监听EditText的变化
使用EditText的addTextChangedListener(TextWatcher watcher)方法对EditText实现监听,TextWatcher是一个接口类,所以必须实现TextWatcher里的抽象方法:
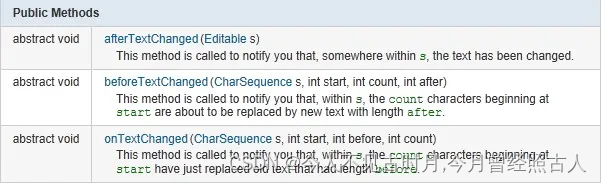
当EditText里面的内容有变化的时候,触发TextChangedListener事件,就会调用TextWatcher里面的抽象方法。
MainActivity.java
package com.lingdududu.watcher;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.AlertDialog;
import android.content.DialogInterface;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.text.Editable;
import android.text.TextWatcher;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.EditText;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private EditText text;
String str;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
text = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.text);
text.addTextChangedListener(textWatcher);
}
private TextWatcher textWatcher = new TextWatcher() {
@Override
public void afterTextChanged(Editable s) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Log.d("TAG","afterTextChanged--------------->");
}
@Override
public void beforeTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int count,
int after) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Log.d("TAG","beforeTextChanged--------------->");
}
@Override
public void onTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int before,
int count) {
Log.d("TAG","onTextChanged--------------->");
str = text.getText().toString();
try {
//if ((heighText.getText().toString())!=null)
Integer.parseInt(str);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
showDialog();
}
}
};
private void showDialog(){
AlertDialog dialog;
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this);
builder.setTitle("消息").setIcon(android.R.drawable.stat_notify_error);
builder.setMessage("你输出的整型数字有误,请改正");
builder.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
});
dialog = builder.create();
dialog.show();
}
} main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="请输入整型数字"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
</LinearLayout>
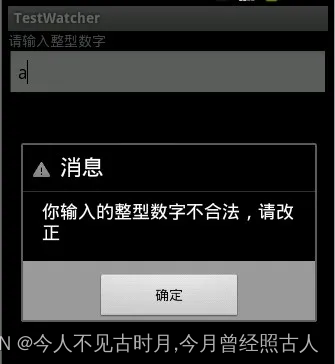
效果图:
当我们在输入框输入不是整型数字的时候,会立刻弹出输入框,提示你改正
在LogCat查看调用这些方法的顺序:
beforeTextChanged-->onTextChanged-->onTextChanged

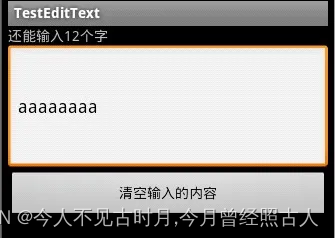
第二个例子实现了提示文本框还能输入多少个字符的功能
package com.lingdududu.test;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.text.Editable;
import android.text.TextWatcher;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private Button clearBtn;
private EditText et;
private TextView tv;
final int MAX_LENGTH = 20;
int Rest_Length = MAX_LENGTH;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
tv =(TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv);
et = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.et);
clearBtn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn);
et.addTextChangedListener(new TextWatcher() {
@Override
public void beforeTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int count,
int after) {
tv.setText("还能输入"+Rest_Length+"个字");
}
@Override
public void afterTextChanged(Editable s) {
tv.setText("还能输入"+Rest_Length+"个字");
}
@Override
public void onTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int before, int count) {
if(Rest_Length>0){
Rest_Length = MAX_LENGTH - et.getText().length();
}
}
});
clearBtn.setOnClickListener(new Button.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
et.setText("");
Rest_Length = MAX_LENGTH;
}
});
}
} 效果图:
-----------------------------------
转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/liangruijun/729505