- 首先必须是接口。
- 接口中只能有一个抽象方法。
- 即,Lambda表达式只能简化接口中只有一个抽象方法的匿名内部类形式。
函数式接口:
- 接口中只有一个抽象方法的接口称为函数式接口。
- 函数式接口注解:@FunctionalInterface 一旦某个接口加上了这个注解,这个接口只能、有且仅有一个抽象方法。
Lambda 语法
每个 Lambda 表达式都遵循以下法则:
( parameter-list ) -> { expression-or-statements }
() 中的 parameter-list 是以逗号分隔的参数。你可以指定参数的类型,也可以不指定(编译器会根据上下文进行推断)。Java 11 后,还可以使用 var 关键字作为参数类型,有点 JavaScript 的味道。
-> 相当于 Lambda 的标识符,就好像见到圣旨就见到了皇上。
{} 中的 expression-or-statements 为 Lambda 的主体,可以是一行语句,也可以多行。
可以通过 Lambda 表达式干很多事情,比如说
1.为变量赋值
Runnable r = () -> { System.out.println("中国"); };
r.run();
2.作为 return 结果

static FileFilter getFilter(String ext)
{
return (pathname) -> pathname.toString().endsWith(ext);
}
3.作为数组元素
final PathMatcher matchers[] =
{
(path) -> path.toString().endsWith("txt"),
(path) -> path.toString().endsWith("java")
};
4.作为普通方法或者构造方法的参数
new Thread(() -> System.out.println("沉默王二")).start();
需要注意 Lambda 表达式的作用域范围
public static void main(String[] args) {
int limit = 10;
Runnable r = () -> {
int limit = 5;
for (int i = 0; i < limit; i++)
System.out.println(i);
};
}
上面这段代码在编译的时候会提示错误:变量 limit 已经定义过了。
和匿名内部类一样,不要在 Lambda 表达式主体内对方法内的局部变量进行修改,否则编译也不会通过:Lambda 表达式中使用的变量必须是 final 的
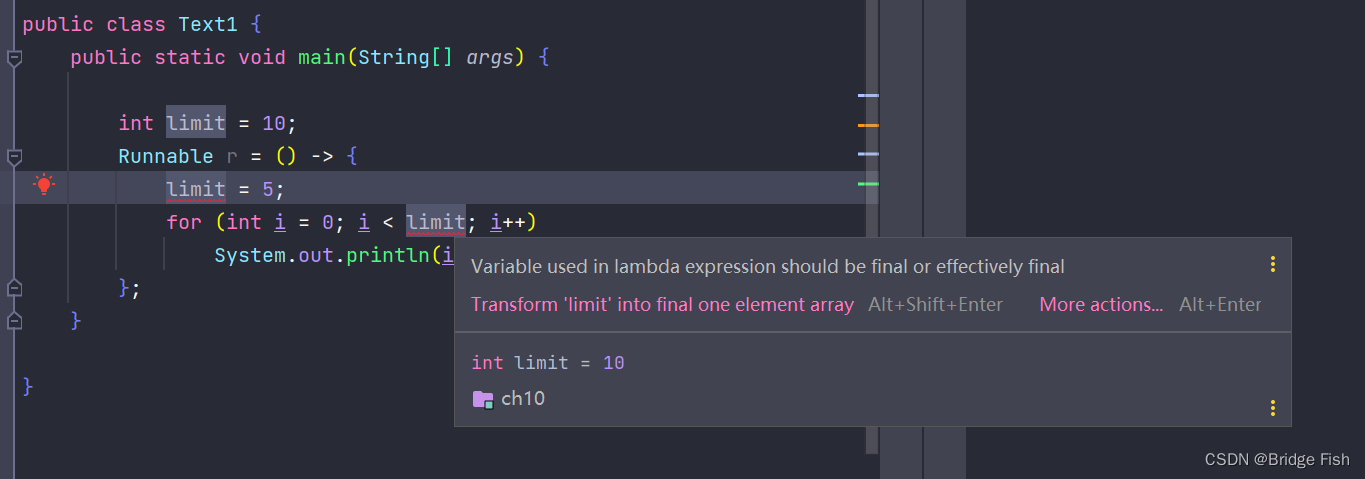
这个问题发生的原因是因为 Java 规范中是这样规定的:
Any local variable, formal parameter, or exception parameter used but not declared in a lambda expression
must either be declared final or be effectively final (§4.12.4),
or a compile-time error occurs where the use is attempted.
