1、使用echo进行格式化输出
- 显示转义字符
[root@yanta ~]# echo "\"This is a test\""
"This is a test"- 读取变量并显示
使用 read 命令从标准输入中读取一行,并把输入行的每个字段的值指定给 shell 变量:
#!/bin/bash
# Name: /home/yanta/read_echo.sh
# Author: Yanta
# Dsc: This is to test reading input arguments
Usage(){
echo "USAGE: /bin/bash /home/yanta/read_echo.sh"
echo "USAGE: This script is to test reading input arguments"
}
Read(){
echo -ne "Please input your name: "
read name
echo "Your name is %name"
}
main(){
[ $# -ne 0 ] && {
Usage
exit -1
}
Read
}
main $*输出结果是:
[root@yanta yanta]# ./read_echo.sh
Please input your name: yanta
Your name is %name- 显示换行和不换行
echo 的 -e 参数开启转义;\n 换行 \c 不换行
[root@yanta yanta]# echo "Hello"
Hello
[root@yanta yanta]# echo -e "Hello"
Hello
[root@yanta yanta]# echo -n "Hello"
Hello[root@yanta yanta]# echo -e "Hello \n"
Hello
[root@yanta yanta]# echo "Hello \n"
Hello \n
[root@yanta yanta]# echo "Hello \c"
Hello \c
[root@yanta yanta]# echo -e "Hello \c"
Hello [root@yanta yanta]# 2、使用printf进行格式化输出
- 语法
printf 命令模仿 C 程序库(library)里的 printf() 程序。
标准所定义,因此使用printf的脚本比使用echo移植性好。
printf 使用引用文本或空格分隔的参数,外面可以在printf中使用格式化字符串,还可以制定字符串的宽度、左右对齐方式等。
