n1, int n2, int n3){
int min2 = n1 > n2 ? n2 : n1;
return min2 > n3 ? n3 : min2;
}
int UglyNum(int n){
vector<int> ugly;
ugly.push_back(1);
int count = 1;
int trace2 = 0;
int trace3 = 0;
int trace5 = 0;
int candidate2 = 0;
int candidate3 = 0;
int candidate5 = 0;
while(count<n){
// 扫描不需要每次从0开始,可以分别从trace2, trace3, trace5开始
for(int i=trace2;i<count;i++){
if(2*ugly[i]>ugly[count-1]){
trace2 = i;
candidate2 = 2*ugly[i];
break;
}
}
for(int i=trace3;i<count;i++){
if(3*ugly[i]>ugly[count-1]){
trace3 = i;
candidate3 = 3*ugly[i];
break;
}
}
for(int i=trace5;i<count;i++){
if(5*ugly[i]>ugly[count-1]){
trace5 = i;
candidate5 = 5*ugly[i];
break;
}
}
ugly.push_back(Min3(candidate2, candidate3, candidate5));
count++;
}
return ugly[count-1];
}
int main(){
int n = 1400;
cout<<UglyNum(n)<<endl;
return 0;
} 6.输出1到最大的N位数
题目:
输入数字n,按顺序输出从1最大的n位10进制数。比如输入3,则输出1、2、3一直到最大的3位数即999。
思路:
如果直接用数值方法加1,当n很大时,算法一可能会溢出,所以考虑大数问题一般用数组或字符串。
n位所有10进制数其实就是n个从0到9的全排列。也就是说,我们把数字的每一位都从0到9排列一遍,就得到了所有的10进制数。只是我们在输出的时候,数字排在前面的0我们不输出罢了。
全排列用递归很容易表达,数字的每一位都可能是0到9中的一个数,然后设置下一位。递归结束的条件是我们已经设置了数字的最后一位。
实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void PrintNumber(string number){
int i = 0;
int len = number.length();
for(;i<len;i++)
if(number[i]!='0')
break;
if(i==len) return;
for(;i<len;i++)
cout<<number[i];
cout<<endl;
}
void PrintFrom1ToN(string number, int index){
if(index==number.length()){
PrintNumber(number);
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
number[index] = '0'+i;
PrintFrom1ToN(number, index+1);
}
}
int main(){
string test(3, '0');
PrintFrom1ToN(test, 0);
return 0;
}
7.把数组排成最小的数
题目:
输入一个正整数数组,将它们连接起来排成一个数,输出能排出的所有数字中最小的一个。例如输入数组{32, 321},则输出这两个能排成的最小数字32132;
思路:
对于由数组元素连接起来的最小数字来说:对任意的ab > ba,则在最小数字中b出现在a之前; 对任意的ab < bc,则在最小数字中a出现在b之前。
我们利用上述理论,可以对数组进行排序,并把数组中的整数连接。比如,若对于任意的b,有ab > ba,则在最小数字中a肯定排最后;同理,若对于任意的b,有ab < ba,则在最下数字中a肯定排最前;
证明(反证法):
存在ab > ba,同时在最小数字中a出现在b之前。
最小数字的形式共有三种情况:
1. aby
2. yab
3. ayb
显然情况1和情况2与题设存在矛盾。下面分析情况3:
易得下列两个推论:
1. ay < ya (1)
2. yb < by (2)
假设a, y, b的位数分别时m, i, n :
由(1)得,
(3)
由(2)得,
(4)
分析(3), (4)易知,通过y联立两条不等式,由
等价于 ,易知与题设矛盾。
实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<sstream>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
// 好好理解cmp得逻辑
bool cmp(string &a, string &b){
string ab = a + b;
string ba = b + a;
return ab>ba ? true : false;
}
template<typename T>
string toString(const T& t){
ostringstream oss;
oss<<t;
return oss.str();
}
string getMinConnect(int arr[], int len){
string *arrStr = new string[len];
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
arrStr[i] = toString(arr[i]);
sort(arrStr, arrStr+len, cmp);
string result = "";
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
result += arrStr[i];
delete[] arrStr;
return result;
}
int main(){
int test[] = {12, 78, 56, 34};
cout<<getMinConnect(test, 4)<<endl;
return 0;
}8.Happy Number
题目:
Write an algorithm to determine if a number is “happy”.
A happy number is a number defined by the following process: Starting with any positive integer, replace the number by the sum of the squares of its digits, and repeat the process until the number equals 1 (where it will stay), or it loops endlessly in a cycle which does not include 1. Those numbers for which this process ends in 1 are happy numbers.
Example: 19 is a happy number
思路:
首先任何数经过这种运算最后都会形成一个环。而1是一个奇异点,自己返回自己。
我们可以利用判断一个链表是否有环的方式。若进入了1的环,则快指针和慢指针都是1。
实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int nextNum(int n) {
int sum = 0;
while(n != 0) {
int remain = n % 10;
sum += remain*remain;
n = n / 10;
}
return sum;
}
bool isHappyNumber(int n) {
// 回忆判断链表是否有环的算法
int slow = n;
int fast = n;
do {
slow = nextNum(slow);
fast = nextNum(nextNum(fast));
}while(slow!=fast);
return slow == 1;
}
int main() {
cout<<isHappyNumber(19)<<endl;
cout<<isHappyNumber(11)<<endl;
return 0;
}9.Factorial Trailing Zeroes
题目:
Given an integer n, return the number of trailing zeroes in n!.
Note: Your solution should be in logarithmic time complexity.
思路:
考虑n!的质数因子。后缀0总是由质因子2和质因子5相乘得来的。如果我们可以计数2和5的个数,问题就解决了。我们很容易观察到质因子中2的个数总是大于等于5的个数。因此只要计数5的个数就可以了。那么怎样计算n!的质因子中所有5的个数呢?