Lambda 表达式中要用到的,但又未在 Lambda 表达式中声明的变量,必须声明为 final 或者是 effectively final,否则就会出现编译错误。
关于 final 和 effectively final 的区别
final int a;
a = 1;
// a = 2;
// 由于 a 是 final 的,所以不能被重新赋值
int b;
b = 1;
// b 此后再未更改
// b 就是 effectively final
int c;
c = 1;
// c 先被赋值为 1,随后又被重新赋值为 2
c = 2;
// c 就不是 effectively final
如果把 limit 定义为 final,那就无法在 Lambda 表达式中修改变量的值。那有什么好的解决办法呢?既能让编译器不发出警告,又能修改变量的值。
(1)把 limit 变量声明为 static。
(2)把 limit 变量声明为 AtomicInteger。
(3)使用数组。
把 limit 变量声明为 static
要想把 limit 变量声明为 static,就必须将 limit 变量放在 main() 方法外部,因为 main() 方法本身是 static 的。
public class ModifyVariable2StaticInsideLambda {
static int limit = 10;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable r = () -> {
limit = 5;
for (int i = 0; i < limit; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
};
new Thread(r).start();
}
}
输出
0
1
2
3
4
把 limit 变量声明为 AtomicInteger
AtomicInteger 可以确保 int 值的修改是原子性的,可以使用 set() 方法设置一个新的 int 值,get() 方法获取当前的 int 值。
public class ModifyVariable2AtomicInsideLambda {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final AtomicInteger limit = new AtomicInteger(10);
Runnable r = () -> {
limit.set(5);
for (int i = 0; i < limit.get(); i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
};
new Thread(r).start();
}
}
输出
0
1
2
3
4
使用数组
使用数组的方式略带一些欺骗的性质,在声明数组的时候设置为 final,但更改 int 的值时却修改的是数组的一个元素。
public class ModifyVariable2ArrayInsideLambda {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final int [] limits = {10};
Runnable r = () -> {
limits[0] = 5;
for (int i = 0; i < limits[0]; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
};
new Thread(r).start();
}
}
输出
0
1
2
3
4
Lambda 和 this 关键字
Lambda 表达式并不会引入新的作用域,这一点和匿名内部类是不同的。也就是说,Lambda 表达式主体内使用的 this 关键字和其所在的类实例相同。
public class LamadaTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new LamadaTest().work();
}
public void work() {
System.out.printf("this = %s%n", this);
Runnable r = new Runnable()
{
@Override
public void run()
{
System.out.printf("this = %s%n", this);
}
};
new Thread(r).start();
new Thread(() -> System.out.printf("this = %s%n", this)).start();
}
}
Tips:%s 代表当前位置输出字符串,%n 代表换行符,也可以使用 \n 代替,但 %n 是跨平台的。
work() 方法中的代码可以分为 3 个部分:
单独的 this 关键字
System.out.printf("this = %s%n", this);
其中 this 为 main() 方法中通过 new 关键字创建的 LamadaTest 对象——new LamadaTest()。
匿名内部类中的 this 关键字
Runnable r = new Runnable()
{
@Override
public void run()
{
System.out.printf("this = %s%n", this);
}
};
其中 this 为 work() 方法中通过 new 关键字创建的 Runnable 对象——new Runnable(){...}。
Lambda 表达式中的 this 关键字
其中 this 关键字和第一个中的相同。
我们来看一下程序的输出结果:
this = com.cmower.java_demo.journal.LamadaTest@3feba861
this = com.cmower.java_demo.journal.LamadaTest$1@64f033cb
this = com.cmower.java_demo.journal.LamadaTest@3feba861
Lambda的简化格式:
(匿名内部类被重写方法的形参列表) -> {
被重写方法的方法体代码。
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用Lambda简化:
// 把"public void run()"简化为"()"。
// 之所以不用指定方法名,是因为函数式接口中有且仅有一个方法,只要一调用,只有那一个方法可以调用
// 方法体保持不变
Thread thread = new Thread( () -> {
System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行了!");
});
thread.start();
}
}再简化
再简化:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//方法体内只有一行代码,可以直接去掉方法体的花括号:{}
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行了!") );
thread.start();
}
}
匿名对象的简化:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//把Thread类转换为匿名对象
new Thread(() -> System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行了!")).start();
}
}- Lambda的作用是简化代码的写法,减少代码量。
- 核心语法是:(参数1,参数2) -> { 方法体(如果方法体可以使用一句代码,则可以省略花括号) }