3. 常用命令
3.1 输出
3.1.1 echo命令
echo是Shell的一个内部指令,用于在屏幕上打印出指定的字符串。命令格式:
echo arg
name="coding" echo '$name\"'+" ${name}" #原样输出 $name\"+ coding echo `date` #当前日期
3.1.2 printf命令
printf 命令用于格式化输出, 是echo命令的增强版。它是C语言printf()库函数的一个有限的变形,并且在语法上有些不同。
printf format-string [arguments...] #format-string 为格式控制字符串,arguments 为参数列表
printf "Hello, Shell\n" #printf 不像 echo 那样会自动换行,必须显式添加换行符(\n) printf "%d %s\n" 1 "abc" #输出 1 abc
3.2 if else语句
if 语句通过关系运算符判断表达式的真假来决定执行哪个分支。Shell 有三种 if ... else 语句:
- if ... fi 语句;
- if ... else ... fi 语句;
- if ... elif ... else ... fi 语句。
3.2.1 if ... fi语句
if [ expression ] then Statement(s) to be executed if expression is true fi
注意:expression 和方括号([ ])之间必须有空格,否则会有语法错误。
3.2.2 if ... else ... fi 语句
if [ expression ] then Statement(s) to be executed if expression is true else Statement(s) to be executed if expression is not true fi
a=10 b=20 if [ $a == $b ] then echo "a is equal to b" else echo "a is not equal to b" fi
if ... else 语句也可以写成一行,以命令的方式来运行,像这样:
if test $[2*3] -eq $[1+5]; then echo 'The two numbers are equal!'; fi;
if ... else 语句也经常与 test 命令结合使用,test 命令用于检查某个条件是否成立,与方括号([ ])类似。
a=10 b=20 if [ ${a} == ${b} ] #if test $[a] -eq $[b] #数值类型比较 $[num]
3.2.3 if ... elif ... fi 语句
if ... elif ... fi 语句可以对多个条件进行判断,语法为:
if [ expression 1 ] then Statement(s) to be executed if expression 1 is true elif [ expression 2 ] then Statement(s) to be executed if expression 2 is true elif [ expression 3 ] then Statement(s) to be executed if expression 3 is true else Statement(s) to be executed if no expression is true fi
哪一个 expression 的值为 true,就执行哪个 expression 后面的语句;如果都为 false,那么不执行任何语句。
a=10 b=20 if [ $a == $b ] then echo "a is equal to b" elif [ $a -gt $b ] then echo "a is greater than b" elif [ $a -lt $b ] then echo "a is less than b" else echo "None of the condition met" fi
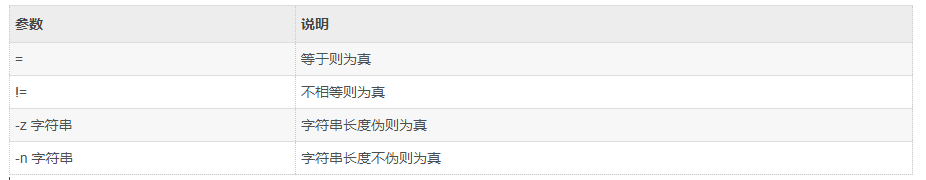
3.3 test命令
test 命令用于检查某个条件是否成立,它可以进行数值、字符和文件三个方面的测试。
3.3.1 数值比较
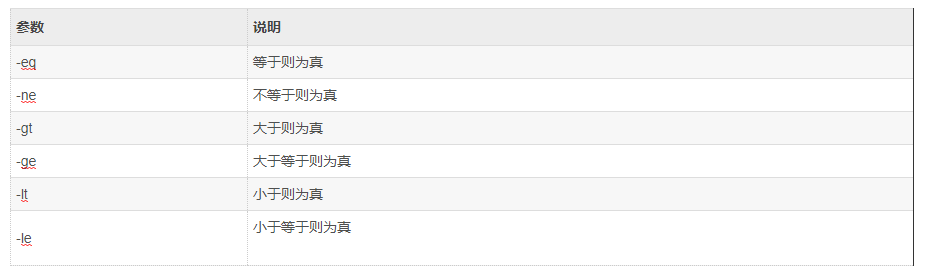
语法:

if test $[num1] -eq $[num2]
3.3.2 字符串比较
语法:
if test str1=str2
3.3.3 文件比较
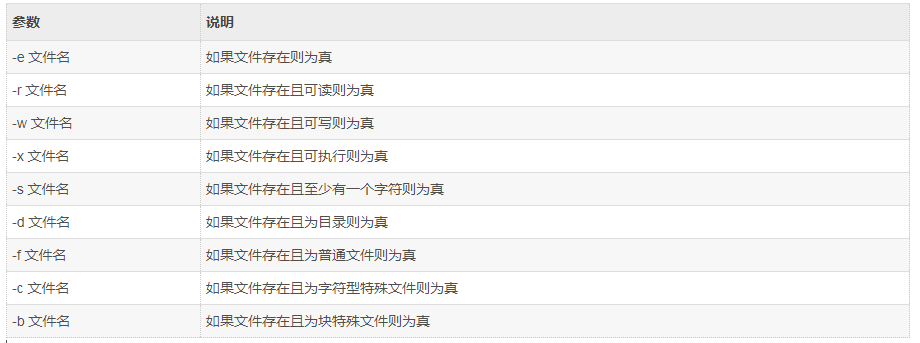
语法:
if test -e ./bash
另外,Shell还提供了与( ! )、或( -o )、非( -a )三个逻辑操作符用于将测试条件连接起来,其优先级为:“!”最高,“-a”次之,“-o”最低。
3.4 case ... esac语句
case ... esac 与其他语言中的 switch ... case 语句类似,是一种多分枝选择结构。
语法:
case 值 in 模式1) command1 command2 command3 ;; 模式2) command1 command2 command3 ;; *) command1 command2 command3 ;; esac
case工作方式如上所示。取值后面必须为关键字 in,每一模式必须以右括号结束。取值可以为变量或常数。匹配发现取值符合某一模式后,其间所有命令开始执行直至 ;;。;; 与其他语言中的 break 类似,意思是跳到整个 case 语句的最后。
取值将检测匹配的每一个模式。一旦模式匹配,则执行完匹配模式相应命令后不再继续其他模式。如果无一匹配模式,使用星号 * 捕获该值,再执行后面的命令。
echo 'Input a number between 1 to 4' echo 'Your number is:\c' read aNum case $aNum in 1) echo 'You select 1' ;; 2) echo 'You select 2' ;; 3) echo 'You select 3' ;; 4) echo 'You select 4' ;; *) echo 'You do not select a number between 1 to 4' ;; esac
3.5 循环
3.5.1 for循环
语法:
for 变量 in 列表 do command1 command2 ... commandN done
列表是一组值(数字、字符串等)组成的序列,每个值通过空格分隔。每循环一次,就将列表中的下一个值赋给变量。
in 列表是可选的,如果不用它,for 循环使用命令行的位置参数。
for loop in 1 2 3 4 5 #for str in 'I love Spring' do echo "The value is: $loop" #echo ${str} done
3.5.2 while循环
while循环用于不断执行一系列命令,也用于从输入文件中读取数据;命令通常为测试条件。
语法:
while command do Statement(s) to be executed if command is true done
COUNTER=0 while [ $COUNTER -lt 5 ] do COUNTER='expr $COUNTER+1' echo $COUNTER done
3.5.3 util循环
until 循环执行一系列命令直至条件为 true 时停止。until 循环与 while 循环在处理方式上刚好相反。一般while循环优于until循环,但在某些时候,也只是极少数情况下,until 循环更加有用。
语法:
until command do Statement(s) to be executed until command is true done
a=0 until [ ! $a -lt 10 ] do echo $a #输出1~9 a=`expr $a + 1` done
3.5.4 break和continue命令
break命令允许跳出所有循环(终止执行后面的所有循环);continue命令会跳出当前循环。
在嵌套循环中,这两个命令还有较高级的用法:
break 2 #跳出2层循环 continue 2
3.6 Shell函数
3.6.1 函数定义
函数可以让我们将一个复杂功能划分成若干模块,让程序结构更加清晰,代码重复利用率更高。像其他编程语言一样,Shell 也支持函数。Shell 函数必须先定义后使用。
函数的定义语法如下:
[ function ] function_name () { list of commands [ return value ] }
函数名前可加上关键字 function,也可不加,效果一样。
函数返回值,可以显式增加return语句;如果不加,会将最后一条命令运行结果作为返回值。
funWithReturn(){ echo "The function is to get the sum of two numbers..." echo -n "Input first number: " read aNum echo -n "Input another number: " read anotherNum echo "The two numbers are $aNum and $anotherNum !" return $(($aNum+$anotherNum)) } funWithReturn # Capture value returnd by last command ret=$? echo "The sum of two numbers is $ret !"
结果:
[root@centoszang testShell]# ./myShell.sh The function is to get the sum of two numbers... Input first number: 4 Input another number: 5 The two numbers are 4 and 5 ! The sum of two numbers is 9 !
像删除变量一样,删除函数也可以使用 unset 命令,不过要加上 .f 选项
unset .f funWithReturn
3.6.2 函数参数
在Shell中,调用函数时可以向其传递参数。在函数体内部,通过 $n 的形式来获取参数的值,例如,$1表示第一个参数,$2表示第二个参数...
注意,$10 不能获取第十个参数,获取第十个参数需要${10}。当n>=10时,需要使用${n}来获取参数。
funWithParam(){ echo "The value of the first parameter is $1 !" echo "The value of the second parameter is $2 !" echo "The value of the tenth parameter is $10 !" echo "The value of the tenth parameter is ${10} !" echo "The value of the eleventh parameter is ${11} !" echo "The amount of the parameters is $# !" # 参数个数 echo "The string of the parameters is $* !" # 传递给函数的所有参数 } funWithParam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 18 77
输出
[root@centoszang testShell]# ./myShell.sh The value of the first parameter is 1 ! The value of the second parameter is 2 ! The value of the tenth parameter is 10 ! The value of the tenth parameter is 18 ! The value of the eleventh parameter is 77 ! The amount of the parameters is 11 ! The string of the parameters is 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 18 77 !
3.7 Shell文件包含
像其他语言一样,Shell 也可以包含外部脚本,将外部脚本的内容合并到当前脚本。
两种语法:
. filename
source filename
创建被调用脚本 test.sh
name="Java Web"
使用主文件 myShell.sh来引用该脚本
. ./test.sh echo ${name} #输出Java Web
需要注意的是,被包含脚本(test.sh)不需要有执行权限。