已知:对于阶乘而言,也就是1*2*3*…*n。[n/k]代表1~n中能被k整除的个数
n/5代表能被5整除的个数,需要加上n/25,因为一些数不仅能被5整除,还能被25整除,若能被25整除是有2个因子,所以加上n/25是一种校正。
所以,结果为
实现:
int trailingZeroes(int n) {
int ret = 0;
while(n) {
ret += n/5;
n = n/5;
}
return ret;
}其他
1.圆形是否与正方形相交
思路:
注意浮点数如何比较大小(1e-6)
实现:
struct Coordinate{
double x;
double y;
};
struct Circle{
// c为圆心
Coordinate c;
double r;
};
struct Square{
// 正方形的四个结点
Coordinate *nodes;
int n;
};
double HyperDistance(Coordinate n1, Coordinate n2){
return (n1.x-n2.x)*(n1.x-n2.x)+(n1.y-n2.y)*(n1.y-n2.y);
}
bool interset(Circle c, Square s){
for(int i=0;i<s.n;i++){
diff = c.r*c.r-HyperDistance(c.c, s.nodes[i]);
// 判断diff是否等于0
if(abs(diff)<1e-6)
return true;
// 判断diff是否大于0
else if(diff > 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
}
2.快速算底数a的n次幂 O(logn)
题目:
实现函数int Qpow(int a,int n)
思路:
递归思路:
- 若n为偶数
- 若n为奇数
迭代思路:
若 ,则 ,不影响乘积结果,所以我们只需考虑 的部分。
注意:
关于取模的问题(防止结果溢出+防止中间结果过大)
实现:
// 递归实现
int Qpow(int a, int n){
if(n==0) return 1;
int tmp = Qpow(a, n/2);
return (n%2==0 ? 1 : a)*tmp*tmp;
}// 迭代实现
int Qpow(int a, int n){
int result = 1;
int base = a;
while(n!=0){
if(n%2==1) result *= base;
base *= base;
n /= 2;
}
return result;
}// 位运算+迭代实现
int Qpow(int a, int n){
int result = 1;
int base = a;
while(n!=0){
if(n&1==1) result *= base;
base *= base;
n >>= 1;
}
return result;
}
3.斐波拉契数列
题目:
0 0
1 1
2 1
3 2
思路:
递归思路:
特别简单,但时间复杂度非常大为
,空间复杂度为
。看下图就十分明了:
迭代思路:
时间复杂度为
,空间复杂度为
。
最优算法思路(矩阵快速幂):
时间复杂度为
,空间复杂度为
。
实现:
// 递归 O(2^n)
int Fibonacci(int n){
if(n==0) return 0;
if(n==1) return 1;
return Fibonacci(n-1)+Fibonacci(n-2)
}// 非递归
int Fibonacci(int n){
if(n==0) return 0;
if(n==1) return 1;
int fa = 0;
int fb = 1;
int fc = 0;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
fc = fb + fa;
fa = fb;
fb = fc;
}
return fc;
}// 最优算法
typedef vector<vector<int> > mat;
typedef long long LL;
// 用于模运算,防止结果溢出
const int M = 1e4;
mat A(2,vector<int>(2));
A[0][0] = 1;
A[0][1] = 1;
A[1][0] = 1;
A[1][1] = 0;
// 矩阵乘法
mat mul(mat &A, mat &B){
// 初始化: 长度+元素
mat C(A.size(), vector<int>(B[0].size()))
// (A.size() x B.size())*(B.size() x B[0].size()) = (A.size() x B[0].size())
for(int i=0;i<A.size();i++)
for(int j=0;j<B[0].size();j++)
for(int k=0;k<B.size();k++)
C[i][j] += (a[i][k] * a[k][j]) % M;
return C;
}
mat pow(mat A, LL n){
mat R(A.size(), vector<int>(A.size()));
// base = A
// R需要先设为单位矩阵,R默认为0矩阵
for(int i = 0; i < R.size(); i++)
R[i][i] = 1;
// R=mul(R, base); base = mul(base, base)会更好理解
while(n!=0){
if (n/2==1) R = mul(R, A)
A = mul(A, A);
n >>= 1;
}
return R;
}4.求解圆圈中最后剩下的数字
题目:
将 0,1,2….n-1 一共n个数字排成一个圆圈。从数字0开始每次从这个圆圈里面删除第m个数字( 1 =< m <= n, 比如第1个数字为0)。求出这个圆圈里面最后剩下的那个数字。
思路:
remain(n, m)指的是0, 1, …, n按照题目规则,从0开始,一直删除第m个数字,最后剩下的数字。
remain(n-1, m)指的是0, 1, …, n-1按照题目规则,从0开始,一直删除第m个数字,最后剩下的数字。
有以下递推规律:
remain(n, m) = (remain(n-1, m) + m)%n
举例: n = 4 m = 2
从数列的第一个数字开始抽
0, 1, 2, 3 -> 2, 3, 0 <=> 2+2 , 0+2, 1+2 <=> 0, 1, 2 +2
实现:
// 递归
int remain(int n, int m){
if(n==1) return 0;
return (remain(n-1, m)+m)%n;
}// 迭代
int remain(int n, int m){
int result = 0;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
result = (result + m) % i
}
return result;
}5.跳台阶问题
题目:
一个台阶总共有n级,如果一次可以跳1级,也可以跳2级。求总共有 多少总跳法?
思路:
本质就是个斐波拉契数列
Count(n) = Count(n-1) + Count(n-2)
Count(1) = 1
Count(2) = 2
实现和算法复杂度分析见斐波拉契数列
6.从1到n的正数中1出现的次数
题目:
输入一个整数n,求从1到n这n个整数的十进制表示中1出现的次数。
例子:
输入12,则从1到12这些整数中包含1的数字有1,10,11和12。因此,1一共出现5次(注意:11中1出现了2次)
思路:
- 首先求1到n这n个整数的十进制表示中1出现的次数可分为统计:个位中出现1的次数+十位中出现1的次数+百位中出现1的次数+…
- 我们考虑第i位,数字可以分成top-target-tail三部分,例如考虑数字n=121056
i = 2 -> top = 1210; target = 5; tail = 6
i = 3 -> top = 121; target = 0; tail = 56
i = 4 -> top = 12; target = 1; tail = 056 = 56
我们进行分类讨论:
- 当target > 1时,出现1的次数为
- 当target = 1时,出现1的次数为 ,其中err指的是与target>1时相比不存在的可能,易得
- 当target = 1时,出现1的次数为 ,其中err指的是与target>1时相比不存在的可能,易得
实现:
int countForOne(int num){
int count = 0;
int base = 10;
int top = -1;
while(top!=0){
top = num / base;
int tail = num % (base/10);
int target = num % base / (base/10);
int err;
if(target == 0)
err = base/10;
else if(target == 1)
err = base/10 -(tail+1);
else
err = 0;
count += (top+1) * (base/10) - err;
base *= 10;
}
return count;
}
时间复杂度:
O(logn)
7.对于一个整数矩阵,存在一种运算,对矩阵中任意元素加一时,需要其相邻(上下左右),某一个元素也加一,现给出一正数矩阵,判断其是否能够由一个全零矩阵经过上述运算得到。
思路:
下面给出充要条件:条件1 & 条件2
条件1:二维坐标和为奇数的元素和与坐标和为偶数的元素和是否相等
条件2:任一元素必须小于等于其相邻元素(上下左右)之和
思考:
条件2保证能量的守恒,条件1保证能量的传递规则
实现:
bool isValidated(int **matrix, int m, int n){
int oddSum = 0;
int evenSum = 0;
// 条件1:二维坐标和为奇数的元素和与坐标和为偶数的元素和是否相等
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if((i+j) % 2 == 0){
