前言
本章主要讲述win32dll hook (x86工程)
1:准备
vs2015
2:代码
1>dlltest 库工程 部分文件如下
dlltest.h
#pragma once
#ifdef DLLTEST_EXPORTS
#define DLLTEST_API __declspec(dllexport)
#else
#define DLLTEST_API __declspec(dllimport)
#endif
DLLTEST_API int MyPrintf(int d);
dlltest.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "dlltest.h"
#include "stdio.h"
// 这是导出函数的一个示例。
DLLTEST_API int MyPrintf(int d)
{
printf("d= %d\n", d);
return d + 1;
}
2>hookdll 库工程
hookdll.h
pragma once
#ifdef DLLTEST_EXPORTS
#define DLLTEST_API __declspec(dllexport)
#else
#define DLLTEST_API __declspec(dllimport)
#endif
/*
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
*/
DLLTEST_API void GetApiEntrance();
DLLTEST_API void HookOn();
DLLTEST_API void HookOff();
DLLTEST_API int MyPrintf_new(int d);
hookddl.cpp 这里是抄了别人的,
说白了,就是hook 就是用myprintf_new 替换 my_printf 用jump 新地址 跳转
// hookdll.cpp : 定义 DLL 应用程序的导出函数。
//
// hookdll.cpp : 定义 DLL 应用程序的导出函数。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "dllhook.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include <assert.h>
typedef int(CALLBACK* LPFNDLLFUNC1)(int);
FARPROC pfOldFun = NULL;
BYTE OldCode[5] = {
0,0,0,0,0 };
BYTE NewCode[5] = {
0,0,0,0,0 };
HANDLE hProcess = NULL;
void GetApiEntrance() {
//获取原API入口地址
HMODULE hmod = ::GetModuleHandle(L"dlltest.dll");
if (hmod == NULL) {
printf("dlltest.dll is NULL");
return;
}
//G:\vsstudio_install\2015\VC\bin\dumpbin.exe /map dlltest.dll > 1.txt
#if C_FLAG < 1
LPFNDLLFUNC1 OldFun = (LPFNDLLFUNC1)::GetProcAddress(hmod, "?MyPrintf@@YAHH@Z");//?MyPrintf@@YAHH@Z //c++ 版
#else
LPFNDLLFUNC1 OldFun = (LPFNDLLFUNC1)::GetProcAddress(hmod, "MyPintf"); //extern "C" 版
#endif
if (OldFun == NULL) {
DWORD nerror = GetLastError();
printf("GetProcAddress error=%d \n", nerror);
return;
}
pfOldFun = (FARPROC)OldFun;
if (pfOldFun == NULL)
{
printf("获取原API入口地址出错");
return;
}
// OldFun(88);
#ifndef WIN64
// 将原API的入口前5个字节代码保存到OldCode[]
//BYTE OldCode[5] = { 0,0,0,0,0 };
//BYTE NewCode[5] = { 0,0,0,0,0 };
_asm
{
lea edi, OldCode //获取OldCode数组的地址,放到edi
mov esi, pfOldFun //获取原API入口地址,放到esi
cld //方向标志位,为以下两条指令做准备
movsd //复制原API入口前4个字节到OldCode数组
movsb //复制原API入口第5个字节到OldCode数组
}
NewCode[0] = 0xe9;//实际上0xe9就相当于jmp指令
//获取MyPintf_new的相对地址,为Jmp做准备
//int nAddr= UserFunAddr – SysFunAddr - (我们定制的这条指令的大小);
//Jmp nAddr;
//(我们定制的这条指令的大小), 这里是5,5个字节嘛
//BYTE NewCode[5];
_asm
{
lea eax, MyPrintf_new //获取我们的MyPrintf_new函数地址
mov ebx, pfOldFun //原系统API函数地址
sub eax, ebx //int nAddr= UserFunAddr – SysFunAddr
sub eax, 5 //nAddr=nAddr-5
mov dword ptr[NewCode + 1], eax //将算出的地址nAddr保存到NewCode后面4个字节
//注:一个函数地址占4个字节
}
#else
// JMP_X64(OldCode, pfOldFun, NewCode);
#endif
//填充完毕,现在NewCode[]里的指令相当于Jmp MyPintf_new
//既然已经获取到了Jmp MyPintf_new
//现在该是将Jmp MyPintf_new写入原API入口前5个字节的时候了
//知道为什么是5个字节吗?
