
LeetCode链接:225. 用队列实现栈 - 力扣(LeetCode)
本文默认读者已经掌握栈与队列的基本知识
或者先看我的另一篇博客:【数据结构】栈与队列_字节连结的博客-CSDN博客
做题思路
由于我们使用的是C语言,不能直接使用队列的操作,
所以做这道题得先把我们之前实现的队列复制过来:
//C语言模拟实现队列
//链式结构:表示队列
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
//队列的结构
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
int size;
}Que;
//初始化队列
void QueueInit(Que* pq);
//销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Que* pq);
//队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Que* pq, QDataType x);
//队头出队列
void QueuePop(Que* pq);
//获取队列头部元素
QDataType QueueFront(Que* pq);
//获取队列队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Que* pq);
//检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0
bool QueueEmpty(Que* pq);
//获取队列中有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Que* pq);
void QueueInit(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Que* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->tail == NULL)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
if (pq->head->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->head->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->tail->data;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;
}
int QueueSize(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}复制完成后进入正题:
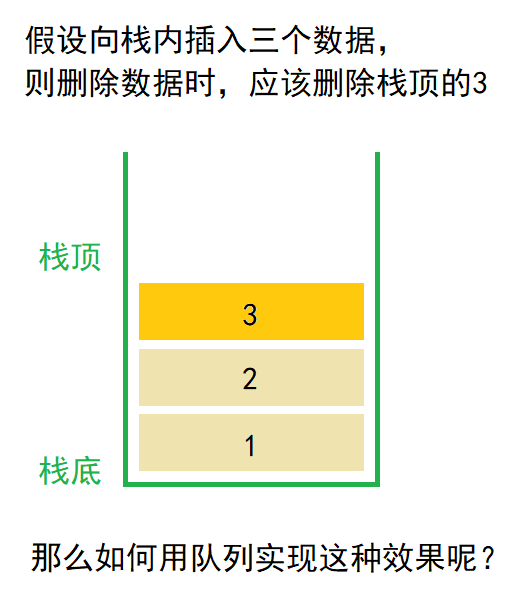
答:用两个队列捯数据的方式来实现后入先出的栈
图文解析:
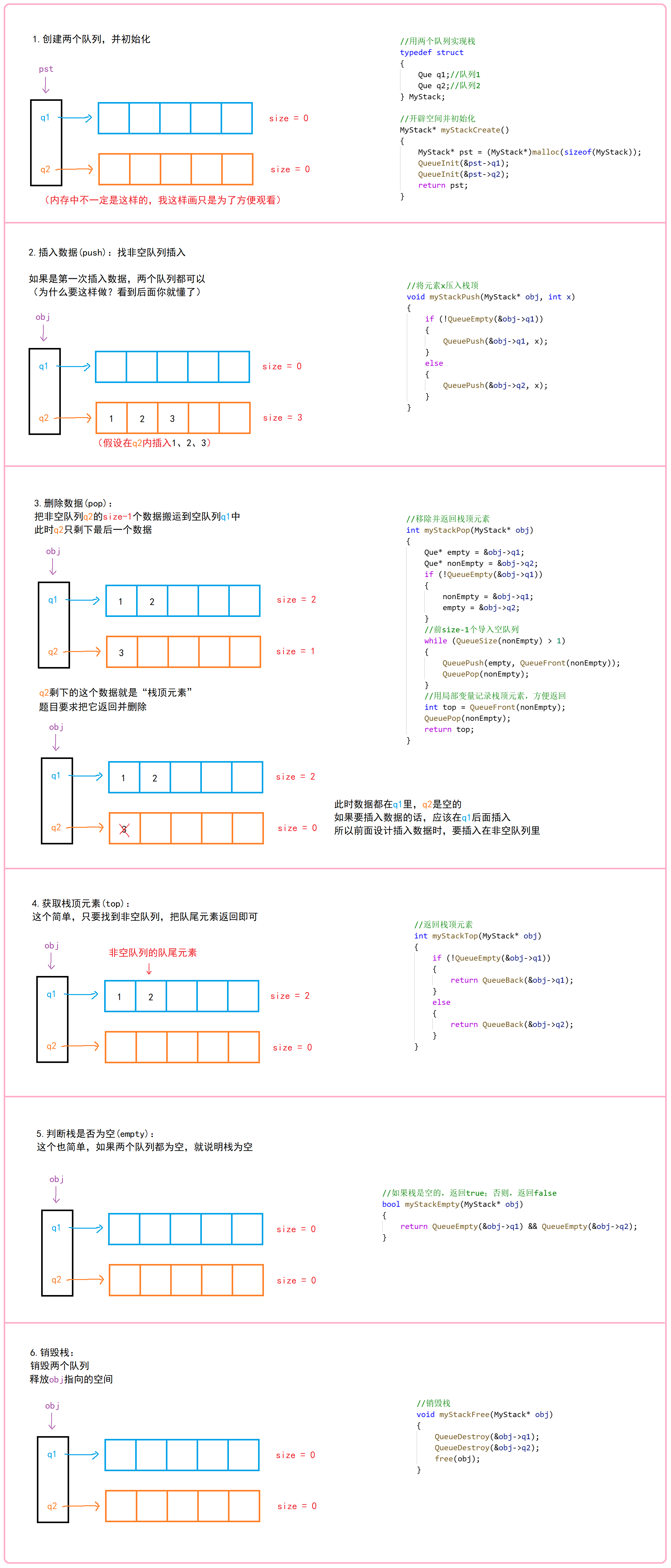
代码:
//用两个队列实现栈
typedef struct
{
Que q1;//队列1
Que q2;//队列2
} MyStack;
//开辟空间并初始化
MyStack* myStackCreate()
{
MyStack* pst = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
QueueInit(&pst->q1);
QueueInit(&pst->q2);
return pst;
}
//将元素x压入栈顶
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x)
{
if (!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q1, x);
}
else
{
QueuePush(&obj->q2, x);
}
}
//移除并返回栈顶元素
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj)
{
Que* empty = &obj->q1;
Que* nonEmpty = &obj->q2;
if (!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
nonEmpty = &obj->q1;
empty = &obj->q2;
}
//前size-1个导入空队列
while (QueueSize(nonEmpty) > 1)
{
QueuePush(empty, QueueFront(nonEmpty));
QueuePop(nonEmpty);
}
//用局部变量记录栈顶元素,方便返回
int top = QueueFront(nonEmpty);
QueuePop(nonEmpty);
return top;
}
//返回栈顶元素
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj)
{
if (!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q1);
}
else
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q2);
}
}
//如果栈是空的,返回true;否则,返回false
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj)
{
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
//销毁栈
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj)
{
QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);
QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}提交代码:
成功通过
本文完