evenSum += matrix[i][j];
}
else{
oddSum += matrix[i][j];
}
}
}
if(oddSum!=evenSum) return false;
// 条件2:任一元素必须小于等于其相邻元素(上下左右)之和
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
int left = j-1>=0 ? matrix[i][j-1] : 0;
int right = j+1<=n ? matrix[i][j+1] : 0;
int up = i-1>=0 ? matrix[i-1][j] : 0;
int down = i+1<=m ? matrix[i+1][j] : 0;
if(left + right + up + down < matrix[i][j]) return false;
}
}
return true;
}8.大数加法&大数乘法
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
string num2string(int x){
switch(x){
case 0: return "0";
case 1: return "1";
case 2: return "2";
case 3: return "3";
case 4: return "4";
case 5: return "5";
case 6: return "6";
case 7: return "7";
case 8: return "8";
case 9: return "9";
}
}
string MultiplyHelper(string a, char c){
int len = a.length();
int mulIn = 0;
string result = "";
for(int i=len-1;i>=0;i--){
int tmp = (c-'0')*(a[i]-'0') + mulIn;
mulIn = tmp / 10;
result = num2string(tmp%10) + result;
}
if(mulIn>0) result = num2string(mulIn) + result;
return result;
}
//大数加法
string Add(string a, string b){
int len1 = a.length();
int len2 = b.length();
int len = len1 > len2 ? len1 : len2;
int i = 0;
int addIn = 0;
string result = "";
while(i<=len-1){
int add1 = i>len1-1? 0 : a[len1-1-i]-'0';
int add2 = i>len2-1? 0 : b[len2-1-i]-'0';
int tmp = add1 + add2 + addIn;
addIn = tmp / 10;
result = num2string(tmp % 10) + result;
i++;
}
if(addIn>0) result = num2string(addIn) + result;
return result;
}
// 大数乘法
string Multiply(string a, string b){
int len2 = b.length();
string result = MultiplyHelper(a, b[len2-1]);
string zeros = "0";
for(int j=1;j<len2;j++){
result = Add(MultiplyHelper(a, b[len2-1-j]) + zeros, result);
zeros = zeros + "0";
}
return result;
}
int main(){
cout<<Multiply("99", "999")<<endl;
cout<<Add("12", "99")<<endl;
cout<<Add("98", "1")<<endl;
cout<<Add("1", "99")<<endl;
return 0;
}
9.判断扑克牌是否是顺子
题目:
从扑克牌中随机抽5张牌,判断是不是一个顺子,即这5张牌是不是连续的。2-10为数字本身,A为1,J为11,Q为12,K为13,而大小王可以看成任意数字。
思路:
首先应该对该问题做数据抽象,5张普通牌可以用数字代替,大小王是特殊牌,我们可以用 0 代替。将大小王和普通牌分离。
检查是否是顺子:
首先应该进行排序,然后统计 0 的个数, 最后统计相邻数字之间的间隔个数。
如果 0 的次数 大于等于 间隔的次数,则是顺子,否则不是顺子。另外,如果出现非0外的相同的数,即对子,则不是顺子。
实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool IsContinue(int pokers[], int num){
sort(pokers, pokers+num);
int trace = 0;
while(pokers[trace] == 0) trace++;
int count = trace;
for(int i=trace+1;i<num;i++){
// 注意这里是pokers[i] - pokers[i-1] - 1
int diff = pokers[i] - pokers[i-1] - 1;
// 注意diff不可以小于0
if(diff<0) return false;
count -= diff;
if(count<0) return false;
}
return true;
}
int main(){
const int len = 5;
int nums1[] = {1,4,5,0,0};
int nums2[] = {1,3,4,5,0};
int nums3[] = {1,3,4,4,0};
int nums4[] = {1,3,4,6,0};
cout<<IsContinue(nums1, len)<<endl;
cout<<IsContinue(nums2, len)<<endl;
cout<<IsContinue(nums3, len)<<endl;
cout<<IsContinue(nums4, len)<<endl;
return 0;
} 10.把n个骰子扔在地上,所有骰子朝上一面的点数之和为S。输入n,打印出S的所有可能的值出现的概率
实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
void PrintQueueAndProbility(queue<int> &q){
int count = q.size();
// 用map来去重 result->first为点数总和,result->second为该点数出现的次数
map<int, int> result;
while(!q.empty()){
result[q.front()]++;
q.pop();
}
map<int, int>::iterator iter;
iter = result.begin();
while(iter != result.end()){
cout<<iter->first<<" : "<<float(iter->second)/count<<endl;
iter++;
}
}
void PrintResult(int level, queue<int> &q){
if(level==0){
PrintQueueAndProbility(q);
return;
}
int size = q.size();
// 注意这样写会有问题,for(int i=0;i<q.size();i++) 因为q.size()会更新
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
int tmp = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int j=1;j<=6;j++){
q.push(tmp+j);
}
}
PrintResult(level-1, q);
}
void PrintAllResult(int level){
queue<int> q;
q.push(0);
PrintResult(level, q);
}
int main(){
PrintAllResult(10);
return 0;
} 11.找出数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
题目:
已知数组中有一个数字出现的次数超过数组长度的一半,请找出这个数字。
例如:
输入一个长度为9的数组{1,2,3,2,2,2,5,4,2}。由于数字2在数组中出现了5次,超过数组长度的一半,因此输出2。
注意:
题目是已经知道存在这样一个数字,如{1, 2, 3}中不存在这样一个数,所以输出结果并具有任何意义。
思路:
- 最先想到的,遍历数组,利用hashmap记录每个数字以及数字出现的次数。时间复杂度为O(N)
- 数组排序,然后中间值肯定是要查找的值。 排序最小的时间复杂度(快速排序)O(NlogN),加上遍历。
- 给数组进行配对,配对到最后得到就是所需结果。这个方法的时间复杂度是O(N),空间复杂度是O(1)。
如{1,2,3,2,2,2,5,4,2}有{1,2}/{3,2}/{2,2,5,4}/{2}
如{1,3,2,2,2,2,5,4,2}有{1,3,2,2}/{2,2,5,4}/{2}
如{1,3,5,2,2,2,2,4,2}有{1,3}/{5,2}/{2,2,2,4,2}
实现:
//思路3
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int getMajor(int arr[], int n){
int cnt = 0;
int pair;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(cnt == 0){
pair = arr[i];
cnt++;
}
else if(arr[i]==pair){
cnt++;
}
else{
cnt--;
}