默认printf不会像 echo 自动添加换行符,我们可以手动添加 \n。
printf 命令的语法:
printf format-string [arguments…]
参数说明:
format-string: 为格式控制字符串
arguments: 为参数列表。
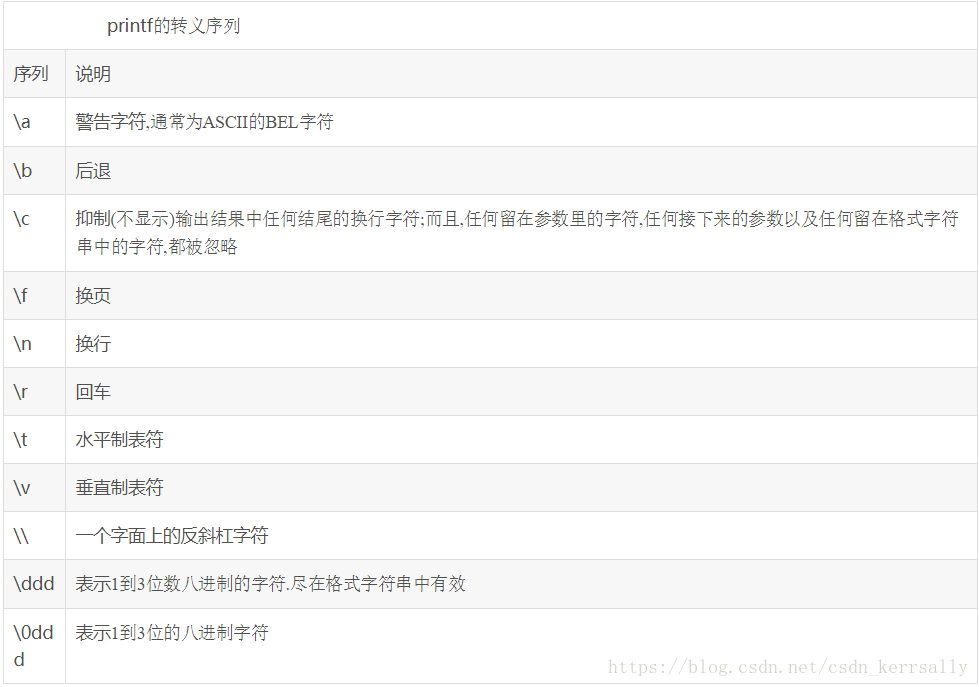
- 转义序列
Note: 转义序列只在格式字符串中会被特别对待,也就是说,出现在参数字符串里的专利序列不会被解释:
[root@yanta yanta]# printf "%s\n" "abc\ndef"
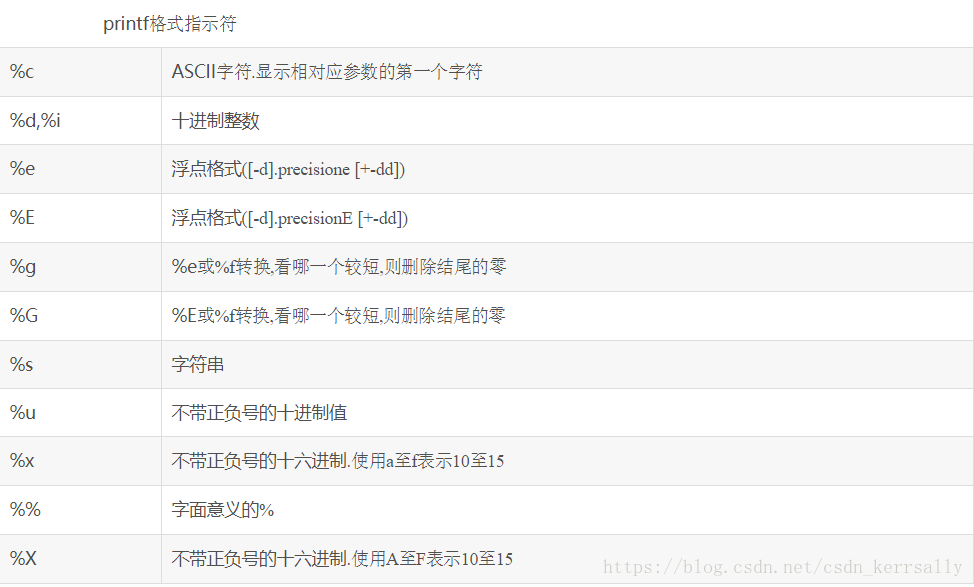
abc\ndef- 格式化指示符
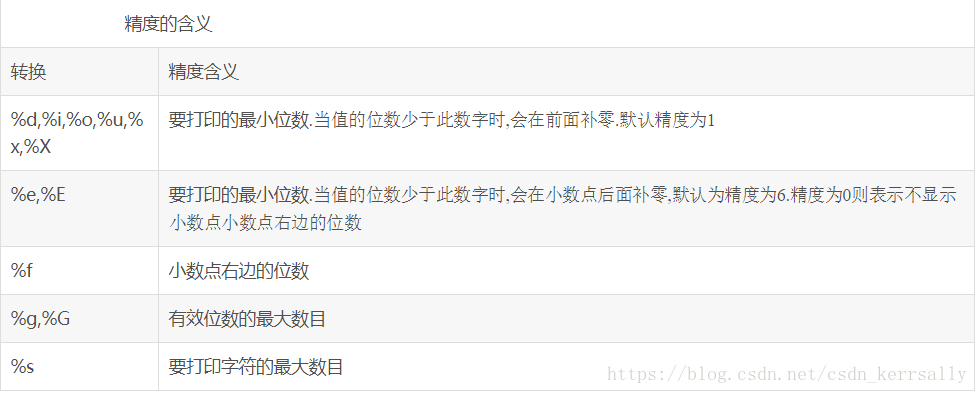
精度
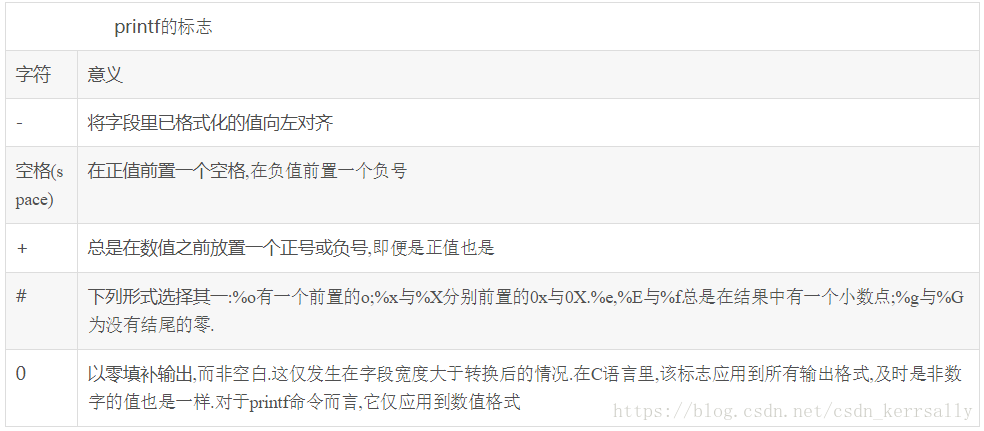
格式标志
实例:
#!/bin/bash
###########
# Name: printf.sh
# Author: Yanta
# Dsc: Test printf format output
###########
Usage(){
echo "USAGE: /bin/bash /home/yanta/printf.sh"
echo "USAGE: This script is to test printf format output"
}
Print(){
for i in sshd ntpd firewalld
do
res=`systemctl status $i | grep -e running | wc -l`
[ $res -ne 0 ] && {
stat=`echo -e "\033[1;5;32mRunning\033[0m"`
} || {
stat=`echo -e "\033[1;5;31mFailed\033[0m"`
}
printf "[%-5s] \t%-s \t[%5s]\n" "$i" "<-->" "$stat"
done
}
main(){
[ $# -ne 0 ] && {
Usage
exit -1
}
Print
}
main $*输出:
[root@yanta yanta]# ./printf.sh
[sshd ] <--> [Running]
[ntpd ] <--> [Running]
[firewalld] <--> [Failed]