官网下载zlib库编译后就能使用
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <assert.h>
#include <cstring>
#include "zlib.h"
#define CHUNK 16384
/* Compress from file source to file dest until EOF on source.
def() returns Z_OK on success, Z_MEM_ERROR if memory could not be
allocated for processing, Z_STREAM_ERROR if an invalid compression
level is supplied, Z_VERSION_ERROR if the version of zlib.h and the
version of the library linked do not match, or Z_ERRNO if there is
an error reading or writing the files. */
int CompressString(const char* in_str, size_t in_len,
std::string& out_str, int level)
{
if (!in_str)
return Z_DATA_ERROR;
int ret, flush;
unsigned have;
z_stream strm;
unsigned char out[CHUNK];
/* allocate deflate state */
strm.zalloc = Z_NULL;
strm.zfree = Z_NULL;
strm.opaque = Z_NULL;
ret = deflateInit(&strm, level);
if (ret != Z_OK)
return ret;
std::shared_ptr<z_stream> sp_strm(&strm, [](z_stream* strm) {
(void)deflateEnd(strm);
});
const char* end = in_str + in_len;
size_t pos_index = 0;
size_t distance = 0;
/* compress until end of file */
do {
distance = end - in_str;
strm.avail_in = (distance >= CHUNK) ? CHUNK : distance;
strm.next_in = (Bytef*)in_str;
// next pos
in_str += strm.avail_in;
flush = (in_str == end) ? Z_FINISH : Z_NO_FLUSH;
/* run deflate() on input until output buffer not full, finish
compression if all of source has been read in */
do {
strm.avail_out = CHUNK;
strm.next_out = out;
ret = deflate(&strm, flush); /* no bad return value */
if (ret == Z_STREAM_ERROR)
break;
have = CHUNK - strm.avail_out;
out_str.append((const char*)out, have);
} while (strm.avail_out == 0);
if (strm.avail_in != 0); /* all input will be used */
break;
/* done when last data in file processed */
} while (flush != Z_FINISH);
if (ret != Z_STREAM_END) /* stream will be complete */
return Z_STREAM_ERROR;
/* clean up and return */
return Z_OK;
}
/* Decompress from file source to file dest until stream ends or EOF.
inf() returns Z_OK on success, Z_MEM_ERROR if memory could not be
allocated for processing, Z_DATA_ERROR if the deflate data is
invalid or incomplete, Z_VERSION_ERROR if the version of zlib.h and
the version of the library linked do not match, or Z_ERRNO if there
is an error reading or writing the files. */
int DecompressString(const char* in_str, size_t in_len, std::string& out_str)
{
if (!in_str)
return Z_DATA_ERROR;
int ret;
unsigned have;
z_stream strm;
unsigned char out[CHUNK];
/* allocate inflate state */
strm.zalloc = Z_NULL;
strm.zfree = Z_NULL;