}
}
int main(){
int test1[] = {1,2,3,2,2,2,5,4,2};
cout<<getMajor(test1, sizeof(test1)/sizeof(int))<<endl;
int test2[] = {1,2,3};
cout<<getMajor(test2, sizeof(test2)/sizeof(int))<<endl;
}12.在数组里查找这样的数,它大于等于左侧所有数,小于等于右侧所有数
题目:
一个int数组, 比如 array[],里面数据无任何限制,要求求出所有这样的数array[i],其左边的数都小于等于它,右边的数都大于等于它。能否只用一个额外数组和少量其它空间实现。
思路:
思路1:
把原数组arr1进行排序得到一个新的数组arr2,然后看arr1和arr2中那些对应的元素是相等的,若相等则就是所求。
思路2:
用两个数组h1、h2。h1[i]、h2[i]分别保存从前到i的最大的数和从后到i的最小的数,这需要两次遍历,然后再遍历一次原数组,将所有data[i]>=h1[i-1]&&data[i]<=h2[i+1]的data[i]找出即可。(用了两个辅佐数组)
思路3:
思路2的变体,只用了一个辅佐数组
思路4:
看代码吧
实现:
// 思路1 有误
// 思路1的判断方法只是 满足题设情况下的充分不必要条件,如{2, 4, 3, 5, 1}
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
void FindDividedPoint(int arr[], int n){
int* carr = new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
carr[i] = arr[i];
sort(carr, carr+n);
cout<<"All points: "<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(carr[i] == arr[i])
cout<<arr[i]<<endl;
}
delete []carr;
}
int main(){
int arr[] = {4, 5, 3, 2, 1};
FindDividedPoint(arr, 5);
return 0;
}// 思路2
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void FindDividedPoint(int arr[], int n) {
int *h1 = new int[n];
int max1 = arr[0];
h1[0] = max1;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++) {
if(arr[i]>max1) {
max1 = arr[i];
}
h1[i] = max1;
}
int *h2 = new int[n];
int min2 = arr[n-1];
h2[n-1] = min2;
for(int i=n-2;i>=0;i--) {
if(arr[i]<min2) {
min2 = arr[i];
}
h2[i] = min2;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
if(i==0 || arr[i]>=h1[i-1]){
if(i==n-1 || arr[i]<h2[i+1]){
cout<<arr[i]<<endl;
}
}
}
delete []h1;
delete []h2;
}
int main(){
int arr[] = {2, 1, 3, 5, 4};
FindDividedPoint(arr, 5);
return 0;
}#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void FindDividedPoint(int arr[], int n) {
int *tmp = new int[n];
int max = arr[0];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
if(arr[i]>max) {
max = arr[i];
}
tmp[i] = max;
}
int min = arr[n-1];
for(int j=n-1;j>=0;j--) {
if(j==n-1 || arr[j]<min) {
if(j==0 || arr[j]>=tmp[j-1]) {
cout<<arr[j]<<endl;
}
}
if(arr[j]<min) {
min = arr[j];
}
}
delete []tmp;
}
int main(){
int arr[] = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
FindDividedPoint(arr, 5);
return 0;
}// 思路4
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void FindDividedPoint(int arr[], int n) {
int *tmp = new int[n];
int count = 0;
tmp[count++] = arr[0];
int max = arr[0];
for(int i=1;i<n;i++) {
// i==n-1时要特殊考虑
if(arr[i]>max || (i==n-1 && arr[i]==max)) {
tmp[count++] = arr[i];
max = arr[i];
}
else {
// arr[i]>max时,必有tmp中的元素小于arr[i]
while(count > 0 && tmp[count-1] >= arr[i])
count--;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<count;i++) {
cout<<tmp[i]<<endl;
}
delete []tmp;
}
int main(){
int arr[] = {5, 5, 5, 5, 5};
FindDividedPoint(arr, 5);
return 0;
}13.Set Matrix Zeroes
题目:
Given a m x n matrix, if an element is 0, set its entire row and column to 0. Do it in place.
Did you use extra space?
A straight forward solution using O(mn) space is probably a bad idea.
A simple improvement uses O(m + n) space, but still not the best solution.
Could you devise a constant space solution?
思路
实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void setZeros(vector<vector<int> > &matrix) {
bool r0 = false;
bool c0 = false;
int rLen = matrix.size();
int cLen = matrix[0].size();
cout<<rLen<<" "<<cLen<<endl;
for(int j=0;j<cLen;j++) {
if(matrix[0][j]==0) {
r0 = true;
break;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<rLen;i++) {
if(matrix[i][0]==0) {
c0 = true;
break;
}
}
for(int j=1;j<cLen;j++) {
for(int i=1;i<rLen;i++) {
if(matrix[i][j]==0) {
matrix[0][j] = 0;
matrix[i][0] = 0;
}
}
}
for(int i=1;i<rLen;i++) {
if(matrix[i][0]==0) {
for(int j=1;j<cLen;j++)
matrix[i][j] = 0;
}
}
for(int j=1;j<cLen;j++) {
if(matrix[0][j]==0) {
for(int i=1;i<rLen;i++)
matrix[i][j] = 0;
}
}
if(r0) {
for(int j=0;j<cLen;j++)
matrix[0][j] = 0;
}
if(c0) {
for(int i=0;i<rLen;i++)
matrix[i][0] = 0;
}
}
int main() {
int args[][4] = {{1, 0, 1, 1}, {2, 3, 4, 0}, {1, 1, 1, 1}};
vector<vector<int> > wA(3, vector<int>(4));
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
for(int j=0;j<4;j++)
wA[i][j] = args[i][j];
setZeros(wA);
for(int i=0;i<3;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<4;j++) {
cout<<wA[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
高精度
博弈论
概率
其他
子数组
二进制
1.整数的二进制表示中1的个数
题目:输入一个整数,求该整数的二进制表达中有多少个1
例如输入10,由于其二进制表示为1010,有两个1,因此输出2。
思路:
xxxxx10000 & (xxxxx10000-1) = xxxxx00000
看需要多少次这样的操作,把所有的1都消调
实现:
int countOf1(int n){