//Jmp指令相当于0xe9,占一个字节的内存空间
// MyPintf_new是一个地址,其实是一个整数,占4个字节的内存空间
//int n=0x123; n占4个字节和MyPintf_new占4个字节是一样的
//1+4=5,知道为什么是5个字节了吧
HookOn();
}
void HookOn() {
#ifdef WIN64
//to do it
#else
DWORD dwPid = ::GetCurrentProcessId();
//printf("pid %d\n", dwPid);
hProcess = OpenProcess(PROCESS_ALL_ACCESS, 0, dwPid);
assert(hProcess != NULL);
//printf("HookOn now,hProcess %d\n", hProcess);
DWORD dwTemp = 0;
DWORD dwOldProtect;
//修改API函数入口前5个字节为jmp xxxxxx
VirtualProtectEx(hProcess, pfOldFun, 5, PAGE_READWRITE, &dwOldProtect);
WriteProcessMemory(hProcess, pfOldFun, NewCode, 5, 0);
VirtualProtectEx(hProcess, pfOldFun, 5, dwOldProtect, &dwTemp);
#endif
printf("HookOn end\n");
}
void HookOff() {
#ifdef WIN64
//to do it
#else
assert(hProcess != NULL);
DWORD dwTemp = 0;
DWORD dwOldProtect;
//恢复API函数入口前5个字节
VirtualProtectEx(hProcess, pfOldFun, 5, PAGE_READWRITE, &dwOldProtect);
WriteProcessMemory(hProcess, pfOldFun, OldCode, 5, 0);
VirtualProtectEx(hProcess, pfOldFun, 5, dwOldProtect, &dwTemp);
#endif
}
int MyPrintf_new(int d) {
printf("new d = %d\n", d);
return d*2 + 10;
}
3:测试
测试工程
#include "stdio.h"
#include "tchar.h"
#include "dlltest.h"
#include "dllhook.h"
#include <windows.h>
//#define LIBPATH(p,f) p##f
//#pragma comment(lib,LIBPATH(__FILE__, "..\\x64\\Debug\\dlltest.lib"))
//#pragma comment(lib, "E:\\prog2015\\winhook\\dlltest\\x64\\Debug\\dlltest.lib") //ok
#ifndef WIN64
#pragma comment(lib, "..\\Debug\\dlltest.lib") // win32
#pragma comment(lib, "..\\Debug\\hookdll.lib") // win32
#else
#pragma comment(lib, "..\\x64\\Debug\\dlltest.lib") //WIN64
#pragma comment(lib, "..\\x64\\Debug\\hookdll.lib") //WIN64
#endif
//导出表 /ALL /map
//G:\vsstudio_install\2015\VC\bin\dumpbin.exe /map dlltest.dll > 2.txt
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int d = 1;
while (true) {
int nn = MyPrintf(d);
printf("d= %d nn=%d \n", d,nn);
// Sleep(20 * 1000);
// ++d;
GetApiEntrance();
nn = MyPrintf(d);
printf("[hook]d= %d nn=%d \n", d, nn);
HookOff();
nn = MyPrintf(d);
printf("[hookoff]d= %d nn=%d \n", d, nn);
break;
}
getchar();
return 0;
}
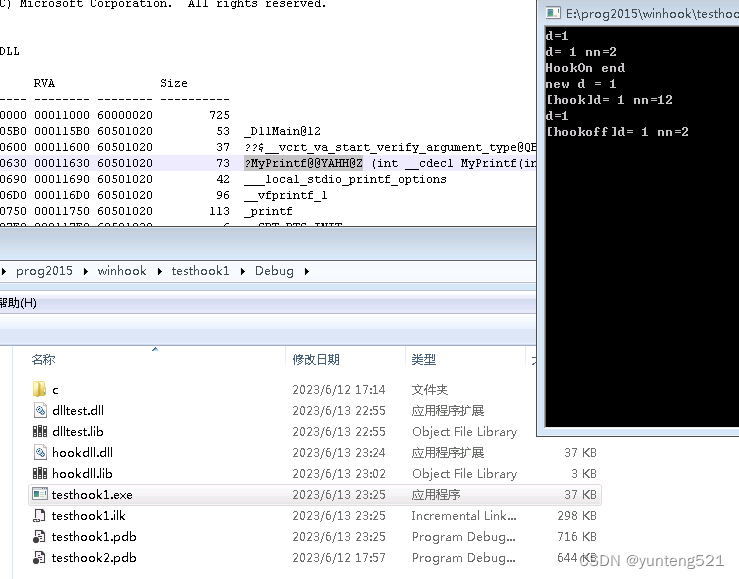
结果
如果觉得有用,麻烦点个赞,加个收藏