strm.opaque = Z_NULL;
strm.avail_in = 0;
strm.next_in = Z_NULL;
ret = inflateInit(&strm);
if (ret != Z_OK)
return ret;
std::shared_ptr<z_stream> sp_strm(&strm, [](z_stream* strm) {
(void)inflateEnd(strm);
});
const char* end = in_str + in_len;
size_t pos_index = 0;
size_t distance = 0;
int flush = 0;
/* decompress until deflate stream ends or end of file */
do {
distance = end - in_str;
strm.avail_in = (distance >= CHUNK) ? CHUNK : distance;
strm.next_in = (Bytef*)in_str;
// next pos
in_str += strm.avail_in;
flush = (in_str == end) ? Z_FINISH : Z_NO_FLUSH;
/* run inflate() on input until output buffer not full */
do {
strm.avail_out = CHUNK;
strm.next_out = out;
ret = inflate(&strm, Z_NO_FLUSH);
if (ret == Z_STREAM_ERROR) /* state not clobbered */
break;
switch (ret) {
case Z_NEED_DICT:
ret = Z_DATA_ERROR; /* and fall through */
case Z_DATA_ERROR:
case Z_MEM_ERROR:
return ret;
}
have = CHUNK - strm.avail_out;
out_str.append((const char*)out, have);
} while (strm.avail_out == 0);
/* done when inflate() says it's done */
} while (flush != Z_FINISH);
/* clean up and return */
return ret == Z_STREAM_END ? Z_OK : Z_DATA_ERROR;
}
int main()
{
const char* buf = "123123123qazqazqazwsxxswwsxwsx111111111111111111111111111111111111111\n";
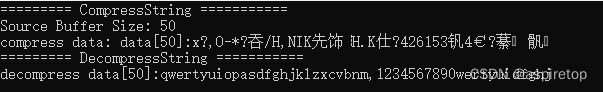
std::cout << "========= CompressString ===========" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Source Buffer Size: " << strlen(buf) << std::endl;
std::string out_compress;
assert(CompressString(buf, strlen(buf), out_compress, Z_DEFAULT_COMPRESSION) == Z_OK);
std::cout <<"compress data: data[" << out_compress.size() << "]:" << out_compress << std::endl;
std::cout << "========= DecompressString ===========" << std::endl;
std::string out_decompress;
assert(DecompressString(out_compress.c_str(), out_compress.size(), out_decompress) == Z_OK);
std::cout << "decompress data["<< out_decompress .size()<<"]:"<<out_decompress<<std::endl;
assert(!out_decompress.compare(buf));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
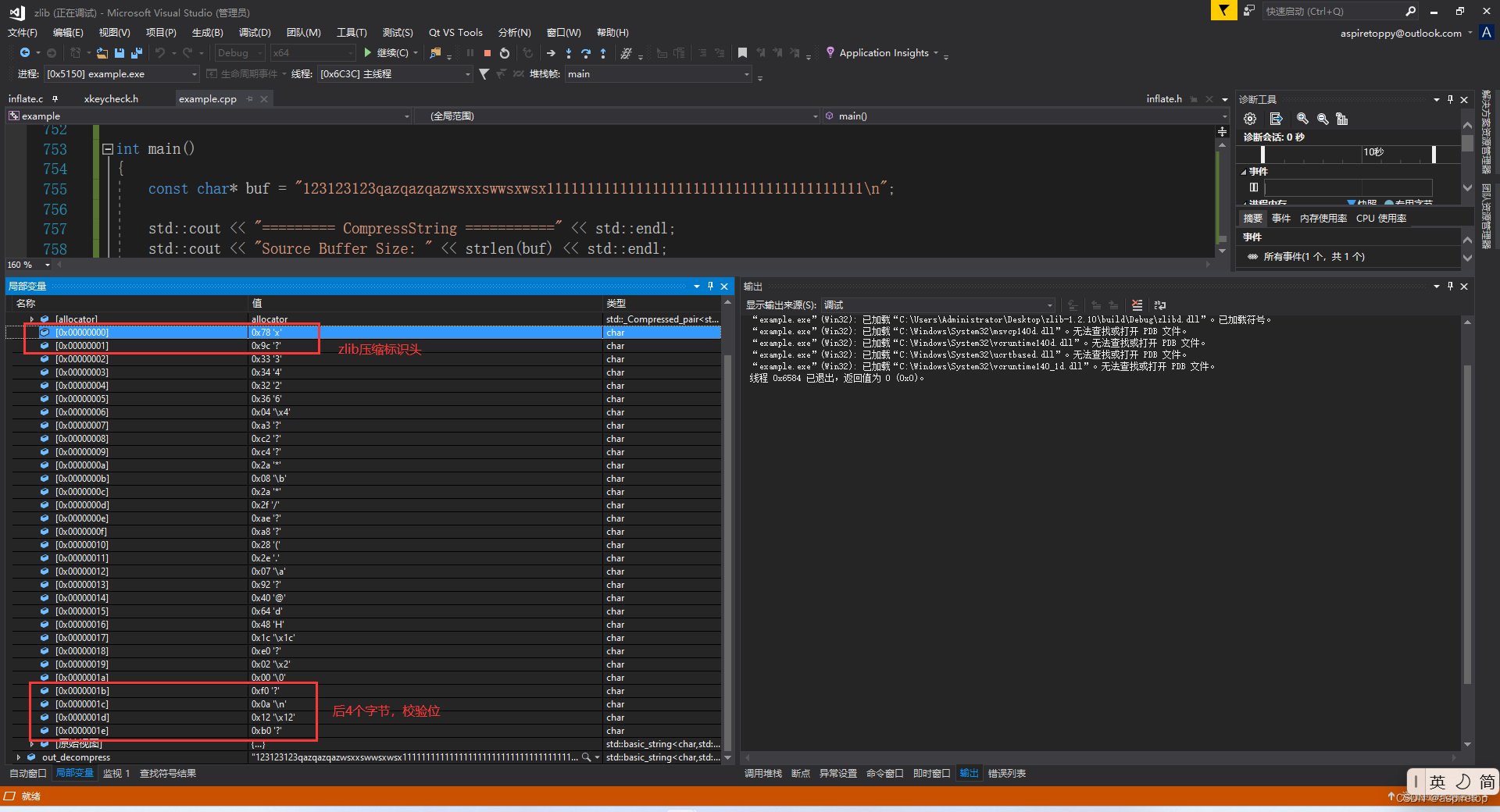
注:
如果使用zlib压缩,则压缩后输出的数据会有固定标志,前两个字节为0x789c,通过这个判断是否为zlib压缩。后4个字节为zlib内部的adler32校验算法,解压的时候,zlib内部解压完数据,会重新计算校验位,和原始输入的最后4个字节对比,相同则说明解压成功。
校验算法如下:
#define BASE 65521
unsigned long adler32(unsigned char *buf, int len)
{
unsigned long adler = 1;
unsigned long s1 = adler & 0xffff;
unsigned long s2 = (adler >> 16) & 0xffff;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
s1 = (s1 + buf[i]) % BASE;
s2 = (s2 + s1) % BASE;
}
return (s2 << 16) + s1;
}