int count = 0;
while(n!=0){
n &= (n-1);
count++;
}
return count;
}
两根指针
1.在有序数组查找和为dest的两个数
题目:
输入一个已经按升序排序过的数组和一个数字, 在数组中查找两个数,使得它们的和正好是输入的那个数字。要求时间复杂度为O(n)。如果有多对数字的和等于输入的数字,输出任意一对即可。
例如:1, 2, 4, 7, 11, 15; dest: 15
输出:4和11
思路:
首尾各2根指针,若和大于dest,则尾指针–;若和小于dest,则首指针++;
实现:
void find2Numbers(int a[], int n, int dest){
int *head = a, *tail = a+n-1;
while(head!=tail){
int sum = *head + *tail;
if(sum == dest){
cout<<*head<<' '<<*tail<<endl;
return;
}
else if(sum > dest)
tail--;
else
head++;
}
cout<<"No such two numbers!"<<endl;
return;
}2.输入一个正数 n,输出所有和为 n 连续正数序列
题目:
输入一个正数 n,输出所有和为 n 连续正数序列
例如输入 15,由于 1+2+3+4+5=4+5+6=7+8=15,所以输出 3 个连续序列 1-5、4-6 和 7-8。
思路:
我们用两个数head和tail分别表示序列的最小值和最大值。首先把small初始化为 1,big初始化为 2。
- 从head到tail的序列的和大于等于n的话,我们向右移动head。
- 从head到tail的序列的和小于n的话,我们向右移动tail。
实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void findSequence(int n){
// 根据题设可知sequence的长度至少为2
int head = 1;
int tail = 2;
int sum = head + tail;
while(head+tail<=n){
if(sum>=n){
if(sum==n) cout<<head<<"-"<<tail<<endl;
sum -= head++;
}
else{
sum += ++tail;
}
}
}
int main(){
findSequence(100);
return 0;
}3.调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
题目:
输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有的奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有的偶数位于位于数组的后半部分,并保证奇数和奇数,偶数和偶数之间的相对位置不变。
思路:
难点在于保持相对位置不变,且不借助另外的空间。
实现:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void oddBeforeEven(int arr[], int n){
int odd = 0;
int even = 0;
while(odd<n && arr[odd] % 2 != 1) odd++;
while(even<n && arr[even] % 2 != 0) even++;
while(odd!=n && even!=n){
if(odd>even){
// 为了保证偶数部分保持原序
int tmp = arr[even];
arr[even] = arr[odd];
int next=odd;
for(int t=odd-1;t>even;t--){
if(arr[t] % 2 ==0){
arr[next] = arr[t];
next = t;
}
}
arr[next] = tmp;
while(even<n && arr[even] % 2 != 0) even++;
while(odd<n && arr[odd] % 2 != 1) odd++;
}
else{
odd++;
while(odd<n && arr[odd] % 2 != 1) odd++;
}
}
}
int main(){
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
oddBeforeEven(arr, 6);
for(int i=0;i<6;i++)
cout<<arr[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}4.函数将字符串中的字符’*’移到串的前部分
题目:
函数将字符串中的字符’*’移到串的前部分,前面的非’*’字符后移,但不能改变非’*’字符的先后顺序,函数返回串中字符’*’的数量。如原始串为:ab**cd**e*12,处理后为*****abcde12,函数并返回值为5。(要求使用尽量少的时间和辅助空间)
思路:
从后往前遍历,先找到一个*的位置star,然后在star的前方寻找非*的字符的位置,然后进行交换。
实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void starFirst(string &src){
int star = src.length()-1;
while(1){
while(star>=0 && src[star]!='*')
star--;
int i = star;
while(i>=0 && src[i]=='*')
i--;
if(i<0 || star<0)
break;
else{
char tmp = src[star];
src[star] = src[i];
src[i] = tmp;
}
}
}
int main(){
string s1 = "123456";
string s2 = "******";
string s3 = "";
string s4 = "ab**cd**e*12";
starFirst(s1);
starFirst(s2);
starFirst(s3);
starFirst(s4);
cout<<s1<<endl;
cout<<s2<<endl;
cout<<s3<<endl;
cout<<s4<<endl;
return 0;
}
前后遍历
1.Sort Colors
题目:
Given an array with n objects colored red, white or blue, sort them so that objects of the same color are adjacent, with the colors in the order red, white and blue.
Here, we will use the integers 0, 1, and 2 to represent the color red, white, and blue respectively.
要求:一次遍历
思路:
l记录第一个1的位置, r记录最后一个1的位置。
实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void sortColors(int arr[], int len) {
int l = 0;
int r = len-1;
int i = 0;
while(i<=r) {
if(arr[i]==0) {
int tmp = arr[l];
arr[l] = arr[i];
arr[i] = tmp;
l++;
i++;
}
else if(arr[i]==1) {
i++;
}
else if(arr[i]==2) {
int tmp = arr[r];
arr[r] = arr[i];
arr[i] = tmp;
r--;
}
}
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2};
int len = 6;
sortColors(arr, len);
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
cout<<arr[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}贪心算法
1.蜂窝结构的图,进行搜索最短路径
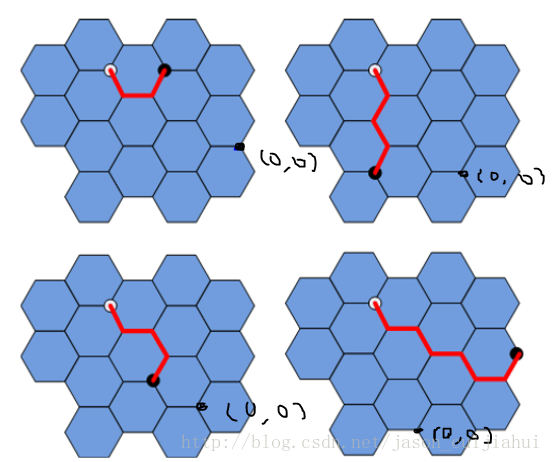
题目:
注意坐标原点的选择,只选择含原点的六边形的边与x轴的负方向重合的点为坐标原点(0, 0)
思路:
分情况讨论
1. 水平方向尽量走水平方向去靠近目的地
2. 垂直方向尽量走垂直方向去靠近目的地
点的坐标可以表示为
实现:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//
struct Point{
int x1;
int x2;
int y;
};
int abs(int x){
return x>=0? x : -x;
}
void printPoint(Point x){
cout<<"Location: ("<<x.x1<<", "<<x.x2<<"| "<<x.y<<")"<<endl;
}
// abs(x1-x2) % 2 == 1 x1:+1 x2:+-1
// abs(x1-x2) % 2 == 0 x1:-1 x2:+-1
// a->b
void CellPath(Point a, Point b){
int lenx1 = b.x1-a.x1;
int lenx2 = b.x2-a.x2;
int leny = b.y-a.y;
Point tmp = a;
printPoint(tmp);
while(lenx1!=0 || lenx2!=0 || leny!=0 ){
bool dirx1 = abs(tmp.x1-tmp.x2)%2 == 1;
if(lenx1>0 && dirx1){
cout<<"Instruction: x1 +1"<<endl;
lenx1--;
tmp.x1++;
}
else if(lenx1<0 && !dirx1){
cout<<"Instruction: x1 -1"<<endl;
lenx1++;
tmp.x1--;
}
else if(leny>0 && dirx1){
cout<<"Instruction: y +1; x2 -1"<<endl;
leny--;
lenx2++;
tmp.y++;
tmp.x2--;
}
else if(leny>0 && !dirx1){
cout<<"Instruction: y +1; x2 +1"<<endl;
leny--;
lenx2--;
tmp.y++;
tmp.x2++;
}
else if(leny<=0 && dirx1){
cout<<"Instruction: y -1; x2 -1"<<endl;
leny++;
lenx2++;
tmp.y--;
tmp.x2--;
}
else if(leny<=0 && !dirx1){
cout<<"Instruction: y -1; x2 +1"<<endl;
leny++;
lenx2--;
tmp.y--;
tmp.x2++;
}
printPoint(tmp);
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
Point a;
a.x1=0;
a.x2=1;
a.y=1;
Point b;
b.x1=-3;
b.x2=-3;
b.y=3;
CellPath(a,b);
return 0;
}排序算法
枚举法
基本实现
1.1+2+3+…+n不能用while、for、if等实现(这年头什么鬼题目都有)
题目:
求1+2+…+n,要求不能使用乘除法、for、while、if、else、switch、case等关键字以及条件判断语句(A?B:C)
实现:
// 递归
int sum(int n){
int tmp = 1;
// 当n==1时,tmp = sum(n-1)+n不会执行,跳到return tmp;
// 当n!=1是,tmp = sum(n-1)+n会执行;
(n!=1)&&(tmp = sum(n-1)+n);
return tmp;
}// 利用类的静态变量和静态函数
class Intern(){
public:
Intern(){
i++;
sum += i;
}
static void Reset(){
i = 0;
sum = 0;
}
static int getSum(){
return sum;
}
private:
static int i;
static int sum;
};
int Sum1toN(int n){
Intern::Reset();
Intern *tmp = new Intern[100];
delete []tmp;
return Intern::getSum();
}
// 这个待理解和梳理
// 利用模板元编程
template<int N>
struct add{
enum {result = N + add<N-1>::result};
};
template<>
struct add<0>
{
enum {result=0};
}; // 这个待理解和梳理
// 宏
// 如果Y&(1<<i)得到非0,则计算X+=(Y<<i)
#define T(X, Y, i) (Y & (1<<i)) && X+=(Y<<i)
int Sum1toN(int n){
int r = 0;
// 32位int整型,符号位为0所以不用担心
for(int i=0; i < 32; i++)
T(r, n, i);
// 得到的r等于n*(n+1)
// 结合公式n*(n+1)/2
return r>>1比特位操作
1.找出数组中两个只出现一次的数字
题目:
一个整型数组里除了两个数字之外,其它的数字都出现了两次。请写程序找出这个只出现一次的数字。要求时间复杂度是O(n),空间复杂度是O(1)。
思路:
难点在于:
1. 空间复杂度为O(1),所以利用异或运算
2. 两个数字,利用汇总异或结果的最低位1,把原数组分成两组,两个数字分别位于两组。
实现
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
bool isThisBit(int num, int bitNum){
return num & bitNum == bitNum;
}
// 求最低为1
int getFirstBit(int num){
return num & ~(num-1);
}
void FindNumsOnce(int data[], int length, int &num1, int &num2){
if(length<2) return;
int resultXOR = 0;
for(int i=0;i<length;i++)
resultXOR ^= data[i];
int bitNum = getFirstBit(resultXOR);
num1 = num2 = 0;
for(int i=0;i<length;i++){
if(isThisBit(data[i], bitNum))
num1 ^= data[i];
else
num2 ^= data[i];
}
}
int main(){
int arr[] = {100, 100, 30, 1, 30, 2};
int num1, num2;
FindNumsOnce(arr, 6, num1, num2);
cout<<num1<<"&"<<num2<<endl;
}2.Sum of Two Integers
题目:
Calculate the sum of two integers a and b, but you are not allowed to use the operator + and -.
Example:
Given a = 1 and b = 2, return 3.
实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int getSum(int a, int b) {
if(b==0) return a;
int p1 = a ^ b;
int p2 = (a & b) << 1;
return getSum(p1, p2);
}
int main() {
cout<<getSum(11, 89)<<endl;
return 0;
}字符串处理
1.写一个函数,它的原型是string continumax(string outputstring)
题目:在字符串中找到连续最长的数字串
实现:
// c++实现
string continumax(string inputstring){
int maxindex = 0;
int maxlen = 0;
int len = 0;
int index =0;
for(int i=0;i<inputstring.length();i++){
if(inputstring[i]<='9' & inputstring[i]>='0'){
len++;
if(i == inputstring.length()-1){
if(len>maxlen){
maxlen = len;
maxindex = index;
}
}
}else{
if(len>maxlen){
maxlen = len;
maxindex = index;
}
index = i+1;
len = 0;
}
}
if(maxlen == 0)
return "";
else
return inputstring.substr(maxindex, maxlen);
}2.数字字符串转化为整数
题目:
输入一个表示整数的字符串,把该字符串转换成整数并输出。
实现:
int intstring2int(string input){
int result = 0;
for(int i=0;i<input.length();i++){
result *= 10
result += input[i]-'0';
}
return result;
}3.在一个字符串中找到第一个只出现一次的字符
题目:
在一个字符串中找到第一个只出现一次的字符。如输入abaccdeff,则输出b。
实现:
char findSingle(string input){
int hashtable[255] = {0};
// 第一次扫描,统计每个字符出现的次数
for(int i=0;i<input.length();i++)
hashtable[input[i]]++;
// 第二次扫描,找出第一个只出现一次的字符
for(int i=0;i<input.length();i++)
if(hashtable[input[i]]==1) return input[i];
return '';
}4.翻转句子中的单词顺序
题目:
“I am a student.” -> “student. a am I”
要求空间复杂度O(1),时间复杂度O(n)
思路:
压栈出栈那套做不到空间复杂度O(1)
是这样的,先把原句子翻转,然后遇到每个单词再翻转(负负得正),但是要对字符串扫描2次。
实现:
void swapWord(string &word, int i, int j){
// 那些越不越界什么的,我就不搞了
while(i<j){
char tmp = word[i];
word[i] = word[j];
word[j] = tmp;
i++;
j--;
}
}
int swapSentence(string &s){
swapWord(s, 0, s.length()-1);
int j=0;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
if(s[i] == ' '){
swapWord(s, j, i-1);
j = i + 1;
}
}
}5.最长串接字符串
题目:
有n个长为m+1的字符串,如果某个字符串的最后m个字符与某个字符串的前m个字符匹配,则两个字符串可以联接,问这n个字符串最多可以连成一个多长的字符串,如果出现循环,则返回错误。
思路:
分析一下,将各个字符串作为一个节点,首尾链接就好比是一条边,将两个节点连接起来,于是问题就变成一个有关图的路径长度的问题。链接所得的字符串最长长度即为从图的某个节点出发所能得到的最长路径问题,与最短路径类似,可以应用弗洛伊德算法求解。对于循环,即可认为各个节点通过其他节点又回到自己,反应在路径长度上,就表示某个节点到自己节点的路径大于零(注:初始化个节点到自己的长度为零)。
Floyd算法求最长路径的核心思想:
longestPath(i, j, k-1)指的是the best path from i to j that only uses vertices 1 through k-1。
并有如下关系:
longestPath(i, j, k) = max(longest(i, j, k-1), longest(i, k, k-1) + longest(k, j, k-1))
实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
// m = n-1
void generateMatchMatrix(string *stringSet, int n, int **w){
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(i==j){
w[i][j] = 0;
continue;
}
w[i][j] = 1;
for(int k=0;k<n-1;k++){
if(stringSet[j][k]!=stringSet[i][k+1]){
w[i][j] = 0;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
int longestPathLength(int n, int **w){
int max = 0;
for(int k=0;k<n;k++)
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(w[i][k]!=0 && w[k][j]!=0){
int tmp = w[i][k] + w[k][j];
if(tmp > w[i][j])
w[i][j] = tmp;
}
// check if loop exists
if(i == j && w[i][j] > 0) return -1;
// record longest path length
if(w[i][j] > max){
max = w[i][j];
}
}
// max = 0 -> single string
return max + 1;
}算法复杂度:
空间复杂度:
时间复杂度:
其他:
- 比对的时候可能可以用hash值比对,这样的效率会高些。
6.一串首尾相连的珠子(m 个),有 N 种颜色(N<=10),取出其中一段,要求包含所有 N 中颜色,并使长度最短
题目:
一串首尾相连的珠子(m 个),有 N 种颜色(N<=10),
设计一个算法,取出其中一段,要求包含所有 N 中颜色,并使长度最短。
并分析时间复杂度与空间复杂度。
思路:
从前到后进行扫描,head和tail之间刚刚好保证颜色全
然后head向前移动直到颜色不全,此时tail开始向后扫描直到颜色全
在这个过程中一直追踪最短长度
实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int shortestFullcolor(int a[], int m, int n){
int head = 0;
int tail = 0;
int color = n;
int minLen = m;
vector<int> colorCount(n);
while(tail<m){
if(colorCount[a[tail]]==0) color--;
colorCount[a[tail]]++;
if(color==0){
while(colorCount[a[head]]>1){
colorCount[a[head]]--;
head++;
}
if(tail-head+1<minLen)
minLen = tail-head+1;
colorCount[head] = 0; // delete color a[head]
color = 1; // color a[head] is left
head++;
}
tail++;
}
return minLen;
}
int main(){
int a[] = {0, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 0, 1};
// n = 4 means that there are 4 different colors represented by 0, 1, 2, 3
cout<<shortestFullcolor(a, sizeof(a)/sizeof(int), 4)<<endl;
int b[] = {0};
// n = 1 means that there is only 1 color represented by 0
cout<<shortestFullcolor(b, sizeof(b)/sizeof(int), 1)<<endl;
}算法复杂度:
1. 时间复杂度:O(m)
2. 空间复杂度:O(n)
其他:
有n种颜色(N<=10)(这个大小的约束有什么意义?)
7.输入两个字符串,从第一字符串中删除第二个字符串中所有的字符
题目:
输入”They are students.”和”aeiou”,则删除之后的第一个字符串变成”Thy r stdnts.”。
思路:
不可避免的是遍历第一个字符串,如果遍历一个字符,都需要去第二个字符串中查找其存不存在,那么复杂度会是O(nm),当然由于字符数有限,所以m是个常量。关于查找速度最快的当然是hash表,对于8位字符,size=2^8足矣。
关于删除字符,后面的字符要往前移,如果每删除一个就移一次,O(n^2)这复杂度实在太高,仅仅用快慢指针就可以搞定,这个方法非常有用,比如求解循环链表。
初始化:快慢指针指向第一个字符
循环:如果快指针指的是不需要的字符,将值赋给慢指针后,快慢指针同时++;如果快指针指向待删除字符,那么直接++;
终止:快指针指向'\0'实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#define ASCIINUM 256
using namespace std;
bool flag[ASCIINUM];
void DeleteString(char *src, char *deleteSet){
if(src==NULL || deleteSet==NULL) return;
memset(flag, 0, sizeof(flag));
int ls = strlen(src);
int ld = strlen(deleteSet);
for(int i=0;i<ld;i++)
flag[deleteSet[i]] = true;
char *fast = src;
char *slow = src;
while(*fast!='\0'){
if(!flag[*fast]){
*slow = *fast;
slow++;
}
fast++;
}
*slow = '\0';
}
int main(){
char src[] = " They are students.";
char deleteSet[] = "aeiou";
// cout<<sizeof(test1)/sizeof(int)<<endl;
// cout<<strlen(test1)<<endl;
DeleteString(src, deleteSet);
cout<<src<<endl;
}8.查找字符串中的最长回文子串
题目:
“exbbcddcbaxexb”的最长回文子串为”bcddcb”
“abbb”的最长回文子串为”bbb”
思路:
我实现了三种思路
1.动态规划
时间复杂度
, 空间复杂度
代表i到j的子串是否是回文串,有以下关系
2.中心扩展法
时间复杂度
, 空间复杂度
对给定的字符串S,分别以该字符串S中的每一个字符C为中心,向两边扩展,记录下以字符C为中心的回文子串的长度。但是有一点需要注意的是,回文的情况可能是 a b a,也可能是 a b b a。
3.Manacher算法
时间复杂度
, 空间复杂度
其实意思就是再rIndex以内可以节省很多运算,随着rIndex右移,可以涵括很多情况。
另外,有个关于统一”aa”和”aba”两种情况的处理。就是”aa”->”#a#a#”,”aba”->”#a#b#a#”
注意:我的实现中并没有再头部加上”$”
实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
// 方法1: 动态规划
string FindLongestPalindrome1(string src){
int len = src.length();
vector<vector<bool> > record(len, vector<bool>(len));
int index = 0;
int maxLen = 1;
// 初始状态
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
record[i][i] = true;
if(i<len-1 && src[i]==src[i+1]){
record[i][i+1] = true;
index = i;
maxLen = 2;
}
}
// 注意先固定j再对i进行迭代
for(int j=2;j<len;j++){
for(int i=0;i<j-1;i++){
if(src[i] == src[j] && record[i+1][j-1]){
record[i][j] = true;
if(j-i+1>maxLen){
maxLen = j-i+1;
index = i;
}
}
}
}
return src.substr(index, maxLen);
}
// 方法2: 中心扩展法
string Method2Helper(string src, int i, int j){
while(src[i] == src[j]){
i--;
j++;
if(i==-1 || j==src.length())
break;
}
int index = i+1;
int len = (j-1) - (i+1) + 1;
return len>0 ? src.substr(index, len) : "";
}
string FindLongestPalindrome2(string src){
string result = "";
// i为搜索中心
// i为src.length()-1时并不需要考虑
for(int i=0;i<src.length()-1;i++){
string tmp1 = Method2Helper(src, i, i);
string tmp2 = Method2Helper(src, i, i+1);
string candidate = tmp1.length() > tmp2.length() ? tmp1 : tmp2;
if(result.length()<candidate.length()){
result = candidate;
}
}
return result;
}
// 方法3: Manacher算法 复杂度O(N)
string Method3Helper(string src){ //生成扩充字符串
string result;
for(int i=0;i<src.length();i++){
result = result + '#' + src[i];
}
result = result + '#';
return result;
}
int min(int a, int b){
return a>b ? b:a;
}
string Manacher(string src){
string srcExpand = Method3Helper(src);
int len = srcExpand.length();
vector<int> record(len);
int maxIndex = 0;
int maxLen = 0;
int p;
int rIndex = 0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
record[i] = 1;
if(i<rIndex){
record[i] = min(record[2*p-i], rIndex-i);
}
int tmpRIndex = i + record[i];
int tmpLIndex = i - record[i];
while((tmpLIndex > 0 || tmpRIndex < len) && srcExpand[tmpLIndex] == srcExpand[tmpRIndex]){
tmpLIndex--;
tmpRIndex++;
record[i]++;
}
// 追踪最大回文串
if(record[i]>maxLen){
maxIndex = i;
maxLen = record[i];
}
if(i + record[i] - 1 > rIndex){
p = i;
rIndex = i + record[i] - 1;
}
}
string result;
for(int i=maxIndex-maxLen+1;i<=maxIndex+maxLen-1;i++){
if(srcExpand[i]!='#')
result = result + srcExpand[i];
}
return result;
}
int main(){
string test("exbbcddcbaxexb");
cout<<FindLongestPalindrome1(test)<<endl;
cout<<FindLongestPalindrome2(test)<<endl;
cout<<Manacher(test)<<endl;
cout<<endl;
string test1("abbb");
cout<<FindLongestPalindrome1(test1)<<endl;
cout<<FindLongestPalindrome2(test1)<<endl;
cout<<Manacher(test1)<<endl;
return 0;
} 9.删除字符串中的数字并压缩字符串
题目:
删除字符串中的数字并压缩字符串 。 如字符串”abc123de4fg56”处理后变为”abcdefg”。注意空间和效率。
实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void DelDigital(char str[]) {
char* i = str;
char* j = str;
while(*i != '\0') {
if(*i>'9' || *i<'0') {
/*
下面一句等价于
*j = *i;
i++;
j++;
*/
*j++ = *i++;
}
else {
i++;
}
}
*j = '\0';
}
int main(){
char test[] = "3y0e";
cout<<test<<endl;
DelDigital(test);
cout<<test<<endl;
return 0;
} 二分法
1.递减数列左移得到的数组中查找一个数
题目:
一个数组是由一个递减数列左移若干位形成的,比如{4,3,2,1,6,5}
是由{6,5,4,3,2,1}左移两位形成的,在这样的数组中找一个数。
思路:
明白这样的数组的某一半为有序数组可以使用二分查找,最终总能得到有序数组。
黑线为数组的分布,首先区分mid在情况1还是情况2,分别处理即可
实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
bool BinarySearch(int arr[], int len, int key){
int l = 0;
int r = len-1;
while(l<=r){
int mid = l + (r-l) / 2;
if(arr[mid]==key) return true;
else if(arr[mid]>arr[r]){ //情况1
if(key<arr[mid]&&key>=arr[r]) l = mid+1;
else r = mid-1;
}
else{ //情况2
if(key>arr[mid] && key<=arr[l]) r = mid-1;
else l = mid+1;
}
}
return false;
}
int main(){
int arr[] = {4, 3, 2, 1, 6, 5};
cout<<BinarySearch(arr, 6, 5)<<endl;
}2.递减数列左移得到的数组中查找最小值
题目:
数组1 2 3 4 5,经过旋转可以旋转成为 2 3 4 5 1,或者 3 4 5 1 2 或者 1 2 3 4 5 或者 5 1 2 3 4 等等。此时,最小值为1。
说的更复杂点,这其中的数字可以重复,那么数组 0 0 1 1 1 1 就可以旋转成为 1 1 1 0 0 1或者 1 1 1 1 0 等等。此时,最小值为0。
思路:
画图分情况考虑,这里有种情况比较特殊arr[l]==arr[mid]==arr[r]。在此中情况下,不能再用二分法缩小搜索范围,因为此时不能最小值在哪边。
实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int findMinOfAdjustedArray(int arr[], int l, int r){
if(arr[l]<arr[r] || l == r)
return arr[l];
else if(arr[l]>arr[r]){
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if(arr[mid]>=arr[l])
return findMinOfAdjustedArray(arr, mid+1, r);
else
return findMinOfAdjustedArray(arr, l, mid);
}
else{ // arr[l] == arr[r]
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if(arr[mid]>arr[l])
return findMinOfAdjustedArray(arr, mid+1, r);
else if(arr[mid]<arr[l])
return findMinOfAdjustedArray(arr, l, mid);
else{// arr[l] == arr[mid] == arr[r]
int min = arr[l];
for(int k=l;k<=r;k++){
if(arr[k]<min)
min = arr[k];
}
return min;
}
}
}
int main(){
int arr1[] = {3, 4, 5, 1, 2};
cout<<findMinOfAdjustedArray(arr1, 0, 4)<<endl;
int arr2[] = {1, 0, 1, 1, 1};
cout<<findMinOfAdjustedArray(arr2, 0, 4)<<endl;
int arr3[] = {1, 1, 1, 0, 1};
cout<<findMinOfAdjustedArray(arr3, 0, 4)<<endl;
int arr4[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
cout<<findMinOfAdjustedArray(arr4, 0, 4)<<endl;
return 0;
}拓扑排序
有序矩阵
整数
这个迟点再搞
给出一个整型数组,按数字出现频率高低进行排序。比如说[1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 3],变为[2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 1]
假设你已经能求出数组的连续最大和子数组(提供现成函数),现在给出一个整形数组,求找出两个不相交子数组,使得它们的差最大。
理解1:
思路很简单:- 先找出数组的连续最大和字数组
- 然后把数组的元素都取反,再找出变换后连续最大和字数组
- 然后把1,2得到数组中相同的元素去掉即可
理解2:
先从左到右扫一遍,求出从开始到每个位置的最大(最小)和,然后再从右到左扫一遍,求出从后面到每个位置的最大(最小)和,在从右到左扫的时候就可以求出结果了。